🕺 行为型设计模式:对象协作的舞蹈家
💡 温馨提示:本文将以轻松有趣的方式带你探索行为型设计模式的世界,就像在观看一场精彩的"对象舞蹈表演"一样!
🚪 传送门 :在开始我们的"对象协作之旅" 之前,建议先通过这个 🎨 Java设计模式详解:让代码优雅如诗的秘密武器 了解设计模式的基础概念和整体架构,然后通过 🏭 创建型设计模式:对象诞生的艺术与智慧 学习对象创建的艺术,再通过 🏗️ 结构型设计模式:代码架构的魔法师 了解对象组合的艺术,这样能让你更好地理解本文内容!就像跳舞要先学会走路一样!💃
🎪 引言:为什么我们需要行为型设计模式?
arduino
🕺 场景:混乱的对象舞蹈现场 🕺
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 💻 程序员小王的一天 💻 │
│ │
│ 😵 对象间通信像鸡同鸭讲! │
│ 🔥 算法选择像选择困难症! │
│ 🐛 状态管理像迷宫一样复杂! │
│ │
│ 💡 突然,行为型设计模式舞者出现了! │
│ 🕺 "让我来编排你们的协作舞蹈!" │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘行为型设计模式就像是"对象协作"的标准舞蹈编排,让对象之间的通信变得优雅、灵活、高效。
本文将带你探索十一种行为型设计模式,就像观看十一个不同的"对象舞蹈表演"一样精彩!
🎯 本文你将学到什么?
🎬 行为型设计模式舞蹈团 🎬
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 🕺 十一位协作舞者登场! │
│ │
│ 👀 观察者:一对多通知机制 │
│ 🎯 策略者:算法选择专家 │
│ 📝 命令者:请求封装大师 │
│ 🔄 状态者:状态变化艺术家 │
│ 📋 模板者:算法框架设计师 │
│ 🔍 迭代者:集合遍历专家 │
│ ⛓️ 责任链:请求处理链 │
│ 🤝 中介者:对象交互协调员 │
│ 👁️ 访问者:元素操作专家 │
│ 💾 备忘录:状态保存专家 │
│ 🗣️ 解释器:语言解释专家 │
│ │
│ 🚀 准备好开始舞蹈之旅了吗? │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘👀 第一部分:观察者模式(Observer Pattern)
arduino
👀 观察者舞者的登场 👀
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 👀 观察者:我是一对多通知专家! │
│ │
│ 📢 主题:"我有新消息!" │
│ 👀 观察者:"我来通知大家!" │
│ 📢 主题:"状态变化了!" │
│ 👀 观察者:"我来更新大家!" │
│ │
│ 💡 核心思想:一对多通知机制 │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘🏗️ 观察者模式UML类图
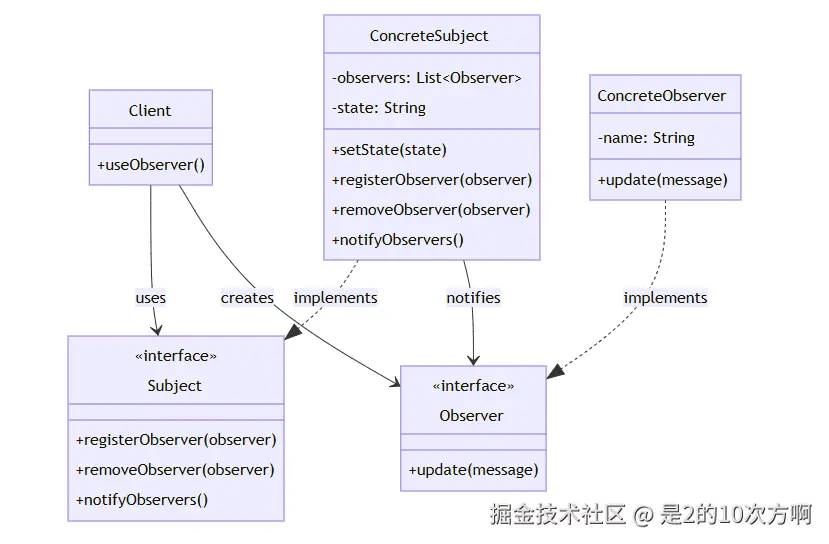
1.1 🎭 什么是观察者模式?
一句话理解:当一个对象状态改变时,自动通知所有依赖它的对象,就像新闻发布一样!
定义:定义对象间的一种一对多的依赖关系,当一个对象的状态发生改变时,所有依赖于它的对象都得到通知并被自动更新。
应用场景:事件处理系统、消息推送、数据绑定、日志记录、GUI事件处理
1.2 🛠️ 观察者模式的实现
1.2.1 🏗️ 基本结构
💡 小贴士:观察者模式就像新闻发布系统,主题是新闻社,观察者是各个新闻频道!
核心组件:
- Subject(主题) :被观察的对象,维护观察者列表
- Observer(观察者) :观察主题的对象,接收通知
- ConcreteSubject(具体主题) :具体的被观察对象
- ConcreteObserver(具体观察者) :具体的观察者实现
1.2.2 🚀 多种实现方式
| 实现方式 | 特点 | 推荐度 |
|---|---|---|
| 推模式 | 主题主动推送数据给观察者 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 拉模式 | 观察者主动从主题获取数据 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
| 事件驱动 | 基于事件的松耦合实现 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
推模式实现:
typescript
// 推模式:主题主动推送数据给观察者
public interface PushObserver {
void update(String data); // 直接接收数据
}
public class PushSubject {
private List<PushObserver> observers = new ArrayList<>();
private String state;
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
notifyObservers(); // 推送状态给所有观察者
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (PushObserver observer : observers) {
observer.update(state); // 直接推送数据
}
}
public void addObserver(PushObserver observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
}
public class PushConcreteObserver implements PushObserver {
private String name;
public PushConcreteObserver(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void update(String data) {
System.out.println(name + " 收到推送数据: " + data);
}
}拉模式实现:
typescript
// 拉模式:观察者主动从主题获取数据
public interface PullObserver {
void update(); // 不传递数据,观察者自己获取
}
public class PullSubject {
private List<PullObserver> observers = new ArrayList<>();
private String state;
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
notifyObservers();
}
public void notifyObservers() {
for (PullObserver observer : observers) {
observer.update(); // 只通知,不传递数据
}
}
public String getState() {
return state; // 观察者通过此方法获取数据
}
public void addObserver(PullObserver observer) {
observers.add(observer);
}
}
public class PullConcreteObserver implements PullObserver {
private String name;
private PullSubject subject;
public PullConcreteObserver(String name, PullSubject subject) {
this.name = name;
this.subject = subject;
}
@Override
public void update() {
String data = subject.getState(); // 主动拉取数据
System.out.println(name + " 拉取到数据: " + data);
}
}事件驱动实现:
csharp
// 事件驱动:基于事件的松耦合实现
public class NewsEvent {
private String news;
private long timestamp;
public NewsEvent(String news) {
this.news = news;
this.timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
public String getNews() { return news; }
public long getTimestamp() { return timestamp; }
}
public interface EventObserver {
void onEvent(NewsEvent event);
}
public class EventSubject {
private Map<String, List<EventObserver>> eventObservers = new HashMap<>();
public void addObserver(String eventType, EventObserver observer) {
eventObservers.computeIfAbsent(eventType, k -> new ArrayList<>()).add(observer);
}
public void publishEvent(String eventType, NewsEvent event) {
List<EventObserver> observers = eventObservers.get(eventType);
if (observers != null) {
for (EventObserver observer : observers) {
observer.onEvent(event);
}
}
}
}
public class EventConcreteObserver implements EventObserver {
private String name;
public EventConcreteObserver(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void onEvent(NewsEvent event) {
System.out.println(name + " 收到事件: " + event.getNews() +
" (时间: " + new Date(event.getTimestamp()) + ")");
}
}1.2.3 🎯 标准实现示例
typescript
// 观察者接口 - 定义观察者的行为
public interface Observer {
void update(String message);
}
// 主题接口 - 定义主题的行为
public interface Subject {
void registerObserver(Observer observer); // 注册观察者
void removeObserver(Observer observer); // 移除观察者
void notifyObservers(); // 通知所有观察者
}
// 具体主题 - 实现主题接口
public class ConcreteSubject implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<>(); // 观察者列表
private String state; // 主题状态
@Override
public void registerObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
System.out.println("观察者 " + observer + " 已注册");
}
@Override
public void removeObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
System.out.println("观察者 " + observer + " 已移除");
}
@Override
public void notifyObservers() {
System.out.println("主题状态变化,通知所有观察者...");
for (Observer observer : observers) {
observer.update(state);
}
}
// 设置状态并通知观察者
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
System.out.println("主题状态设置为: " + state);
notifyObservers(); // 状态变化时自动通知
}
}
// 具体观察者 - 实现观察者接口
public class ConcreteObserver implements Observer {
private String name; // 观察者名称
public ConcreteObserver(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void update(String message) {
System.out.println(name + " 收到通知: " + message);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}1.2.4 📰 实际应用示例
💡 场景:新闻社发布新闻,各个新闻频道自动接收并报道!
问题:新闻社需要及时通知所有订阅的新闻频道
typescript
// 新闻发布系统 - 具体主题
public class NewsAgency implements Subject {
private List<Observer> observers = new ArrayList<>(); // 新闻频道列表
private String news; // 最新新闻
@Override
public void registerObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.add(observer);
System.out.println("新闻频道 " + observer + " 已订阅");
}
@Override
public void removeObserver(Observer observer) {
observers.remove(observer);
System.out.println("新闻频道 " + observer + " 已取消订阅");
}
@Override
public void notifyObservers() {
System.out.println("📢 新闻社发布新闻,通知所有频道...");
for (Observer observer : observers) {
observer.update(news);
}
}
// 发布新闻
public void publishNews(String news) {
this.news = news;
System.out.println("📰 新闻社发布新闻: " + news);
notifyObservers();
}
}
// 新闻频道 - 具体观察者
public class NewsChannel implements Observer {
private String name; // 频道名称
public NewsChannel(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void update(String news) {
System.out.println("📺 " + name + " 频道报道: " + news);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
// 使用示例
public class ObserverPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建新闻社
NewsAgency newsAgency = new NewsAgency();
// 创建新闻频道
NewsChannel cctv = new NewsChannel("CCTV");
NewsChannel bbc = new NewsChannel("BBC");
NewsChannel cnn = new NewsChannel("CNN");
// 频道订阅新闻社
newsAgency.registerObserver(cctv);
newsAgency.registerObserver(bbc);
newsAgency.registerObserver(cnn);
System.out.println("\n=== 发布第一条新闻 ===");
newsAgency.publishNews("重大新闻:人工智能技术取得突破性进展!");
System.out.println("\n=== BBC取消订阅 ===");
newsAgency.removeObserver(bbc);
System.out.println("\n=== 发布第二条新闻 ===");
newsAgency.publishNews("科技新闻:新型电动汽车即将上市!");
}
}🎯 第二部分:策略模式(Strategy Pattern)
arduino
🎯 策略舞者的登场 🎯
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 🎯 策略者:我是算法选择专家! │
│ │
│ 💰 客户:"我要用支付宝支付!" │
│ 🎯 策略者:"我来切换策略!" │
│ 💰 客户:"我要用微信支付!" │
│ 🎯 策略者:"继续切换策略!" │
│ │
│ 💡 核心思想:算法可以互相替换 │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘🏗️ 策略模式UML类图
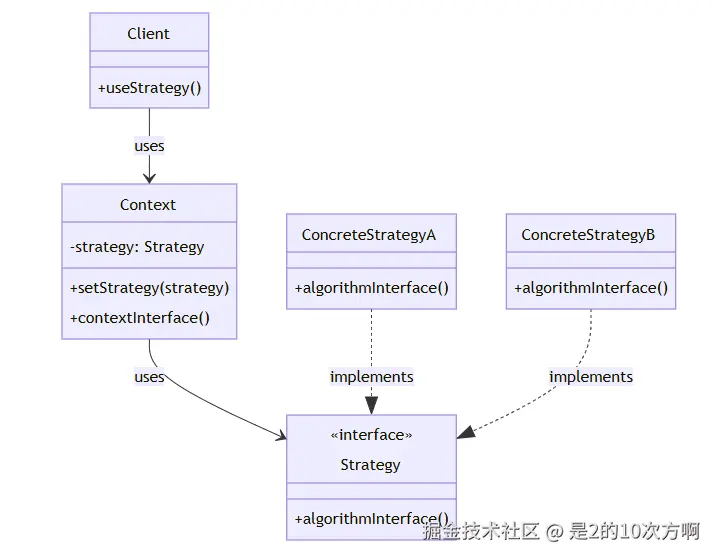
2.1 🎭 什么是策略模式?
一句话理解:定义一系列算法,让它们可以互相替换,就像选择不同的支付方式一样!
定义:定义一系列的算法,把它们一个个封装起来,并且使它们可以互相替换。
应用场景:支付方式选择、排序算法选择、压缩算法选择、游戏角色技能选择
2.2 🛠️ 策略模式的实现
2.2.1 🏗️ 基本结构
💡 小贴士:策略模式就像游戏中的技能选择,玩家可以根据需要切换不同的技能!
核心组件:
- Strategy(策略) :算法的抽象接口
- ConcreteStrategy(具体策略) :具体的算法实现
- Context(上下文) :使用策略的客户端
2.2.2 🚀 多种实现方式
| 实现方式 | 特点 | 推荐度 |
|---|---|---|
| 接口策略 | 通过接口定义策略 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 枚举策略 | 使用枚举简化策略 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 函数式策略 | 使用Lambda表达式 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
接口策略实现:
ini
// 接口策略:通过接口定义策略
public interface SortStrategy {
void sort(int[] array);
}
public class BubbleSortStrategy implements SortStrategy {
@Override
public void sort(int[] array) {
System.out.println("使用冒泡排序");
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}
public class QuickSortStrategy implements SortStrategy {
@Override
public void sort(int[] array) {
System.out.println("使用快速排序");
quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
private void quickSort(int[] array, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
private int partition(int[] array, int low, int high) {
int pivot = array[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
}
public class SortContext {
private SortStrategy strategy;
public void setStrategy(SortStrategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void executeSort(int[] array) {
strategy.sort(array);
}
}枚举策略实现:
ini
// 枚举策略:使用枚举简化策略
public enum SortStrategyEnum {
BUBBLE_SORT {
@Override
public void sort(int[] array) {
System.out.println("使用冒泡排序");
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
},
QUICK_SORT {
@Override
public void sort(int[] array) {
System.out.println("使用快速排序");
quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
private void quickSort(int[] array, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
private int partition(int[] array, int low, int high) {
int pivot = array[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
},
MERGE_SORT {
@Override
public void sort(int[] array) {
System.out.println("使用归并排序");
mergeSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
}
private void mergeSort(int[] array, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
mergeSort(array, left, mid);
mergeSort(array, mid + 1, right);
merge(array, left, mid, right);
}
}
private void merge(int[] array, int left, int mid, int right) {
int[] temp = new int[right - left + 1];
int i = left, j = mid + 1, k = 0;
while (i <= mid && j <= right) {
if (array[i] <= array[j]) {
temp[k++] = array[i++];
} else {
temp[k++] = array[j++];
}
}
while (i <= mid) temp[k++] = array[i++];
while (j <= right) temp[k++] = array[j++];
for (i = 0; i < k; i++) {
array[left + i] = temp[i];
}
}
};
public abstract void sort(int[] array);
}
public class EnumSortContext {
private SortStrategyEnum strategy;
public void setStrategy(SortStrategyEnum strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
public void executeSort(int[] array) {
strategy.sort(array);
}
}函数式策略实现:
ini
// 函数式策略:使用Lambda表达式
@FunctionalInterface
public interface SortFunction {
void sort(int[] array);
}
public class FunctionalSortContext {
private SortFunction sortFunction;
public void setSortFunction(SortFunction sortFunction) {
this.sortFunction = sortFunction;
}
public void executeSort(int[] array) {
sortFunction.sort(array);
}
// 预定义的排序策略
public static final SortFunction BUBBLE_SORT = array -> {
System.out.println("使用冒泡排序");
for (int i = 0; i < array.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < array.length - 1 - i; j++) {
if (array[j] > array[j + 1]) {
int temp = array[j];
array[j] = array[j + 1];
array[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
public static final SortFunction QUICK_SORT = array -> {
System.out.println("使用快速排序");
quickSort(array, 0, array.length - 1);
};
private static void quickSort(int[] array, int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(array, low, high);
quickSort(array, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(array, pi + 1, high);
}
}
private static int partition(int[] array, int low, int high) {
int pivot = array[high];
int i = low - 1;
for (int j = low; j < high; j++) {
if (array[j] <= pivot) {
i++;
int temp = array[i];
array[i] = array[j];
array[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = array[i + 1];
array[i + 1] = array[high];
array[high] = temp;
return i + 1;
}
}2.2.3 🎯 标准实现示例
csharp
// 策略接口 - 定义算法的抽象
public interface Strategy {
void algorithmInterface();
}
// 具体策略A - 实现算法A
public class ConcreteStrategyA implements Strategy {
@Override
public void algorithmInterface() {
System.out.println("🎯 执行策略A的算法");
}
}
// 具体策略B - 实现算法B
public class ConcreteStrategyB implements Strategy {
@Override
public void algorithmInterface() {
System.out.println("🎯 执行策略B的算法");
}
}
// 上下文 - 使用策略的客户端
public class Context {
private Strategy strategy; // 当前使用的策略
public Context(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
}
// 设置策略
public void setStrategy(Strategy strategy) {
this.strategy = strategy;
System.out.println("🔄 策略已切换");
}
// 执行策略
public void contextInterface() {
System.out.println("🚀 开始执行策略...");
strategy.algorithmInterface();
}
}2.2.4 💰 实际应用示例
💡 场景:电商平台支持多种支付方式,用户可以根据需要选择不同的支付策略!
问题:需要支持多种支付方式,并且可以灵活切换
java
// 支付策略接口 - 定义支付行为的抽象
public interface PaymentStrategy {
void pay(double amount);
}
// 支付宝支付策略
public class AlipayStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("💰 使用支付宝支付: " + amount + " 元");
System.out.println("📱 跳转到支付宝支付页面...");
System.out.println("✅ 支付宝支付成功!");
}
}
// 微信支付策略
public class WechatStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("💰 使用微信支付: " + amount + " 元");
System.out.println("📱 跳转到微信支付页面...");
System.out.println("✅ 微信支付成功!");
}
}
// 银行卡支付策略
public class BankCardStrategy implements PaymentStrategy {
@Override
public void pay(double amount) {
System.out.println("💰 使用银行卡支付: " + amount + " 元");
System.out.println("💳 请输入银行卡信息...");
System.out.println("✅ 银行卡支付成功!");
}
}
// 购物车 - 使用支付策略的上下文
public class ShoppingCart {
private PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy; // 当前支付策略
// 设置支付策略
public void setPaymentStrategy(PaymentStrategy paymentStrategy) {
this.paymentStrategy = paymentStrategy;
System.out.println("🔄 支付方式已切换");
}
// 结账
public void checkout(double amount) {
if (paymentStrategy == null) {
System.out.println("❌ 请先选择支付方式!");
return;
}
System.out.println("🛒 开始结账,金额: " + amount + " 元");
paymentStrategy.pay(amount);
System.out.println("🎉 订单完成!");
}
}
// 使用示例
public class StrategyPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建购物车
ShoppingCart cart = new ShoppingCart();
// 创建不同的支付策略
PaymentStrategy alipay = new AlipayStrategy();
PaymentStrategy wechat = new WechatStrategy();
PaymentStrategy bankCard = new BankCardStrategy();
System.out.println("=== 使用支付宝支付 ===");
cart.setPaymentStrategy(alipay);
cart.checkout(100.0);
System.out.println("\n=== 使用微信支付 ===");
cart.setPaymentStrategy(wechat);
cart.checkout(200.0);
System.out.println("\n=== 使用银行卡支付 ===");
cart.setPaymentStrategy(bankCard);
cart.checkout(300.0);
}
}📝 第三部分:命令模式(Command Pattern)
arduino
📝 命令舞者的登场 📝
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 📝 命令者:我是请求封装大师! │
│ │
│ 🎮 遥控器:"我要开灯!" │
│ 📝 命令者:"我来封装请求!" │
│ 🎮 遥控器:"我要关灯!" │
│ 📝 命令者:"继续封装请求!" │
│ │
│ 💡 核心思想:将请求封装为对象 │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘🏗️ 命令模式UML类图
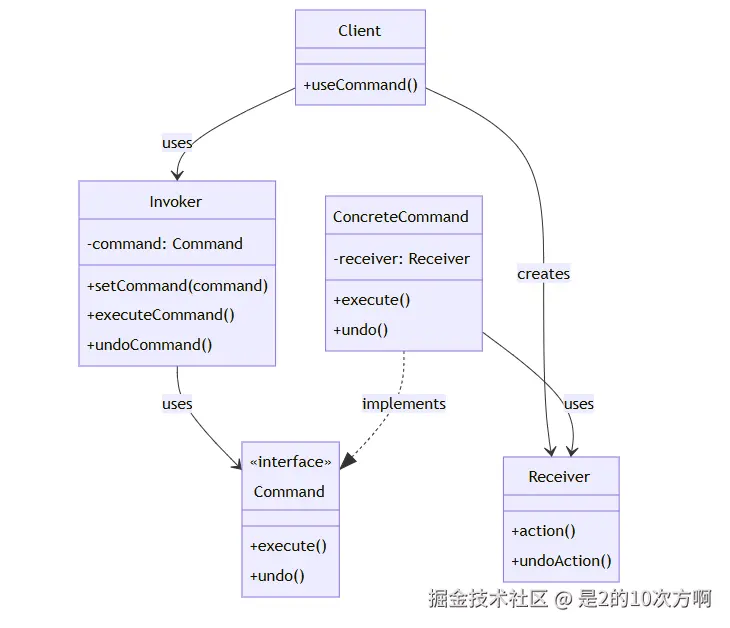
3.1 🎭 什么是命令模式?
一句话理解:将请求封装为对象,支持撤销和重做,就像遥控器一样!
定义:将一个请求封装为一个对象,从而使你可用不同的请求对客户进行参数化。
应用场景:遥控器系统、撤销/重做功能、宏命令、日志记录、事务处理
3.2 🛠️ 命令模式的实现
3.2.1 🏗️ 基本结构
💡 小贴士:命令模式就像遥控器,每个按钮对应一个命令,可以轻松实现撤销重做!
核心组件:
- Command(命令) :封装请求的接口
- ConcreteCommand(具体命令) :具体的命令实现
- Receiver(接收者) :执行命令的对象
- Invoker(调用者) :使用命令的客户端
3.2.2 🚀 多种实现方式
| 实现方式 | 特点 | 推荐度 |
|---|---|---|
| 简单命令 | 一个命令对应一个接收者 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 宏命令 | 一个命令包含多个子命令 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 撤销重做 | 支持命令的撤销和重做 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
简单命令实现:
csharp
// 简单命令:一个命令对应一个接收者
public interface SimpleCommand {
void execute();
}
public class Light {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("电灯打开");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("电灯关闭");
}
}
public class LightOnCommand implements SimpleCommand {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOn();
}
}
public class LightOffCommand implements SimpleCommand {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOff();
}
}
public class SimpleRemoteControl {
private SimpleCommand command;
public void setCommand(SimpleCommand command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void pressButton() {
command.execute();
}
}宏命令实现:
csharp
// 宏命令:一个命令包含多个子命令
public interface MacroCommand extends SimpleCommand {
void addCommand(SimpleCommand command);
void removeCommand(SimpleCommand command);
}
public class MacroCommandImpl implements MacroCommand {
private List<SimpleCommand> commands = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void addCommand(SimpleCommand command) {
commands.add(command);
}
@Override
public void removeCommand(SimpleCommand command) {
commands.remove(command);
}
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("执行宏命令,包含 " + commands.size() + " 个子命令");
for (SimpleCommand command : commands) {
command.execute();
}
}
}
public class TV {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("电视打开");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("电视关闭");
}
}
public class Stereo {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("音响打开");
}
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("音响关闭");
}
public void setVolume(int volume) {
System.out.println("音响音量设置为: " + volume);
}
}
public class TVOnCommand implements SimpleCommand {
private TV tv;
public TVOnCommand(TV tv) {
this.tv = tv;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
tv.turnOn();
}
}
public class StereoOnCommand implements SimpleCommand {
private Stereo stereo;
public StereoOnCommand(Stereo stereo) {
this.stereo = stereo;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
stereo.turnOn();
stereo.setVolume(11);
}
}撤销重做实现:
ini
// 撤销重做:支持命令的撤销和重做
public interface UndoableCommand extends SimpleCommand {
void undo();
}
public class LightOnCommandWithUndo implements UndoableCommand {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommandWithUndo(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOn();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.turnOff();
}
}
public class LightOffCommandWithUndo implements UndoableCommand {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommandWithUndo(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOff();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.turnOn();
}
}
public class CeilingFan {
public static final int HIGH = 3;
public static final int MEDIUM = 2;
public static final int LOW = 1;
public static final int OFF = 0;
private String location;
private int speed;
public CeilingFan(String location) {
this.location = location;
this.speed = OFF;
}
public void high() {
speed = HIGH;
System.out.println(location + " 风扇设置为高速");
}
public void medium() {
speed = MEDIUM;
System.out.println(location + " 风扇设置为中速");
}
public void low() {
speed = LOW;
System.out.println(location + " 风扇设置为低速");
}
public void off() {
speed = OFF;
System.out.println(location + " 风扇关闭");
}
public int getSpeed() {
return speed;
}
}
public class CeilingFanHighCommand implements UndoableCommand {
private CeilingFan ceilingFan;
private int prevSpeed;
public CeilingFanHighCommand(CeilingFan ceilingFan) {
this.ceilingFan = ceilingFan;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
prevSpeed = ceilingFan.getSpeed();
ceilingFan.high();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
switch (prevSpeed) {
case CeilingFan.HIGH:
ceilingFan.high();
break;
case CeilingFan.MEDIUM:
ceilingFan.medium();
break;
case CeilingFan.LOW:
ceilingFan.low();
break;
default:
ceilingFan.off();
break;
}
}
}
public class RemoteControlWithUndo {
private UndoableCommand[] onCommands;
private UndoableCommand[] offCommands;
private UndoableCommand undoCommand;
public RemoteControlWithUndo() {
onCommands = new UndoableCommand[7];
offCommands = new UndoableCommand[7];
UndoableCommand noCommand = new NoCommand();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
onCommands[i] = noCommand;
offCommands[i] = noCommand;
}
undoCommand = noCommand;
}
public void setCommand(int slot, UndoableCommand onCommand, UndoableCommand offCommand) {
onCommands[slot] = onCommand;
offCommands[slot] = offCommand;
}
public void onButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
onCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = onCommands[slot];
}
public void offButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
offCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = offCommands[slot];
}
public void undoButtonWasPushed() {
undoCommand.undo();
}
}
public class NoCommand implements UndoableCommand {
@Override
public void execute() {
// 什么都不做
}
@Override
public void undo() {
// 什么都不做
}
}3.2.3 🎯 标准实现示例
csharp
// 命令接口 - 定义命令的行为
public interface Command {
void execute();
void undo();
}
// 接收者 - 执行具体操作的对象
public class Receiver {
public void action() {
System.out.println("接收者执行操作");
}
public void undoAction() {
System.out.println("接收者撤销操作");
}
}
// 具体命令 - 实现命令接口
public class ConcreteCommand implements Command {
private Receiver receiver;
public ConcreteCommand(Receiver receiver) {
this.receiver = receiver;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
receiver.action();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
receiver.undoAction();
}
}
// 调用者 - 使用命令的客户端
public class Invoker {
private Command command;
public void setCommand(Command command) {
this.command = command;
}
public void executeCommand() {
command.execute();
}
public void undoCommand() {
command.undo();
}
}3.2.4 🎯 实际应用示例
csharp
// 电器接口
public interface Device {
void turnOn();
void turnOff();
}
// 电灯
public class Light implements Device {
@Override
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("电灯打开");
}
@Override
public void turnOff() {
System.out.println("电灯关闭");
}
}
// 开灯命令
public class LightOnCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOn();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.turnOff();
}
}
// 关灯命令
public class LightOffCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.turnOff();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.turnOn();
}
}
// 遥控器
public class RemoteControl {
private Command[] onCommands;
private Command[] offCommands;
private Command undoCommand;
public RemoteControl() {
onCommands = new Command[7];
offCommands = new Command[7];
Command noCommand = new NoCommand();
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
onCommands[i] = noCommand;
offCommands[i] = noCommand;
}
undoCommand = noCommand;
}
public void setCommand(int slot, Command onCommand, Command offCommand) {
onCommands[slot] = onCommand;
offCommands[slot] = offCommand;
}
public void onButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
onCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = onCommands[slot];
}
public void offButtonWasPushed(int slot) {
offCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = offCommands[slot];
}
public void undoButtonWasPushed() {
undoCommand.undo();
}
}本文使用 markdown.com.cn 排版