- 一、线程的创建
-
#include <pthread.h>
-
pthread_create :int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine)(void *), void *arg);
- 功能:创建一个新的线程
- 参数:thread:保存线程ID的变量地址;attr:线程属性的对象地址;NULL:按照默认属性创建;start_routine:函数的指针:指向线程启动后要执行的任务(线程任务函数);arg:为线程任务函数传递的参数
- 返回值:成功:0;失败:非0
-
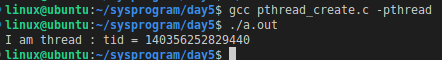
eg.需要注意的是,线程相关函数在编译时需要链接pthread库(-pthread)
-
- 线程的调度 :线程调度由操作系统内核管理
- 线程的终止
- pthread_exit :void pthread_exit(void *retval);
- 功能:退出一个线程任务
- 参数:retval:向回收的线程传递的参数的地址;NULL:表示不传递参数
- pthread_join :int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval)
- 功能:阻塞等待线程结束,回收线程资源空间
- 参数:thread:要回收的线程ID;retval:用来保存线程退出时传递的参数;NULL:不接受参数
- 返回值:成功:0;失败:-1
- int pthread_detach(pthread_t thread);
- 功能:将线程设置成分离属性的线程,线程结束后自动释放资源
- pthread_exit :void pthread_exit(void *retval);
- 二、线程的回收策略
- 分离属性的线程:不需要回收,由操作系统回收(没有空闲的线程可帮忙回收时)
- 非分离属性的线程:pthread_join()阻塞回收
- 线程的属性
- 分离属性:不需要被其他线程回收的线程称为分离属性得到线程,将来会被操作系统所回收
- 非分离属性:可以被其他线程回收或者结束的线程,称为非分离属性的线程(默认属性:非分离属性)
- 函数指针:
- 定义:
- 返回值类型(*指针名称)(形参表);
- void *(*pfun)(void *)
- 函数指针指针初始化:
- 返回值类型(*指针名称)(形参表)=函数的地址;
- void * (*pfun)(void *)= main_ctl(函数名);
- 函数指针赋值:
- 函数指针名称=函数的入口地址;
- void *(*pfun)(void *)=NULL;
- pfun=main_ctl;
- 函数指针怎么使用:
- 函数名(实参表);
- 函数指针(实参表);
- 定义:
- 函数指针数组:保存多个函数指针
- 返回值类型型(*数组名称[n])(形参表);
- void*(*pfun[5])(void *)
- 三、线程间通信
- 全局变量通信
- 临界资源:多个线程可以同时访问的资源称为临界资源;比如,全局变量、共享内存区域等多个线程在访问临界资源时,存在资源竞争问题
- 如何解决资源竞争问题:
- 互斥机制:多个线程访问临界资源时,具有排他性访问的机制(一次只允许一个线程对该临界资源进行访问)
- 全局队列
- 共享内存区域
- 全局变量通信
- 四、互斥锁:是线程同步的基本工具,用于保护共享资源,防止多个线程同时访问导致的数据竞争问题
- 创建互斥锁
- pthread_mutex_t
- 初始化互斥锁
- int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
- 功能:初始化互斥锁
- 参数:mutex:锁对象地址;attr:锁的属性(NULL:默认属性)
- 返回值:成功:0;失败:-1
- int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex,const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
- 加锁
- int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t*mutex);
- 解锁
- int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
- 销毁锁
- int pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
- 确保没有线程持有或等待该锁
- 静态初始化的互斥锁不需要销毁
- 互斥锁使用模式
- 创建互斥锁
