本文核心观点
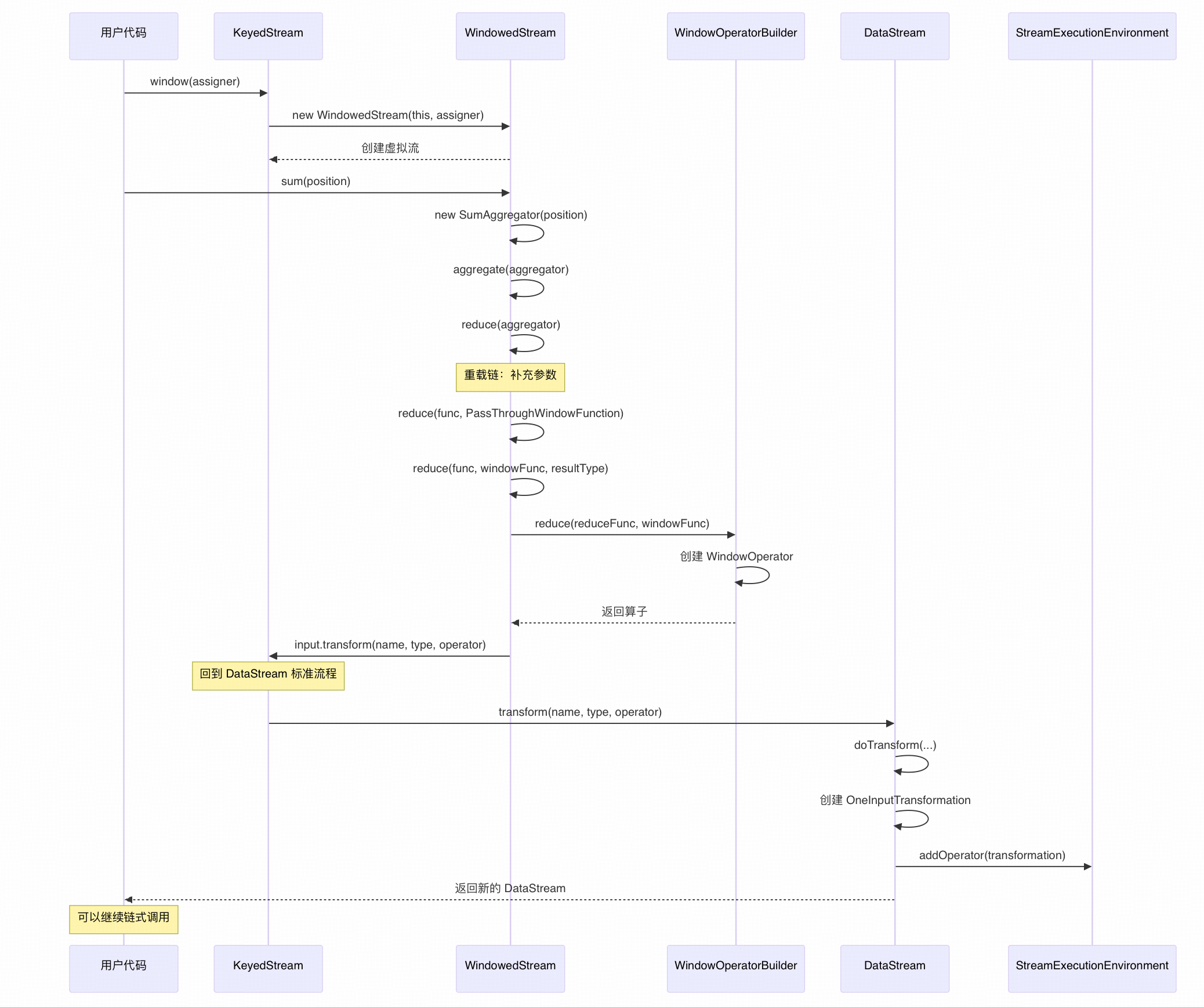
核心观点:WindowedStream 是一个"假流",它比 KeyedStream 更虚,只是一个 API 的过渡器,不是真正意义上的 DataStream,需要调用函数回归。
虚拟化时刻:从真实流到虚拟流
KeyedStream<T,K> keyedStream = ...; // 半虚拟流
WindowedStream<T,K,W> windowedStream = keyedStream.window(assigner); // 完全虚拟流
回归时刻:从虚拟流回到真实流
windowedStream.sum()
return input.transform(opName, resultType, operator); // 回到DataStream标准流程
一、window() 方法的特殊性发现
1.1 只有 KeyedStream 才有 window 方法
java
// DataStream 上没有 window 方法
DataStream<String> stream = ...;
// stream.window(assigner); // 编译错误!
// 只有 KeyedStream 才有 window 方法
KeyedStream<String, String> keyedStream = stream.keyBy(...);
WindowedStream<String, String, TimeWindow> windowedStream = keyedStream.window(assigner);为什么这样设计?
- 窗口操作需要基于 Key 进行分组
- 每个 Key 都有独立的窗口状态
- 保证相同 Key 的数据进入同一个窗口实例
1.2 KeyedStream 的特殊 API 设计
java
public class KeyedStream<T, KEY> extends DataStream<T> {
// 继承 DataStream 的所有方法:map, filter, flatMap...
// KeyedStream 特有的窗口 API
public <W extends Window> WindowedStream<T, KEY, W> window(WindowAssigner<? super T, W> assigner);
public WindowedStream<T, KEY, GlobalWindow> countWindow(long size);
// KeyedStream 特有的聚合 API
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> reduce(ReduceFunction<T> function);
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> sum(int positionToSum);
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> max(int positionToMax);
// ... 其他聚合操作
}设计理念:
- 继承性:保留 DataStream 的所有基础能力
- 扩展性:增加基于 Key 的特殊操作
- 状态性:支持有状态的聚合操作
二、WindowedStream 的"虚拟"本质
2.1 WindowedStream 的创建过程
java
// KeyedStream.java
public <W extends Window> WindowedStream<T, KEY, W> window(
WindowAssigner<? super T, W> assigner) {
return new WindowedStream<>(this, assigner); // 仅仅是创建对象
}关键发现:window() 方法没有创建任何 Transformation!
2.2 WindowedStream 的内部结构
java
public class WindowedStream<T, K, W extends Window> {
// 仅有两个成员变量
private final KeyedStream<T, K> input; // 上游流的引用
private final WindowOperatorBuilder<T, K, W> builder; // 算子构建器
// 注意:没有继承 DataStream!
}2.3 WindowedStream 构造函数解析
java
public WindowedStream(KeyedStream<T, K> input, WindowAssigner<? super T, W> windowAssigner) {
this.input = input; // 保存上游流引用
// 创建窗口算子构建器,用于构建窗口操作的核心组件
// WindowOperatorBuilder是构建者模式的实现,负责组装窗口操作所需的各种组件
this.builder = new WindowOperatorBuilder<>(
// 窗口分配器:决定数据元素被分配到哪个窗口
// 例如:TumblingEventTimeWindows、SlidingEventTimeWindows等
windowAssigner,
// 窗口触发器:决定何时触发窗口计算和输出结果
// 每种窗口分配器都有其默认的触发器策略
// 例如:EventTimeTrigger用于事件时间窗口,ProcessingTimeTrigger用于处理时间窗口
windowAssigner.getDefaultTrigger(input.getExecutionEnvironment()),
// 执行配置:包含序列化器、并行度等运行时配置信息
input.getExecutionConfig(),
// 输入数据类型信息:用于序列化和反序列化输入数据
input.getType(),
// Key选择器:从输入数据中提取分组键,确保相同key的数据进入同一个窗口实例
input.getKeySelector(),
// Key类型信息:用于序列化和反序列化分组键
input.getKeyType());
}重要理解:
- 构造函数只是组装配置信息,没有创建算子
- 比 KeyedStream 更"虚",KeyedStream 好歹有个 PartitionTransformation
- WindowedStream 什么 Transformation 都没有
2.4 WindowedStream 的"虚拟"特性
| 流类型 | 虚拟化程度 | 特性描述 |
|---|---|---|
| DataStream | 🟢 真实流 | ✅ 有 Transformation ✅ 支持链式调用 ✅ 可直接执行 |
| KeyedStream | 🟡 半虚拟流 | ✅ 有 PartitionTransformation ✅ 支持链式调用 ✅ 支持窗口API ⚠️ 无实际算子 |
| WindowedStream | 🔴 完全虚拟流 | ❌ 无 Transformation ❌ 断开链式调用 ✅ 只支持窗口聚合API ⚠️ 纯过渡器 |
WindowedStream 的特殊性:
- 不继承 DataStream - 彻底断开链式调用
- 纯 API 过渡器 - 只是工具类,不是真正的流
- 强制聚合 - 必须调用聚合操作才能回到正常流
- 临时状态 - 无法直接使用,必须转换
WindowedStream 的特殊性:
- 不继承 DataStream - 彻底断开链式调用
- 纯 API 过渡器 - 只是工具类,不是真正的流
- 强制聚合 - 必须调用聚合操作才能回到正常流
- 临时状态 - 无法直接使用,必须转换
三、sum() 方法的完整解析
3.1 sum() 方法的调用链
java
// WindowedStream.java - 入口方法
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> sum(int positionToSum) {
// 创建内置的求和聚合器
return aggregate(new SumAggregator<>(positionToSum, input.getType(), input.getExecutionConfig()));
}
// aggregate 方法 - 中转
private SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> aggregate(AggregationFunction<T> aggregator) {
return reduce(aggregator); // 转发给 reduce
}关键理解:
- sum() 只是一个便利方法
- 内部使用 Flink 预定义的
SumAggregator - 最终还是调用 reduce() 方法
3.2 SumAggregator 的本质
java
// SumAggregator 的继承关系
public class SumAggregator<T> extends AggregationFunction<T> implements ReduceFunction<T> {
private final int positionToSum; // 要求和的字段位置
// 实现具体的求和逻辑
}重要发现:
SumAggregator就是一个ReduceFunction- 与用户自定义的
MapFunction地位完全相同 - Flink 内部预写好的函数,用户也可以自己实现
3.3 reduce() 方法的三层重载
java
// 第一层:只有 ReduceFunction(我们的入口)
public SingleOutputStreamOperator<T> reduce(ReduceFunction<T> function) {
function = input.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(function); // 清理函数
return reduce(function, new PassThroughWindowFunction<>()); // 添加默认 WindowFunction
}
// 第二层:ReduceFunction + WindowFunction
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> reduce(
ReduceFunction<T> reduceFunction,
WindowFunction<T, R, K, W> function) {
// 推断输出类型
TypeInformation<R> resultType = getWindowFunctionReturnType(function, inputType);
return reduce(reduceFunction, function, resultType); // 继续传递
}
// 第三层:完整参数(最终实现)
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> reduce(
ReduceFunction<T> reduceFunction,
WindowFunction<T, R, K, W> function,
TypeInformation<R> resultType) {
// 1. 清理函数(序列化检查)
function = input.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(function);
reduceFunction = input.getExecutionEnvironment().clean(reduceFunction);
// 2. 生成算子名称和描述
final String opName = builder.generateOperatorName();
final String opDescription = builder.generateOperatorDescription(reduceFunction, function);
// 3. 通过 builder 根据function 创建WindowOperator
OneInputStreamOperator<T, R> operator = builder.reduce(reduceFunction, function);
// 4. 根据Operator 创建 OperatorFactory -> transformation -> DataStream
return input.transform(opName, resultType, operator).setDescription(opDescription);
}重载链的设计目的:
- 逐步补充参数:从简单到复杂
- 提供默认值:PassThroughWindowFunction 作为默认窗口函数
- 类型推断:自动推断输出类型
- 函数清理:确保函数可序列化
3.4 PassThroughWindowFunction 的巧妙设计
java
// 第一层 reduce 方法中的关键一行
return reduce(function, new PassThroughWindowFunction<>());PassThroughWindowFunction 的作用:
java
// PassThroughWindowFunction 的简化实现
public class PassThroughWindowFunction<T, K, W extends Window>
implements WindowFunction<T, T, K, W> {
@Override
public void apply(K key, W window, Iterable<T> input, Collector<T> out) {
// 直接透传,不做任何处理
for (T element : input) {
out.collect(element);
}
}
}为什么需要 PassThroughWindowFunction?
- 接口统一:WindowOperator 需要 ReduceFunction + WindowFunction 两个函数
- 透明传递:用户只想要聚合结果,不需要额外处理
- 适配器模式:将单一的 ReduceFunction 适配为完整的窗口处理流程
用户调用sum 只有ReduceFunction
SumAggregator 自动添加
PassThroughWindowFunction WindowOperator需要的
完整函数对
五、回到 DataStream 的标准流程
5.1 关键的回归时刻
java
// WindowedStream 的最后一步 - 回到正轨!
return input.transform(opName, resultType, operator);这一行代码的重要性:
input是KeyedStream(继承自DataStream)- 调用的是
DataStream.transform()方法 - WindowedStream 完成使命,回到标准流程
5.2 transform() 方法的标准处理
java
// DataStream.java - 标准的 transform 方法
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> transform(
String operatorName,
TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo,
OneInputStreamOperator<T, R> operator) {
// 包装算子为工厂
return doTransform(operatorName, outTypeInfo, SimpleOperatorFactory.of(operator));
}5.3 doTransform() 的核心逻辑
java
protected <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> doTransform(...) {
// 1. 创建物理 Transformation
OneInputTransformation<T, R> resultTransform = new OneInputTransformation<>(
this.transformation, // 上游:PartitionTransformation (keyBy产生的)
operatorName, // "Window(TumblingEventTimeWindows(5000), EventTimeTrigger, SumAggregator, PassThroughWindowFunction)"
operatorFactory, // SimpleOperatorFactory(WindowOperator)
outTypeInfo, // 输出类型信息
environment.getParallelism(), // 并行度
false); // 不是并行度敏感的
// 2. 创建新的 DataStream
SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> returnStream =
new SingleOutputStreamOperator<>(environment, resultTransform);
// 3. 添加到执行环境 - 重要!
getExecutionEnvironment().addOperator(resultTransform);
return returnStream;
}关键步骤解析:
- 创建物理 Transformation:包含真正的算子
- 构建新的 DataStream:恢复正常的流
- 注册到环境:只有物理 Transformation 才会被注册
六、调用时序图
导航链接
上节链接 :Flink Stream API 源码走读 - keyBy
下节预告:Flink Stream API 源码走读 - print