哲学家就餐问题(Dining Philosophers Problem)是计算机科学中一个经典的并发控制问题 ,常用来解释多线程环境下的同步 与死锁 问题。本文将结合 Java 的 Semaphore(信号量)机制 ,先演示死锁场景,再介绍两种常见的解决方案。
1 问题背景
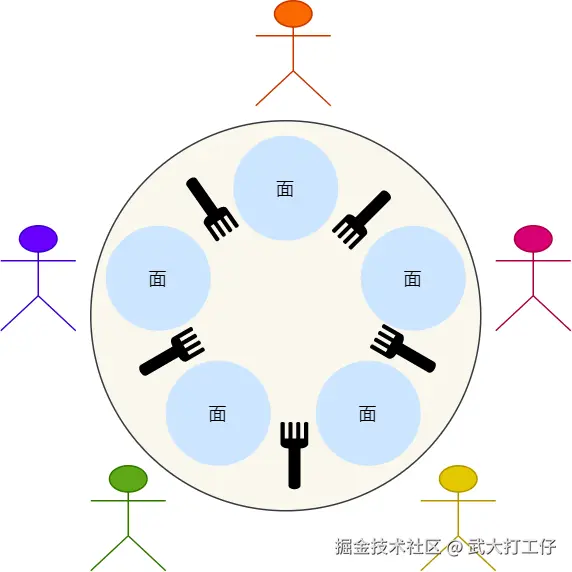
- 有 5 个哲学家围坐在圆桌旁,每人左右各有一根筷子。
- 哲学家需要 两根筷子 才能进餐。
- 每个哲学家有两个动作:思考 (think) 和进餐 (eat)。
如果所有哲学家都先拿左手边的筷子,再尝试拿右手边的筷子,就可能出现所有人都拿了一根筷子并等待另一根筷子的情况,导致整个系统进入死锁。
2 死锁场景复现
Java 实现(死锁版本)
java
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
class Philosopher extends Thread {
private int id;
private Semaphore[] chopsticks;
public Philosopher(int id, Semaphore[] chopsticks) {
this.id = id;
this.chopsticks = chopsticks;
}
private void think() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("哲学家 " + id + " 正在思考...");
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 1000));
}
private void eat() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("哲学家 " + id + " 正在吃饭...");
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 1000));
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
think();
// 所有人都先拿左手边的筷子
chopsticks[id].acquire();
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].acquire();
eat();
chopsticks[id].release();
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].release();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class DiningPhilosophersDeadlock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 5;
Semaphore[] chopsticks = new Semaphore[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) chopsticks[i] = new Semaphore(1);
Philosopher[] philosophers = new Philosopher[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
philosophers[i] = new Philosopher(i, chopsticks);
philosophers[i].start();
}
}
}死锁现象
运行一段时间后,可能出现以下情况:
plain
哲学家 0 拿起左手筷子,等待右手筷子...
哲学家 1 拿起左手筷子,等待右手筷子...
哲学家 2 拿起左手筷子,等待右手筷子...
哲学家 3 拿起左手筷子,等待右手筷子...
哲学家 4 拿起左手筷子,等待右手筷子...所有哲学家都拿了一根筷子,互相等待,导致死锁。
3 解决办法
哲学家就餐问题的核心挑战是:如何避免死锁 ,同时尽量减少等待。下面介绍两种常见的解决方案。
方法一:服务员方案(限制同时拿筷子人数)
思路
- 使用一个"服务员"信号量,最多允许
N-1个哲学家同时拿筷子。 - 这样就不会出现所有人都占用一根筷子的情况。
Java 实现
java
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
class Philosopher extends Thread {
private int id;
private Semaphore[] chopsticks;
private Semaphore waiter;
public Philosopher(int id, Semaphore[] chopsticks, Semaphore waiter) {
this.id = id;
this.chopsticks = chopsticks;
this.waiter = waiter;
}
private void think() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("哲学家 " + id + " 正在思考...");
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 1000));
}
private void eat() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("哲学家 " + id + " 正在吃饭...");
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 1000));
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
think();
waiter.acquire();
chopsticks[id].acquire();
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].acquire();
eat();
chopsticks[id].release();
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].release();
waiter.release();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class DiningPhilosophersWaiter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 5;
Semaphore[] chopsticks = new Semaphore[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) chopsticks[i] = new Semaphore(1);
Semaphore waiter = new Semaphore(N - 1);
Philosopher[] philosophers = new Philosopher[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
philosophers[i] = new Philosopher(i, chopsticks, waiter);
philosophers[i].start();
}
}
}特点
✅ 简单可靠,避免死锁。
❌ 引入了额外的"服务员"角色。
方法二:奇偶编号方案(打破环路)
思路
- 给哲学家编号:
- 偶数编号:先拿左手筷子,再拿右手筷子。
- 奇数编号:先拿右手筷子,再拿左手筷子。
- 打破了"环路等待"条件,从而避免死锁。
Java 实现
java
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
class Philosopher extends Thread {
private int id;
private Semaphore[] chopsticks;
public Philosopher(int id, Semaphore[] chopsticks) {
this.id = id;
this.chopsticks = chopsticks;
}
private void think() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("哲学家 " + id + " 正在思考...");
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 1000));
}
private void eat() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("哲学家 " + id + " 正在吃饭...");
Thread.sleep((int) (Math.random() * 1000));
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true) {
think();
if (id % 2 == 0) {
chopsticks[id].acquire();
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].acquire();
} else {
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].acquire();
chopsticks[id].acquire();
}
eat();
chopsticks[id].release();
chopsticks[(id + 1) % chopsticks.length].release();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class DiningPhilosophersOddEven {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = 5;
Semaphore[] chopsticks = new Semaphore[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) chopsticks[i] = new Semaphore(1);
Philosopher[] philosophers = new Philosopher[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
philosophers[i] = new Philosopher(i, chopsticks);
philosophers[i].start();
}
}
}特点
✅ 不需要额外的"服务员",逻辑更简洁。
❌ 可能存在哲学家饥饿(长时间没机会进餐)的情况。
4 总结
哲学家就餐问题反映了多线程编程中的核心挑战:
- 死锁:多个线程相互等待资源,最终阻塞。
- 饥饿:某些线程长时间得不到资源。
本文给出了:
- 死锁场景(所有人先拿左手筷子)。
- 服务员方案:用信号量限制并发度,避免死锁。
- 奇偶编号方案:通过调整拿筷子顺序打破环路。
👉 这三种实现很好地展示了操作系统课本中"死锁条件"与"死锁避免"的思想。