目录
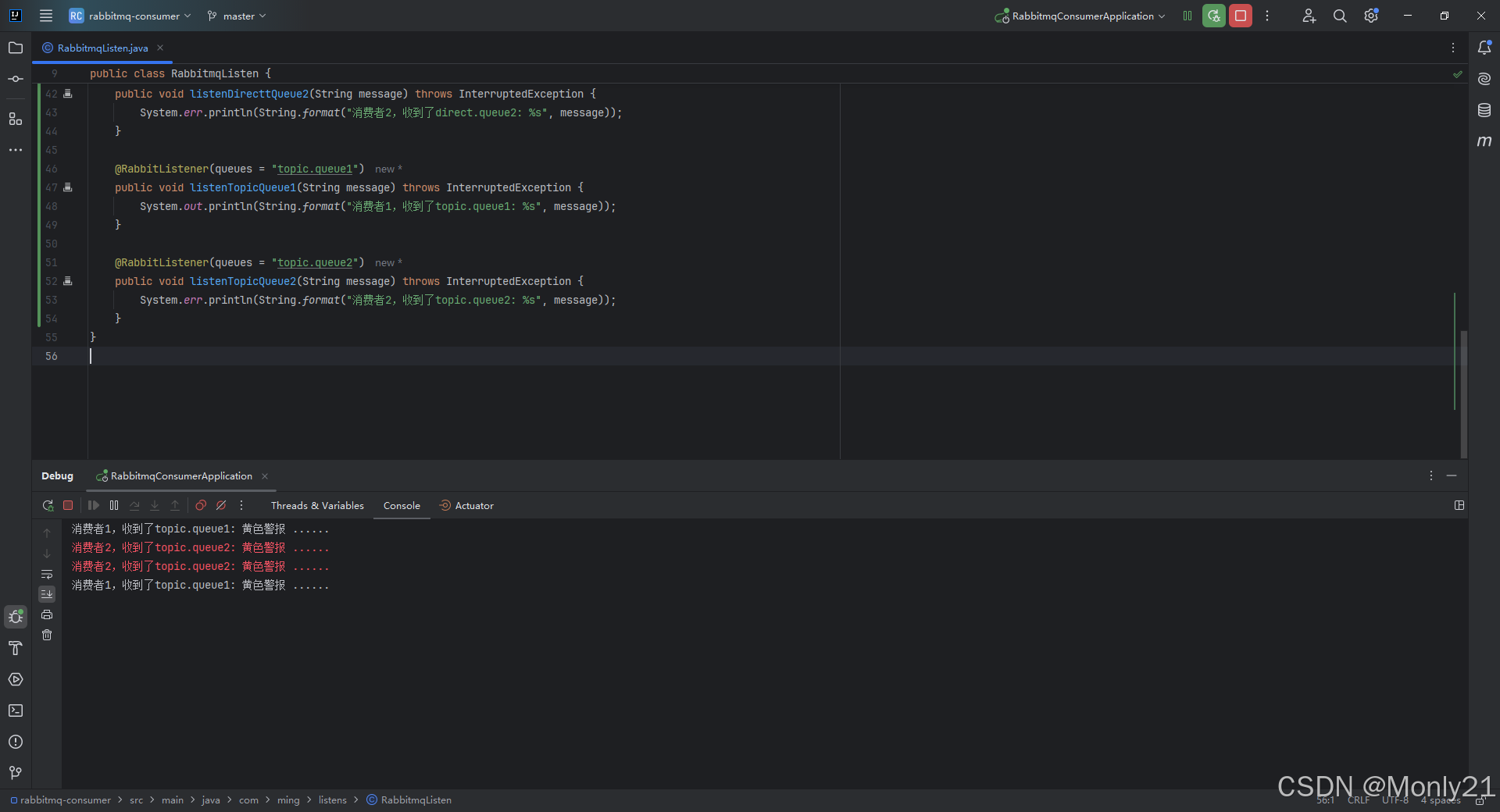
TopicExchange与DirectExchange类似,区别在于RoutingKey可以是多个单次的列表,并且以.分割。
Queue与Exchange指定BindingKey时可以使用通配符:
#:代指0个或多个单词。*:代指一个单词。
一、案例需求
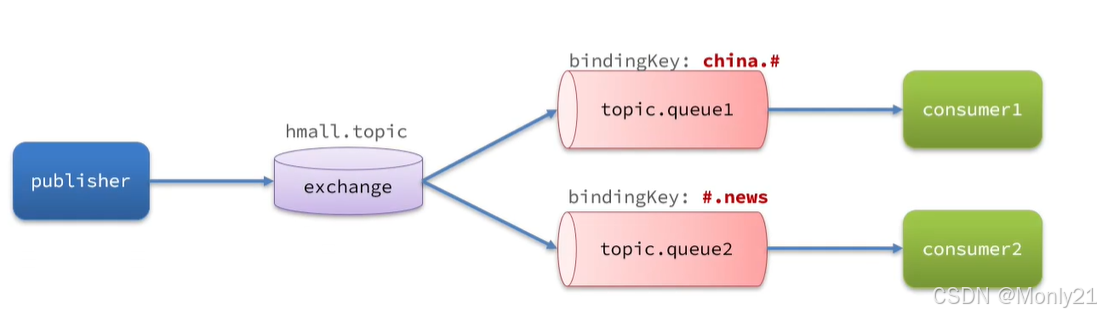
- 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明队列
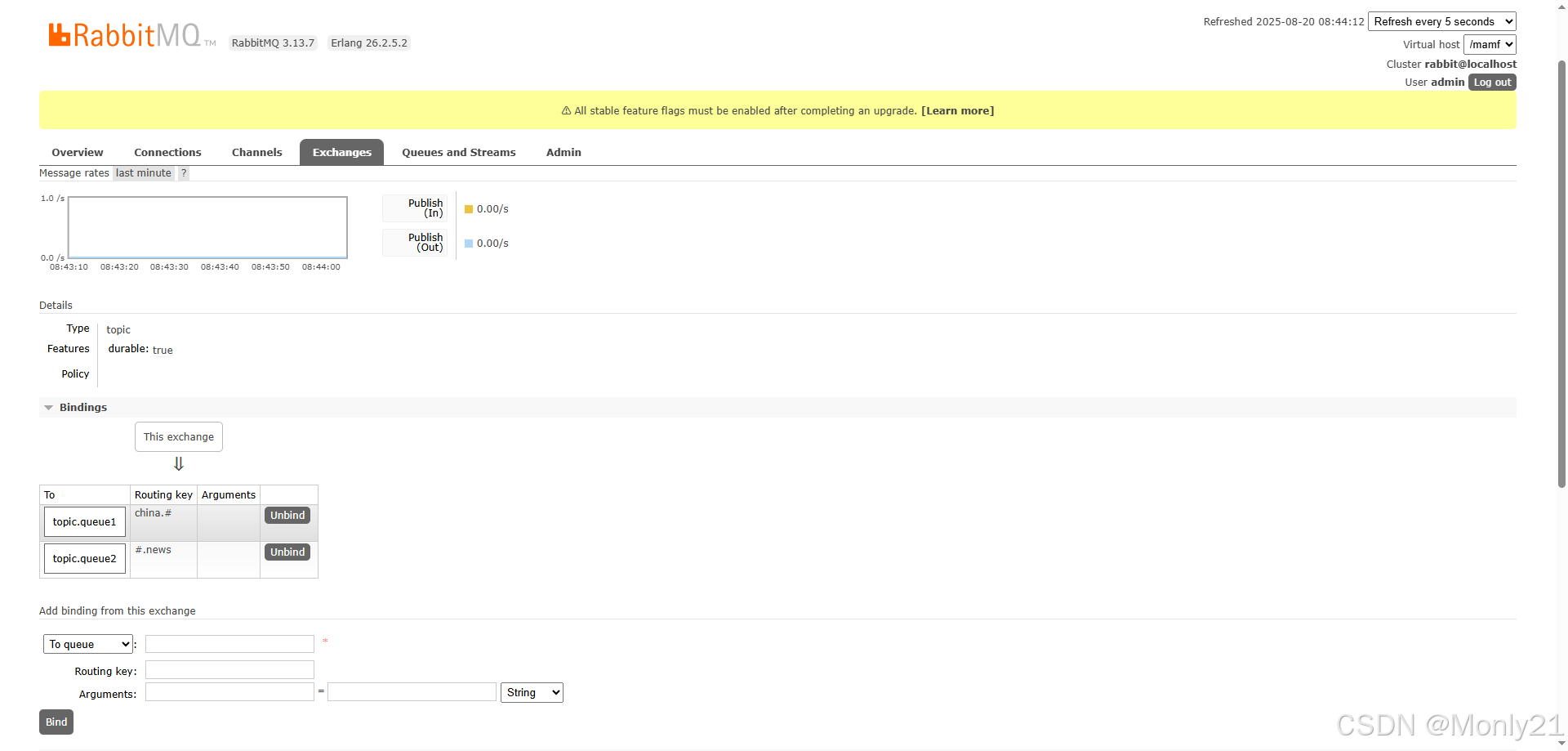
topic.queue1和topic.queue2。 - 在RabbitMQ控制台中,声明交换机
mt.topic,将两个队列与其绑定。 - 在生产者服务中,利用不同的
RoutingKey向mt.topic交换机发送消息。 - 在消费者服务中,编写两个消费者,分别监听队列
topic.queue1和topic.queue2。
二、基础配置
首先创建两个队列topic.queue1和topic.queue2。
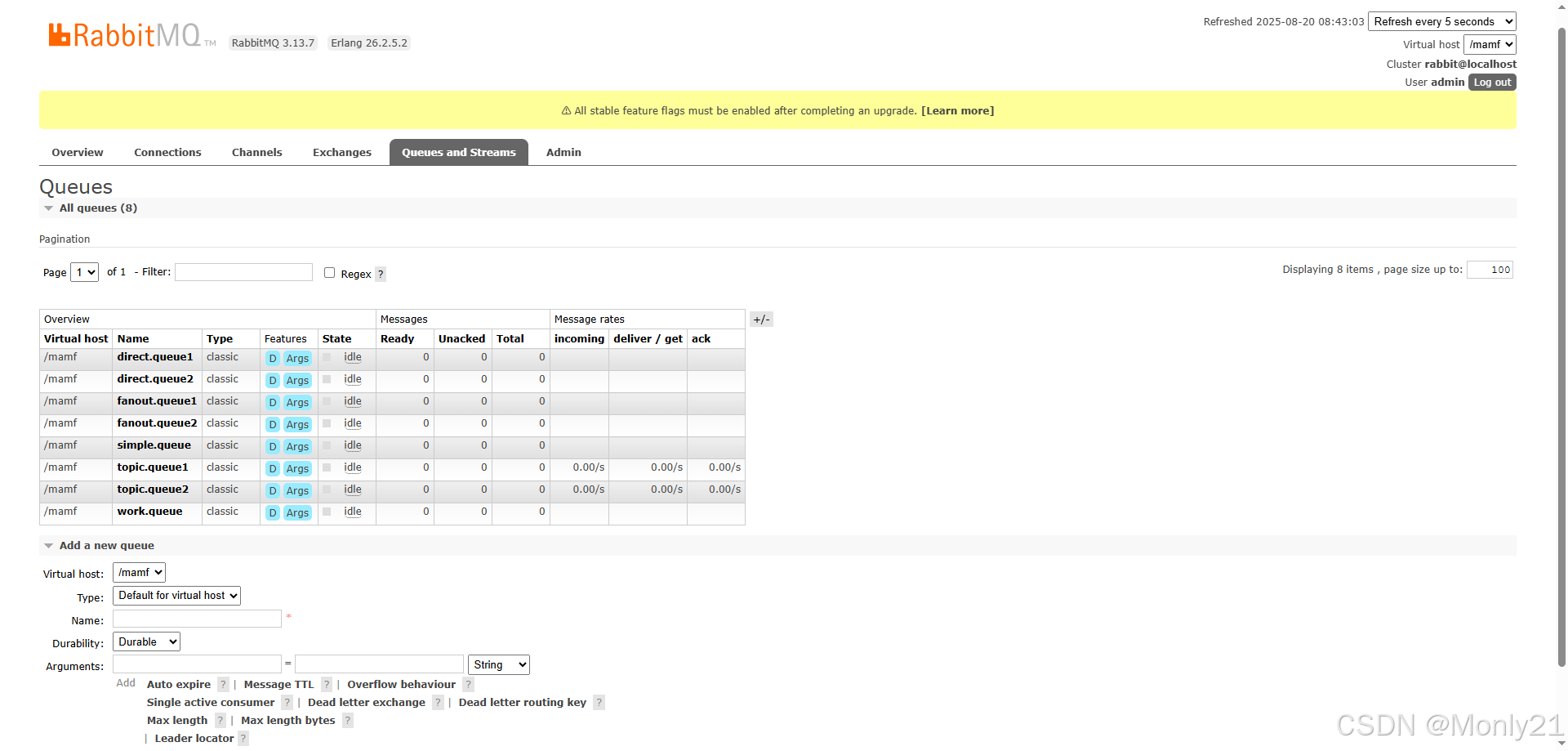
创建一个主题交换机mt.topic,需要注意的是,在创建交换机的时候需要修改交换机的类型topic主题交换机。
交换机创建之后,点击交换机的名称,绑定交换机与队列之间的关系。
三、代码实现
生产者
java
/**
* 给交换机发送消息(主题交换机)
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
@Test
public void topicExchangeTest() throws InterruptedException {
String exchangeName = "mt.topic";
String message = "黄色警报 ......";
// rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.news", message);
// rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "japan.news", message);
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.weather", message);
}消费者
java
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue1")
public void listenTopicQueue1(String message) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(String.format("消费者1,收到了topic.queue1: %s", message));
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue2")
public void listenTopicQueue2(String message) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println(String.format("消费者2,收到了topic.queue2: %s", message));
}