在前几篇文章中,我们已经学习了 无泄露 PCA 的降维流程,以及如何在单个分类器上实现整图预测。今天我们进一步扩展:
👉 使用 多个分类器(SVM、RF、kNN、Logistic、AdaBoost) 对比精度
👉 给出 OA / AA / Kappa 三个指标的对比条形图
👉 新增 整图预测可视化,通过 2×2 子图直观展示不同分类器在整幅影像上的预测结果差异
数据与任务
我们使用 KSC 高光谱影像 (KSC.mat) 及其地物标注 (KSC_gt.mat)。完成:
StandardScaler标准化 +PCA降维(只用训练集fit,再对整图transform)- 五类经典分类器(SVM、随机森林、kNN、Logistic、AdaBoost)对比
- 指标:OA / AA / Kappa / F1(macro)
- 整图预测的 2×2 可视化(SVM / RF / kNN / Logistic)
1) 环境与全局参数
Sklearn 亮点:
train_test_split支持stratify分层抽样;StandardScaler/PCA是常见的"先标准化、再降维"预处理管道;- 设定随机种子有助于复现实验。
python
# 1) 依赖与参数
import os, time
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as sio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier, AdaBoostClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import (confusion_matrix, classification_report,
accuracy_score, cohen_kappa_score, f1_score)
# ===== 修改为你的数据路径(包含 KSC.mat 与 KSC_gt.mat)=====
DATA_DIR = r"your_path"
# 实验参数
PCA_DIM = 30
TRAIN_RATIO = 0.3
SEED = 422) 读取与抽取有标注像素
Sklearn 亮点:本段暂不调用算法;目的是把数据整理成 sklearn 善用的"样本×特征"二维表。
python
# 2) 加载 KSC 影像与标注
X = sio.loadmat(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "KSC.mat"))["KSC"].astype(np.float32) # (H, W, B)
Y = sio.loadmat(os.path.join(DATA_DIR, "KSC_gt.mat"))["KSC_gt"].astype(int) # (H, W)
h, w, b = X.shape
coords = np.argwhere(Y != 0) # 有标签像素的坐标
labels = Y[coords[:, 0], coords[:, 1]] - 1 # 0-based 标签(sklearn 常用)
num_classes = int(labels.max() + 1)
print(f"H×W×Bands = {h}×{w}×{b}, labeled={len(coords)}, classes={num_classes}")3) 分层划分训练/测试集
Sklearn 亮点:
train_test_split(..., stratify=labels)让每个类别在 train/test 中"成分相似"。- 这一步只在有标签像素上进行。
python
# 3) 分层抽样划分
train_ids, test_ids = train_test_split(
np.arange(len(coords)),
train_size=TRAIN_RATIO,
stratify=labels,
random_state=SEED
)
print(f"train={len(train_ids)}, test={len(test_ids)}")4) 无泄露预处理:StandardScaler + PCA
Sklearn 使用:
StandardScaler().fit(训练像素):只在训练集fit,避免把测试信息泄露进数据分布;PCA(n_components=PCA_DIM):在标准化之后做降维;- 对整图先
reshape成(H*W, B),再transform,最后还原形状。
python
# 4) 仅用训练像素拟合 StandardScaler 与 PCA
train_pixels = X[coords[train_ids, 0], coords[train_ids, 1]] # (N_train, B)
scaler = StandardScaler().fit(train_pixels) # 只用训练集 fit
pca = PCA(n_components=PCA_DIM, random_state=SEED).fit(scaler.transform(train_pixels))
# 整图统一 transform(不会泄露)
X_flat = X.reshape(-1, b)
X_std = scaler.transform(X_flat)
X_pca_flat = pca.transform(X_std)
X_pca = X_pca_flat.reshape(h, w, PCA_DIM)
# 从降维后的整图中抽样训练/测试像素
X_train = X_pca[coords[train_ids, 0], coords[train_ids, 1]]
y_train = labels[train_ids]
X_test = X_pca[coords[test_ids, 0], coords[test_ids, 1]]
y_test = labels[test_ids]
print("X_train:", X_train.shape, "X_test:", X_test.shape)5) 定义五类经典分类器
Sklearn 使用(核心参数):
-
SVC(kernel='rbf', C, gamma):C越大越"重罚误分"(可能过拟合),gamma控制 RBF 核宽度(越大越"窄");
-
RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators, max_depth):- 多棵随机树投票,
n_estimators越多越稳但更慢;
- 多棵随机树投票,
-
KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors, weights):weights='distance'常比等权投票更稳;
-
LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', max_iter):- 多类别默认为"multinomial",
max_iter需足够大保证收敛;
- 多类别默认为"multinomial",
-
AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators):- 迭代强调难分类样本的权重,适合弱学习器提升。
python
# 5) 五类模型
models = {
"SVM": SVC(kernel="rbf", C=20, gamma=0.005),
"RF": RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=400, max_depth=20, random_state=SEED, n_jobs=-1),
"kNN": KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5, weights="distance", n_jobs=-1),
"Logistic": LogisticRegression(max_iter=2000, tol=1e-4, solver="lbfgs"), # 不显式设置 multi_class(>=1.5 已默认 multinomial)
"AdaBoost": AdaBoostClassifier(n_estimators=200, random_state=SEED)
}6) 训练与评估(OA / AA / Kappa / F1)
Sklearn 使用:
classification_report一次给出 per-class Precision/Recall/F1;accuracy_score= OA;- AA(Average Accuracy) 可理解为召回的宏平均 :
np.mean(diag(cm)/row_sum); cohen_kappa_score衡量与随机一致性的改进;f1_score(..., average='macro')得到宏平均 F1。
python
# 6) 训练与评估
results = {}
y_preds = {} # 留作后续整图预测/对比
for name, clf in models.items():
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
y_preds[name] = y_pred
# 基础指标
oa = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
kappa = cohen_kappa_score(y_test, y_pred)
cm = confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred, labels=np.arange(num_classes))
aa = float(np.nanmean(np.diag(cm) / np.maximum(cm.sum(axis=1), 1)))
f1m = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, average='macro')
results[name] = {"OA": oa, "AA": aa, "Kappa": kappa, "F1_macro": f1m}
print(f"\n=== {name} ===")
print(f"OA={oa*100:.2f}% AA={aa*100:.2f}% Kappa={kappa:.4f} F1_macro={f1m*100:.2f}%")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred, digits=4))7) 指标横向对比条形图
Sklearn 使用 :评价指标都在 sklearn.metrics 里;这里我们把 OA/AA/Kappa/F1 宏平均绘到同一张图上,更直观。
python
# 7) 可视化对比
labels_plot = ["SVM", "RF", "kNN", "Logistic", "AdaBoost"]
oa_vals = [results[m]["OA"]*100 for m in labels_plot]
aa_vals = [results[m]["AA"]*100 for m in labels_plot]
kappa_vals = [results[m]["Kappa"]*100 for m in labels_plot]
f1_vals = [results[m]["F1_macro"]*100 for m in labels_plot]
x = np.arange(len(labels_plot))
width = 0.2
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5.5))
plt.bar(x - 1.5*width, oa_vals, width, label="OA")
plt.bar(x - 0.5*width, aa_vals, width, label="AA")
plt.bar(x + 0.5*width, kappa_vals, width, label="Kappa*100")
plt.bar(x + 1.5*width, f1_vals, width, label="F1 (macro)")
plt.xticks(x, labels_plot)
plt.ylabel("指标(%)")
plt.title("多分类器对比(OA/AA/Kappa/F1_macro)")
plt.legend(frameon=False)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()8) 整图预测(2×2 子图对比:SVM / RF / kNN / Logistic)
Sklearn 使用:
- 训练好的
estimator可直接对(H*W, PCA_DIM)的整图特征进行predict; matplotlib配合BoundaryNorm把色标做成离散类别,避免"连续 colormap"的误导;constrained_layout=True自动处理子图与 colorbar 布局,不会互相遮挡。
python
# 8) 整图预测与 2×2 对比
from matplotlib.colors import ListedColormap, BoundaryNorm
# 只展示四个模型(可按需扩展)
show_keys = ["SVM", "RF", "kNN", "Logistic"]
# 每个模型的整图预测(类别改为 1..C 便于阅读)
pred_maps = {}
for key in show_keys:
pred = models[key].predict(X_pca_flat) # (H*W,)
pred_maps[key] = pred.reshape(h, w) + 1 # (H, W), 1..C
# 统一调色板(离散类别对齐到整数刻度)
base_cmap = plt.get_cmap('tab20')
colors = [base_cmap(i % 20) for i in range(num_classes)]
cmap = ListedColormap(colors)
boundaries = np.arange(0.5, num_classes + 1.5, 1)
norm = BoundaryNorm(boundaries, cmap.N)
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 2, figsize=(12, 9), constrained_layout=True)
axes = axes.ravel()
ims = []
for ax, key in zip(axes, show_keys):
im = ax.imshow(pred_maps[key], cmap=cmap, norm=norm, interpolation='nearest')
ax.set_title(f"{key} 分类图", fontsize=12)
ax.axis('off')
ims.append(im)
# 共享一个总色条,离散刻度;适当抽稀刻度避免过密
cbar = fig.colorbar(
ims[0],
ax=axes.tolist(),
location='right',
shrink=0.9,
pad=0.02,
boundaries=boundaries,
ticks=np.arange(1, num_classes + 1, max(1, num_classes // 12))
)
cbar.set_label("类别ID", rotation=90)
plt.show()结果展示
精度结果:
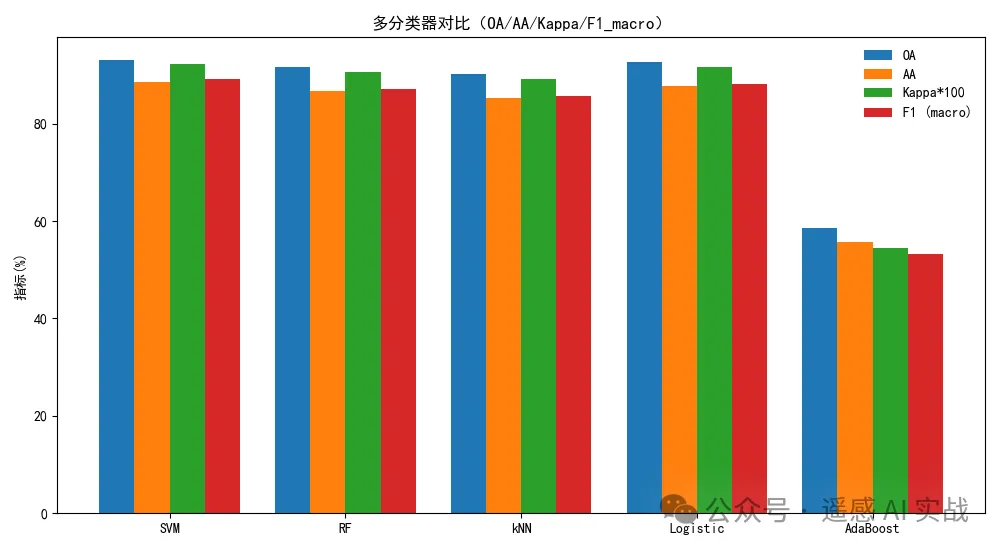
在前几篇文章中,我们已经学习了 无泄露 PCA 的降维流程,以及如何在单个分类器上实现整图预测。
今天我们进一步扩展:
👉 使用 多个分类器(SVM、RF、kNN、Logistic、AdaBoost) 对比精度
👉 给出 OA / AA / Kappa 三个指标的对比条形图
👉 新增 整图预测可视化,通过 2×2 子图直观展示不同分类器在整幅影像上的预测结果差异
分类图:
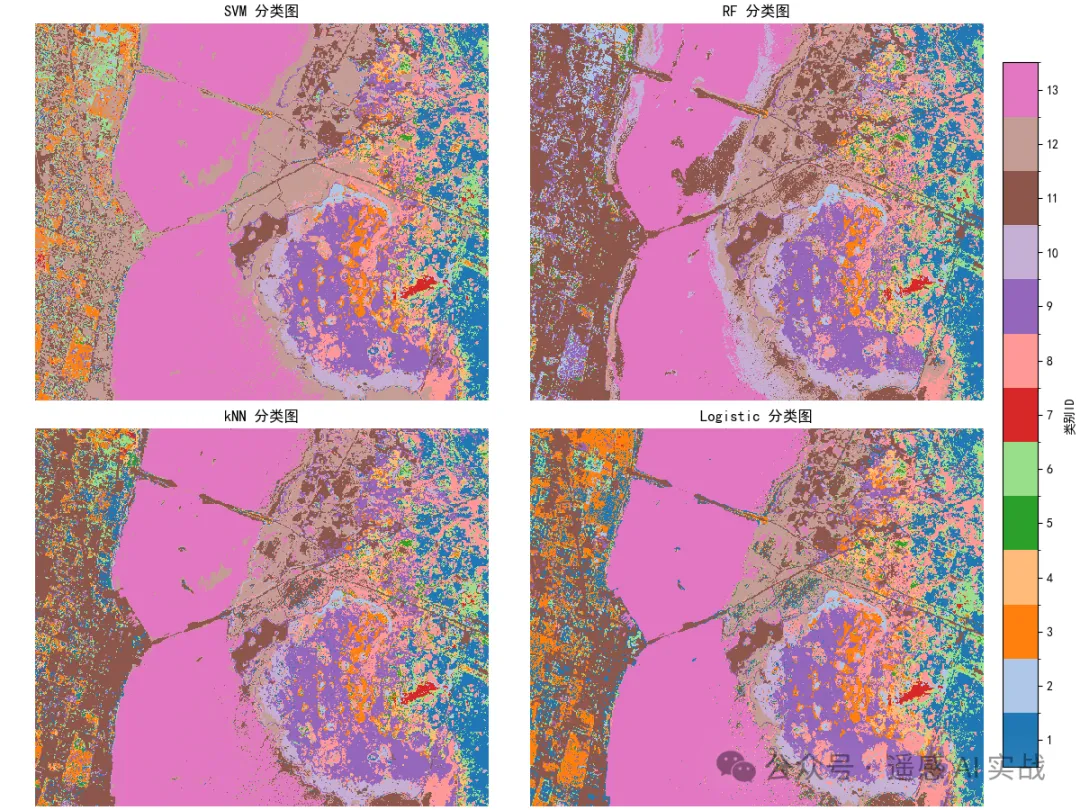
进一步思考
- SVM 参数里,
C与gamma十分关键:若你想系统搜索,建议使用GridSearchCV或HalvingGridSearchCV。 - 随机森林 的
feature_importances_可帮助理解哪些主成分(或波段组合)更重要。 - kNN 对距离度量敏感,标准化与降维往往显著提升效果。
- Logistic 若仍提示收敛,可增大
max_iter或将solver='saga'(更适合大样本或带正则化的场景)。 - AdaBoost 默认基学习器是
DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1)(桩树),也可替换为更强的弱学习器(注意计算代价与过拟合)。
你现在可以做的扩展
- 在本框架中加入 混淆矩阵可视化(计数/归一化两版)以定位"易混类"。
- 引入 交叉验证 进行参数搜索,并把
cv_results_绘成热力图(第③篇已示范)。 - 使用 Voting/Stacking 把多个模型组合起来(可作为第五篇主题)。
欢迎大家关注下方我的公众获取更多内容!