在Spring Security中,AuthenticationEntryPoint 是一个关键接口,用于定义当用户尝试访问受保护资源但未提供凭据或凭据无效时的系统响应行为。其主要职责是通知客户端需要进行身份验证。
📌 接口定义
java
/**
* Used by {@link ExceptionTranslationFilter} to commence an authentication scheme.
*
* @author Ben Alex
*/
public interface AuthenticationEntryPoint {
/**
* Commences an authentication scheme.
* <p>
* <code>ExceptionTranslationFilter</code> will populate the <code>HttpSession</code>
* attribute named
* <code>AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter.SPRING_SECURITY_SAVED_REQUEST_KEY</code>
* with the requested target URL before calling this method.
* <p>
* Implementations should modify the headers on the <code>ServletResponse</code> as
* necessary to commence the authentication process.
* @param request that resulted in an <code>AuthenticationException</code>
* @param response so that the user agent can begin authentication
* @param authException that caused the invocation
*/
void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, AuthenticationException authException)
throws IOException, ServletException;
}commence:意思是"开始",就是"开始认证"的意思。- 当系统发现用户没登录(
Authentication为null或authenticated == false),就会调用这个方法。 - 开发者通过实现这个方法,决定 如何引导用户去认证。
🧩 使用场景
通过上面的接口文档我们知道,接口的作用是引导用户如何去认证,所以根据使用场景可以有不同的认证方式
✅ 场景1:传统 Web 应用(前后端不分离)
java
new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint("/login.html")- 作用:用户访问
/admin,发现没登录 → 跳转到/login.html - 这是最常见的"重定向到登录页"
✅ 场景2:前后端分离 / REST API / 微服务
java
@Override
public void commence(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException e) throws IOException {
response.setStatus(401);
response.setContentType("application/json");
response.getWriter().write("{"error":"Unauthorized", "message":"请先登录"}");
}- 作用:返回一个 JSON 格式的 401 错误,告诉前端"你没登录"
- 前端收到后,可以跳转到登录页或刷新 token
✅ 场景3:OAuth2 资源服务器(Bearer Token)
Spring Security 默认使用 BearerTokenAuthenticationEntryPoint:
-
返回:
httpWWW-Authenticate: Bearer error="invalid_token", error_description="..." Status: 401 Unauthorized -
符合 RFC 6750 规范,告诉客户端"你的 token 有问题
-
在客户端未发送有效Bearer的情况下,即错误发生时,资源服务器须发送WWW-Authenticate头,上面就是返回示例,细节可以去参考
RFC 6750规范
🧩 AuthenticationEntryPoint触发环节?
我在AuthorizationFilter授权过滤器的文章中提及过,当用户尝试访问受保护的资源时(接口),过滤器会利用authorizationManager进行授权决策,如果授权不通过会主动抛出AccessDeniedException异常。下面的代码只保留了相关授权决策流程。
java
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain chain)
throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) servletRequest;
HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse) servletResponse;
....
try {
AuthorizationDecision decision = this.authorizationManager.check(this::getAuthentication, request);
if (decision != null && !decision.isGranted()) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("Access Denied");
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
....
}AccessDeniedException异常会被ExceptionTranslationFilter过滤器捕获,ExceptionTranslationFilter从名字推断功能,异常翻译过滤器
ExceptionTranslationFilter 的作用是:捕获后续过滤器中抛出的安全异常(如未认证、权限不足),并将其"翻译"成标准的 HTTP 响应行为,比如:
- ❌ 未登录 → 跳转到登录页 或 返回
401 Unauthorized - 🚫 已登录但权限不够 → 返回
403 Forbidden
🔍 ExceptionTranslationFilter
scss
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Exception ex) {
// Try to extract a SpringSecurityException from the stacktrace
Throwable[] causeChain = this.throwableAnalyzer.determineCauseChain(ex);
RuntimeException securityException = (AuthenticationException) this.throwableAnalyzer
.getFirstThrowableOfType(AuthenticationException.class, causeChain);
....
handleSpringSecurityException(request, response, chain, securityException);
}
}捕获异常之后调用handleSpringSecurityException处理异常,它将异常分为两类
- 认证异常 调用handleAuthenticationException来处理
- 授权拒绝异常 调用handleAccessDeniedException来处理
java
private void handleSpringSecurityException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain, RuntimeException exception) throws IOException, ServletException {
if (exception instanceof AuthenticationException) {
handleAuthenticationException(request, response, chain, (AuthenticationException) exception);
}
else if (exception instanceof AccessDeniedException) {
handleAccessDeniedException(request, response, chain, (AccessDeniedException) exception);
}
}如果是认证异常直接调用sendStartAuthentication,引导用户开启一个认证流程,但是具体引导用户跳转到登录页还是返回401,取决于使用场景和用户的配置
java
private void handleAuthenticationException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain, AuthenticationException exception) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.logger.trace("Sending to authentication entry point since authentication failed", exception);
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain, exception);
}如果是授权异常,正常情况下调用accessDeniedHandler来处理accessDeniedException,但是这里springsecurity进行了不同情况的判断。
java
private void handleAccessDeniedException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain, AccessDeniedException exception) throws ServletException, IOException {
Authentication authentication = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.getContext().getAuthentication();
boolean isAnonymous = this.authenticationTrustResolver.isAnonymous(authentication);
if (isAnonymous || this.authenticationTrustResolver.isRememberMe(authentication)) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(LogMessage.format("Sending %s to authentication entry point since access is denied",
authentication), exception);
}
sendStartAuthentication(request, response, chain,
new InsufficientAuthenticationException(
this.messages.getMessage("ExceptionTranslationFilter.insufficientAuthentication",
"Full authentication is required to access this resource")));
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
LogMessage.format("Sending %s to access denied handler since access is denied", authentication),
exception);
}
this.accessDeniedHandler.handle(request, response, exception);
}
}如果用户是匿名或者记住我登录的,引导用户开启认证流程。我们来分析下这么设计的意图
🎯 设计哲学: "匿名拒绝" ≠ "权限不足"
Spring Security 遵循一个原则:
💡 如果你连身份都没证明(匿名),那拒绝你不是"权限不足",而是"需要先认证" 。
所以它会:
- 抛出
AccessDeniedException - 但在处理时判断:"哦,你是匿名的"
- → 不走
accessDeniedHandler(那是给"已认证用户"的) - → 走
authenticationEntryPoint,引导你去登录
❓ "为什么 remember-me(记住我)登录的用户,被拒绝时也不走 accessDeniedHandler,而是被当作'需要重新认证'处理?"
因为 remember-me 是一种"弱认证"(weak authentication),Spring Security 认为它不足以访问高权限资源。
当 remember-me 用户被拒绝时,系统会认为:"你虽然是自动登录的,但这次操作需要主动登录 来确认身份",所以引导你去重新认证,而不是简单返回 403。
从上面的代码可以看出引导用户去认证是通过调用sendStartAuthentication方法实现的
java
protected void sendStartAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
AuthenticationException reason) throws ServletException, IOException {
// SEC-112: Clear the SecurityContextHolder's Authentication, as the
// existing Authentication is no longer considered valid
SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context);
this.requestCache.saveRequest(request, response);
this.authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);
}底层调用了this.authenticationEntryPoint.commence(request, response, reason);来发起认证。所以我们整篇文章讨论到这里 已经很清晰了。AuthenticationEntryPoint作为开启认证的入口,是说ExceptionTranslationFilter在拦截到用户的异常之后,如果发现用户是未认证的,就会调用过滤器内部的维护的authenticationEntryPoint来引导用户进行认证。
🛡️ ExceptionTranslationFilter中是如何维护authenticationEntryPoint?
scala
public class ExceptionTranslationFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements MessageSourceAware {
...
private AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint;
private final RequestCache requestCache;
public ExceptionTranslationFilter(AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint) {
this(authenticationEntryPoint, new HttpSessionRequestCache());
}
public ExceptionTranslationFilter(AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint, RequestCache requestCache) {
Assert.notNull(authenticationEntryPoint, "authenticationEntryPoint cannot be null");
Assert.notNull(requestCache, "requestCache cannot be null");
this.authenticationEntryPoint = authenticationEntryPoint;
this.requestCache = requestCache;
}从源码可以看出ExceptionTranslationFilter内部维护了一个属性AuthenticationEntryPoint,并且从构造器可以推断出AuthenticationEntryPoint属性还是不能为空,也就是说构建ExceptionTranslationFilter的时候必须传递进来。那么问题来了?谁来负责创建ExceptionTranslationFilter呢?
这个要分以下几种情况
- 使用springsecurity默认配置
- 如果用户自定义配置了表单登录FormLoginConfigurer
ini
http
.formLogin();- 用户显示配置了http.exceptionHandling
less
http
.exceptionHandling(e -> e
.authenticationEntryPoint(myAuthEntryPoint) // 401 处理
.accessDeniedHandler(myAccessDeniedHandler) // 403 处理
);- OAuth2 资源服务器专用入口
less
http
.oauth2ResourceServer(oauth2 -> o2
.jwt(jwt -> {})
.authenticationEntryPoint(jwtEntryPoint) // 用于 Bearer Token 认证失败
);这上面我主要讲表单配置那一项,其他方式尤其是第四种oauth2资源服务器的方式我会专门写一篇文章。
FormLoginConfigurer
当用户使用http.formLogin()进行各种配置的时候,底层使用的是FormLoginConfigurer这个配置类
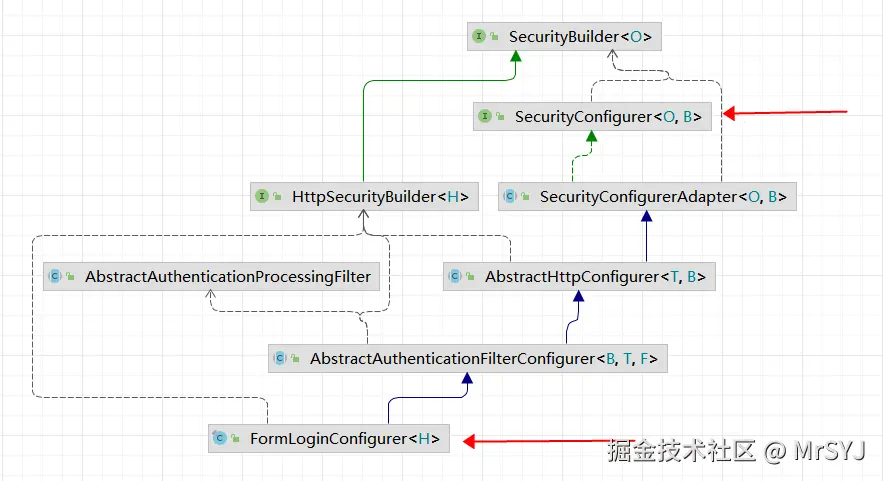
当调用http.formLogin()的时候,最后会调用到void add(C configurer) 然后将FormLoginConfigurer收集到configurers map集合中,从集合的泛型可以看出目的是收集类型为SecurityConfigurer的配置类,从FormLoginConfigurer的继承图来看,它就是一个SecurityConfigurer的实现类。
java
// 集合收集所有的SecurityConfigurer类型的配置类
private final LinkedHashMap<Class<? extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>>, List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>>> configurers = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private <C extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> void add(C configurer) {
Assert.notNull(configurer, "configurer cannot be null");
Class<? extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> clazz = (Class<? extends SecurityConfigurer<O, B>>) configurer
.getClass();
synchronized (this.configurers) {
if (this.buildState.isConfigured()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot apply " + configurer + " to already built object");
}
List<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configs = null;
if (this.allowConfigurersOfSameType) {
configs = this.configurers.get(clazz);
}
configs = (configs != null) ? configs : new ArrayList<>(1);
configs.add(configurer);
this.configurers.put(clazz, configs);
if (this.buildState.isInitializing()) {
this.configurersAddedInInitializing.add(configurer);
}
}
}最后在触发http.build();构建的过程中,会经历不同的阶段。init阶段,configure阶段
ini
protected final O doBuild() throws Exception {
synchronized (this.configurers) {
this.buildState = BuildState.INITIALIZING;
beforeInit();
init();
this.buildState = BuildState.CONFIGURING;
beforeConfigure();
configure();
this.buildState = BuildState.BUILDING;
O result = performBuild();
this.buildState = BuildState.BUILT;
return result;
}
}init阶段就会把收集的所有SecurityConfigurer配置类的init方法全部执行一遍
kotlin
private void init() throws Exception {
Collection<SecurityConfigurer<O, B>> configurers = getConfigurers();
for (SecurityConfigurer<O, B> configurer : configurers) {
configurer.init((B) this);
}
for (SecurityConfigurer<O, B> configurer : this.configurersAddedInInitializing) {
configurer.init((B) this);
}
}恰好FormLoginConfigurer重写了init方法,然后调用 registerAuthenticationEntryPoint(http, this.authenticationEntryPoint);来实现AuthenticationEntryPoint的注册。而this.authenticationEntryPoint的类型是LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint
typescript
private void setLoginPage(String loginPage) {
this.loginPage = loginPage;
this.authenticationEntryPoint = new LoginUrlAuthenticationEntryPoint(loginPage);
}
scss
@Override
public void init(B http) throws Exception {
updateAuthenticationDefaults();
updateAccessDefaults(http);
// 注册一个AuthenticationEntryPoint
registerDefaultAuthenticationEntryPoint(http);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected final void registerDefaultAuthenticationEntryPoint(B http) {
registerAuthenticationEntryPoint(http, this.authenticationEntryPoint);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected final void registerAuthenticationEntryPoint(B http, AuthenticationEntryPoint authenticationEntryPoint) {
ExceptionHandlingConfigurer<B> exceptionHandling = http.getConfigurer(ExceptionHandlingConfigurer.class);
if (exceptionHandling == null) {
return;
}
exceptionHandling.defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor(postProcess(authenticationEntryPoint),
getAuthenticationEntryPointMatcher(http));
}而所谓的注册实际是将authenticationEntryPoint注册到ExceptionHandlingConfigurer中。核心是调用exceptionHandling.defaultAuthenticationEntryPointFor(postProcess(authenticationEntryPoint), getAuthenticationEntryPointMatcher(http)); 将其注入到ExceptionHandlingConfigurer 的一个属性中:defaultEntryPointMappings。ExceptionHandlingConfigurer是用来配置ExceptionTranslationFilter的,将来构建ExceptionTranslationFilter的时候就会用到上面注册的defaultEntryPointMappings。
java
private LinkedHashMap<RequestMatcher, AuthenticationEntryPoint> defaultEntryPointMappings = new LinkedHashMap<>();后面我单独写一篇关于ExceptionTranslationFilter的文章,讲解它是如何配置的,以及是如何创建的。
总结
- AuthenticationEntryPoint是用来引导用户开启认证的。
- ExceptionTranslationFilter在捕获到异常之后,发现如果是未认证的,就会调用AuthenticationEntryPoint来引导用户进行认证
- AuthenticationEntryPoint是ExceptionTranslationFilter中的一个必填的属性。需要依靠它来将异常
翻译成http响应 - ExceptionTranslationFilter中的AuthenticationEntryPoint属性最终是由ExceptionHandlingConfigurer进行配置的,具体怎么生效的后面单独讲一期。下面贴出一小段ExceptionHandlingConfigurer中的代码,大家自己理解下。
kotlin
private AuthenticationEntryPoint createDefaultEntryPoint(H http) {
if (this.defaultEntryPointMappings.isEmpty()) {
return new Http403ForbiddenEntryPoint();
}
if (this.defaultEntryPointMappings.size() == 1) {
return this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator().next();
}
DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint entryPoint = new DelegatingAuthenticationEntryPoint(
this.defaultEntryPointMappings);
entryPoint.setDefaultEntryPoint(this.defaultEntryPointMappings.values().iterator().next());
return entryPoint;
}