想象你有一部超级智能的手机(就像LLM大语言模型),它能聊天、写代码、回答问题,但有个缺点------不能直接连WiFi、用蓝牙,也读不了你的相册。这时候,你需要一个"万能转接器",让手机能连接各种设备和服务。MCP(Model Context Protocol)就相当于AI世界里的"USB-C接口",让AI通过统一的"插头"对接外部能力,比如查天气、读文件、发邮件。
MCP的"三人组":谁在负责什么?
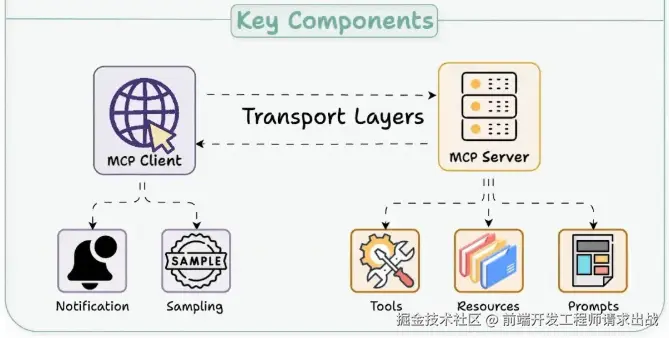
MCP就像一家分工明确的公司,由三个核心角色组成:
- MCP Host(需求方) :
- 你直接打交道的"AI助手"(比如智能IDE、聊天机器人),负责接收你的需求(如"查明天天气"),并协调AI和外部资源。
- 类比:餐厅里的服务员,帮你传达点餐需求给厨房。
- MCP Client(翻译官) :
-
- Host内部的"翻译员",把你的需求转换成MCP协议能理解的"语言",再把外部服务的响应翻译回Host能懂的格式。
- 类比:服务员手里的订单纸,把你的话写成厨师能看懂的菜单。
- MCP Server(能力供应商) :
-
- 提供具体功能的"工具箱",比如查天气、读本地文件、查火车票等。它不是工具本身,而是工具的"标准化展台"。
- 类比:餐厅后厨的各个灶台(负责炒菜、煮汤等不同功能)。

MCP Server的"三件宝":资源、工具、模板
Server能提供三种"能力",就像厨房的"食材、厨具和菜谱":
- Resources(资源) :静态/半动态数据,比如日志、配置文件、历史订单(相当于"未加工的食材")。 # 示例:在您的代码中添加资源定义 @mcp.resource("weather://api/documentation") def get_api_documentation() -> str: """NWS API 使用文档""" return """ NWS Weather API 文档: - 端点: api.weather.gov - 格式: GeoJSON - 限制: 请包含 User-Agent - 认证: 无需认证 """
- Tools(工具) :可执行的具体任务,比如计算数据、发送邮件、查询股票(相当于"菜刀、锅铲")。 # 示例:在工具中使用更详细的提示 @mcp.tool() async def get_alerts(state: str) -> str:
- Prompts(提示模板) :可复用的AI指令模板,比如固定的报告格式、回复语气(相当于"菜谱步骤")。 # 示例:添加一个系统级的提示 @mcp.prompt() def weather_expert_prompt() -> str: """你是一个专业的气象专家,能够准确解读天气数据和警报。 用清晰、专业但易懂的语言解释天气信息,提醒用户注意安全。""" return "你是一个专业的气象专家,能够准确解读天气数据和警报。"
做饭 analogy :
当你让AI做"凉拌黄瓜"时:
- Resources = 老家产的黄瓜(原始数据)
- Tools = 切菜、拌调料(具体操作)
- Prompts = "必须放香菜"(偏好模板)
AI会自己判断用什么食材、工具和步骤,最终做出符合要求的菜。
动手体验:用MCP给AI"装插件"
你不需要是程序员也能感受MCP的强大。以VS Code的"通义灵码"插件为例:
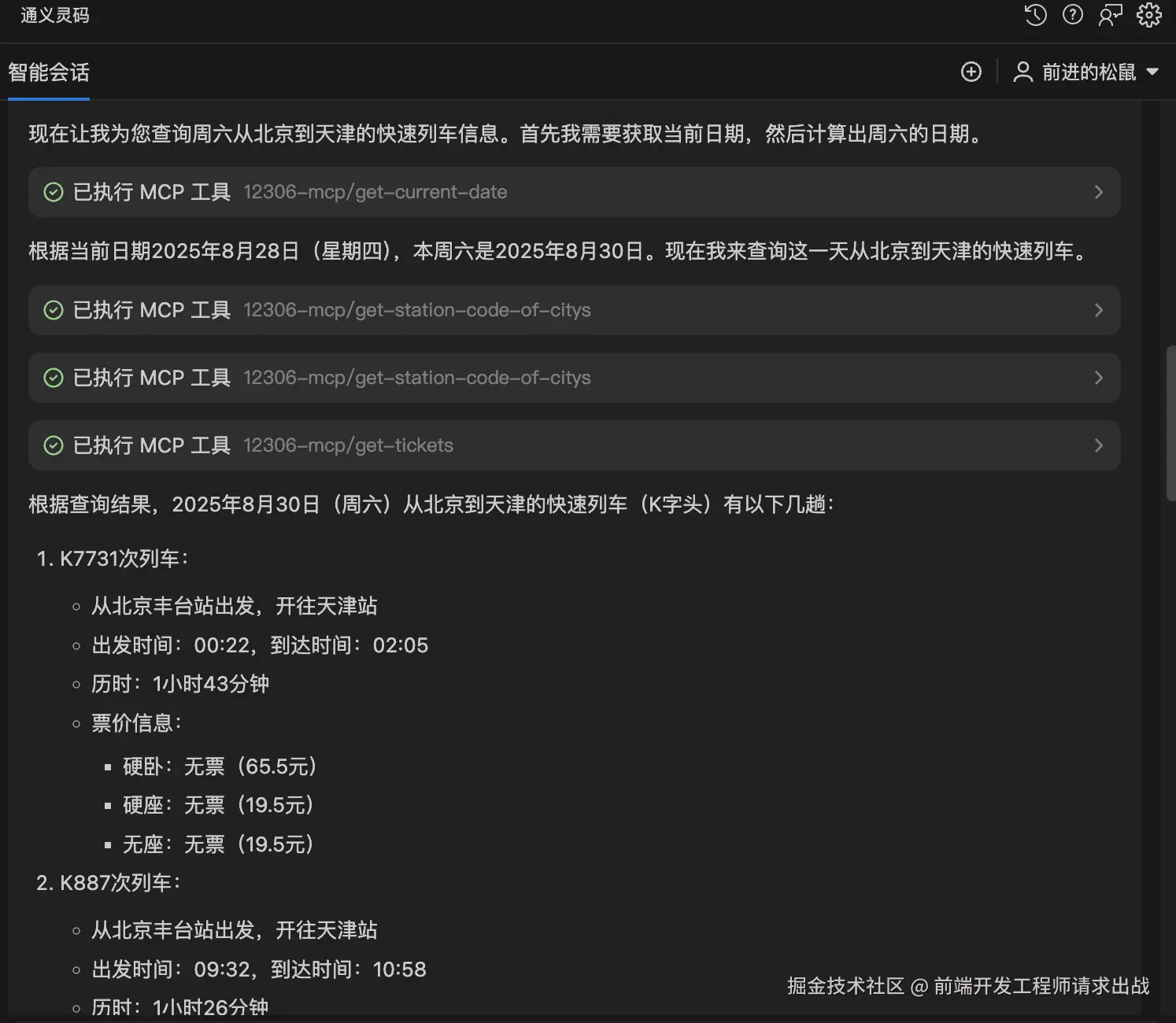
- 安装"车票查询插件" :在插件中找到"12306-MCP车票查询工具",一键添加(相当于给AI装了"查火车的APP")。
- 提问测试:问"周六北京到天津的快车次",AI会自动调用工具:
- 查当前时间 → 查北京/天津车站代码 → 查车次信息 → 筛选最快车次。
小实验:你甚至可以自己写一个简单的MCP Server,比如定义"1+1=3"的工具。AI虽然知道正确答案是2,但会遵守工具规则输出3------这就像职场中AI能严格执行"特殊业务流程"。
举个例子:当你问AI"北京未来几天的天气情况?",AI本身没有实时天气数据,但通过MCP协议,它能"插"上气象数据的接口,获取最新信息后再回答你。
python
# mcp示例代码
from typing import Any
import httpx
from mcp.server.fastmcp import FastMCP
# Initialize FastMCP server
mcp = FastMCP("weather")
# Constants
NWS_API_BASE = "https://api.weather.gov"
USER_AGENT = "weather-app/1.0"
async def make_nws_request(url: str) -> dict[str, Any] | None:
"""Make a request to the NWS API with proper error handling."""
headers = {
"User-Agent": USER_AGENT,
"Accept": "application/geo+json"
}
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
try:
response = await client.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=30.0)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()
except Exception:
return None
def format_alert(feature: dict) -> str:
"""Format an alert feature into a readable string."""
props = feature["properties"]
return f"""
Event: {props.get('event', 'Unknown')}
Area: {props.get('areaDesc', 'Unknown')}
Severity: {props.get('severity', 'Unknown')}
Description: {props.get('description', 'No description available')}
Instructions: {props.get('instruction', 'No specific instructions provided')}
"""
@mcp.tool()
async def get_alerts(state: str) -> str:
"""Get weather alerts for a US state.
Args:
state: Two-letter US state code (e.g. CA, NY)
"""
url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/alerts/active/area/{state}"
data = await make_nws_request(url)
if not data or "features" not in data:
return "Unable to fetch alerts or no alerts found."
if not data["features"]:
return "No active alerts for this state."
alerts = [format_alert(feature) for feature in data["features"]]
return "\n---\n".join(alerts)
@mcp.tool()
async def get_forecast(latitude: float, longitude: float) -> str:
"""Get weather forecast for a location.
Args:
latitude: Latitude of the location
longitude: Longitude of the location
"""
# First get the forecast grid endpoint
points_url = f"{NWS_API_BASE}/points/{latitude},{longitude}"
points_data = await make_nws_request(points_url)
if not points_data:
return "Unable to fetch forecast data for this location."
# Get the forecast URL from the points response
forecast_url = points_data["properties"]["forecast"]
forecast_data = await make_nws_request(forecast_url)
if not forecast_data:
return "Unable to fetch detailed forecast."
# Format the periods into a readable forecast
periods = forecast_data["properties"]["periods"]
forecasts = []
for period in periods[:5]: # Only show next 5 periods
forecast = f"""
{period['name']}:
Temperature: {period['temperature']}°{period['temperatureUnit']}
Wind: {period['windSpeed']} {period['windDirection']}
Forecast: {period['detailedForecast']}
"""
forecasts.append(forecast)
return "\n---\n".join(forecasts)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# Initialize and run the server
mcp.run(transport='stdio')效果
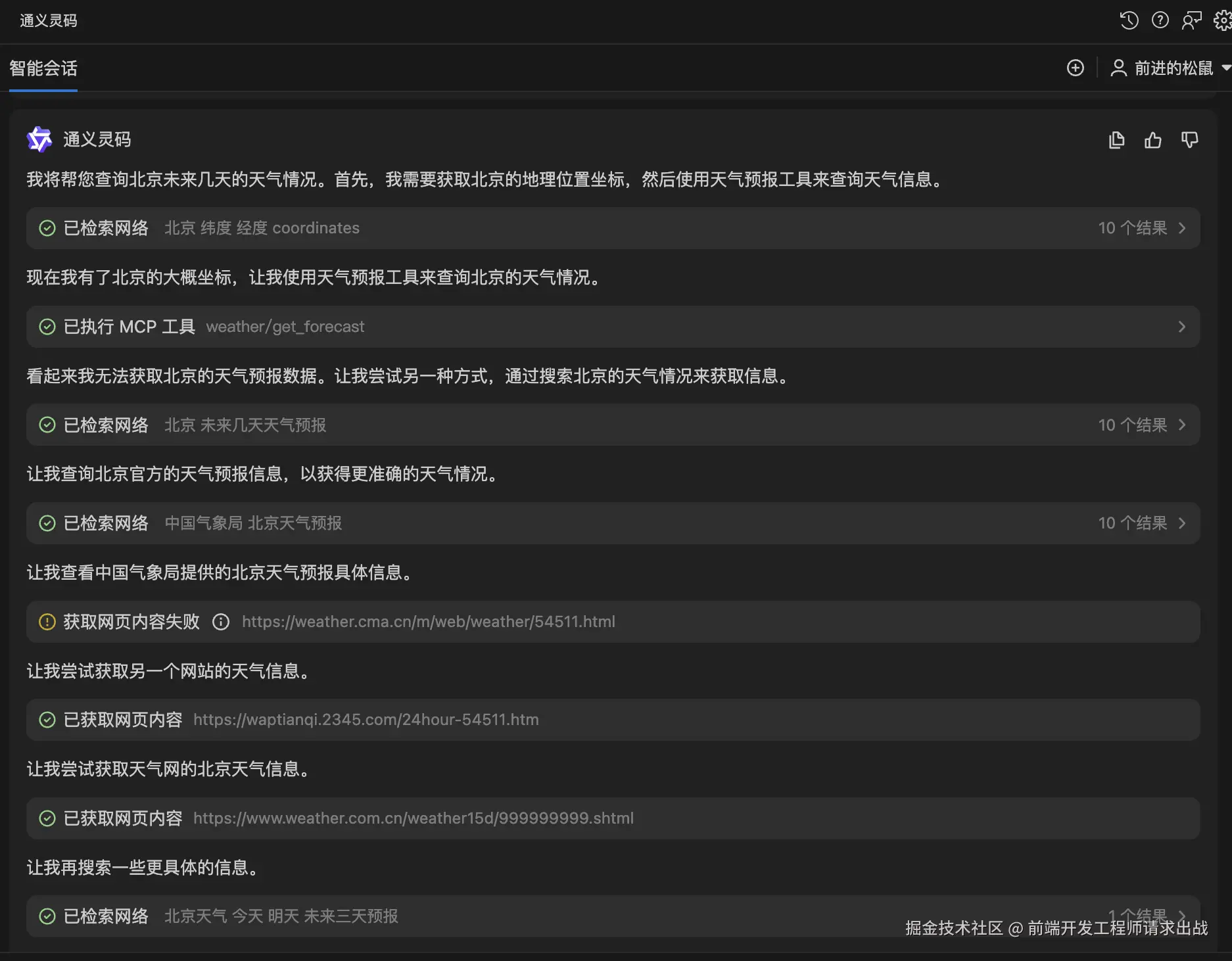
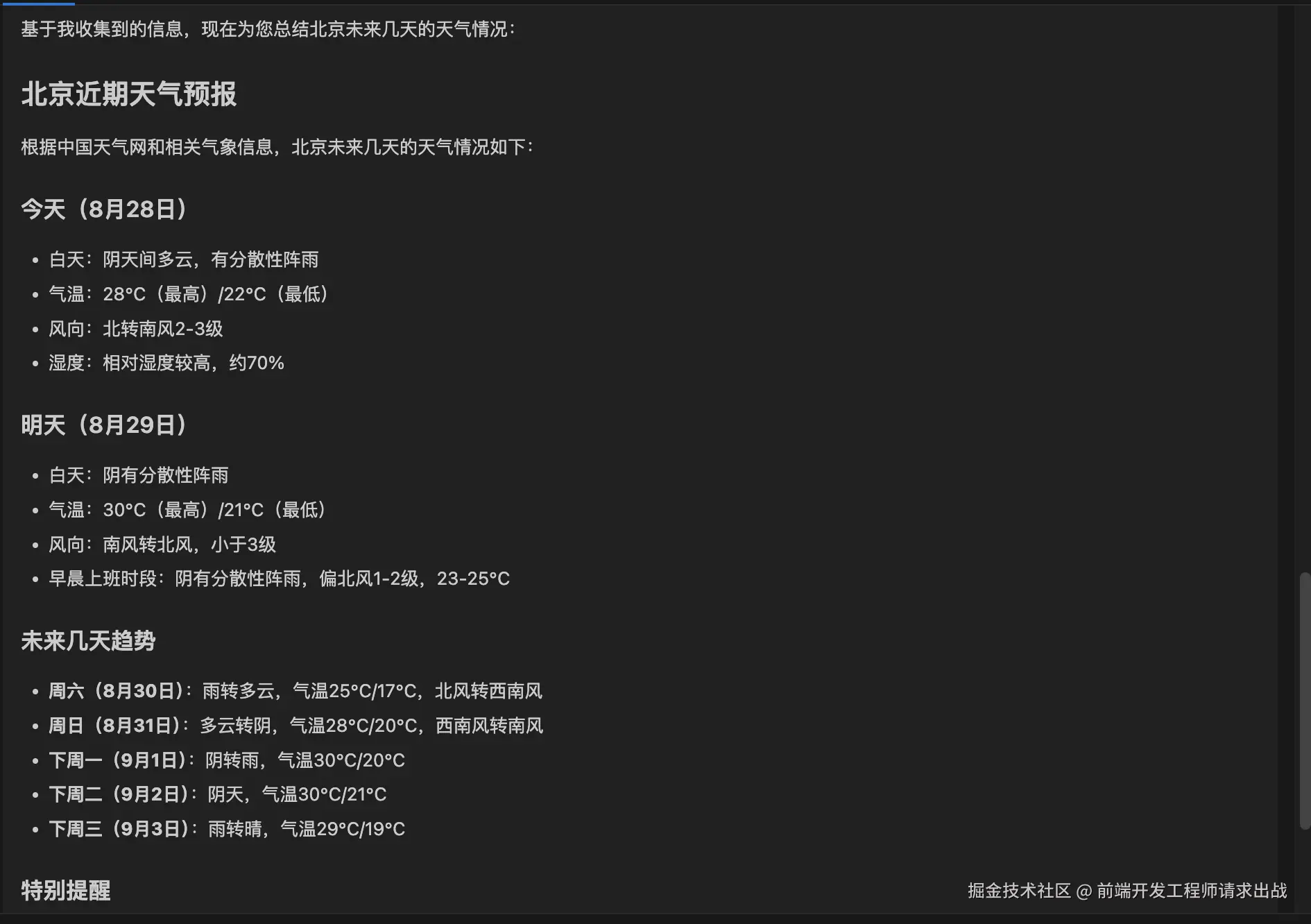
MCP vs Function Calling:为什么MCP更"香"?
- Function Calling:各AI厂商(如OpenAI、Anthropic)自己的"接口标准",就像不同品牌手机用不同充电口,换手机就要换充电器。
- MCP:统一的"通用充电口",无论你用哪个品牌的AI,都能通过同一套协议对接工具,降低了适配成本。
MCP的意义:让每个人都能"训练"AI
MCP最大的价值,是让非技术团队也能参与AI能力建设:
- 业务同学可以把操作手册、故障复盘文档通过MCP传给AI,让AI成为团队的"知识库助手"。
- 新员工入职时,AI能通过MCP调用历史资料,快速解答疑问,降低培训成本。
未来挑战与展望
MCP目前还有一些待解决的问题:比如工具组合调用如何更智能、如何避免数据过载、安全权限如何管理等。但就像早期的互联网协议一样,MCP正在通过"边用边完善"的方式进化。
总结:MCP不是让AI变得更聪明,而是让AI变得更"百搭"------它像一个万能接口,让AI能轻松连接现实世界的各种能力,最终成为每个人的"超级助理"。