一,综述
EngineAI ROS 包:
- 高层开发模式:用户可通过发布身体速度指令,直接调用 EngineAI 机器人的行走控制器。
- 底层开发模式:用户可通过发布关节指令,自主开发专属的控制器。
- ROS2 package:全称为 "Robot Operating System 2 Package"(机器人操作系统 2 功能包),是 ROS2 生态中用于组织代码、配置文件等资源的基本单元,便于模块化开发与复用。
- body velocity command:"身体速度指令",通常包含机器人在三维空间中的线速度(如前后、左右移动速度)和角速度(如转向速度),是高层控制中常用的指令类型,无需用户关注单个关节的运动细节。
- joint command:"关节指令",针对机器人单个或多个关节的控制指令(如目标角度、角速度等),底层开发模式下用户需通过该指令精确控制关节运动,以实现自定义动作或控制逻辑。
二,接口协议
| Topic/Service Name | Type | Rate | Message | Description | DataStructure |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| /hardware/gamepad_keys | Topic Publish | >=500hz | GamepadKeys.msg | Gamepad Message Feedback | # Timestamp field using ROS2 header uint8 LB = 0 uint8 RB = 1 uint8 A = 2 uint8 B = 3 uint8 X = 4 uint8 Y = 5 uint8 BACK = 6 uint8 START = 7 uint8 CROSS_X_UP = 8 uint8 CROSS_X_DOWN = 9 uint8 CROSS_Y_LEFT = 10 uint8 CROSS_Y_RIGHT = 11 uint8 LT = 0 uint8 RT = 1 uint8 LEFT_STICK_X = 2 uint8 LEFT_STICK_Y = 3 uint8 RIGHT_STICK_X = 4 uint8 RIGHT_STICK_Y = 5 std_msgs/Header header # Digital buttons (0 = released, 1 = pressed) int32[12] digital_states # Fixed size array of 12 elements # Analog inputs (range: -1.0 to 1.0) float64[6] analog_states # Fixed size array of 6 elements |
| /hardware/imu_info | Topic Publish | >=500hz | IMUInfo.msg | IMU Sensor Feedback | std_msgs/Header header geometry_msgs/Quaternion quaternion geometry_msgs/Vector3 rpy geometry_msgs/Vector3 linear_acceleration geometry_msgs/Vector3 angular_velocity |
| /hardware/joint_state | Topic Publish | >=500hz | JointState.msg | Joint Status Feedback | std_msgs/Header header float64[] position float64[] velocity float64[] torque |
| /hardware/joint_command | Topic Subscription | 0~500hz | JointCommand.msg | Joint Command Subscription | std_msgs/Header header float64[] position float64[] velocity float64[] feed_forward_torque float64[] torque float64[] stiffness float64[] damping uint8 parallel_parser_type |
| /motion/motion_state | Topic Publish | >=5hz | MotionState.msg | Motion Status Feedback of Robot | string current_motion_task |
| /hardware/motor_debug | Topic Publish | >=50hz | MotorDebug.msg | Feedback of Temperature, Tau, etc. | float64[] tau_cmd float64[] mos_temperature float64[] motor_temperature |
| /motion/body_vel_cmd | Topic Publish | >=5hz | BodyVelCmd.msg | body velocity command publish, linear_x_vel ranges [-0.5m/s +0.5m/s] linear_y_vel ranges [-0.2m/s, +0.2m/s], yaw_vel rangs [-0.5rad/s, 0.5rad/s] | std_msgs/Header header float64[] linear_velocity float64 yaw_velocity |
| /heartbeat | std_msgs/Header header string node_name int64 startup_timestamp # idle, running, error, sleep string node_status int64 error_code string error_message | ||||
| /enablemotor | serve | EnableMotor.srv | bool enable --- bool success string message |
三,工作区架构及编译环境
└── src
├── interface_example # Interface examples, recommended to run on Nezha
├── interface_protocol # Interface protocols, common modules
├── third_party # Third-party libraries
├── simulation # Simulation environment running on host- Ubuntu 22.04
- ROS2 Humble Desktop
- GCC >= 11
- CMake >= 3.22
- Python >= 3.10
四,FSM 三个模式:操纵杆模式,高层开发模式,底层开发模式
操纵杆模式、高层开发模式和底层开发模式的有限状态机(FSM)
操纵杆状态机
注意:LB+CORSS_Y_LEFT 是切入 joint commands即低层开发控制
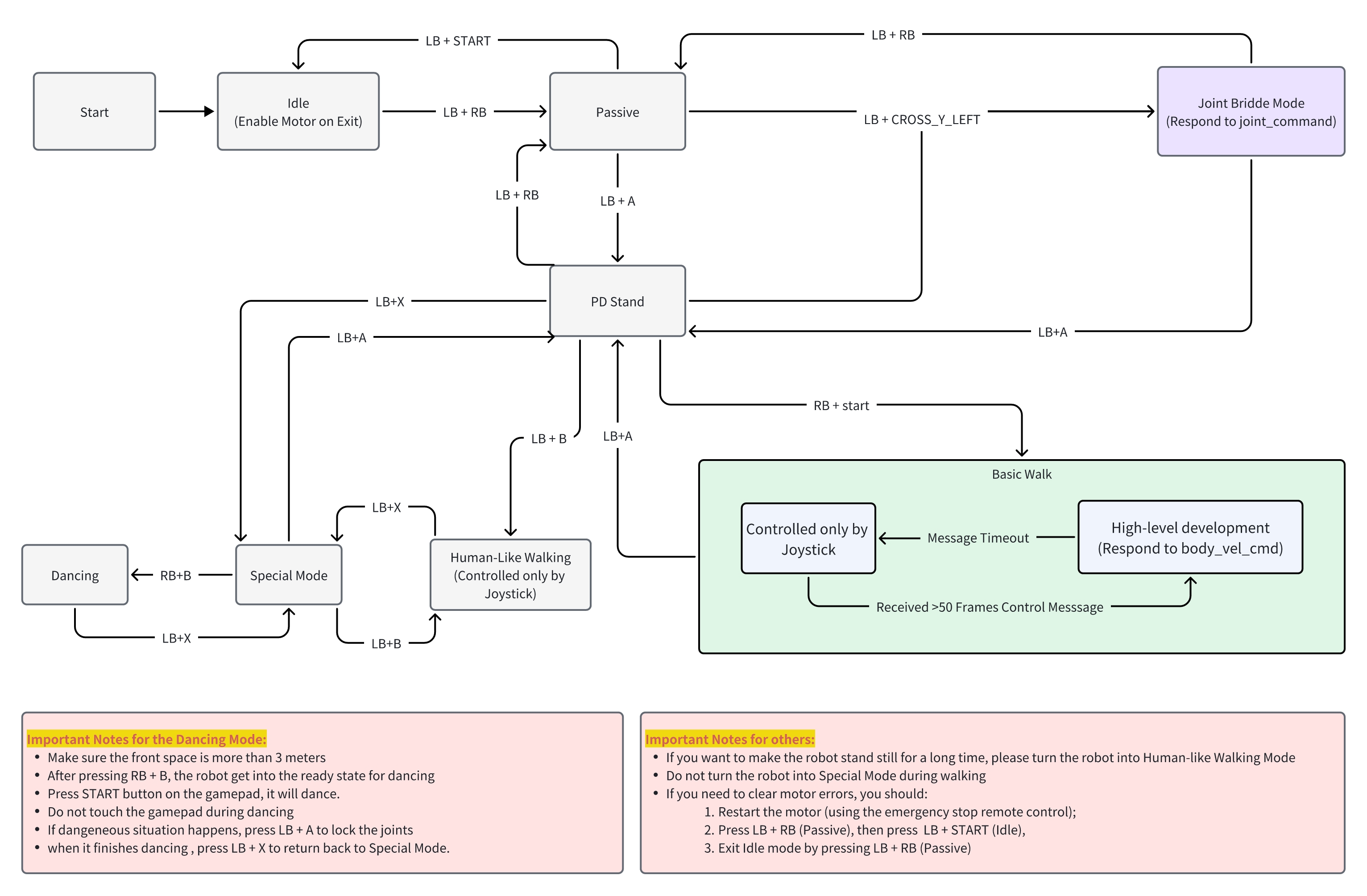
高层开发模式
Body Velocity Control
底层开发模式
底层开发(Low-level Development)允许用户使用基于 EngineAI 开源强化学习(RL)训练框架(仓库地址:https://github.com/engineai-robotics/engineai_gym)训练的自定义强化学习控制器。用户可按照以下步骤逐步操作,实现基于 Mujoco 模拟器的 "仿真到仿真"(sim2sim)功能及实际部署。
五,部署操作:
在主机上运行 rl_basic_example 程序
步骤 1:进入 PD 站立模式(pd-stand mode)
- 确保机器人稳固放置在平整地面上,且周围有足够操作空间;
- 使用遥控器进入 PD 站立模式;
- 继续操作前,请确认机器人已稳定站立。
步骤 2:进入关节桥接模式(joint bridge mode)
关节桥接模式支持通过关节指令对机器人进行控制,操作步骤如下:
-
当机器人处于 PD 站立模式时,按下遥控器的【LB 键 + 左十字键 Y 向(CROSS_Y_LEFT)】组合键;
-
机器人将进入关节桥接模式,此时可通过关节指令对其进行控制;
-
执行以下命令验证机器人状态: bash
# 在主机端执行 ros2 topic echo /motion/motion_state -
继续操作前,请确认运动状态(motion state)显示为 "joint_bridge"。
步骤 3:运行强化学习(RL)示例程序
安全警告(SAFETY WARNING)
- 确保所有人员与机器人保持安全距离;
- 若机器人出现异常动作,请随时准备紧急停止(可按下急停按钮或使机器人进入被动模式)。
启动示例程序 执行以下命令启动示例程序:bash
# 在主机端执行
ros2 launch interface_example rl_basic_example.launch.py六,编译
几个脚本梳理:
1)同步代码到板级
在主机(host) 端执行以下命令:./scripts/sync_src.sh nezha
(说明:"nezha" 指 "哪吒" 目标板,是该机器人系统适配的硬件设备;sync_src.sh为代码同步脚本,用于将主机端的开发代码传输到目标板,确保两端代码一致性。)
2)构建工作空间
首先通过 SSH 连接到哪吒板(Nezha board),并进入工作空间目录:
cd ~/source/engineai_workspace
(说明:~/source/engineai_workspace是代码在目标板上的默认工作空间路径,cd命令用于切换到该目录。)
然后执行构建脚本,编译节点代码:
./scripts/build_nodes.sh
(说明:build_nodes.sh是用于编译机器人功能节点的脚本,"nodes" 指 ROS 2 框架中的 "节点",是实现具体功能的可执行单元,编译后生成可运行的程序文件。)
3)运行 PlotJuggler 进行数据监控
在主机(host) 端编译interface_protocol功能包:
in host
colcon build --packages-select interface_protocol
(说明:colcon是 ROS 2 的官方构建工具,--packages-select interface_protocol表示仅编译 "interface_protocol" 这一个功能包,该包通常包含机器人的数据通信协议相关代码。)
source install/setup.bash
(说明:source命令用于加载脚本文件,install/setup.bash是编译后生成的环境配置脚本,加载后主机才能识别并运行后续的 ROS 2 程序。)
ros2 run plotjuggler plotjuggler -n
(说明:ros2 run用于启动 ROS 2 功能包中的可执行程序,-n是 PlotJuggler 的参数,全称 "--no-config",表示不自动加载之前保存的配置文件,便于用户重新选择需监控的数据话题。)
src/interface_protocol/pm_data_layout.xml
(说明:"layout file"(布局文件)包含数据图表的排列、待监控的话题选择等配置,加载后无需手动设置即可直接查看预设的机器人关键数据,如关节角度、电机电流等。)
check_format.sh
使用场景
这个脚本通常会集成到 CI/CD 流程中,在代码提交或 PR 创建时自动运行,确保提交的代码符合项目的格式规范。也可以在开发过程中手动运行,提前发现并修复格式问题。
依赖工具
脚本需要以下工具在系统中可用:
- clang-format (用于 C/C++ 格式化)
- yamllint (用于 YAML 文件检查)
- autopep8 (用于 Python 格式检查)
- git (用于检查文件变更)
如果需要修改检查规则,可以相应调整各工具的配置文件(如.clang-format、.yamllint 等)。
七,代码解析
interface_example
--components
message_handler.cc 一个 ROS 2 消息处理器类MessageHandler,负责订阅和发布各种 ROS 消息,是 ROS 2 节点与外部通信的关键组件
功能简述:MessageHandler类封装了 ROS 2 的订阅者 (subscriber) 和发布者 (publisher),用于处理与硬件和运动控制相关的消息,包括游戏手柄输入、IMU 传感器数据、关节状态和运动状态,并能发布关节控制命令
cpp
#include "message_handler.hpp"
#include <rclcpp/qos.hpp>
namespace example {
/*
接收一个 ROS 2 节点的智能指针并存储,所有的 ROS 通信操作都依赖这个节点对象
这是 ROS 2 中常见的设计模式,将通信功能封装在独立类中,通过节点指针与 ROS 系统交互
*/
MessageHandler::MessageHandler(rclcpp::Node::SharedPtr node) : node_(node) {}
void MessageHandler::Initialize() {
rclcpp::QoS qos(3);
qos.best_effort();
qos.durability_volatile();
/*
rclcpp::QoS qos(3):创建 QoS 配置,设置消息队列深度为 3
qos.best_effort():使用 "尽力而为" 策略,不保证消息可靠传递但开销小
qos.durability_volatile():非持久化,新订阅者不会收到历史消息
这种配置适合实时性要求高但对消息丢失不敏感的场景(如传感器数据)
*/
// Initialize subscribers 初始化订阅
// 游戏手柄消息订阅
/*
模板参数指定消息类型:interface_protocol::msg::GamepadKeys
第一个参数是订阅的话题名:/hardware/gamepad_keys
第二个参数是 QoS 配置
第三个参数是回调函数绑定,当收到消息时调用GamepadCallback 会在回调函数再去做内部变量的传递
*/
gamepad_sub_ = node_->create_subscription<interface_protocol::msg::GamepadKeys>(
"/hardware/gamepad_keys", qos,
std::bind(&MessageHandler::GamepadCallback, this, std::placeholders::_1));
imu_sub_ = node_->create_subscription<interface_protocol::msg::ImuInfo>(
"/hardware/imu_info", qos,
std::bind(&MessageHandler::ImuCallback, this, std::placeholders::_1));
joint_state_sub_ = node_->create_subscription<interface_protocol::msg::JointState>(
"/hardware/joint_state", qos,
std::bind(&MessageHandler::JointStateCallback, this, std::placeholders::_1));
// Initialize publisher 初始化发布
//发布joint_command
/*
创建发布者,用于发布interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand类型消息
发布到/hardware/joint_command话题,使用前面定义的 QoS 配置
*/
joint_cmd_pub_ = node_->create_publisher<interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand>("/hardware/joint_command", qos);
motion_state_sub_ = node_->create_subscription<interface_protocol::msg::MotionState>(
"/motion/motion_state", 1, std::bind(&MessageHandler::MotionStateCallback, this, std::placeholders::_1));
}
void MessageHandler::MotionStateCallback(const interface_protocol::msg::MotionState::SharedPtr msg) {
latest_motion_state_ = msg;
}
void MessageHandler::GamepadCallback(const interface_protocol::msg::GamepadKeys::SharedPtr msg) {
latest_gamepad_ = msg;
}
void MessageHandler::ImuCallback(const interface_protocol::msg::ImuInfo::SharedPtr msg) { latest_imu_ = msg; }
void MessageHandler::JointStateCallback(const interface_protocol::msg::JointState::SharedPtr msg) {
latest_joint_state_ = msg;
}
//PublishJointCommand 俩种重载形式:1接收智能指针 2接收对象索引
void MessageHandler::PublishJointCommand(const interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand::SharedPtr command) {
joint_cmd_pub_->publish(*command);
}
void MessageHandler::PublishJointCommand(const interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand& command) {
joint_cmd_pub_->publish(command);
}
} // namespace example--src
hold_joint_status.cc
功能描述:这个节点的核心功能是 "关节保持":
1,等待并获取当前关节状态
2,以当前关节位置为目标位置,构建控制命令
3,以 500Hz 的频率持续发布控制命令,使关节保持在初始位置
cpp
#include <chrono>
#include <interface_protocol/msg/detail/motor_command__struct.hpp>
#include <memory>
#include <rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp>
#include "components/message_handler.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
auto node = std::make_shared<rclcpp::Node>("joint_test_example");
/*
rclcpp::init():初始化 ROS 2 运行时环境,解析命令行参数
rclcpp::Node:创建名为joint_test_example的节点,是 ROS 2 中所有通信的基础
*/
auto message_handler = std::make_shared<example::MessageHandler>(node);
message_handler->Initialize();
/*
实例化消息处理器,将节点指针传入,用于创建订阅者和发布者
Initialize()方法会初始化所有 ROS 2 通信接口(见之前的MessageHandler代码)
*/
interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand hold_joint_command;
while (!message_handler->GetLatestJointState()) {
rclcpp::spin_some(node);
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
RCLCPP_INFO_THROTTLE(node->get_logger(), *node->get_clock(), 1000, "Waiting for first joint state...");
}
/*
rclcpp::spin_some():处理当前队列中的所有回调,非阻塞式
RCLCPP_INFO_THROTTLE:带节流的日志输出,避免日志刷屏
这段逻辑确保在获取到第一个关节状态之前程序不会继续执行,相当于初始化
*/
auto latest_joint_state = message_handler->GetLatestJointState();
//print latest_joint_state 打印最新的关节状态
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "Latest joint state size: " << latest_joint_state->position.size() << "\nvalues: " ;
for (size_t i = 0; i < latest_joint_state->position.size(); i++) {
ss << " " << latest_joint_state->position[i];
}
RCLCPP_INFO(node->get_logger(), "%s", ss.str().c_str());
// Example: Copy current positions and add some feed-forward torque
hold_joint_command.position = latest_joint_state->position;
hold_joint_command.feed_forward_torque = latest_joint_state->torque;
hold_joint_command.torque = latest_joint_state->torque;
hold_joint_command.velocity.resize(latest_joint_state->position.size(), 0.0);
hold_joint_command.stiffness.resize(latest_joint_state->position.size(), 400.0); // Example stiffness
hold_joint_command.damping.resize(latest_joint_state->position.size(), 5.0); // Example damping
// Create timer for publishing motor commands at 500Hz
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer =
node->create_wall_timer(2ms, // 500Hz = 2ms period
[&]() {
hold_joint_command.header.stamp = node->get_clock()->now();
message_handler->PublishJointCommand(hold_joint_command);
});
/*
create_wall_timer:创建一个墙壁时钟定时器,每 2ms 触发一次回调
回调函数中更新消息时间戳并发布关节控制命令
500Hz 的发布频率对于实时控制来说是比较合理的选择
*/
rclcpp::spin(node); // 阻塞式运行节点,处理回调和定时器
rclcpp::shutdown(); // 退出时清理ROS 2资源
return 0;
}joint_test_example.cc
功能描述:一个基于 ROS 2 的机器人关节控制节点程序,相比之前的版本增加了轨迹规划功能,能够根据配置文件生成关节点轨迹并控制关节运动到目标位置。
1,程序启动,加载配置文件参数
2,等待并获取初始关节状态
3,根据初始位置和目标位置生成线性插值轨迹
4,以 500Hz 频率循环发布控制命令,使关节按轨迹运动
5,当所有关节到达目标位置时,输出提示信息
cpp
#include <yaml-cpp/yaml.h>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
#include <chrono>
#include <memory>
#include <rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp>
#include "components/message_handler.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
namespace {
// Constants Default 这么写是个好习惯,当然放到XML更好,可以不用编译
constexpr double kControlFrequency = 500.0; // Control frequency in Hz
constexpr double kControlPeriod = 1.0 / kControlFrequency; // Control period in seconds
} // namespace
class JointTestExample : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
JointTestExample(const std::string& config_dir_path)
: Node("joint_test_example"), joint_test_config_path_(config_dir_path + "/joint_test.yaml") {
// Load motor parameters from yaml
LoadJointTestParams();
}
/*
类继承自rclcpp::Node,使节点功能更内聚
JointTestExample 接收配置文件路径,拼接出关节测试配置文件的完整路径
调用LoadJointTestParams()从 YAML 文件加载控制参数
*/
//初始化消息处理器,获取初始关节状态,很好的编程习惯用了try catch
bool Initialize() {
try {
// Initialize message handler
msg_handler_ = std::make_shared<example::MessageHandler>(shared_from_this());
msg_handler_->Initialize();
// Wait for first motor state
while (!msg_handler_->GetLatestJointState()) {
rclcpp::spin_some(shared_from_this());
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
RCLCPP_INFO_THROTTLE(get_logger(), *get_clock(), 1000, "Waiting for first motor state...");
}
// Get initial motor state
auto initial_state = msg_handler_->GetLatestJointState();
initial_positions_ = initial_state->position;
// Print initial positions
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "\nInitial positions:\n[";
for (size_t i = 0; i < initial_positions_.size(); ++i) {
ss << std::fixed << std::setprecision(3) << initial_positions_[i];
if (i < initial_positions_.size() - 1) {
ss << ", ";
// Add newline every 6 elements for better readability
if ((i + 1) % 6 == 0) {
ss << "\n ";
}
}
}
ss << "]\n";
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "%s", ss.str().c_str());
// Convert initial motor positions to joint positions and generate trajectories
GenerateTrajectories();
// Create timer for periodic execution
timer_ = create_wall_timer(std::chrono::duration<double>(kControlPeriod),
std::bind(&JointTestExample::TimerCallback, this));
return true;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(get_logger(), "Failed to initialize: %s", e.what());
return false;
}
}
private:
//生成从初始位置到目标位置的插值轨迹
void GenerateTrajectories() {
// Convert initial motor positions to joint positions
current_joint_positions_ = Eigen::VectorXd(initial_positions_.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < initial_positions_.size(); ++i) {
current_joint_positions_[i] = initial_positions_[i];
}
// Initialize interpolation for each joint
interpolated_positions_.resize(initial_positions_.size());
current_steps_.resize(initial_positions_.size(), 0);
reached_targets_.resize(initial_positions_.size(), false);
// Generate interpolated trajectories for each joint
for (size_t i = 0; i < initial_positions_.size(); ++i) {
interpolated_positions_[i].resize(num_steps_[i]);
double step = (target_positions_[i] - current_joint_positions_[i]) / (num_steps_[i] - 1);
for (int j = 0; j < num_steps_[i]; ++j) {
interpolated_positions_[i][j] = current_joint_positions_[i] + step * j;
}
}
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "Trajectories generated for %ld joints", initial_positions_.size());
}
//从 YAML 配置文件加载关节控制参数(目标位置、步数、PID 参数等)
void LoadJointTestParams() {
try {
YAML::Node config = YAML::LoadFile(joint_test_config_path_);
// Load parameters
auto target_pos = config["target_position"];
auto steps = config["num_steps"];
auto kp = config["kp"];
auto kd = config["kd"];
// Clear vectors
target_positions_.clear();
num_steps_.clear();
kp_.clear();
kd_.clear();
// Concatenate all groups into single vectors
for (const auto& pos_group : target_pos) {
auto vec = pos_group.as<std::vector<double>>();
target_positions_.insert(target_positions_.end(), vec.begin(), vec.end());
}
for (const auto& steps_group : steps) {
auto vec = steps_group.as<std::vector<double>>();
num_steps_.insert(num_steps_.end(), vec.begin(), vec.end());
}
for (const auto& kp_group : kp) {
auto vec = kp_group.as<std::vector<double>>();
kp_.insert(kp_.end(), vec.begin(), vec.end());
}
for (const auto& kd_group : kd) {
auto vec = kd_group.as<std::vector<double>>();
kd_.insert(kd_.end(), vec.begin(), vec.end());
}
// Print loaded parameters for verification
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "Loaded joint test parameters:");
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "Number of joints: %ld", target_positions_.size());
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(get_logger(), "Failed to load joint test parameters: %s", e.what());
throw;
}
}
//以固定频率(500Hz)发布关节控制命令,使关节按轨迹运动,监控运动状态,当所有关节到达目标位置时给出提示
void TimerCallback() {
auto joint_command = std::make_shared<interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand>();
joint_command->position.resize(initial_positions_.size());
joint_command->velocity.resize(initial_positions_.size());
joint_command->feed_forward_torque.resize(initial_positions_.size(), 0.0);
joint_command->torque.resize(initial_positions_.size(), 0.0);
joint_command->stiffness.resize(initial_positions_.size(), 400.0);
joint_command->damping.resize(initial_positions_.size(), 5.0);
bool all_reached = true;
for (size_t i = 0; i < initial_positions_.size(); ++i) {
if (!reached_targets_[i]) {
// 如果还没到达目标位置,发送当前插值点
if (current_steps_[i] < num_steps_[i]) {
double joint_pos = interpolated_positions_[i][current_steps_[i]];
joint_command->position[i] = joint_pos;
joint_command->velocity[i] = 0.0; // Zero velocity for position control
current_steps_[i]++;
} else {
// Hold at target position // 已到达目标位置某些关节,保持目标位置
double joint_pos = target_positions_[i];
joint_command->position[i] = joint_pos;
joint_command->velocity[i] = 0.0;
reached_targets_[i] = true;
}
all_reached = false;
} else {
// Keep sending the target position // 已到达目标,持续发送目标位置
double joint_pos = target_positions_[i];
joint_command->position[i] = joint_pos;
joint_command->velocity[i] = 0.0;
}
}
// Print initial positions
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "\nCurrent positions:\n[";
for (size_t i = 0; i < joint_command->position.size(); ++i) {
ss << std::fixed << std::setprecision(3) << joint_command->position[i];
if (i < joint_command->position.size() - 1) {
ss << ", ";
// Add newline every 6 elements for better readability
if ((i + 1) % 6 == 0) {
ss << "\n ";
}
}
}
ss << "]\n";
// RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "%s", ss.str().c_str()); 这也是ROS2自带函数RCLCPP_INFO
// 检查是否所有关节都到达目标
if (all_reached) {
RCLCPP_INFO_ONCE(get_logger(), "All joints have reached their target positions!");
return;
}
msg_handler_->PublishJointCommand(joint_command);
}
std::string config_path_;
std::string joint_test_config_path_;
std::shared_ptr<example::MessageHandler> msg_handler_;
std::vector<double> initial_positions_;
// Joint test parameters
std::vector<double> target_positions_;
std::vector<double> num_steps_;
std::vector<double> kp_;
std::vector<double> kd_;
std::vector<std::vector<double>> interpolated_positions_;
std::vector<int> current_steps_;
std::vector<bool> reached_targets_;
Eigen::VectorXd current_joint_positions_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
};
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <path_to_config_directory>" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
// Remove trailing slash if present
std::string config_dir = argv[1];
if (!config_dir.empty() && config_dir.back() == '/') {
config_dir.pop_back();
}
auto node = std::make_shared<JointTestExample>(config_dir);
if (!node->Initialize()) {
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 1;
}
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}rl_basic_example.cc
功能描述:一个基于 ROS 2 的强化学习 (RL) 基础运行器节点RlBasicRunner,用于通过强化学习模型生成机器人关节控制命令
目录
[四,FSM 三个模式:操纵杆模式,高层开发模式,底层开发模式](#四,FSM 三个模式:操纵杆模式,高层开发模式,底层开发模式)
[Body Velocity Control](#Body Velocity Control)
[步骤 1:进入 PD 站立模式(pd-stand mode)](#步骤 1:进入 PD 站立模式(pd-stand mode))
[步骤 2:进入关节桥接模式(joint bridge mode)](#步骤 2:进入关节桥接模式(joint bridge mode))
[步骤 3:运行强化学习(RL)示例程序](#步骤 3:运行强化学习(RL)示例程序)
[安全警告(SAFETY WARNING)](#安全警告(SAFETY WARNING))
[启动示例程序 执行以下命令启动示例程序:bash](#启动示例程序 执行以下命令启动示例程序:bash)
cpp
#include <chrono>
#include <memory>
#include <rclcpp/logging.hpp>
#include <rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp>
#include <thread>
#include "components/message_handler.hpp"
#include "math/concatenate_vector.h"
#include "math/mnn_model.h"
#include "math/rotation_matrix.h"
#include "parameter/rl_basic_param.h"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
namespace example {
class RlBasicRunner : public rclcpp::Node {
public:
//在 ROS 2 节点类中,explicit这种写法很常见,因为节点构造通常需要明确的参数(如配置路径),不希望被编译器自动转换,避免逻辑错误。
explicit RlBasicRunner(const std::string& config_file_dir) : Node("rl_basic_runner") {
std::string config_file = config_file_dir + "/rl_basic_param.yaml";
param_ = std::make_shared<RlBasicParam>(config_file);
config_file_dir_ = config_file_dir;
joint_command_ = std::make_shared<interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand>();
}
bool Initialize() {
try {
// Initialize message handler 初始化发布和订阅
message_handler_ = std::make_shared<MessageHandler>(shared_from_this());
message_handler_->Initialize();
// Wait for first motion state 等待获取初始关节状态
while (!message_handler_->GetLatestMotionState() ||
message_handler_->GetLatestMotionState()->current_motion_task != "joint_bridge") {
rclcpp::spin_some(shared_from_this());
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(100));
RCLCPP_INFO_THROTTLE(get_logger(), *get_clock(), 1000, "Waiting for joint bridge state...");
}
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "Already in joint bridge state");
// Get initial joint positions 获取初始关节状态
auto initial_state = message_handler_->GetLatestJointState();
if (!initial_state) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(get_logger(), "Failed to get initial joint state");
return false;
}
initial_joint_q_ =
Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd>(initial_state->position.data(), initial_state->position.size());
RCLCPP_INFO_STREAM(get_logger(), "Initial joint positions: " << initial_joint_q_.transpose());
// Initialize active joint indices 初始化关节参数(从配置文件拼接)
active_joint_idx_ = param_->active_joint_idx;
// Concatenate joint parameters from yaml
default_joint_q_ = math::ConcatenateVectors(param_->default_joint_q);
joint_kp_ = math::ConcatenateVectors(param_->joint_kp);
joint_kd_ = math::ConcatenateVectors(param_->joint_kd);
action_scale_ = math::ConcatenateVectors(param_->action_scale);
// Initialize MNN model // 初始化MNN神经网络模型
mlp_net_ = std::make_unique<math::MnnModel>(config_file_dir_ + "/" + param_->policy_file);
mlp_net_observation_.setZero(param_->num_observations, param_->num_include_obs_steps);
mlp_net_action_.setZero(param_->num_actions);
// Initialize control variables
time_ = 0.0;
global_phase_ = 0.0;
is_first_time_ = true;
RCLCPP_INFO(get_logger(), "Starting control loop");
// Create control timer
control_timer_ = create_wall_timer(std::chrono::duration<double>(param_->control_dt),
std::bind(&RlBasicRunner::ControlCallback, this));
return true;
} catch (const std::exception& e) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(get_logger(), "Failed to initialize: %s", e.what());
return false;
}
}
private:
void ControlCallback() {
//检查当前运动状态是否为"joint_bridge"
if (message_handler_->GetLatestMotionState()->current_motion_task != "joint_bridge") {
time_ = 0.0;
is_first_time_ = true;
return;
}
auto joint_state = message_handler_->GetLatestJointState();
if (!joint_state) return; // Skip if no joint state received yet // 无关节状态则跳过
// 控制流程:更新状态 -> 计算观测 -> 计算命令 -> 发送命令
UpdateState(joint_state);
CalculateObservation();
CalculateMotorCommand();
SendMotorCommand();
time_ += param_->control_dt; // 更新控制时间
}
void UpdateState(const interface_protocol::msg::JointState::SharedPtr& joint_state) {
// Update joint states // 更新关节状态(位置、速度)
q_real_ = Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd>(joint_state->position.data(), joint_state->position.size());
qd_real_ = Eigen::Map<const Eigen::VectorXd>(joint_state->velocity.data(), joint_state->velocity.size());
// Update command from gamepad // 处理游戏手柄输入命令 command x,y,z
auto gamepad = message_handler_->GetLatestGamepad();
if (gamepad) {
command_.x() =
gamepad->analog_states[interface_protocol::msg::GamepadKeys::LEFT_STICK_X] * param_->command_scale.x();
command_.y() =
gamepad->analog_states[interface_protocol::msg::GamepadKeys::LEFT_STICK_Y] * param_->command_scale.y();
command_.z() =
gamepad->analog_states[interface_protocol::msg::GamepadKeys::RIGHT_STICK_Y] * param_->command_scale.z();
}
}
//构建强化学习的观测向量
void CalculateObservation() {
// Calculate phase info // 计算全局相位(周期信号)
global_phase_ += param_->control_dt / param_->cycle_time;
global_phase_ -= static_cast<int>(global_phase_);
// Get IMU data // 处理IMU数据(旋转矩阵、欧拉角)
auto imu = message_handler_->GetLatestImu();
Eigen::Matrix3d R_real =
Eigen::Quaterniond(imu->quaternion.w, imu->quaternion.x, imu->quaternion.y, imu->quaternion.z)
.toRotationMatrix();
Eigen::Vector3d w_real = Eigen::Vector3d(imu->angular_velocity.x, imu->angular_velocity.y, imu->angular_velocity.z);
// ZYX顺序的欧拉角(等同于RPY)
Eigen::Vector3d euler_xyz = math::CalcRollPitchYawFromRotationMatrix(R_real);
// Stack the observation
Eigen::VectorXd mlp_net_observation_single = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(param_->num_observations);
// if (param_->mix) {
// mlp_net_observation_single << // command
// (q_real_ - default_joint_q_)(active_joint_idx_), // joint position - joint default position: kDoFs
// qd_real_(active_joint_idx_), // joint velocity: kDoFs
// mlp_net_action_, // last joint action: kDoFs
// w_real, // base angular velocity w.r.t base frame: 3
// euler_xyz; // base euler angle rpy w.r.t base frame: 3
// } else {
// mlp_net_observation_single << clock_signal, // phase signals: 2
// command_, // command
// (q_real_ - default_joint_q_)(active_joint_idx_), // joint position - joint default position: kDoFs
// qd_real_(active_joint_idx_), // joint velocity: kDoFs
// mlp_net_action_, // last joint action: kDoFs
// w_real, // base angular velocity w.r.t base frame: 3
// euler_xyz; // base euler angle rpy w.r.t base frame: 3
// }
mlp_net_observation_single << (q_real_ - default_joint_q_)(
active_joint_idx_), // joint position - joint default position: kDoFs // 关节位置偏差
qd_real_(active_joint_idx_), // joint velocity: kDoFs // 关节速度
mlp_net_action_, // last joint action: kDoFs // 上一时刻动作
w_real, // base angular velocity w.r.t base frame: 3 // IMU角速度
euler_xyz; // base euler angle rpy w.r.t base frame: 3 // 欧拉角
// Scales and clips the observation
// Scale and clip the observation // 观测值缩放和裁剪
mlp_net_observation_single.array() *= param_->observation_scale.array();
mlp_net_observation_single =
mlp_net_observation_single.cwiseMax(-param_->observation_clip).cwiseMin(param_->observation_clip);
// Update the observation buffer // 更新观测缓冲区(多步观测),可能用于时序建模
// mlp_net_observation_ 是一个 Eigen 矩阵,维度为 [param_->num_observations × param_->num_include_obs_steps]
// mlp_net_observation_single 是一个 Eigen 向量,维度为 [param_->num_observations × 1]
if (is_first_time_) {
is_first_time_ = false;
mlp_net_observation_.setZero(param_->num_observations, param_->num_include_obs_steps);
mlp_net_action_.setZero(param_->num_actions);
mlp_net_observation_.rightCols(1) = mlp_net_observation_single;
} else {
//将矩阵中右侧的 n-1 列数据整体左移,覆盖最左侧的 n-1 列
mlp_net_observation_.leftCols(param_->num_include_obs_steps - 1) =
mlp_net_observation_.rightCols(param_->num_include_obs_steps - 1);
//将当前最新的观测数据 mlp_net_observation_single 放入矩阵最右侧的新列中
mlp_net_observation_.rightCols(1) = mlp_net_observation_single;
}
/*
假设
[ t0_obs1, t1_obs1, t2_obs1 ]
[ t0_obs2, t1_obs2, t2_obs2 ]
[ ... ... ... ]
经过第一步
[ t1_obs1, t2_obs1, t2_obs1 ] // 注意最后一列临时保留原值,下一步会被覆盖
[ t1_obs2, t2_obs2, t2_obs2 ]
[ ... ... ... ]
经过第二步
[ t1_obs1, t2_obs1, t3_obs1 ] // 完成窗口滑动,包含 t1, t2, t3 三步观测
[ t1_obs2, t2_obs2, t3_obs2 ]
[ ... ... ... ]
*/
}
void CalculateMotorCommand() {
// 构建完整的模型输入(包含时钟信号和命令)
Eigen::Vector2d clock_signal(std::sin(2 * M_PI * global_phase_), std::cos(2 * M_PI * global_phase_));
Eigen::VectorXd obs = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(
param_->num_observations * param_->num_include_obs_steps +
param_->num_clock_signal +
param_->num_commands
); // 组合观测、时钟信号和命令
obs = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(param_->num_observations * param_->num_include_obs_steps + param_->num_clock_signal + param_->num_commands);
obs.head(param_->num_observations * param_->num_include_obs_steps) =
Eigen::Map<Eigen::VectorXd>(mlp_net_observation_.transpose().data(), mlp_net_observation_.size());
command_.array() *= param_->obs_commands_scale.array();
obs.tail(param_->num_clock_signal + param_->num_commands) << clock_signal, command_;
// Get MNN // MNN模型推理得到动作
mlp_net_action_ = mlp_net_->Inference(obs.cast<float>()).cast<double>();
mlp_net_action_ = mlp_net_action_.cwiseMax(-param_->action_clip).cwiseMin(param_->action_clip);
// Calculate desired joint positions // 计算期望关节位置
q_des_ = default_joint_q_; // Use concatenated default_joint_q_
q_des_(active_joint_idx_) += mlp_net_action_.cwiseProduct(action_scale_); // Use concatenated action_scale_
// 过渡阶段处理(从初始位置平滑过渡)
if (time_ < param_->transition_time) {
float ratio = time_ / param_->transition_time;
q_des_ = ratio * q_des_ + (1 - ratio) * initial_joint_q_;
}
}
void SendMotorCommand() {
// Convert Eigen vectors to std::vector
joint_command_->position = std::vector<double>(q_des_.data(), q_des_.data() + q_des_.size());
joint_command_->velocity = std::vector<double>(q_des_.size(), 0.0);
joint_command_->feed_forward_torque = std::vector<double>(q_des_.size(), 0.0);
joint_command_->torque = std::vector<double>(q_des_.size(), 0.0);
joint_command_->stiffness = std::vector<double>(joint_kp_.data(), joint_kp_.data() + joint_kp_.size());
joint_command_->damping = std::vector<double>(joint_kd_.data(), joint_kd_.data() + joint_kd_.size());
joint_command_->parallel_parser_type = interface_protocol::msg::ParallelParserType::RL_PARSER;
// Send command through message handler
message_handler_->PublishJointCommand(*joint_command_);
}
// Parameters
std::shared_ptr<RlBasicParam> param_;
// Message handling
std::shared_ptr<MessageHandler> message_handler_;
// MNN model
std::unique_ptr<math::MnnModel> mlp_net_;
Eigen::MatrixXd mlp_net_observation_;
Eigen::VectorXd mlp_net_action_;
// State variables
double time_;
double global_phase_;
bool is_first_time_;
Eigen::Vector3d command_;
Eigen::VectorXd q_real_;
Eigen::VectorXd qd_real_;
Eigen::VectorXd q_des_;
Eigen::VectorXi active_joint_idx_;
Eigen::VectorXd initial_joint_q_;
Eigen::VectorXd default_joint_q_;
Eigen::VectorXd joint_kp_;
Eigen::VectorXd joint_kd_;
Eigen::VectorXd action_scale_;
// ROS timer
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr control_timer_;
std::string config_file_dir_;
interface_protocol::msg::JointCommand::SharedPtr joint_command_;
};
} // namespace example
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
if (argc < 2) {
RCLCPP_ERROR(rclcpp::get_logger("rl_basic_example"), "Usage: rl_basic_example <config_file_dir>");
return 1;
}
auto node = std::make_shared<example::RlBasicRunner>(argv[1]);
if (!node->Initialize()) {
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 1;
}
rclcpp::spin(node);
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}simulation
功能描述:一个基于 ROS(Robot Operating System,机器人操作系统) 与 MuJoCo(一款物理模拟引擎) 结合的项目代码架构,整体遵循典型的 ROS 功能包组织方式,同时融入了 MuJoCo 模拟相关的模块与依赖管理
架构:整体架构的核心逻辑是:通过 launch 启动文件一键启动,SimManager 协调 MuJoCo 模拟与 ROS 通信,ConfigLoader 加载配置,ROSInterface 处理机器人与外部系统的通信,simulate 模块结合 GLFW 实现可视化物理模拟,同时通过跨平台适配层支持多操作系统运行。
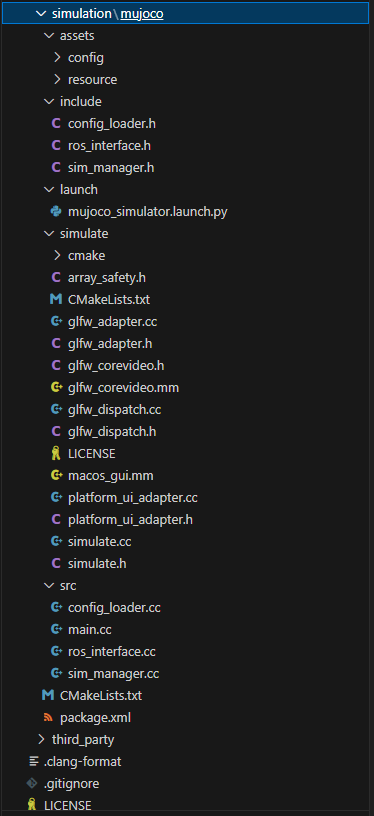
simulation\mujoco是根目录层级
1)asserts目录 :通常用于存放非代码类资源
config:模拟参数、机器人模型等配置文件(如 XML 格式的 MuJoCo 模型描述、ROS 参数服务器配置)。
resource:环境(ground,chair等xml)、模型 mesh 文件(STL文件)、数据文件,urdf等资源(若项目涉及可视化或复杂模型)
2)include目录 :存放公共头文件, 供项目内多个源文件引用,定义类、函数的接口(声明):config_loader.h:配置加载模块的接口,负责解析 assets/config 中的配置文件。ros_interface.h:ROS 通信接口,封装话题(Topic)、服务(Service)、动作(Action)等 ROS 通信逻辑。
sim_manager.h:模拟管理模块的接口,协调 MuJoCo 物理模拟的初始化、步进(Step)、终止等流程。
3)launch目录 :存放 ROS 启动文件 (.launch.py 是 ROS 2 的 Python 格式启动文件)
mujoco_simulator.launch.py:一键启动整个模拟系统的脚本,会按顺序启动 simulate 节点、加载配置、初始化 ROS 通信等。
4)simulate目录 :核心的模拟功能模块,包含 MuJoCo 模拟的实现与跨平台界面适配:
cmake:可能存放与 CMake 构建相关的自定义脚本(如平台特定的编译选项)。array_safety.h:数组安全操作的工具头文件(如边界检查、安全访问封装)。CMakeLists.txt:该子模块的 CMake 构建规则,指定编译源文件、链接库(如 MuJoCo、ROS 库)。glfw_*.cc/.h/.mm:与 GLFW(轻量级窗口库) 相关的适配代码,用于创建模拟可视化窗口(如glfw_adapter封装窗口创建,glfw_corevideo处理 macOS 平台的视频 / 显示接口,glfw_dispatch做跨平台函数分发)。macos_gui.mm:macOS 平台特有的图形界面实现(.mm是 Objective-C++ 后缀,用于混编 C++ 与 Objective-C)。platform_ui_adapter.{cc/h}:跨平台 UI 适配层,屏蔽不同操作系统(如 Linux、macOS)的界面差异,向上提供统一的窗口 / 交互接口。
simulate.{cc/h}:MuJoCo 模拟的核心实现,包含物理世界初始化、模拟步进循环、与 ROS 模块的数据交互等逻辑
5)SRC目录 存放源文件 ,实现 include 中声明的接口,以及程序入口:
config_loader.cc:config_loader.h接口的实现,解析配置文件并将参数传递给模拟模块。main.cc:程序入口点 ,初始化 ROS 节点、创建SimManager实例、启动模拟循环。ros_interface.cc:ros_interface.h接口的实现,处理 ROS 话题发布 / 订阅、服务调用等通信逻辑。sim_manager.cc:sim_manager.h接口的实现,管理 MuJoCo 模拟的生命周期(初始化、运行、停止)。CMakeLists.txt:整个功能包的 CMake 构建规则,指定编译所有src与simulate下的源文件、链接依赖(如 MuJoCo 库、ROS 相关库)。package.xml:ROS 功能包的元数据文件 ,声明依赖的 ROS 包(如rclcpp、mujoco_ros等)、功能包名称、版本、维护者等信息。
6)third_party 目录(推测,因截图中为展开状态)
通常用于存放第三方依赖库(如 MuJoCo 库的源码 / 预编译文件、GLFW 库等),若项目未使用系统全局安装的依赖,会将第三方库源码放在此处并通过 CMake 引入编译。