系列文章目录
目录
[2.1 算法](#2.1 算法)
[2.2 辅助技术](#2.2 辅助技术)
[2.3 实用工具](#2.3 实用工具)
前言
RSL-RL是一款专为机器人领域定制的开源强化学习库。不同于通用框架,其设计理念注重代码库的紧凑性与可修改性,使研究人员能以最低开销适配和扩展算法。该库聚焦机器人领域最广泛采用的算法,并辅以解决机器人特定挑战的辅助技术。RSL-RL针对纯GPU训练进行优化,在大型仿真环境中实现高吞吐量性能。其有效性已在仿真基准测试和真实机器人实验中得到验证,证明其作为轻量级、可扩展且实用的框架,能有效开发基于学习的机器人控制器。该库开源地址:https://github.com/leggedrobotics/rsl_rl。
关键词:强化学习,知识蒸馏,机器人学,PyTorch
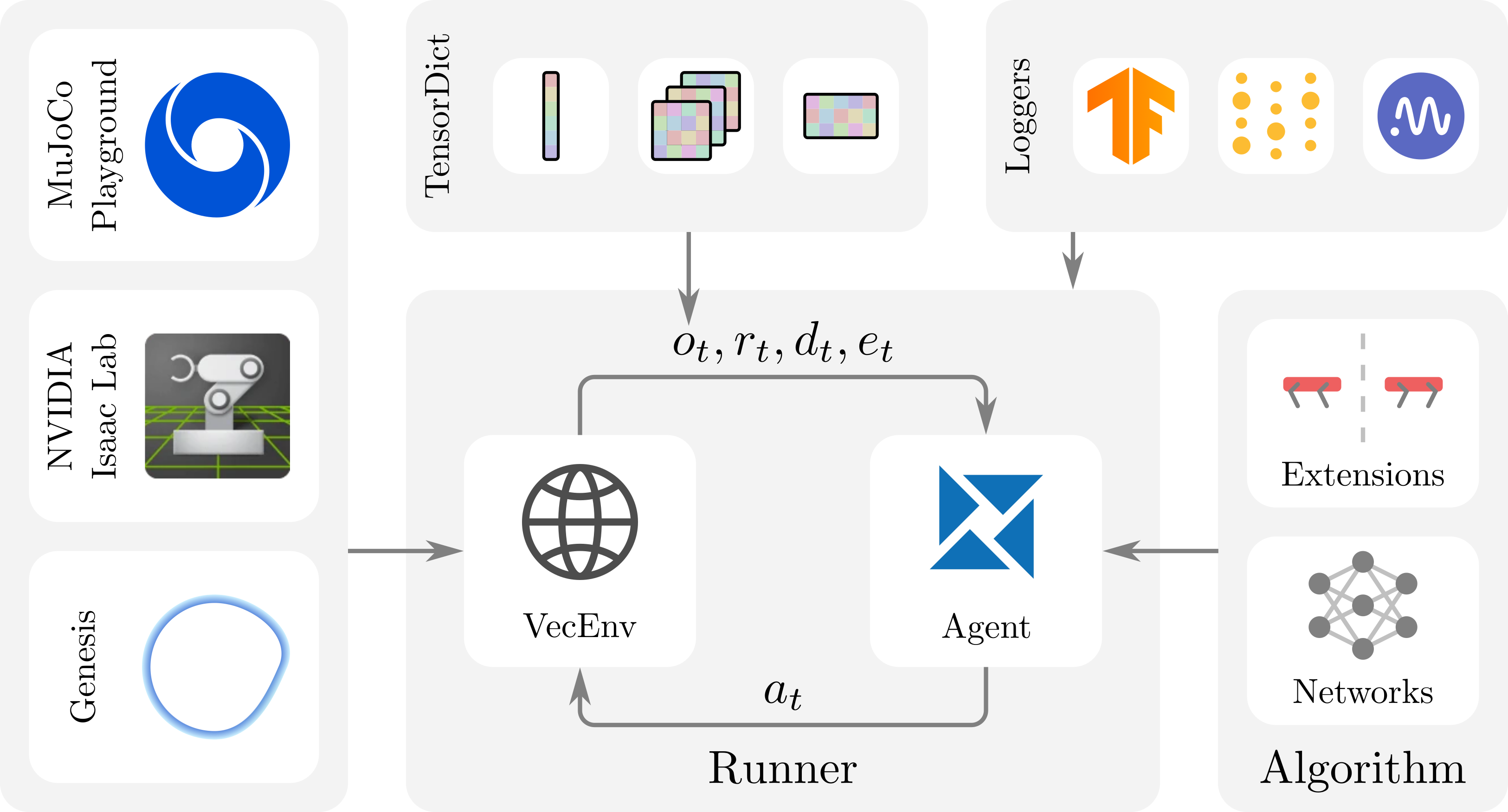 图1:框架概述。RSL-RL由三个主要组件构成:运行器、算法和网络,这些组件可独立进行便捷修改。该框架支持常见日志记录选项,并为机器人技术提供了实用扩展功能。
图1:框架概述。RSL-RL由三个主要组件构成:运行器、算法和网络,这些组件可独立进行便捷修改。该框架支持常见日志记录选项,并为机器人技术提供了实用扩展功能。
一、引言
强化学习(RL)在解决复杂规划与控制问题方面已证明具有极高成效,其表现往往超越传统基于模型的方法(Hwangbo等,2019;Miki等,2022;Handa等,2023)。这些进展得益于更优学习算法的开发(Schulman et al., 2017)以及GPU加速物理模拟器的出现(Makoviychuk et al., 2021; Mittal et al., 2023; Zakka et al., 2025),后者使基于消费级硬件的大规模并行训练成为可能。
尽管现有多种RL库可供使用(Raffin等人,2021;Liang等人,2018;Huang等人,2022b;Serrano-Munoz等人,2023;Makoviichuk和Makoviychuk,2021;Bou等人,2023),但多数是为更广泛的机器学习社区开发的。其算法广度虽便于基准测试,但由此产生的模块化特性却使代码难以适配与扩展,导致机器人领域的应用受限。尽管机器人学能受益于基础算法研究的进展,但研究人员往往更重视紧凑且易于修改的代码库,以高效利用大规模仿真。同时,机器人应用常需专用功能,例如将学习策略蒸馏为实际部署工具的工具。
RSL-RL通过采用极简而强大的设计理念突破了这些局限,其核心在于精选广泛应用的前沿算法集,并针对机器人研究者需求定制功能特性。该框架的核心特征如下:
- 极简设计:紧凑易读的代码库,配备清晰的扩展点(运行器、算法、网络),支持快速研究原型开发。
- 机器人优先方法:包含近似策略优化(PPO)和DAgger风格的行为克隆(BC),以及通用RL库中罕见的辅助技术(对称性增强与好奇心驱动探索)。
- 高吞吐量训练:专为大规模批量训练设计的GPU管道,原生支持多GPU/多节点协同。
- 成熟封装方案:经众多机器人研究论文验证,并集成NVIDIA Isaac Lab、MuJoCo Playground、Genesis等GPU加速仿真框架,实现开箱即用。
二、功能特性
本文将介绍截至撰写时RSL-RL的主要功能。虽然未来计划增加更多算法和特性,但该库旨在保持可适配性,我们的首要目标是确保其简单易用。
2.1 算法
当前RSL-RL包含两种算法:PPO(Schulman等,2017)及类似DAgger(Ross等,2011)的BC算法。PPO作为一种无模型、基于策略的强化学习方法,因其鲁棒性与简洁性已成为机器人学习领域的标准方案(Shakya等,2023)。该算法无需先验知识或示范即可从零学习复杂任务,在机器人领域主要应用于运动控制、操作执行、路径规划及导航等连续控制问题。
BC算法作为监督学习方法,通过将专家策略的行为蒸馏为学生策略实现学习。其工作流程包括:迭代执行学生策略收集数据、用专家动作重新标注数据,并据此训练学生策略。当强化学习训练与硬件部署要求存在差异时,该算法尤为有效。此时可将仅依赖仿真信息的强化学习智能体行为,蒸馏为无需此类信息的策略。
2.2 辅助技术
除核心算法外,本库还包含提升机器人应用性能的技术。目前已实现两项扩展技术,未来将持续扩充。首项技术"对称性增强"通过利用机器人物理对称性,在采集数据中添加镜像状态以加速样本生成(Mittal et al., 2024)。这能产生更对称的行为模式,并可通过额外添加对称性损失项强化该效果。
第二项技术基于随机网络蒸馏(RND)构建好奇心驱动的内在奖励机制,用于改善稀疏奖励环境下的探索效率(Burda et al., 2019)。但与原始RND方案不同,本实现仅使用系统完整状态的子集计算奖励。此项改进使智能体的好奇心能聚焦于状态空间的特定区域。好奇心驱动的探索能大幅降低人工设计密集型奖励的需求。例如,Schwarke等人(2023)仅通过单一二元任务奖励,就训练机器人在双腿平衡状态下完成开门操作。
2.3 实用工具
RSL-RL提供多种实验记录与评估方案。最简易的选择是TensorBoard(Abadi等人,2016),可实现本地实验日志记录。针对更复杂的评估需求,该库支持Weights & Biases(Biewald,2020)和Neptune(neptune.ai,2024)。这些工具在计算集群上训练时表现优异,支持实时在线监控实验。但需注意:使用这些服务需注册用户账户,且会将数据上传至对应云平台。本库同时支持双算法的多节点分布式训练及多GPU配置,可实现大规模实验部署。
三、实现细节
该框架由三个主要组件构成,如图1所示:(i) 负责管理环境步进和智能体学习的运行器;(ii) 定义学习智能体的算法;(iii) 算法使用的网络架构。对于大多数应用场景,用户仅需修改这三个文件。该框架采用PyTorch(Paszke et al., 2019)和Python实现,设计直观且易于扩展。
框架定义了专属的VecEnv接口,要求环境实现同步重置模式(Towers et al., 2024)。step方法必须返回PyTorch张量,观测数据需以TensorDict结构呈现(Bou et al., 2023)。TensorDict为批量张量提供灵活的字典式容器,支持观测组件向不同网络模块的可选路由,并天然兼容RND或潜在重建等正则化辅助技术。
所包含的PPO算法融入了Huang等人(2022a)强调的若干实现细节,例如对事件超时的妥善处理。在大批量训练中,多个环境往往在训练初期同时终止,导致滚动样本相关性增强。为缓解此问题,本框架支持在初始化阶段对事件进行随机提前终止,从而提升样本多样性并稳定学习过程。无论是强化学习还是知识蒸馏场景,本框架均通过跨滚动样本显式管理隐藏状态及正确处理时间反向传播(BPTT)来支持循环神经网络。
四、研究应用
RSL-RL最初被引入旨在展示大规模并行仿真和基于GPU的训练在腿足运动中的优势,仅需数分钟即可生成行走策略(Rudin等人,2022)。此后,该方法已成为广泛机器人研究的基础。
在此基础上,研究者将该框架应用于模拟到真实环境的敏捷运动控制(Cheng et al., 2023; Margolis and Agrawal, 2023)及全身协调控制(Fu et al., 2023; He et al., 2024; Arm et al., 2024)。Hoeller等人(2024)将该框架扩展为采用混合动作分布,用于训练协调多项专家技能的高级导航策略。Rudin等人(2025)则运用师徒知识蒸馏技术训练通用移动策略。近期研究将注意力机制网络架构应用于稀疏地形行走(He et al., 2025)及深度导航(Yang et al., 2025)。通过引入示范数据,多项研究将框架扩展至对抗性风格训练(Vollenweider等人,2022)和DeepMimic风格训练(Sleiman等人,2024)。其他研究(Lee et al., 2024; Dadiotis et al., 2025)通过P3O(Zhang et al., 2022)和CaT(Chane-Sane et al., 2024)增强了PPO实现,以处理训练过程中的约束条件。最后,框架中基于对称性的增强方法已被应用于多智能体协调(Li et al., 2025)和低级控制(Zhang et al., 2024a, b)。
五、何时使用RSL-RL以及何时不应使用它
RSL-RL专为需要紧凑、可修改且经过充分验证的学习代码库的机器人研究人员设计。它支持通过强化学习推动机器人技术前沿的研究,允许用户实现新想法或直接应用该库来增强真实机器人的能力。其特性专为提升性能和促进模拟到真实环境的成功迁移而构建,这是验证新方法的关键步骤。
该库不适用于基础或通用机器学习研究。其设计包含有限的算法集,因此不适合直接用于其他RL算法的基准测试。此外,RSL-RL不提供对纯模仿学习的原生支持。
六、致谢与资金披露
Nikita Rudin与David Hoeller在苏黎世联邦理工学院及英伟达任职期间,共同开发了本库初始版本(v1.0.2),该版本用于Rudin等人(2022)的研究。此后Clemens Schwarke与Mayank Mittal持续维护并扩展了本库。作者谨向所有开源贡献者致谢。本工作由英伟达提供支持。
七、参考文献
- Abadi et al. (2016)Martín Abadi, Ashish Agarwal, Paul Barham, Eugene Brevdo, Zhifeng Chen, Craig Citro, Greg S Corrado, Andy Davis, Jeffrey Dean, Matthieu Devin, et al.Tensorflow: Large-scale machine learning on heterogeneous distributed systems.arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv--1603, 2016.
- Arm et al. (2024)Philip Arm, Mayank Mittal, Hendrik Kolvenbach, and Marco Hutter.Pedipulate: Enabling manipulation skills using a quadruped robot's leg.In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 5717--5723. IEEE, 2024.
- Biewald (2020)Lukas Biewald.Experiment tracking with weights and biases, 2020.URL https://www.wandb.com/.Software available from wandb.com.
- Bou et al. (2023)Albert Bou, Matteo Bettini, Sebastian Dittert, Vikash Kumar, Shagun Sodhani, Xiaomeng Yang, Gianni De Fabritiis, and Vincent Moens.Torchrl: A data-driven decision-making library for pytorch, 2023.
- Burda et al. (2019)Yuri Burda, Harrison Edwards, Amos Storkey, and Oleg Klimov.Exploration by random network distillation.In International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR), pages 1--17, 2019.
- Chane-Sane et al. (2024)Elliot Chane-Sane, Pierre-Alexandre Leziart, Thomas Flayols, Olivier Stasse, Philippe Souères, and Nicolas Mansard.Cat: Constraints as terminations for legged locomotion reinforcement learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pages 13303--13310. IEEE, 2024.
- Cheng et al. (2023)Xuxin Cheng, Kexin Shi, Ananye Agarwal, and Deepak Pathak.Extreme parkour with legged robots.Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), 2023.
- Dadiotis et al. (2025)Ioannis Dadiotis, Mayank Mittal, Nikos Tsagarakis, and Marco Hutter.Dynamic object goal pushing with mobile manipulators through model-free constrained reinforcement learning.Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2025.
- Fu et al. (2023)Zipeng Fu, Xuxin Cheng, and Deepak Pathak.Deep whole-body control: learning a unified policy for manipulation and locomotion.In Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), pages 138--149. PMLR, 2023.
- Handa et al. (2023)Ankur Handa, Arthur Allshire, Viktor Makoviychuk, Aleksei Petrenko, Ritvik Singh, Jingzhou Liu, Denys Makoviichuk, Karl Van Wyk, Alexander Zhurkevich, Balakumar Sundaralingam, et al.Dextreme: Transfer of agile in-hand manipulation from simulation to reality.In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 5977--5984. IEEE, 2023.
- He et al. (2025)Junzhe He, Chong Zhang, Fabian Jenelten, Ruben Grandia, Moritz Bächer, and Marco Hutter.Attention-based map encoding for learning generalized legged locomotion.Science Robotics, 10(105):eadv3604, 2025.
- He et al. (2024)Tairan He, Wenli Xiao, Toru Lin, Zhengyi Luo, Zhenjia Xu, Zhenyu Jiang, Jan Kautz, Changliu Liu, Guanya Shi, Xiaolong Wang, et al.Hover: Versatile neural whole-body controller for humanoid robots.arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.21229, 2024.
- Hoeller et al. (2024)David Hoeller, Nikita Rudin, Dhionis Sako, and Marco Hutter.Anymal parkour: Learning agile navigation for quadrupedal robots.Science Robotics, 9(88):eadi7566, 2024.
- Huang et al. (2022a)Shengyi Huang, Rousslan Fernand Julien Dossa, Antonin Raffin, Anssi Kanervisto, and Weixun Wang.The 37 implementation details of proximal policy optimization.In ICLR Blog Track , 2022a.URL https://iclr-blog-track.github.io/2022/03/25/ppo-implementation-details/.https://iclr-blog-track.github.io/2022/03/25/ppo-implementation-details/.
- Huang et al. (2022b)Shengyi Huang, Rousslan Fernand Julien Dossa, Chang Ye, Jeff Braga, Dipam Chakraborty, Kinal Mehta, and JoÃĢo GM AraÚjo.Cleanrl: High-quality single-file implementations of deep reinforcement learning algorithms.Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), 23(274):1--18, 2022b.
- Hwangbo et al. (2019)Jemin Hwangbo, Joonho Lee, Alexey Dosovitskiy, Dario Bellicoso, Vassilios Tsounis, Vladlen Koltun, and Marco Hutter.Learning agile and dynamic motor skills for legged robots.Science Robotics, 4(26):eaau5872, 2019.
- Lee et al. (2024)Joonho Lee, Marko Bjelonic, Alexander Reske, Lorenz Wellhausen, Takahiro Miki, and Marco Hutter.Learning robust autonomous navigation and locomotion for wheeled-legged robots.Science Robotics, 9(89):eadi9641, 2024.
- Li et al. (2025)Zichong Li, Filip Bjelonic, Victor Klemm, and Marco Hutter.Marladona-towards cooperative team play using multi-agent reinforcement learning.In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2025.
- Liang et al. (2018)Eric Liang, Richard Liaw, Robert Nishihara, Philipp Moritz, Roy Fox, Ken Goldberg, Joseph Gonzalez, Michael Jordan, and Ion Stoica.Rllib: Abstractions for distributed reinforcement learning.In International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), pages 3053--3062, 2018.
- Makoviichuk and Makoviychuk (2021)Denys Makoviichuk and Viktor Makoviychuk.rl-games: A high-performance framework for reinforcement learning.https://github.com/Denys88/rl_games, May 2021.
- Makoviychuk et al. (2021)Viktor Makoviychuk, Lukasz Wawrzyniak, Yunrong Guo, Michelle Lu, Kier Storey, Miles Macklin, David Hoeller, Nikita Rudin, Arthur Allshire, Ankur Handa, and Gavriel State.Isaac gym: High performance gpu based physics simulation for robot learning.In Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks, volume 1, 2021.
- Margolis and Agrawal (2023)Gabriel B. Margolis and Pulkit Agrawal.Walk these ways: Tuning robot control for generalization with multiplicity of behavior.In Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), volume 205, pages 22--31. PMLR, 2023.
- Miki et al. (2022)Takahiro Miki, Joonho Lee, Jemin Hwangbo, Lorenz Wellhausen, Vladlen Koltun, and Marco Hutter.Learning robust perceptive locomotion for quadrupedal robots in the wild.Science Robotics, 7(62), 2022.
- Mittal et al. (2023)Mayank Mittal, Calvin Yu, Qinxi Yu, Jingzhou Liu, Nikita Rudin, David Hoeller, Jia Lin Yuan, Ritvik Singh, Yunrong Guo, Hammad Mazhar, et al.Orbit: A unified simulation framework for interactive robot learning environments.IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), 8(6):3740--3747, 2023.
- Mittal et al. (2024)Mayank Mittal, Nikita Rudin, Victor Klemm, Arthur Allshire, and Marco Hutter.Symmetry considerations for learning task symmetric robot policies.In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), pages 7433--7439. IEEE, 2024.
- neptune.ai (2024)neptune.ai.neptune.ai: experiment tracker, 2024.URL https://neptune.ai.
- Paszke et al. (2019)Adam Paszke, Sam Gross, Francisco Massa, Adam Lerer, James Bradbury, Gregory Chanan, Trevor Killeen, Zeming Lin, Natalia Gimelshein, Luca Antiga, et al.Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library.Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 32, 2019.
- Raffin et al. (2021)Antonin Raffin, Ashley Hill, Adam Gleave, Anssi Kanervisto, Maximilian Ernestus, and Noah Dormann.Stable-baselines3: Reliable reinforcement learning implementations.Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), 22(268):1--8, 2021.
- Ross et al. (2011)Stéphane Ross, Geoffrey Gordon, and Drew Bagnell.A reduction of imitation learning and structured prediction to no-regret online learning.In Proceedings of the fourteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics, pages 627--635. JMLR Workshop and Conference Proceedings, 2011.
- Rudin et al. (2022)Nikita Rudin, David Hoeller, Philipp Reist, and Marco Hutter.Learning to walk in minutes using massively parallel deep reinforcement learning.In Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), pages 91--100, 2022.
- Rudin et al. (2025)Nikita Rudin, Junzhe He, Joshua Aurand, and Marco Hutter.Parkour in the wild: Learning a general and extensible agile locomotion policy using multi-expert distillation and rl fine-tuning.International Journal of Robotics Research (IJRR), 2025.
- Schulman et al. (2017)John Schulman, Filip Wolski, Prafulla Dhariwal, Alec Radford, and Oleg Klimov.Proximal policy optimization algorithms.arXiv e-prints, pages arXiv--1707, 2017.
- Schwarke et al. (2023)Clemens Schwarke, Victor Klemm, Matthijs Van der Boon, Marko Bjelonic, and Marco Hutter.Curiosity-driven learning of joint locomotion and manipulation tasks.In Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), volume 229, pages 2594--2610, 2023.
- Serrano-Munoz et al. (2023)Antonio Serrano-Munoz, Dimitrios Chrysostomou, Simon Bøgh, and Nestor Arana-Arexolaleiba.skrl: Modular and flexible library for reinforcement learning.Journal of Machine Learning Research (JMLR), 24(254):1--9, 2023.
- Shakya et al. (2023)Ashish Kumar Shakya, Gopinatha Pillai, and Sohom Chakrabarty.Reinforcement learning algorithms: A brief survey.Expert Systems with Applications, 231:120495, 2023.
- Sleiman et al. (2024)Jean-Pierre Sleiman, Mayank Mittal, and Marco Hutter.Guided reinforcement learning for robust multi-contact loco-manipulation.In Conference on Robot Learning (CoRL), 2024.
- Towers et al. (2024)Mark Towers, Ariel Kwiatkowski, Jordan Terry, John U Balis, Gianluca De Cola, Tristan Deleu, Manuel Goulão, Andreas Kallinteris, Markus Krimmel, Arjun KG, et al.Gymnasium: A standard interface for reinforcement learning environments.arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.17032, 2024.
- Vollenweider et al. (2022)Eric Vollenweider, Marko Bjelonic, Victor Klemm, Nikita Rudin, Joonho Lee, and Marco Hutter.Advanced skills through multiple adversarial motion priors in reinforcement learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.14912, 2022.
- Yang et al. (2025)Fan Yang, Per Frivik, David Hoeller, Chen Wang, Cesar Cadena, and Marco Hutter.Improving long-range navigation with spatially-enhanced recurrent memory via end-to-end reinforcement learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2506.05997, 2025.
- Zakka et al. (2025)Kevin Zakka, Baruch Tabanpour, Qiayuan Liao, Mustafa Haiderbhai, Samuel Holt, Jing Yuan Luo, Arthur Allshire, Erik Frey, Koushil Sreenath, Lueder A Kahrs, et al.Mujoco playground.Robotics: Science and Systems (RSS), 2025.
- Zhang et al. (2024a)Chong Zhang, Nikita Rudin, David Hoeller, and Marco Hutter.Learning agile locomotion on risky terrains.In 2024 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS), pages 11864--11871. IEEE, 2024a.
- Zhang et al. (2024b)Chong Zhang, Wenli Xiao, Tairan He, and Guanya Shi.Wococo: Learning whole-body humanoid control with sequential contacts.arXiv preprint arXiv:2406.06005, 2024b.
- Zhang et al. (2022)Linrui Zhang, Li Shen, Long Yang, Shixiang Chen, Bo Yuan, Xueqian Wang, and Dacheng Tao.Penalized proximal policy optimization for safe reinforcement learning.arXiv preprint arXiv:2205.11814, 2022.