设计模式第一章(建造者模式)
建造者模式(Builder Pattern)是一种创建型设计模式,将复杂对象的构建过程与其表示分离,使同一构建流程能生成不同形态的对象。 例如:工厂 单列 原型 目的都是造对象。
前言
核心思想
通过拆分构建步骤与对象结构,将复杂对象的创建分为多个独立模块。客户端通过指挥者类间接构建对象,无需直接调用具体构建逻辑,从而隐藏实现细节并提升代码可维护性。
角色分工
-
**建造者(Builder)**:定义构建复杂对象的接口,包含多个抽象方法对应不同构建阶段。
-
**具体建造者(ConcreteBuilder)**:实现建造者接口,负责按步骤组装对象部件。
**指挥者(Director)**:控制构建流程,通过调用建造者方法生成最终对象,不直接暴露构建细节。
优势
- 分离构建与表示:降低代码耦合度,同一构建逻辑可适配不同产品形态。
- 逐步构建:通过分步组装简化复杂对象创建流程。
- 封装性:客户端仅需指定对象类型和参数,无需了解内部构建细节。
- 灵活性:修改构建逻辑时无需改动客户端代码,便于维护和扩展。
代码部分
- 第一版本 ~ 最终的版本
- 每个版本的需求变化已经不足之处
- 如果优化每个版本的缺陷
- 最终写一个应用的场景
- 核心思想-链式调用
V1
- 需求背景
- 我们现在有一个普通的javabean对象,需求为,如果年龄大小于10并且名字为 tom那么我们就提示不能创建;
- 如果年龄大于10,并且名字叫 Jerry 的话,也不能创建
java 代码部分
markdown
public class UserV1 {
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public boolean check() {
if (age < 10 && "Tom".equals(name)) {
return false;
}
if (age > 10 && "Jerry".equals(name)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 10 岁不能叫 tom
// 大于 10岁 jetty 也不行
UserV1 userV1 = new UserV1();
userV1.setAge(1);
userV1.setName("Tom");
//传统判断 调用时机不对,不调用都有可能
// 有没有一种方案是 必须是设置了属性后再校验, 因为属性可能需要上下文
if (userV1.check()) {
}
}缺陷部分
我们看到上面的代码缺陷部分,调用时机不对,如果调用者不使用,那么就不能校验了,而且这个校验需要有上下文的时机,必须是属性都设置了后再调用
V2
我们针对上面的缺点进行改进,使用一个内部的builder 对象构建
代码部分
java
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private User() {
}
public static Builder builder() {
return new Builder();
}
//创建一个内部类
public static class Builder {
private String name;
private int age;
private Builder() {
}
public User build() throws IllegalAccessException {
User user = new User();
user.name = this.name;
user.age = this.age;
if (age < 10 && "Tom".equals(name)) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("年龄小于10不能叫Tom");
}
if (age > 10 && "Jerry".equals(name)) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("年龄大于10不能叫Jerry");
}
return user;
}
public Builder name(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Builder age(int age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}使用部分
我们通过User.builder()方法得到一个用户对象,在最红调用build的时候,我们进行校验,这样就保证了上下文的顺序
java
public class TestV2Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
// 缺陷 user创建之后还可以修改里面的属性,实际上是一次性的对象
User user = User.builder().name("Tom").age(11).build();
user.setAge(222);
}
}缺陷部分
当我们build完后这个对象,我们还是可以通过set更改里面的属性,实际上这个对象是一次性的,当我们设置后,就不能够进行更改。类似于我们发起的 http对象
V3
对外提供的builde方法,在创建之后就不让修改
代码部分
java
public class User {
private final String name;
private final int age;
private User(Builder builder) {
this.name = builder.name;
this.age = builder.age;
}
public static Builder builder() {
return new Builder();
}
//创建一个内部类
public static class Builder {
private String name;
private int age;
private Builder() {
}
public User build() throws IllegalAccessException {
// 可以判断 必须设置值
User user = new User(this);
if (age < 10 && "Tom".equals(name)) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("年龄小于10不能叫Tom");
}
if (age > 10 && "Jerry".equals(name)) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("年龄大于10不能叫Jerry");
}
return user;
}
public Builder name(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public Builder age(int age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
}使用部分
java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IllegalAccessException {
// dsl
User user = User.builder().name("Tom").age(11).build();
user.setAge()//会报错,没有该方法
// 案例演示
List.of(1,2,3,4).stream().map(String::valueOf).filter(x -> x.length() > 1).collect(Collectors.toList());
}总结
该部分代码的演变为,增加一个私有构造方法,使之外面不能直接new,然后去掉set方法,只保留get方法,在 builder 里面进行复制,内部类的使用方式
使用案例
我们根据传入的参数,构建一个 sql 的查询和修改的类,使之做到 dsl
v1
我们定义了枚举,SELECT,DELETE,UPDATE 采用 Switch 实现,记住一点,如果我们一开始想不出来使用设计模式,那么我们就按照最基本的方式,先把功能实现
代码部分
markdown
public class SqlWarp {
private SqlWarp () {
}
public static SqlBuilder builder(SqlType sqlType) {
return new SqlBuilder(sqlType);
}
public static class SqlBuilder {
final SqlType sqlType;
// 查询的列
private String[] columns;
//查询的表名
private String tableNm;
// 查询的where 条件
private String where;
private Map<String,String> setMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private SqlBuilder(SqlType sqlType) {
this.sqlType = sqlType;
}
public SqlBuilder select(String ...columns) {
this.columns = columns;
return this;
}
public SqlBuilder table(String tableNm) {
this.tableNm = tableNm;
return this;
}
public SqlBuilder where(String where) {
this.where = where;
return this;
}
public SqlBuilder set(String column,String columnValue) {
setMap.put(column,columnValue);
return this;
}
public String buildSql() {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
switch (sqlType) {
case SELECT -> {
sql.append(" SELECT ").append(String.join(",",columns)).append(" FROM ").append(tableNm);
if (where != null) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(where);
}
}
case UPDATE -> {
sql.append(" UPDATE ").append(tableNm).append(" SET ");
sql.append(setMap.entrySet().stream()
.map(entry -> entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue())
.collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
if (where != null) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(where);
}
}
case INSERT -> {
}
case DELETE -> {
}
default -> throw new UnsupportedOperationException("暂不支持该类型的参数");
}
return sql.toString();
}
}
enum SqlType {
SELECT,
UPDATE,
DELETE,
INSERT,
}
}使用部分
java
public class SqlTestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 问题点,如果我是 select 我还是可以调用set方法,那么有没有一种功能,限制调用的api
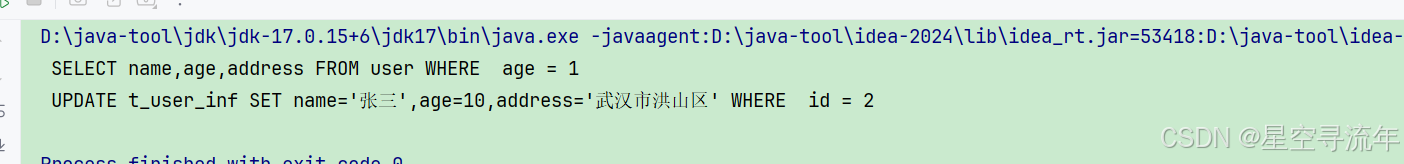
String sql = SqlWarp.builder(SqlWarp.SqlType.SELECT)
.select("name", "age", "address")
.table("user")
.where(" age = 1")
.buildSql();
System.out.println(sql);
String updSql = SqlWarp.builder(SqlWarp.SqlType.UPDATE).table("t_user_inf")
.set("name", "'张三'")
.set("age", "10")
.set("address", "'武汉市洪山区'")
.where(" id = 2")
.buildSql();
System.out.println(updSql);
}
}
缺陷部分
当我们使用查询(select)方法的时候,我们也可以调用 set方法,实际上,该方法是给update 使用的,那么有没有一种方式是,如果是 select 我只有我需要的那部分 api 其他的不对外开放,那么下一部分就是优化该部分
javaString sql = SqlWarp.builder(SqlWarp.SqlType.SELECT) .select("name", "age", "address") .set("aa","111") .table("user") .where(" age = 1") .buildSql();
v2
优化查询不能调用 set 方法
代码部分
java
public class SQL {
private SQL() {}
public static SelectBuilder select(String ...column) {
return new SelectBuilder(column);
}
public static UpdateBuilder update() {
return new UpdateBuilder();
}
/**
* 查询 builder
*/
static class SelectBuilder {
// 要查询的列
private final String[] columns;
//所属表
private String table;
//where 条件
private String where;
private SelectBuilder(String[] columns) {
this.columns = columns;
}
public SelectBuilder from(String table) {
this.table = table;
return this;
}
public SelectBuilder where(String where) {
this.where = where;
return this;
}
public String buildSql() {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
sql.append(" SELECT ").append(String.join(",",columns)).append(" FROM ").append(table);
if (where != null) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(where);
}
return sql.toString();
}
}
//更新
public static class UpdateBuilder {
// 设置列的条件
private Map<String,String> setMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//表名
private String table;
//where 条件
private String where;
private UpdateBuilder() {
}
public UpdateBuilder table(String table) {
this.table = table;
return this;
}
public UpdateBuilder set(String key,String value) {
setMap.put(key,value);
return this;
}
public UpdateBuilder where(String where) {
this.where = where;
return this;
}
public String buildSql() {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
sql.append(" UPDATE ").append(table).append(" SET ")
.append(setMap.entrySet().stream()
.map(entry -> entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue())
.collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
if (where != null) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(where);
}
return sql.toString();
}
}
}使用部分
java
public class SQLTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
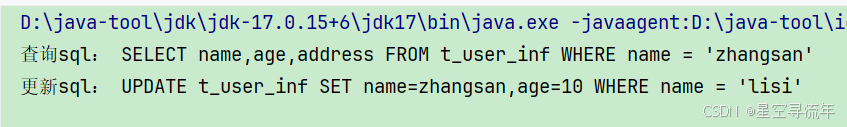
//查询
String sql = SQL
.select("name", "age", "address")
.from("t_user_inf")
.where("name = 'zhangsan'")
.buildSql();
System.out.println("查询sql:"+sql);
String updSql = SQL.update()
.table("t_user_inf")
.set("name", "zhangsan")
.set("age", "10")
.where("name = 'lisi'")
.buildSql();
System.out.println("更新sql:"+updSql);
}
缺陷部分
虽然我们限制了 查询不能使用set方法,但是,如果我们可以同时设置多个 from 方法,多个where 方法,不能称之为一次性对象,下一节使用接口实现,最终版的 dsl 方式DSL(领域特定语言)
V3
- 查询实现
- 修改的实现
- 删除的实现
查询dsl
- 查询需要设置的值,定义一套接口
代码部分
java
public class SqlSelect {
private SqlSelect() {}
public static TableStage select() {
return new SelectBuilder();
}
static class SelectBuilder implements TableStage,ColumnStage,WhereStage {
// 要查询的列
private String[] columns;
// 要查询的表
private String table;
// where 条件
private String where;
@Override
public WhereStage column(String... columns) {
this.columns = columns;
return this;
}
@Override
public ColumnStage from(String table) {
this.table = table;
return this;
}
@Override
public WhereStage where(String where) {
this.where = where;
return this;
}
@Override
public String buildSql() {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
sql.append(" SELECT ").append(String.join(",",columns)).append(" FROM ").append(table);
if (where != null) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(where);
}
return sql.toString();
}
}
// table 策略
interface TableStage {
ColumnStage from(String table);
}
// 查询的列
interface ColumnStage {
WhereStage column(String ...column);
}
// where 条件
interface WhereStage {
WhereStage where(String where);
String buildSql();
}
}使用部分
java
public class TestMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String updSql = SqlSelect.select().from("t_user_inf")
.column("name", "age", "address")
.where(" id = 6")
.buildSql();
}
}修改dsl
- 接口部分
- 接口实现
- 调用部分
接口部分
java
public class SQLStrategy {
// 查询 table , update table set aa where
interface TableStrategy {
SetStrategy table(String tableName);
}
// 设置列 stage
interface SetStrategy {
SetStrategy set(String name,String value);
WhereStrategy where(String where);
}
// where条件
interface WhereStrategy {
String buildSql();
}
}接口实现
markdown
public class SQL {
private SQL() {}
public static SQLStrategy.TableStrategy update() {
return new UpdateBuilder();
}
public static SqlDelete.TableStrategy delete() {
return new SqlDelete.SqlDeleteBuilder();
}
static class UpdateBuilder implements SQLStrategy.TableStrategy, SQLStrategy.SetStrategy, SQLStrategy.WhereStrategy {
private String[] columns;
private Map<String,String> setMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private String where;
private String table;
@Override
public SQLStrategy.SetStrategy table(String table) {
this.table = table;
return this;
}
@Override
public SQLStrategy.SetStrategy set(String name, String value) {
setMap.put(name,value);
return this;
}
@Override
public SQLStrategy.WhereStrategy where(String where) {
this.where = where;
return this;
}
@Override
public String buildSql() {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
sql.append(" UPDATE ").append(table).append(" SET ");
sql.append(setMap.entrySet().stream()
.map(entry -> entry.getKey() + "=" + entry.getValue())
.collect(Collectors.joining(",")));
if (where != null) {
sql.append(" WHERE ").append(where);
}
return sql.toString();
}
}
}使用部分
java
String sql = SQL.update()
.table("t_user_inf")
.set("name", "'张三'")
.set("age", "12")
.where("where id = 15")
.buildSql();
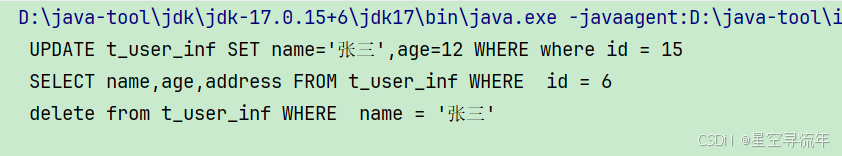
System.out.println(sql);删除dsl
- 蜜封属性
代码部分
java
public class SqlDelete {
private SqlDelete() {
}
public static TableStrategy delete() {
return new SqlDeleteBuilder();
}
public static class SqlDeleteBuilder implements TableStrategy,WhereStrategy {
private String table;
private String where;
@Override
public WhereStrategy table(String tableName) {
this.table = tableName;
return this;
}
@Override
public WhereStrategy where(String where) {
this.where = where;
return this;
}
@Override
public String buildSql() {
StringBuilder sql = new StringBuilder();
sql.append(" delete from ").append(table).append(" WHERE ").append(where);
return sql.toString();
}
}
// 查询 table , update table set aa where
interface TableStrategy {
WhereStrategy table(String tableName);
}
// where条件
interface WhereStrategy {
WhereStrategy where(String where);
String buildSql();
}
}使用部分
java
String delSql = SQL.delete()
.table("t_user_inf").where(" name = '张三'").buildSql();
System.out.println(delSql);dsl 输出结果