大家吼!刚刚 Kotlin v2.2.20 已经发布, 更新的内容也已经在官网上更新:What's new in Kotlin 2.2.20 。 那么接下来,就让我来看看哪些是我最喜欢的新特性吧~!
注意!这里主要阐述一些我感兴趣的语言特性和库的更新。如果你还有其他关系的、但是我没有提到的,记得去官方日志看看喔~
下文中的代码示例等内容,如无特殊说明,均来自/改自官方更新日志。
语言特性
一如既往,让我们先来看看有哪些有趣的语言特性更新。
改进具有 suspend 的 Lambda 函数类型的重载解析
不知道你之前是否遇到这种情况,你定义了两个函数,它们的参数一个有 suspend,而一个没有。 当你需要调用它们的时候,IDE就分不清谁是谁了:
Kotlin
// Defines two overloads
fun transform(block: () -> Int) {}
fun transform(block: suspend () -> Int) {}
fun test() {
// Fails with overload resolution ambiguity
transform({ 42 })
// Uses an explicit cast, but the compiler incorrectly reports
// a "No cast needed" warning
transform({ 42 } as () -> Int)
}可以看到,我们需要用强制类型转化 as () -> Int 来指明,但是这时候IDE又会提示你"非必要转化"。
现在,我们可以直接使用 suspend 来标记 Lambda 参数,解决上面提到的痛点了:
Kotlin
// Resolves to transform(() -> Int)
transform({ 42 })
// Resolves to transform(suspend () -> Int)
transform(suspend { 42 })可以看到,直接使用 suspend { 42 } 即可指明使用带 suspend 的 Lambda 的那个对应的函数。
这个特性在下一个大版本也就是 2.3.0 中会默认启用。如果你现在就想体验,可以使用编译器参数:
diff
-language-version 2.3或者在 Gradle 构建脚本中配置语言版本:
bash
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
languageVersion.set(org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.KotlinVersion.KOTLIN_2_3)
}
}执行表达式函数体中使用 return
在以前,你不能直接在一个表达式函数体中使用 return:
Kotlin
fun example() = return 42
// Error: Returns are prohibited for functions with an expression body而现在,可以了!
Kotlin
// Specifies the return type explicitly
fun getDisplayNameOrDefault(userId: String?): String = getDisplayName(userId ?: return "default")
// Fails because it doesn't specify the return type explicitly
fun getDisplayNameOrDefault(userId: String?) = getDisplayName(userId ?: return "default")不过对应地,你的函数需要显式标明返回值类型。同样地,在过去的版本中有些"取巧"的写法也可以达成直接在表达式中写 return, 并且不需要显式标明返回值类型,现在也对它们做了检测和弃用处理:
Kotlin
// Return type isn't explicitly specified, and the return statement is inside a lambda
// which will be deprecated
fun returnInsideLambda() = run { return 42 }
// Return type isn't explicitly specified, and the return statement is inside the initializer
// of a local variable, which will be deprecated
fun returnInsideIf() = when {
else -> {
val result = if (someCondition()) return "" else "value"
result
}
}这个特性在下一个大版本也就是 2.3.0 中会默认启用。如果你现在就想体验,可以使用编译器参数:
diff
-language-version 2.3或者在 Gradle 构建脚本中配置语言版本:
bash
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
languageVersion.set(org.jetbrains.kotlin.gradle.dsl.KotlinVersion.KOTLIN_2_3)
}
}基于数据流的表达式穷举性检查
在之前的版本中,Kotlin对一些内容(比如枚举)的穷举性检查只限定在 when 的范围内。 而现在,如果数据流表明了某些数据不会存在,那么 when 的穷举依然能够生效:
Kotlin
enum class UserRole { ADMIN, MEMBER, GUEST }
fun getPermissionLevel(role: UserRole): Int {
// Covers the Admin case outside of the when expression
if (role == UserRole.ADMIN) return 99
return when (role) {
UserRole.MEMBER -> 10
UserRole.GUEST -> 1
// You no longer have to include this else branch
// else -> throw IllegalStateException()
}
}这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xdata-flow-based-exhaustiveness")
}
}在 catch 中支持 reified 类型
如字面意思所述,现在可以在有 reified 的 inline 函数中的 catch 中使用这个 reified 类型了:
Kotlin
inline fun <reified ExceptionType : Throwable> handleException(block: () -> Unit) {
try {
block()
// This is now allowed after the change
} catch (e: ExceptionType) {
println("Caught specific exception: ${e::class.simpleName}")
}
}
fun main() {
// Tries to perform an action that might throw an IOException
handleException<java.io.IOException> {
throw java.io.IOException("File not found")
}
// Caught specific exception: IOException
}这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xallow-reified-type-in-catch")
}
}改进 Kotlin 的 contracts
在 2.2.20,Kotlin 改进了一些跟 contracts 相关的东西:
- Support for generics in contract type assertions.
支持在契约类型断言中使用泛型。 - Support for contracts inside property accessors and specific operator functions.
支持在属性访问器和特定运算符函数中使用契约。 - Support for the
returnsNotNull()function in contracts, allowing you to assume conditions are true when passed inside lambdas.
支持在契约中使用returnsNotNull()函数,允许你在 lambda 内部假设条件为真。 - New
holdsInkeyword as a way to ensure a non-null return value when a condition is met.
新增holdsIn关键字,用于在满足条件时确保返回值非空。
虽然这东西平时写代码的时候用的会比较少,不过如果是一个库作者或者官方的std中,倒也没那么少见。
这些新的东西也都是实验性的 。使用它们会有对应的
@OptIn需要你去标记,以及还有各自对应的编译器参数。
支持在契约类型断言中使用泛型
看标题大概也可能看出来,可以在 contract 中使用泛型了。
Kotlin
import kotlin.contracts.*
sealed class Failure {
class HttpError(val code: Int) : Failure()
// Insert other failure types here
}
sealed class Result<out T, out F : Failure> {
class Success<T>(val data: T) : Result<T, Nothing>()
class Failed<F : Failure>(val failure: F) : Result<Nothing, F>()
}
@OptIn(ExperimentalContracts::class)
// Uses a contract to assert a generic type
fun <T, F : Failure> Result<T, F>.isHttpError(): Boolean {
contract {
returns(true) implies (this@isHttpError is Result.Failed<Failure.HttpError>)
}
return this is Result.Failed && this.failure is Failure.HttpError
}这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xallow-contracts-on-more-functions")
}
}支持在属性访问器和特定运算符函数中使用契约。
这个我有印象!之前曾尝试过在 getter 中写 contract,结果大败而归。现在不用担心了,可以在属性访问器中使用了~
Kotlin
import kotlin.contracts.*
val Any.isHelloString: Boolean
get() {
@OptIn(ExperimentalContracts::class)
// Enables smart casting the receiver to String when the getter returns true
contract { returns(true) implies (this@isHelloString is String) }
return "hello" == this
}
fun printIfHelloString(x: Any) {
if (x.isHelloString) {
// Prints the length after the smart cast of the receiver to String
println(x.length)
// 5
}
}除了属性访问器,在以下这些 operator 函数中也可以使用了:
invokecontainsrangeTo,rangeUntilcomponentNiteratorunaryPlus,unaryMinus,notinc,dec
官方的一个示例:
Kotlin
import kotlin.contracts.*
class Runner {
@OptIn(ExperimentalContracts::class)
// Enables initialization of variables assigned inside the lambda
operator fun invoke(block: () -> Unit) {
contract {
callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.EXACTLY_ONCE)
}
block()
}
}
fun testOperator(runner: Runner) {
val number: Int
runner {
number = 1
}
// Prints the value after definite initialization guaranteed by the contract
println(number)
// 1
}这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xallow-contracts-on-more-functions")
}
}支持在契约中使用 returnsNotNull() 函数,允许你在 lambda 内部假设条件为真。
即使返回值可能是null,但是现在也可以通过契约来声明在满足特定情况下的非null返回条件了。
Kotlin
import kotlin.contracts.*
@OptIn(ExperimentalContracts::class, ExperimentalExtendedContracts::class)
fun decode(encoded: String?): String? {
contract {
// Guarantees a non-null return value when the input is non-null
(encoded != null) implies (returnsNotNull())
}
if (encoded == null) return null
return java.net.URLDecoder.decode(encoded, "UTF-8")
}
fun useDecodedValue(s: String?) {
// Uses a safe call since the return value may be null
decode(s)?.length
if (s != null) {
// Treats the return value as non-null after the smart cast
decode(s).length
}
}这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xallow-condition-implies-returns-contracts")
}
}新增 holdsIn 关键字,用于在满足条件时确保返回值非空。
这是一个很有趣的特性。它为契约增加了一个新的关键字 holdsIn,来使得当一个条件满足时, 让这个条件...怎么说呢,覆盖到整个lambda中。
先看官方的示例:
Kotlin
import kotlin.contracts.*
@OptIn(ExperimentalContracts::class, ExperimentalExtendedContracts::class)
fun <T> T.alsoIf(condition: Boolean, block: (T) -> Unit): T {
contract {
// Declares that the lambda runs at most once
callsInPlace(block, InvocationKind.AT_MOST_ONCE)
// Declares that the condition is assumed to be true inside the lambda
condition holdsIn block
}
if (condition) block(this)
return this
}
fun useApplyIf(input: Any) {
val result = listOf(1, 2, 3)
.first()
.alsoIf(input is Int) {
// The input parameter is smart cast to Int inside the lambda
// Prints the sum of input and first list element
println(input + it)
// 2
}
.toString()
}根据官方的介绍手法,它似乎利好一些对于特定领域、语言的场景。考虑到 Kotlin 目前正在紧锣密鼓地推进 KMP 的发展, 这个功能也确实便于后续的各类功能的开发、以及相应的用户体验。
同样的,我觉得这也是一个很利好库作者的功能。一个很常见的例子,在一个 ORM 框架中,你的 where 条件要满足第一个 condition 才可以通过后面的 Lambda 加入到你的 SQL 条件里, 假如函数是这样的:
Kotlin
val username: String? = ...
predicate.and(username != null) { name ->
table.nameSize eq name.length() // ERROR! name is nullable here.
}
// expect output SQL: select * from example_table t where t.name_size = ?在过去,这类API,尽管已经 username != null,在后面的 Lambda 中,name -> 的这个 name 依旧是一个 nullable 的类型。 而现在,holdsIn 似乎可以解决这个问题了。
这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xallow-holdsin-contract")
}
}Kotlin/JVM: when 中支持 invokedynamic
接下来来到 Kotlin/JVM 的专场~ 这一次 Kotlin/JVM 层面的更新并不多(就这一个),因此它们直接在一个大标题中用了 Kotlin/JVM, 倒也不浪费。
不过从标题来看,这个更新也的确是"语言"层面,但不是语言层面。它们优化了 Kotlin/JVM 的编译结果,在一个长长的 when 中, 现在可以与 invokedynamic 进行配合了,而不是像过去那样,会产生很多、很长的 instanceof 链。
因此,在条件满足的情况下,就像 Java switch 那样可以配合 invokedynamic生成更紧凑的字节码。
而这些条件,官方也为我们列出来了:
-
All conditions except for else are is or null checks.
除了 else 以外的所有条件都是 is 或 null 的检查。
-
The expression doesn't contain guard conditions (if).
表达式中不包含守卫条件(if)。
-
The conditions don't include types that can't be type-checked directly, such as mutable Kotlin collections (MutableList) or function types (kotlin.Function1, kotlin.Function2, and so on).
条件中不包含无法直接类型检查的类型,例如可变 Kotlin 集合(MutableList)或函数类型(kotlin.Function1、kotlin.Function2 等)。
-
There are at least two conditions besides else.
除了 else 外至少有两个条件。
-
All branches check the same subject of the when expression.
所有分支都检查相同的 when 表达式主体。
一个例子:
Kotlin
open class Example
class A : Example()
class B : Example()
class C : Example()
fun test(e: Example) = when (e) {
// Uses invokedynamic with SwitchBootstraps.typeSwitch
is A -> 1
is B -> 2
is C -> 3
else -> 0
}这时候,when 会被直接编译为一个 invokedynamic 而不是一堆 instanceof。
要启用此特性,首先确保使用 JDK21+ 编译 Kotlin。 然后,使用编译器参数:
ini
-Xwhen-expressions=indy或在 build.gradle.kts 中:
csharp
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xwhen-expressions=indy")
}
}Kotlin Multiplatform
好家伙,接下来,就都是 JVM 以外的更新了。考虑到我对 KMP 的关注点没那么全面,接下来我只会挑选一些我比较感兴趣(以及能看得懂)的内容以大标题呈现, 其他的内容就放在最后列个列表啦~
共享 js 和 wasmJs 目标的源码集
这的确是个不错的改动。之前 js 和 wasmJs 的源码集是分开的。尽管它们之前的确差异很大,但是都多少沾点儿 JS 属性,有时候还是有不少东西能共享的。 以前想要共享一些 js 可以通用的东西还要费上一番功夫。不过现在好了,现在它们提供了 webMain 和 webTest (也就是 web 源码集), 并且在使用 default hierarchy template 时生效。
官方图例:
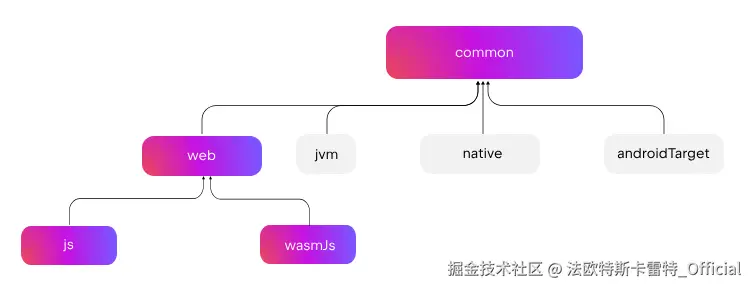
现在,可以直接在 web 平台中共享一些代码了:
Kotlin
// commonMain
expect suspend fun readCopiedText(): String
// webMain
external interface Navigator { val clipboard: Clipboard }
external interface Clipboard { fun readText(): Promise<JsString> }
external val navigator: Navigator
actual suspend fun readCopiedText(): String {
return navigator.clipboard.readText().await().toString()
}当然,我没记错的话,compose之前说也要为了兼容一些旧版浏览器而提供 js 平台的降级兼容(默认是 wasmJs 产物), 再加上这个源码集共享的能力,就可以更灵活地提供产品了。
启用也很简单,使用 applyDefaultHierarchyTemplate 就可以生效:
scss
kotlin {
js()
wasmJs()
// Enables the default source set hierarchy, including webMain and webTest
applyDefaultHierarchyTemplate()
}稳定对库的交叉编译
又是一个库开发利好的特性~ 在很久之前,想要发布一个多平台的库可是要费了老鼻子劲儿了,为了改善这种情况, 之前的版本中推出了实验性的多平台交叉编译功能,而现在它稳定下来了。
如果你之前为了开启这个功能添加了 gradle 属性 kotlin.native.enableKlibsCrossCompilation=true, 现在可以去掉它了 ------ 它现在是默认启用状态。
当然,还有一些限制。如果你有如下几种情况之一,你还是得拿Mac机器(或环境)编译项目:
- 库或任何依赖模块存在 cinterop 依赖关系。
- 项目中已配置 CocoaPods 集成。
- 需要为 Apple 目标构建或测试最终二进制文件。
声明公共依赖项的新方法
如果你比较熟悉 KMP 的话,你应该比较了解:在之前的 KMP 项目中,想要声明公共依赖(也就是在 commonMain 或 commonTest 中声明依赖), 你要在 kotlin { sourceSets { commonMain { /* 这里 */ } } } 这里声明,层数很多很杂乱,也不是很符合使用 Gradle 的习惯。
现在,Kotlin 的 Gradle API 提供了新的更简单的公共依赖声明方式:
Kotlin
kotlin {
@OptIn(ExperimentalKotlinGradlePluginApi::class)
dependencies {
implementation("org.jetbrains.kotlinx:kotlinx-coroutines-core:1.10.2")
}
}如你所见,直接在 kotlin {} 顶层即可。
Kotlin/Native
好吧,Kotlin/Native 中的大多数内容对我来说都比较陌生了。我虽然写 KMP 的库,但不会深入了解某个特定的 native 平台, 更别说做什么 Swift 或者 iOS 了。总之,K/Native 的大部分内容我都整理到最后的"其他"栏目中了。感兴趣的小伙伴们等到了最后的时候再看看吧。
Kotlin/Wasm
分离 npm 依赖项
这个不得不说(或许)是个不错的改动。在之前,你的 yarn.lock 或 package-lock.json 中,除了保存了你项目里的依赖以外, 也囊括了工具链本身的依赖。这也是为什么有时候依赖啥也没动,光改了个 Kotlin 版本或者什么工具链的版本,lock 文件就要求你更新一下,烦得很。
现在工具链的依赖和用户(也就是你)的依赖的记录位置分开了:
- 工具链:
<kotlin-user-home>/kotlin-npm-tooling/<yarn|npm>/hash/node_modules - 用户:
build/wasm/node_modules
这个改动默认启用。不过需要注意的是:这个改动只针对 wasm-js 平台 。 对 js 平台的改动也在"计划中",不过现在还没有。
改进的Kotlin/Wasm与JavaScript互操作异常处理
虽然单独调试 K/Wasm 中的错误的情况很少,不过我记得对异常的抓取之前限制非常多,甚至 wasm 抛出的异常在 Kotlin 中是抓不到的, 或者被包装为 WebAssembly.Exception 进而丢失很多细节。
而现在,2.2.20 改进了双向的异常处理体验:
- 当异常从 JS 抛出时,Kotlin 端能获取更多信息。当此类异常通过 Kotlin 传播回 JS 时,将不再被封装为 WebAssembly.Exception。
- 当异常从 Kotlin 抛出时,现在可在 JS 端作为 JS 错误进行捕获。
新的异常处理机制在支持 WebAssembly.JSTag 功能的现代浏览器中自动生效:
- Chrome 115+
- Firefox 129+
- Safari 18.4+
(言外之意,老的浏览器就先别想了)
无需配置即可在浏览器中支持调试功能
如上一节所述,我其实调试 K/Wasm 的情况非常少,不过对于他们给的示例我还是有印象的:
Kotlin
devServer = (devServer ?: KotlinWebpackConfig.DevServer()).apply {
static = (static ?: mutableListOf()).apply {
add(project.rootDir.path)
}
}在之前,你需要如此配置一番才可以通过浏览器支持调试功能。而现在,你不用配置就可以了,调试功能默认启用于所有 *DevRun 的 Gradle 任务。
小心不要在生产环境或者云服务器之类的敏感地方使用喔,避免源码泄露等问题的出现。
Kotlin/JS
接下来就是 K/JS 的主场咯~
使用 BigInt 类型来表示 Kotlin 的 Long 类型
JavaScript 的类型系统是世界上最伟大的设计。 OK,言归正传。经常在 K/JS 中导出 .d.ts 类型的小伙伴们都知道,Long 类型在 JS 中是没有直接匹配的类型的:毕竟JS的数字嘛...懂得都懂, 因此一个 Long 很可能会超出 JS 的数字精度或上限的,毕竟一个最大精准整数在53位的 number 装不下一个64位的 Long。
在过去,Kotlin 编译器在处理 Long 的时候,会将它编译为一个类似于装了两个 number 的对象来处理的。
不过比较熟悉 JS 的小伙伴们知道,ES2020 标准里是有一个 BigInt 类型的。 所以这个特性也很明显了,就是在满足条件的情况下(使用 ES2020 为目标时),将 Kotlin 的 Long 编译为 BigInt,增加互操作性和兼容性。
这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-Xes-long-as-bigint")
}
}在导出声明中使用 Long 类型
欸,上文刚说完,往下一翻发现就提到了导出 .d.ts 的类型声明的情况了。 跟上节相关,可以通过特性来在导出 Long 的时候支持使用 BigInt 来表示 Long。
这个特性是实验性的 ,可以通过下面的编译器参数在 build.gradle.kts 中来启用它:
Kotlin
kotlin {
compilerOptions {
freeCompilerArgs.add("-XXLanguage:+JsAllowLongInExportedDeclarations")
}
}新增DSL功能,实现更简洁的参数传递
一个有关 K/JS 运行在 Node.js 上时,main 函数的 args 参数数量的问题。 对我来说不痛不痒,简单来说就是以前 args 里除了命令行参数以外,前两个元素是 Node 的运行目录和当前脚本的目录。 但是这不太符合预期:因为 args 应该就是只是命令行参数而已。
在过去,你需要手动 drop 掉它们:
Kotlin
fun main(args: Array<String>) {
println(args.drop(2).joinToString(", "))
}而现在,在 build.gradle.kts 中通过一个 DSL 函数就可以去掉它们:
Kotlin
kotlin {
js {
nodejs {
passCliArgumentsToMainFunction()
}
}
}Gradle
来到 Gradle 环节~ 简单看了看,似乎也有一些值得一提的内容,所以就不整篇跳过了,来看看吧!
预览改进的Kotlin/JVM增量编译功能
自 Kotlin 2.2.0 起,引入了优化前端的 K2 编译器。 而这次,在此基础上地再一次提升了新前端在复杂增量场景中的性能。
这些优化默认的禁用的,可以通过 gradle.properties 追加属性来开启:
properties
kotlin.incremental.jvm.fir=true需要注意的是:当前 kapt 编译器插件尚不兼容此新行为。不过他们说他们"正致力于在未来版本中添加支持",总之,未来可期。
增量编译可检测内联函数中lambda表达式的变更
看来也是一个书接上文的变动。好像也不算,但是都跟"增量编译"有关。总之是优化或修改了在 inline fun 中的 lambda 表达式有变更的情况下、 增量编译不会处理它们的问题。
Maven: 在 kotlin-maven-plugin 中支持 Kotlin 的守护进程
Maven 十分罕见地登场了!总之就是在 Maven 的 kotlin-maven-plugin 插件中也支持了 Kotlin 编译器的独立守护进程。 现在默认开启,如果你想关闭,可以添加:
xml
<properties>
<kotlin.compiler.daemon>false</kotlin.compiler.daemon>
</properties>如果想要指定属性,可以添加:
xml
<properties>
<kotlin.compiler.daemon.jvmArgs>Xmx1500m,Xms500m</kotlin.compiler.daemon.jvmArgs>
</properties>标准库
哦我的天哪!这次怎么把标准库放在这么靠下的位置。我还以为这次没啥标准库更新呢。我相信看到这里的你也一定和我一样惊讶吧,一定一定吧?
通过反射识别接口类型的Kotlin/JS支持
看起来是在 Kotlin/JS 中对反射的一个更好地支持,现在可以判断出一个 KClass 是不是一个接口了。
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalStdlibApi::class)
fun inspect(klass: KClass<*>) {
// Prints true for interfaces
println(klass.isInterface)
}不过不得不说,Kotlin 在 JVM 以外的反射能力的确都很贫瘠。或者说是 JVM 的反射太丰满了?
公共原子类型的新 update 函数
给前阵子加到 common 标准库的原子类们添加了一些新的与更新行为相关的函数。总而言之就是更好用啦~
update()andupdateAt()set a new value without returning a result.
update()和updateAt()设置新值但不返回结果。fetchAndUpdate()andfetchAndUpdateAt()set a new value and return the previous value before the change.
fetchAndUpdate()和fetchAndUpdateAt()设置新值并返回更改前的旧值。updateAndFetch()andupdateAndFetchAt()set a new value and return the updated value after the change.
updateAndFetch()和updateAndFetchAt()设置新值并返回更改后的新值。
Kotlin
import kotlin.concurrent.atomics.*
import kotlin.random.Random
@OptIn(ExperimentalAtomicApi::class)
fun main() {
val counter = AtomicLong(Random.nextLong())
val minSetBitsThreshold = 20
// Sets a new value without using the result
counter.update { if (it < 0xDECAF) 0xCACA0 else 0xC0FFEE }
// Retrieves the current value, then updates it
val previousValue = counter.fetchAndUpdate { 0x1CEDL.shl(Long.SIZE_BITS - it.countLeadingZeroBits()) or it }
// Updates the value, then retrieves the result
val current = counter.updateAndFetch {
if (it.countOneBits() < minSetBitsThreshold) it.shl(20) or 0x15BADL else it
}
val hexFormat = HexFormat {
upperCase = true
number {
removeLeadingZeros = true
}
}
println("Previous value: ${previousValue.toHexString(hexFormat)}")
println("Current value: ${current.toHexString(hexFormat)}")
println("Expected status flag set: ${current and 0xBAD != 0xBADL}")
}支持数组的 copyOf() 重载
嗯,给数组的 copyOf 增加了新的重载函数。
Kotlin
@OptIn(ExperimentalStdlibApi::class)
fun main() {
val row1: Array<String> = arrayOf("one", "two")
// Resizes the array and populates the new elements using the lambda
val row2: Array<String> = row1.copyOf(4) { "default" }
println(row2.contentToString())
// [one, two, default, default]
}Compose 编译器
到了我会写、但是也仅限于会写的内容了。有对细节感兴趣的伙伴们可以去看看官方文档喔。
破坏性变更
惊了!居然还有破坏性变更?不过定睛一看,内容只有一条:
The kapt compiler plugin now uses the K2 compiler by default. As a result, the
kapt.use.k2property, which controls whether the plugin uses the K2 compiler, is deprecated. If you set this property to false to opt out of using the K2 compiler, Gradle shows a warning.
也就是说:kapt 编译器插件现默认使用 K2 编译器。 因此,用于控制插件是否使用 K2 编译器的 kapt.use.k2 属性已被弃用。若将该属性设置为 false 以禁用 K2 编译器,Gradle 将显示警告。
好吧,是跟 kapt 相关的。
其他
- KMP: Swift export available by default
Swift 导出默认可用 - KMP: New diagnostic for target support in dependencies
用于依赖项中目标支持的新诊断工具 - K/Native: Support for stack canaries in binaries
二进制文件中支持栈哨兵机制 - K/Native: Smaller binary size for release binaries
发布二进制文件的体积更小 - K/Native: Improved debugger object summaries
改进的调试器对象摘要 - K/Native: Explicit names in block types for Objective-C headers
Objective-C headers 中块类型的显式名称 - K/Native: Reduced size of Kotlin/Native distribution
Kotlin/Native 发行包体积缩减 - K/Native: Exporting KDocs to Objective-C headers by default
默认将 KDocs 导出到 Objective-C headers - K/Native: Deprecation of x86_64 Apple targets
弃用苹果的 x86_64 架构目标们 - K/Wasm: Handle repeated reloads during debugging
处理调试过程中的重复加载 - K/Wasm: Elimination of empty
yarn.lockfiles
清除空的yarn.lock文件 - K/Wasm: New compiler error in fully qualified class names
完全限定类名中出现新的编译器错误 - Gradle: New compiler performance metrics in build reports for Kotlin/Native tasks
尾声
写作 2.2.20,实则是 2.3.0 的前瞻特别节目。东西比预想的多,但是又感觉没那么多,哈哈哈。 这次我最感兴趣的其实是对 contacts 的优化改进中的 New holdsIn keyword,是一个感觉发挥空间比较大的新玩具。 当然啦,其他的很多优化啦、编译改进啦(比如 Long -> BigInt 也很解痛)都不错。
你嘞?你最感兴趣的内容是哪个呢?