链表
链表的存储结构
c
typedef struct Node{
int data; // 数据域
struct Node *next; // 指针域(就是和当前节点同类型的另一个节点)
}Node;链表初始化
- 带头结点
c
// 一般都采用动态的方式去创建
// 初始化带头结点的链表
Node* InitNode(){
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}- 不带头结点
c
Node* InitNode(){
return NULL;
}链表的插入
注:下面的几个基本操作都是带头结点的
- 按位置插入
c
// 表头插入
void InsertNode(Node* head, int e)
{
// 检查头结点是否有效
if(head == NULL)
{
return;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); // 这里还可以加一步看是否初始化成功
s->data = e;
s->next = head->next;
head->next = s;
}
// 指定位置插入
// 思路:需要找到目标位置的前驱结点
void InsertNode(Node* head, int i, int e)
{
// 检查头结点是否有效
if(head == NULL)
{
return;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node* p = head;
int count = 0;
while(p != NULL && count < i-1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
s->data = e;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
}链表的删除
c
// 按值删除
void DeleteNode(Node* head, int e)
{
Node* p = head;
while(p != NULL && p->next->data != e)
{
p = p->next; // 待删除结点的前驱结点
}
if(p->next == NULL)
{
printf("Not find.");
return;
}
Node* temp = p->next;
p->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
temp = NULL; // 避免野指针
}链表的查找
- 按值查找,返回位置
c
int FindNode(Node* head, int e)
{
Node* p = head;
int count = 1;
while(p != NULL)
{
if(p->data == e)
{
return count
}
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return -1 // 返回值是int类型
}链表的修改
- 按位置修改
c
void modifyNode(Node* head, int i, int e)
{
Node* p = head;
int count = 1;
while(p != NULL && count < i)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("Invalid location.");
return;
}
p->data = e;
}带头结点链表基本操作的完整代码
- 在使用带头结点链表的过程中,一定要正确区分头节点和数据节点,请看下面错误示例
c
// 错误示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data; // 数据域
struct Node* next; // 指针域
}Node;
Node* InitNode() {
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
head->next = NULL;
return head;
}
void InsertNode(Node** head, int i, int e)
{
// 检查头结点是否有效
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
Node* p = *head;
int count = 0;
// 找到指定位置的前驱结点
while (p != NULL && count < i - 1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
s->data = e;
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
}
//按值删除
void DeleteNode(Node** head, int e)
{
Node* p = *head;
while (p != NULL && p->next->data != e)
{
p = p->next; // 待删除结点的前驱结点
}
if (p->next == NULL)
{
printf("Not find.");
return;
}
Node* temp = p->next;
p->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
temp = NULL; // 避免野指针
}
// 按位修改
void modifyNode(Node** head, int i, int e)
{
Node* p = *head;
int count = 1;
while (p != NULL && count < i)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("Invalid location.");
return;
}
p->data = e;
}
// 按值查找,返回位置
int FindNode(Node* head, int e)
{
Node* p = head;
int count = 1;
while (p != NULL)
{
if (p->data == e)
{
printf("Find it at position %d\n", count);
return count;
}
p = p->next;
count++;
}
return -1; // 返回值是int类型
}
void PrintNode(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) {
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
Node* p = head;
printf("链表元素: ");
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
Node* head = InitNode(); // 初始化顺序表
// 测试插入操作
InsertNode(&head, 1, 10);
InsertNode(&head, 2, 20);
InsertNode(&head, 3, 30);
PrintNode(head);
DeleteNode(&head, 30);
PrintNode(head); // 应该输出: 10 20
modifyNode(&head, 2, 25);
PrintNode(head); // 应该输出: 10 25
FindNode(head, 25); // 应该返回: 2
return 0;
}输出:
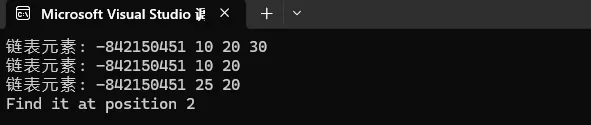
原因:
- 头节点的
data未初始化,导致打印出随机垃圾值 - 插入、查找、修改等操作都错误地包含了头节点,导致位置计算偏移
正确代码:
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data; // 数据域
struct Node* next; // 指针域
} Node;
// 初始化带头节点的链表(头节点不存储实际数据)
Node* InitNode() {
Node* head = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (head == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败\n");
return NULL;
}
head->next = NULL; // 头节点的next初始化为NULL
// 头节点数据域可以不用初始化(因为不使用)
return head;
}
// 在第i个位置插入元素e(i从1开始,从第一个数据节点计数)
void InsertNode(Node** head, int i, int e) {
// 检查参数合法性
if (head == NULL || *head == NULL || i < 1) {
printf("插入失败:参数不合法或链表未初始化\n");
return;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if (s == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败\n");
return;
}
s->data = e;
Node* p = *head; // p指向头节点(前驱节点的起点)
int count = 0; // 头节点对应count=0,数据节点从count=1开始
// 找到第i-1个数据节点的前驱(头节点或某个数据节点)
while (p != NULL && count < i - 1) {
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL) {
printf("插入位置超出链表长度\n");
free(s);
return;
}
// 插入新节点
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
}
// 按值删除节点(删除第一个匹配的节点)
void DeleteNode(Node** head, int e) {
if (head == NULL || *head == NULL || (*head)->next == NULL) {
printf("删除失败:链表为空或未初始化\n");
return;
}
Node* p = *head; // p指向头节点(从这里开始查找前驱)
// 查找待删除节点的前驱(停在待删除节点的前一个节点)
while (p->next != NULL && p->next->data != e) {
p = p->next;
}
if (p->next == NULL) {
printf("未找到值为%d的节点\n", e);
return;
}
// 删除节点
Node* temp = p->next;
p->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
temp = NULL;
}
// 按位置修改节点值(i从1开始,从第一个数据节点计数)
void modifyNode(Node** head, int i, int e) {
if (head == NULL || *head == NULL || (*head)->next == NULL || i < 1) {
printf("修改失败:链表为空或位置不合法\n");
return;
}
Node* p = (*head)->next; // 直接指向第一个数据节点
int count = 1; // 数据节点从1开始计数
// 找到第i个数据节点
while (p != NULL && count < i) {
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL) {
printf("修改位置超出链表长度\n");
return;
}
p->data = e;
}
// 按值查找,返回位置(从1开始,从第一个数据节点计数)
int FindNode(Node* head, int e) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
printf("查找失败:链表为空\n");
return -1;
}
Node* p = head->next; // 跳过头节点,从第一个数据节点开始
int count = 1; // 数据节点从1开始计数
while (p != NULL) {
if (p->data == e) {
printf("Find it at position %d\n", count);
return count;
}
p = p->next;
count++;
}
printf("未找到值为%d的节点\n", e);
return -1;
}
// 打印所有数据节点(跳过头节点)
void PrintNode(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) {
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
Node* p = head->next; // 跳过头节点,从第一个数据节点开始打印
printf("链表元素: ");
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
Node* head = InitNode(); // 初始化带头节点的链表
// 测试插入操作
InsertNode(&head, 1, 10); // 位置1插入10
InsertNode(&head, 2, 20); // 位置2插入20
InsertNode(&head, 3, 30); // 位置3插入30
PrintNode(head); // 输出:链表元素: 10 20 30
// 测试删除操作
DeleteNode(&head, 30);
PrintNode(head); // 输出:链表元素: 10 20
// 测试修改操作
modifyNode(&head, 2, 25);
PrintNode(head); // 输出:链表元素: 10 25
// 测试查找操作
FindNode(head, 25); // 输出:Find it at position 2
return 0;
}注:这里再说明一个问题:
c
head == NULL || *head == NULL 这个检查是很有必要的,是对两种错误场景进行检查
head == NULL:表示传递给函数的二级指针本身就是无效的 (比如调用者错误地传入了NULL作为参数,如InsertNode(NULL, 1, 10))。这种情况下,连head都不能访问(会直接触发空指针解引用错误),必须优先检查。head == NULL:表示二级指针head本身有效(非空),但它指向的头节点指针是无效的 (比如链表未初始化)。这种情况下,head是合法指针,但head是空指针,需要单独处理。
无头结点链表的增删改查
- 注:这里使用了二级指针,不同于之前的顺序表,其操作的是结构体,当我们传递
SqList* L(一级指针)时,已经可以通过指针访问并修改结构体内部的所有成员(数组和长度) - 而链表为什么使用二级指针的原因是:C语言的函数参数传递是值传递---函数接收的是参数的副本,而非参数,所以如果使用一级指针(
Node*)作为参数,函数内部修改的只是头指针的副本 ,无法影响外部实际的头指针。只有通过二级指针(Node**),才能真正修改外部头指针的指向
c
// 错误示例:使用一级指针
void InsertAtHead(Node* head, int value) {
Node* newNode = createNode(value);
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode; // 这里修改的只是函数内部的副本,外部头指针不变
}
// 正确示例:使用二级指针
void InsertAtHead(Node** head, int value) {
Node* newNode = createNode(value);
newNode->next = *head; // *head表示外部的头指针
*head = newNode; // 直接修改外部头指针的指向
}- 如果操作会改变头指针的指向,就必须用二级指针;如果只是修改节点内部的数据或 next 指针,一级指针就足够了
完整代码:
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef struct Node {
int data; // 数据域
struct Node* next; // 指针域
}Node;
Node* InitNode() {
return NULL;
}
// 使用二级指针才能修改头指针
void InsertNode(Node** head, int i, int e)
{
// 判断位置是否合法
while (i < 1)
{
return;
}
Node* s = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node));
s->data = e;
// 表头插入
if (i == 1)
{
s->next = *head;
*head = s;
return;
}
Node* p = *head;
int count = 1;
while (p != NULL && count < i - 1)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
if (p == NULL) {
printf("插入位置超出链表长度\n");
free(s); // 释放已分配的内存
return;
}
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;
return;
}
//按值删除
void DeleteNode(Node** head, int e)
{
// 处理空链表
if(*head == NULL)
{
printf("Empty list.");
return;
}
Node* p = *head;
Node* prev = NULL;
// 查找要删除的结点及其前驱结点
while (p != NULL && p->data != e)
{
prev = p;
p = p->next;
}
// 未找到
if(p == NULL)
{
printf("Not find.");
return;
}
// 处理头结点的删除
if(prev == NULL)
{
*head = p->next;
}
else {
prev->next = p->next;
}
free(p);
p = NULL; // 避免野指针
}
// 按位修改
bool UpdateNodeByIndex(Node** head, int i, int e)
{
if(*head == NULL || i < 1)
{
printf("Empty list or invalid position.");
return false;
}
Node* p = *head;
int count = 1;
while(p != NULL && count < i)
{
p = p->next;
count++;
}
p->data = e;
return true;
}
void PrintNode(Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) {
printf("链表为空\n");
return;
}
Node* p = head;
printf("链表元素: ");
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d ", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
Node* head = InitNode(); // 初始化顺序表
// 测试插入操作
InsertNode(&head, 1, 10);
InsertNode(&head, 2, 20);
InsertNode(&head, 3, 30);
PrintNode(head);
DeleteNode(&head, 30);
PrintNode(head); // 应该输出: 10 20
UpdateNodeByIndex(&head, 2, 25);
PrintNode(head); // 应该输出: 10 25
return 0;
}