1、概述
Redis之所以快,一个原因是因为无锁化的单线程内存快,另一个原因就是内部的数据结构采用的算法很快。当然还有一个本身的主从架构模型支持。
2、查看底层数据结构的命令
Redis提供了Object命令可以查看底层数据结构
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> object help
1) OBJECT <subcommand> [<arg> [value] [opt] ...]. Subcommands are:
2) ENCODING <key>
3) Return the kind of internal representation used in order to store the value
4) associated with a <key>.
5) FREQ <key>
6) Return the access frequency index of the <key>. The returned integer is
7) proportional to the logarithm of the recent access frequency of the key.
8) IDLETIME <key>
9) Return the idle time of the <key>, that is the approximated number of
10) seconds elapsed since the last access to the key.
11) REFCOUNT <key>
12) Return the number of references of the value associated with the specified
13) <key>.
14) HELP
15) Prints this help.示例
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> set yy aa
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding yy # 查看key的内部类型
"embstr" # 可以看到value是一个embstr类型而我们在Redis中的常见对象例如List、set、zset这些value在底层是以redisObject定义存储的。
c
struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or frequency*/
int refcount;
void *ptr;
};当然List、set、zset本身的数据结构类型是不同的,也就是基于这个基类,各自会做自己的进一步封装。
其中type字段是上层的类型,示例:
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> type yy # type的内容就是可以使用type查看的,我们应用层看到的类型。
string encoding字段存储的就是Redis内部的类型
lru则表示使用LRU算法清除内存的对象
refcount表时引用次数,可以使用object refcount查看
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> object refcount yy
(integer) 1*ptr则是指向真正的数据结构的实现,例如set的实现,而encoding字段存的只是真正的实现类型的内部名称。
另外需要注意的是,上层的同一个数据类型,实际上在Redis底层中采用的实际存储结构是不一样的,例如string
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> set k2 1
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> type k2
string
127.0.0.1:6379> object encoding k2
"int"
127.0.0.1:6379> set k3
aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> type k3
string0
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING k3
"raw"上面中可以看到同样都是string的set操作,但是在Redis底层却用了不同的对象类型结构。也就是说type与encoding之间的对象关系不是一一对应的,真实更加的复杂。
对应关系概览
| Redis版本 | string | set | zset | list | hash |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redis6.x | SDS(动态字符串) | intset + hashtable | skiplist + ziplist | quicklist + ziplist | hashtable + ziplist |
| Redis7.x | SDS | intset + listpack+hashtable | skiplist + listpack | quicklist + listpack | hashtable + list |
Redis7.x相比于Redis6.x是使用listpack替代了ziplist。
3、string
string在底层有三种不同的类型:int、embstr、raw。
1、int:当value可以转换为一个long类型时,就会以int类型存储。如果是一个浮点数,则会使用embstr类型存储。(本质也是redisObjec)
2、embstr:就是上面提到SDS(Simple Dynamic String)。如果字符串长度小于44个字节的字符串,就会使用这个embstr类型存储。
SDS类型:
其实就是封装了不同长度的SDS对象(5、8、16、32、64字节)
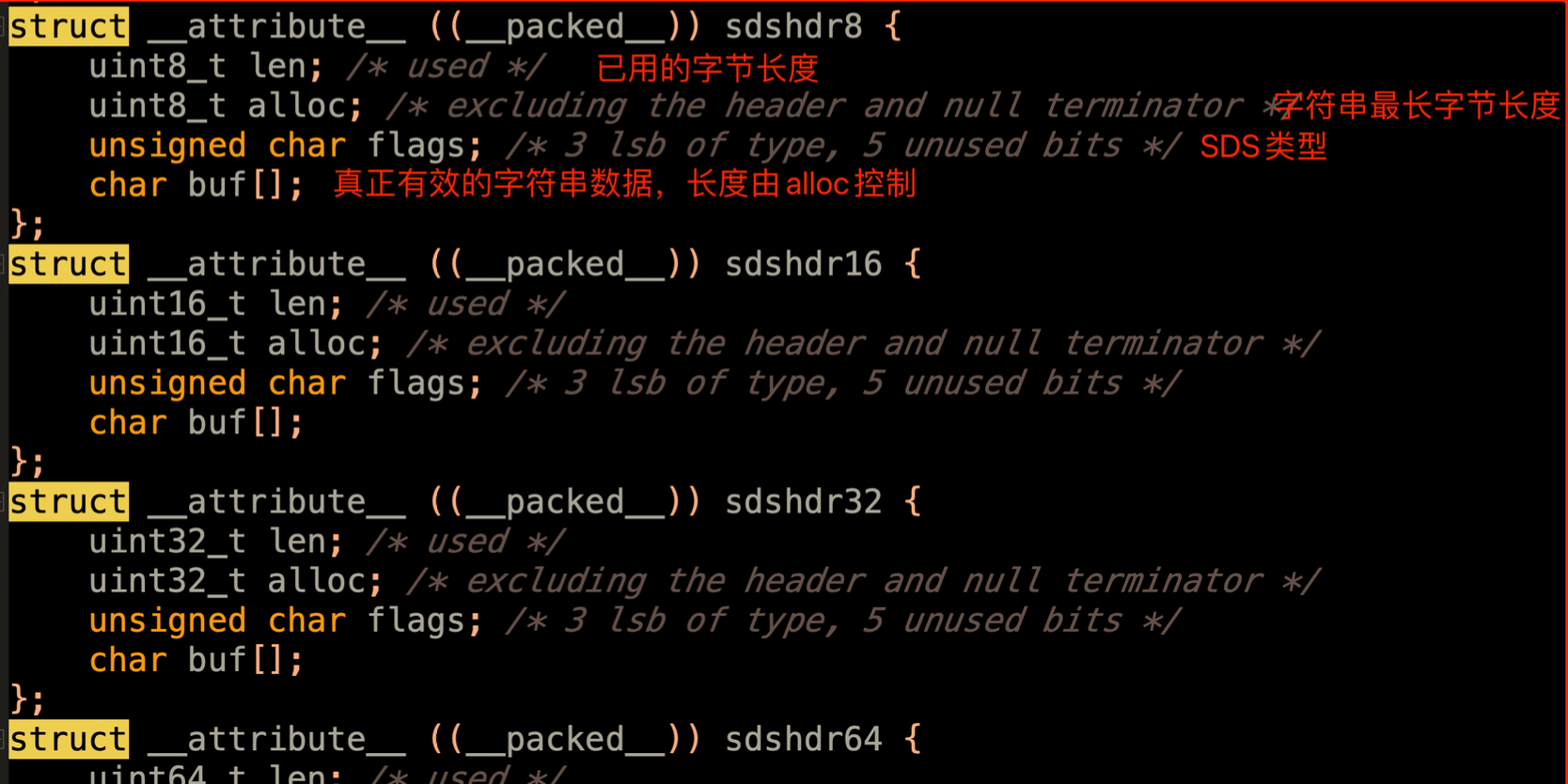
这样做的好处:1、从内存中读取字符串数组,是每个内存地址就重复读取一次,但是封装为对象后,对象中有alloc长度字段,这样就提前知道了字符串的长度,仅花一次内存io就读取到了。 2、c语言中的字符串的结尾有'\0'结尾,但是如果字符串本身就有'\0'的话,就会存在歧义。 封装成对象后也就消除了这样的歧义。
3、raw:长度大于44个字节的字符串,就会使用raw存储。
说明
如果value小于1000,会直接返回一个共享对象的内存,类似Java中的Integer的-128 <= value <= 127的情况
三者区别
1、int类型:尽量的在robj中指向一个小于1000的缓存共享对象。还有一个好处就是本身读取一个不确定长度的字符串需要依次遍历读,但是转为long之后,就是直接固定读取8个字节,很快。
2、embstr类型:会将value对象直接放在robj内存地址的后面(同时也避免内存碎片),这样读取效率更高。这里需要注意: 如果value发生了append,就算也没有超过44个字节,这里会重新新创建一个raw类型!。(即本身为不可变字符串)
c
o->ptr = sh + 1 # 内存地址直接连续放3、raw类型:兜底类型,当int、embstr无法满足时,就会单独创建一个SDS对象,然后使用ptr指针指向。(非连续内存,分开申请的内存)
4、hash
Redis6.x中使用ziplist + hashtable
Redis7.x中使用listpack +hashtable
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> hset user:1 id 1 name roy
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> type user:1
hash
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING user:1
"listpack"
127.0.0.1:6379> config set hash-max-listpack-entries 3
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> config set hash-max-listpack-value 8
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> hset user:1 name royaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaa
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING user:1
"hashtable"
127.0.0.1:6379> hset user:2 id 1 name roy score 100 age 18
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING user:2
"hashtable"如果value较小,就会使用packlist、ziplist
阈值参数
shell
hash-max-listpack-entries # 键值对个数,默认512,超过则使用hash
hash-max-listpack-value # 单个value占用大小,默认64字节,任意单个超过则使用hash
对应的也要Redis6.x的配置
hash-max-ziplist-entries
hash-max-ziplist-value4.1、ziplist
1、本质上是将hash表构造成一个顺序列表,使用连续的内存,这样寻址更快。
| 属性 | 类型 | 长度 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| zlbytes | uint32_t | 4字节 | 记录整个压缩列表占用的字节数 |
| zltail | uint32_t | 4字节 | 列表起始地址到列表尾节点的字节偏移量,通过这个就可以直接拿到尾节点 |
| zllen | uint16_t | 2字节 | 记录了整个列表的节点数,最大值65534,如果实际列表超过了这个值,就会固定位65535,真实的节点个数就需要遍历整个列表才知道。 |
| entry | 列表节点 | 不定 | 节点本身的长度由其自身决定。 |
| zlend | uint8_t | 1字节 | 特殊值OxFF(255),用于标记列表末端 |
entry
| 属性 | 类型 | 长度 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|---|
| previous_entry_length | 前节点长度 | 1 或5字节 | 记录前面一个entry长度,oxfe开头。能用1字节存,就不会用5字节 |
| encoding | 编码属性 | - | 记录content的数据类型是字符串还是整数 & content长度 |
| content | - | - | 保存节点数据 |
一般双链表中节点记录的是前和后的指针,但是这里仅存储的长度,可以体现其极致的压缩机制。
这种数据结构能快速的找到列表头和尾节点,但是对于range查询,就只能逐个遍历,因此该列表长度不能太长。
4.2、listpack
核心的结构还是和ziplist一致,只是做了增强,这也是后面Redis7.x使用listpack替代了ziplist的原因。
连锁更新问题
核心点在ziplist中的entry中的previous_entry_length,如果前一个节点的长度原本是1字节,但是新值变成了5字节后,其后一个的本节点也会受到影响,也需要将本节点进行更新变长。这是连续级联影响的。
listpack是这样解决这个问题的:
previous_entry_length原本是记录前一个节点的长度,listpack中将其改为记录自身的长度,这样自身变动时就仅变更自身的长度即可,而不需要级联变别的节点的长度字段。
4.3、总结
1、hash底层更多的是使用ziplist或listpack存储
2、如果hash的value个数超过512(默认),或者任意单个value的超过值64个字节,就会转为hashtable存储
3、ziplist、listpack可以升级为hashtable,而hashtable不会降为listpack。
5、list
以listpack(Redis6.x是ziplist) + quicklist底层类型存储。
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush l1 a1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> rpush l1 a2
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> type l1
list
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING l1
"listpack"和hash一样,同样也有参数阈值
shell
list-max-listpack-size # 个数超过这个时,就会使用quicklist, 当为负数时,就是按照大小,默认-2 8kb阈值
相对应的6.x版本有
list-max-ziplist-size具体参数
shell
# Lists are also encoded in a special way to save a lot of space.
# The number of entries allowed per internal list node can be specified # as a fixed maximum size or a maximum number of elements.
# For a fixed maximum size, use -5 through -1, meaning:
# -5: max size: 64 Kb <-- not recommended for normal workloads
# -4: max size: 32 Kb <-- not recommended
# -3: max size: 16 Kb <-- probably not recommended
# -2: max size: 8 Kb <-- good
# -1: max size: 4 Kb <-- good
# Positive numbers mean store up to _exactly_ that number of elements
# per list node.
# The highest performing option is usually -2 (8 Kb size) or -1 (4 Kb size),
# but if your use case is unique, adjust the settings as necessary. #-- list -1-5
list-max-listpack-size -2其它关键参数(listpack压缩级别)
shell
# Lists may also be compressed.
# Compress depth is the number of quicklist ziplist nodes from *each*
side of
# the list to *exclude* from compression. The head and tail of the
list
# are always uncompressed for fast push/pop operations. Settings
are:
# 0: disable all list compression
# 1: depth 1 means "don't start compressing until after 1 node into
the list,
# going from either the head or tail"
# So: [head]->node->node->...->node->[tail]
# [head], [tail] will always be uncompressed; inner nodes will
compress.
# 2: [head]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[tail]
# 2 here means: don't compress head or head->next or tail->prev or
tail,
# but compress all nodes between them.
# 3: [head]->[next]->[next]->node->node->...->node->[prev]->[prev]->
[tail]
# etc.
list-compress-depth 05.1、quicklist
listpack在范围检索这方面如果数据量不大的情况下,遍历还可以接受,但是在增删数据的时候就比较费劲,例如在中间插入一个元素,那么后面的每个元素都需要往后移。
解决方式:
为了解决快速增删,其实双向链表就很方便,但是双向链表遍历很难,为了结合数组和链表的优点,就出现了quicklist这样的设计(结合了链表与数组,在大数量下很提效):
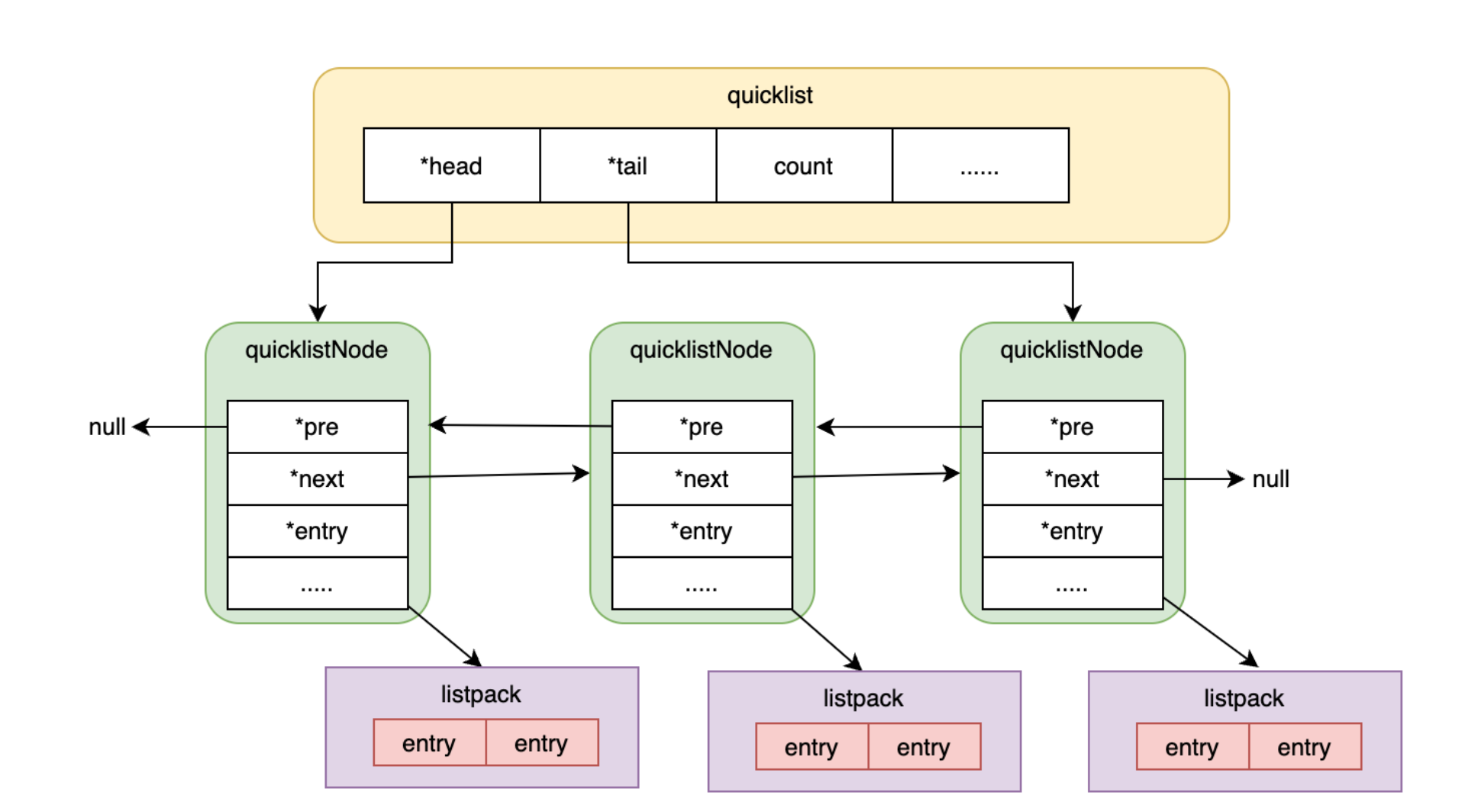
其中每个listpack的长度可以设置,默认16
6、set
使用intset + listpack + hashtable底层类型存储。
intset 本质上是一个int数组。int8_t[]
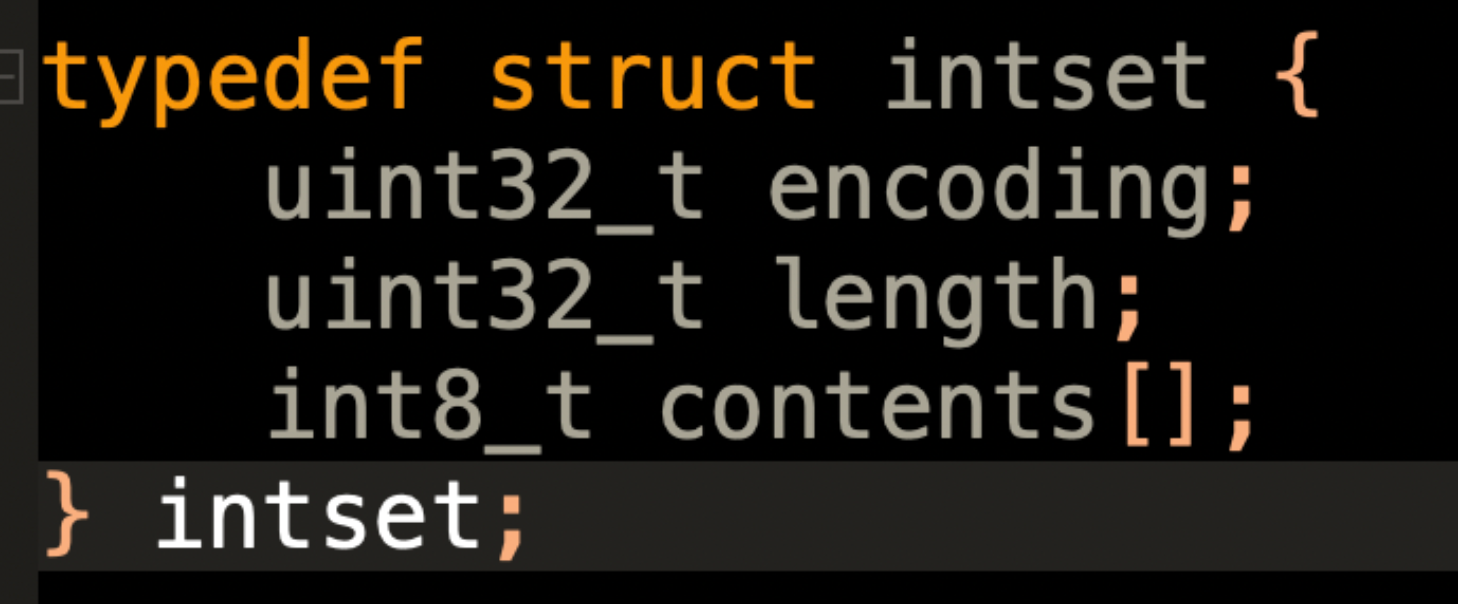
set本身也是kv类型,但是value的值是null。
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd s1 1 2 3 4 5
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING s1
"intset"
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd s2 a b c d e
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING s2
"listpack"
127.0.0.1:6379> config set set-max-listpack-entries 2
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd s3 a b c d e
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING s3
"hashtable"关键参数
shell
# Sets have a special encoding when a set is composed
# of just strings that happen to be integers in radix 10 in the range
# of 64 bit signed integers.
# The following configuration setting sets the limit in the size of the # set in order to use this special memory saving encoding.
# -- set 64 ( long ). intset set-max-intset-entries 512
# Sets containing non-integer values are also encoded using a memory
efficient
# data structure when they have a small number of entries, and the
biggest entry
# does not exceed a given threshold. These thresholds can be configured using
# the following directives.
# -- set
# --
set-max-listpack-entries 128
set-max-listpack-value 647、zset
使用listpack + skiplist底层类型存储。
shell
127.0.0.1:6379> config get zset*
1) "zset-max-ziplist-value"
2) "64"
3) "zset-max-listpack-entries"
4) "128"
5) "zset-max-ziplist-entries"
6) "128"
7) "zset-max-listpack-value"
8) "64"
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd z1 80 a
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING z1
"listpack"
127.0.0.1:6379> config set zset-max-listpack-entries 3
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd z2 80 a 90 b 91 c 95 d
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> OBJECT ENCODING z2
"skiplist"关键参数
shell
# Similarly to hashes and lists, sorted sets are also specially encoded
in
# order to save a lot of space. This encoding is only used when the
length and
# elements of a sorted set are below the following limits:
zset-max-listpack-entries 128
zset-max-listpack-value 647.1、skiplist
跳表
zset有个特性,除了常规的去重,还会根据score进行排序,那么就以为这元素的位置需要频繁移动,如果数量少的情况下,数组listpack也可以接受,但是数据量大了就不行了。
链表的话,在遍历上面太差了。
但是跳表的设计:
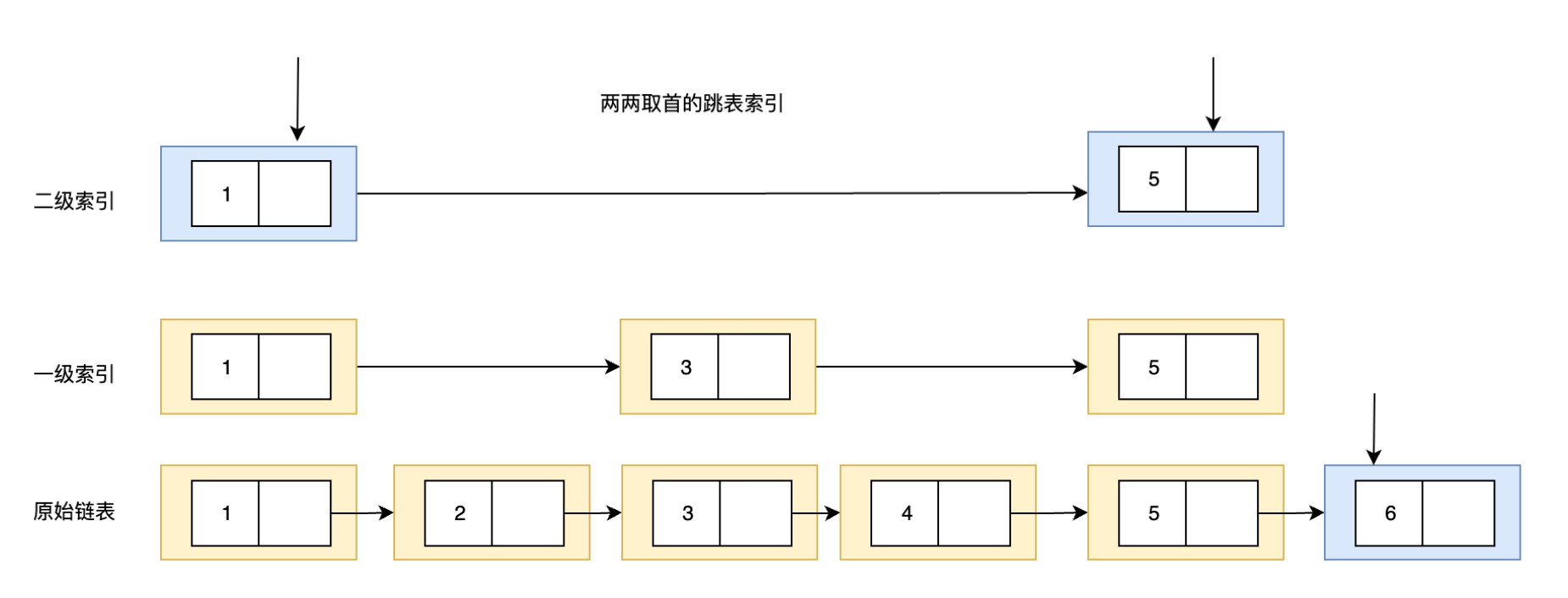
就可以实现遍历快 + 链表本身的移动元素方便,2个优点。这种属于空间换时间。
但是缺点也很明显,维护成本高,但是Redis刚刚好去掉了这个缺点,Redis本身就是干读多写少的事情。