扫描线

题目1

1851. 包含每个查询的最小区间 - 力扣(LeetCode)
1.先将查询的数按照大小排序,再将区间按照左边界的大小排序
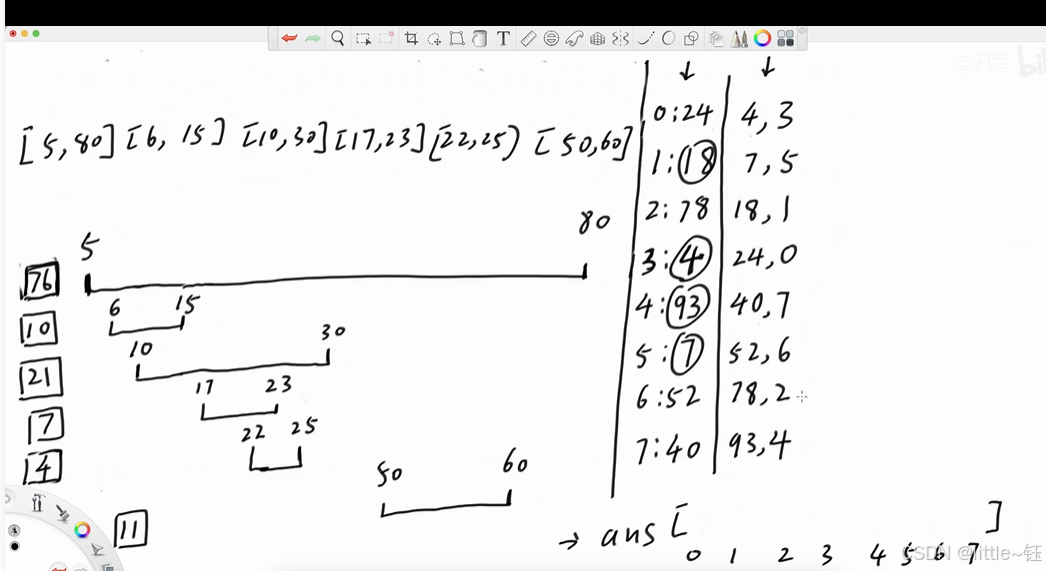
2.先建立一个按照区间大小的排序的小根堆,并且带有其过期的位置。
遍历查询的数,相当于有一根扫描线扫过区间,只要大于开头,就放到小根堆里;然后看堆顶,只要堆顶的元素过期了,就弹出。最后记录堆顶的答案
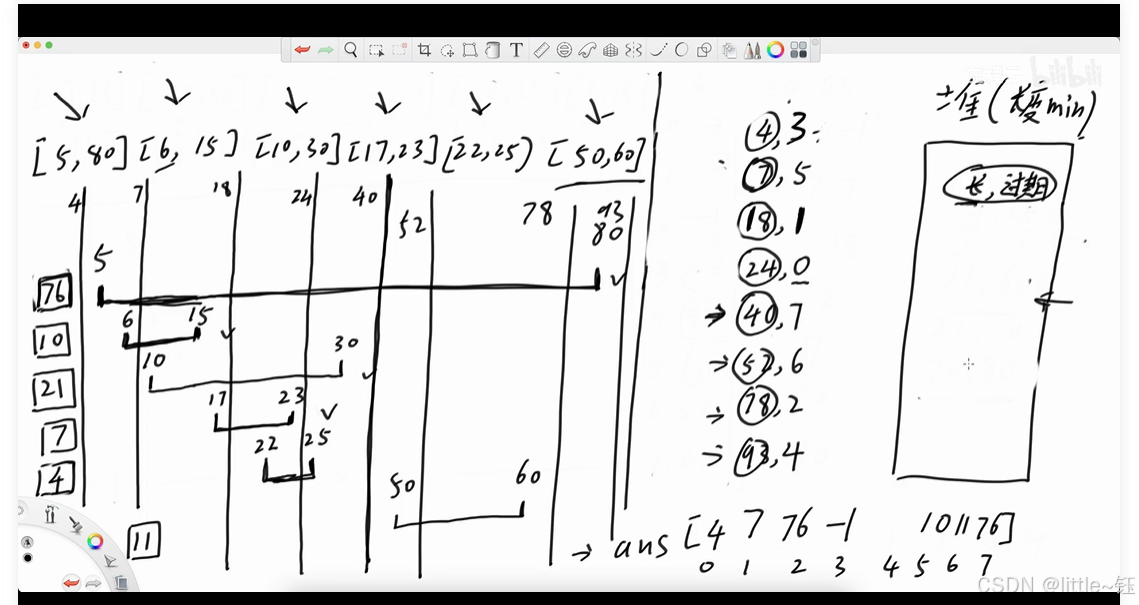
默认堆实现:
java
// 包含每个查询的最小区间
// 给你一个二维整数数组intervals,其中intervals[i] = [l, r]
// 表示第i个区间开始于l,结束于r,区间的长度是r-l+1
// 给你一个整数数组queries,queries[i]表示要查询的位置
// 答案是所有包含queries[i]的区间中,最小长度的区间是多长
// 返回数组对应查询的所有答案,如果不存在这样的区间那么答案是-1
// 测试链接 : https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-interval-to-include-each-query/
public class Code01_MinimumIntervalQuery1 {
// 堆结构是现成结构
public static int[] minInterval(int[][] intervals, int[] queries) {
int n = intervals.length;
int m = queries.length;
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int[][] ques = new int[m][2];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
ques[i][0] = queries[i];
ques[i][1] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(ques, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
// 0 : 长度
// 1 : 影响到的位置
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (; j < n && intervals[j][0] <= ques[i][0]; j++) {
heap.add(new int[] { intervals[j][1] - intervals[j][0] + 1, intervals[j][1] });
}
while (!heap.isEmpty() && heap.peek()[1] < ques[i][0]) {
heap.poll();
}
if (!heap.isEmpty()) {
ans[ques[i][1]] = heap.peek()[0];
} else {
ans[ques[i][1]] = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}自定义堆实现:
java
// 包含每个查询的最小区间
// 给你一个二维整数数组intervals,其中intervals[i] = [l, r]
// 表示第i个区间开始于l,结束于r,区间的长度是r-l+1
// 给你一个整数数组queries,queries[i]表示要查询的位置
// 答案是所有包含queries[i]的区间中,最小长度的区间是多长
// 返回数组对应查询的所有答案,如果不存在这样的区间那么答案是-1
// 测试链接 : https://leetcode.cn/problems/minimum-interval-to-include-each-query/
public class Code01_MinimumIntervalQuery2 {
// 堆结构由自己实现
public static int[] minInterval(int[][] intervals, int[] queries) {
int n = intervals.length;
int m = queries.length;
Arrays.sort(intervals, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
int[][] ques = new int[m][2];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
ques[i][0] = queries[i];
ques[i][1] = i;
}
Arrays.sort(ques, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
heapSize = 0;
int[] ans = new int[m];
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (; j < n && intervals[j][0] <= ques[i][0]; j++) {
push(intervals[j][1] - intervals[j][0] + 1, intervals[j][1]);
}
while (!isEmpty() && peekEnd() < ques[i][0]) {
poll();
}
if (!isEmpty()) {
ans[ques[i][1]] = peekLength();
} else {
ans[ques[i][1]] = -1;
}
}
return ans;
}
public static int MAXN = 100001;
public static int[][] heap = new int[MAXN][2];
public static int heapSize;
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return heapSize == 0;
}
public static int peekLength() {
return heap[0][0];
}
public static int peekEnd() {
return heap[0][1];
}
public static void push(int h, int e) {
heap[heapSize][0] = h;
heap[heapSize][1] = e;
heapInsert(heapSize++);
}
public static void poll() {
swap(0, --heapSize);
heapify(0);
}
public static void heapInsert(int i) {
while (heap[i][0] < heap[(i - 1) / 2][0]) {
swap(i, (i - 1) / 2);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
public static void heapify(int i) {
int l = i * 2 + 1;
while (l < heapSize) {
int best = l + 1 < heapSize && heap[l + 1][0] < heap[l][0] ? l + 1 : l;
best = heap[best][0] < heap[i][0] ? best : i;
if (best == i) {
break;
}
swap(best, i);
i = best;
l = i * 2 + 1;
}
}
public static void swap(int i, int j) {
int[] tmp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[j];
heap[j] = tmp;
}
}题目2
1.开区间处理边界问题
2.离散化
java
public class Solution {
// 堆结构是现成结构
public static List<List<Integer>> getSkyline(int[][] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
int m = prepare(arr, n);
// 0 : 高度
// 1 : 影响到的位置
PriorityQueue<int[]> heap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b[0] - a[0]);
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i <= m; i++) {
for (; j < n && arr[j][0] <= i; j++) {
heap.add(new int[] { arr[j][2], arr[j][1] });
}
while (!heap.isEmpty() && heap.peek()[1] < i) {
heap.poll();
}
if (!heap.isEmpty()) {
height[i] = heap.peek()[0];
}
}
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 1, pre = 0; i <= m; i++) {
if (pre != height[i]) {
ans.add(Arrays.asList(xsort[i], height[i]));
}
pre = height[i];
}
return ans;
}
public static int MAXN = 100001;
public static int[] xsort = new int[MAXN];
public static int[] height = new int[MAXN];
// 准备工作如下
// 1) 收集大楼左边界、右边界-1、右边界的值
// 2) 收集的所有值排序、去重
// 3) 大楼的左边界和右边界,修改成排名值
// 4) 大楼根据左边界排序
// 5) 清空height数组
// 6) 返回离散值的个数
public static int prepare(int[][] arr, int n) {
int size = 0;
// 大楼的左边界、右边界-1、右边界,三个值都去离散化
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
xsort[++size] = arr[i][0];
xsort[++size] = arr[i][1] - 1;
xsort[++size] = arr[i][1];
}
Arrays.sort(xsort, 1, size + 1);
// 排序之后去重,去重后的数值有m个
int m = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= size; i++) {
if (xsort[m] != xsort[i]) {
xsort[++m] = xsort[i];
}
}
// 修改大楼影响到的左右边界,都变成排名值
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
arr[i][0] = rank(m, arr[i][0]);
// 大楼影响到的右边界,减少1!
// 课上重点说明的内容
arr[i][1] = rank(m, arr[i][1] - 1);
}
// 所有大楼根据左边界排序
Arrays.sort(arr, 0, n, (a, b) -> a[0] - b[0]);
// 高度数组清空
Arrays.fill(height, 1, m + 1, 0);
// 返回有多少个不同的离散值
return m;
}
// 查询数值v的排名(离散值)
public static int rank(int n, int v) {
int ans = 0;
int l = 1, r = n, mid;
while (l <= r) {
mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (xsort[mid] >= v) {
ans = mid;
r = mid - 1;
} else {
l = mid + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}扫描线+线段树
题目1

1.求矩形的面积和,不包过重叠的面积
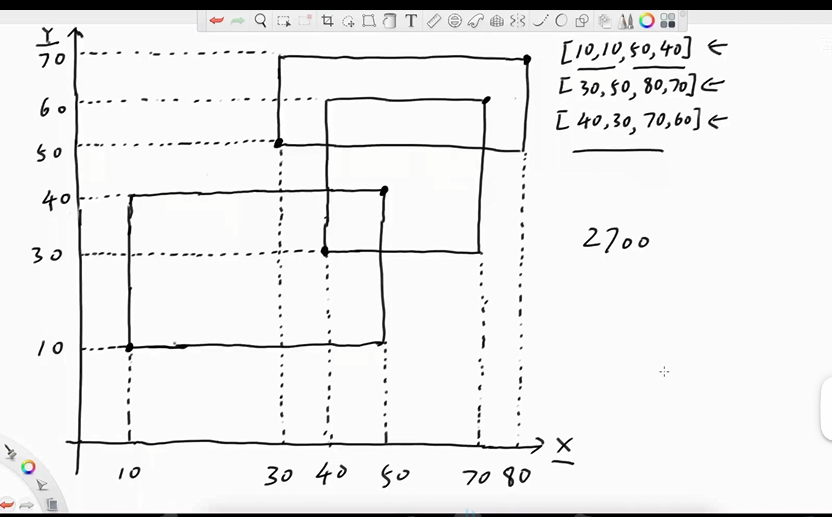
2.以上面的例题为例,按左边界增1,有边界减1,得到6个事件
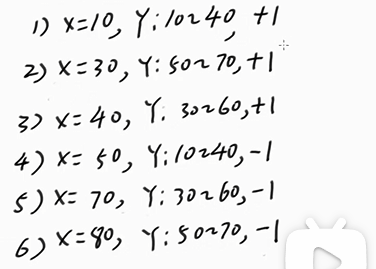
3.扫描线首先来到10,没有产生面积,10-40加1;然后扫到30,产生面积为10-70的覆盖长度乘以20;后面扫到的位置同样方法处理,用10-70的覆盖长度乘以此时的边界和上个边界的距离,然后左边界有加1,右边界就减1
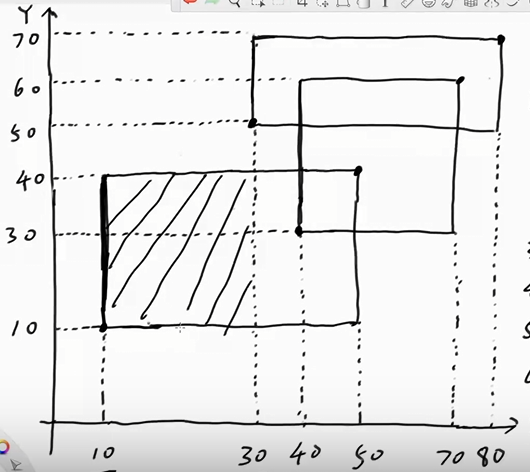
4.预处理:把y值离散化;离散化后,如果一个矩形边界为离散化的编号为x~y,那就在x~y-1这段线段上加1或减1。
维护好总长度,覆盖长度,覆盖的次数(全覆盖)这三个信息。为了维护好总长度,要额外增加一个9:3100,
因为线段树上x~y的总长度就等于离散化后的编号(y+1)对应的原坐标减x对应的原坐标
