目录

Task1 Introduction 引言
The main challenge when studying networking protocols is that we don't get a chance to see the protocol "conversations" taking place. All the technical complexities are hidden behind friendly and elegant user interfaces. You access resources on your local network without ever seeing an ARP query. Similarly, you would access Internet services for years without seeing a single three-way handshake till you check a networking book or inspect a network traffic capture. The best study aid would be capturing network traffic and taking a closer look at the various protocols; this helps us better understand how networks work.
研究网络协议的主要挑战在于,我们没有机会看到协议 "对话" 的发生。所有技术复杂性都隐藏在友好和优雅的用户界面背后。你访问本地网络上的资源时,从未看到过 ARP 查询。同样,你可能连续多年访问互联网服务,却从未看到过一次三方握手,直到你查看了一本网络手册或检查了网络流量捕获。最好的研究帮助是捕获网络流量,并仔细观察各种协议;这有助于我们更好地理解网络是如何工作的。
This room introduces some basic command-line arguments for using Tcpdump. The Tcpdump tool and its libpcap library are written in C and C++ and were released for Unix-like systems in the late 1980s or early 1990s. Consequently, they are very stable and offer optimal speed. The libpcap library is the foundation for various other networking tools today. Moreover, it was ported to MS Windows as winpcap.
这个房间介绍了一些使用 Tcpdump 的基本命令行参数。Tcpdump 工具及其 libpcap 库是用 C 和 C++ 语言编写的,并在 20 世纪 80 年代末或 90 年代初为类 Unix 系统发布。因此,它们非常稳定,并提供了最佳速度。libpcap 库是当今各种其他网络工具的基础。此外,它作为 winpcap 被移植到了 MS Windows。
Learning Objectives学习目标
This room aims to provide you with the basics necessary to use tcpdump. In particular, you will learn how to:
这个房间旨在为你提供使用 tcpdump 所需的基础知识。具体来说,你将学习如何:
- Capture packets and save them to a file
捕获数据包并将其保存到文件 - Set filters on captured packets在捕获的数据包上设置过滤器
- Control how captured packets are displayed
控制捕获的数据包的显示方式
Room Prerequisites房间前提条件
We recommend the user be familiar with the TCP/IP model, its related concepts, and its various protocols. The following rooms provide the necessary knowledge to make the best use of this room:
我们建议用户熟悉 TCP/IP 模型及其相关概念和各种协议。以下房间提供了充分利用本房间所需的知识:
- Networking Concepts网络概念
- Networking Essentials网络基础知识
- Networking Core Protocols网络核心协议
- Networking Secure Protocols网络安全协议
Click on the Start Machine button, wait for it to boot, and follow along. A terminal will display in your browser.
点击 "启动机器" 按钮,等待它启动,然后继续操作。一个终端将显示在您的浏览器中。
Start Machine启动机
It uses the following SSH credentials in case you need them:
它使用以下 SSH 凭据,以备不时之需:
- Username:
user用户名:用户 - Password:
THM123密码:THM123
Answer the questions below请回答以下问题
Task2 Basic Packet Capture 基本数据包捕获
图片版



文字版
You can run tcpdump without providing any arguments; however, this is only useful to test that you have it installed! In any real scenario, we must be specific about what to listen to, where to write, and how to display the packets.
你可以在不提供任何参数的情况下运行 tcpdump; 然而,这只有在测试你是否安装了它时才有用!在任何真实场景中,我们必须具体说明要监听什么、在哪里写入以及如何显示数据包。
Specify the Network Interface指定网络接口
The first thing to decide is which network interface to listen to using -i INTERFACE. You can choose to listen on all available interfaces using -i any; alternatively, you can specify an interface you want to listen on, such as -i eth0.
首先要决定使用 - i INTERFACE 监听哪个网络接口。你可以选择使用 - i any 监听所有可用的接口;或者,你可以指定一个想要监听的接口,例如 - i eth0。
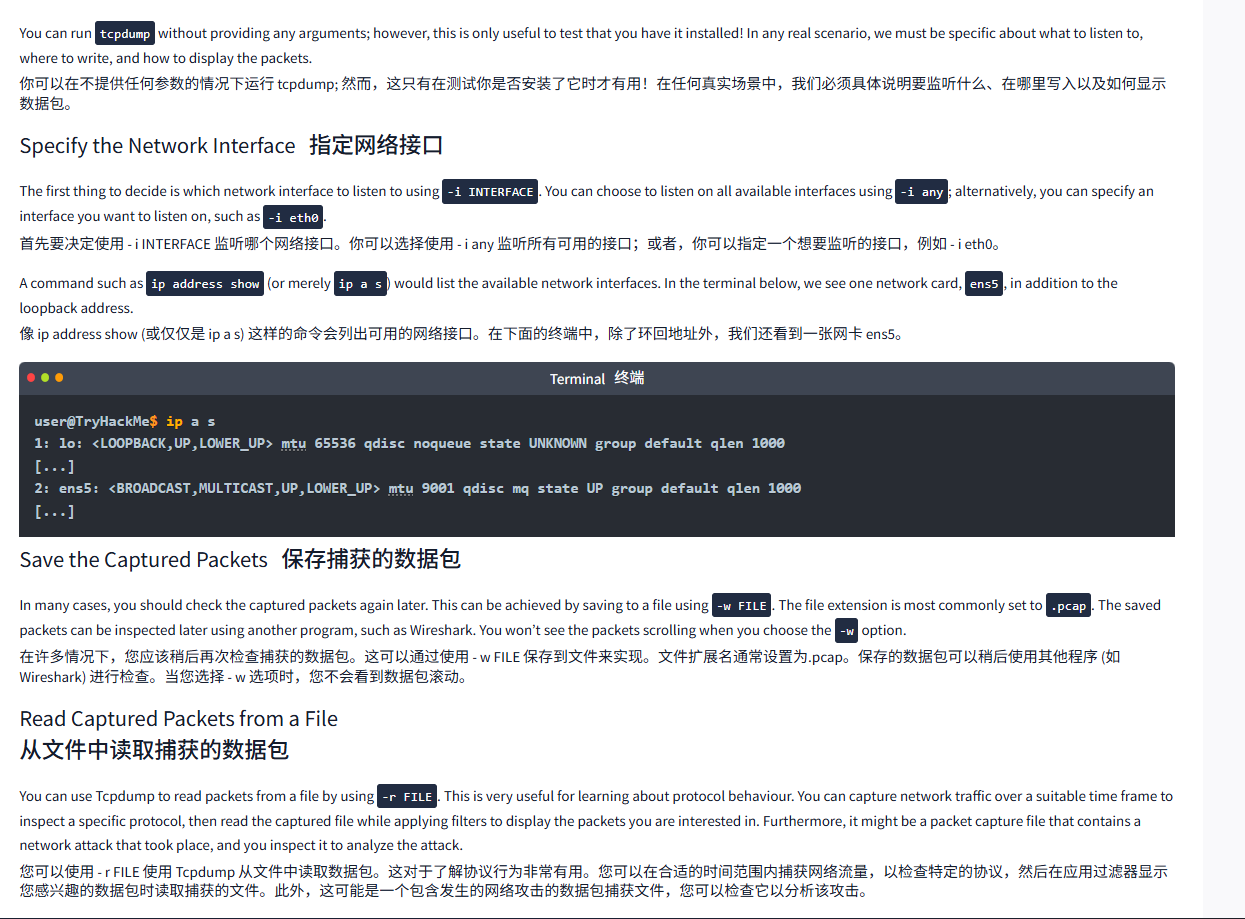
A command such as ip address show (or merely ip a s) would list the available network interfaces. In the terminal below, we see one network card, ens5, in addition to the loopback address.
像 ip address show (或仅仅是 ip a s) 这样的命令会列出可用的网络接口。在下面的终端中,除了环回地址外,我们还看到一张网卡 ens5。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ ip a s
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
[...]
2: ens5: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 9001 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
[...]Save the Captured Packets保存捕获的数据包
In many cases, you should check the captured packets again later. This can be achieved by saving to a file using -w FILE. The file extension is most commonly set to .pcap. The saved packets can be inspected later using another program, such as Wireshark. You won't see the packets scrolling when you choose the -w option.
在许多情况下,您应该稍后再次检查捕获的数据包。这可以通过使用 - w FILE 保存到文件来实现。文件扩展名通常设置为.pcap。保存的数据包可以稍后使用其他程序 (如 Wireshark) 进行检查。当您选择 - w 选项时,您不会看到数据包滚动。
Read Captured Packets from a File
从文件中读取捕获的数据包
You can use Tcpdump to read packets from a file by using -r FILE. This is very useful for learning about protocol behaviour. You can capture network traffic over a suitable time frame to inspect a specific protocol, then read the captured file while applying filters to display the packets you are interested in. Furthermore, it might be a packet capture file that contains a network attack that took place, and you inspect it to analyze the attack.
您可以使用 - r FILE 使用 Tcpdump 从文件中读取数据包。这对于了解协议行为非常有用。您可以在合适的时间范围内捕获网络流量,以检查特定的协议,然后在应用过滤器显示您感兴趣的数据包时读取捕获的文件。此外,这可能是一个包含发生的网络攻击的数据包捕获文件,您可以检查它以分析该攻击。
Limit the Number of Captured Packets
限制捕获的数据包数量
You can specify the number of packets to capture by specifying the count using -c COUNT. Without specifying a count, the packet capture will continue till you interrupt it, for example, by pressing CTRL-C. Depending on your goal, you only need a limited number of packets.
您可以使用 - c COUNT 指定要捕获的数据包数量。如果不指定计数,数据包捕获将持续进行,直到您中断它,例如,按下 CTRL-C 键。根据您的目标,您只需要有限数量的数据包。
Don't Resolve IP Addresses and Port Numbers
不要解析 IP 地址和端口号
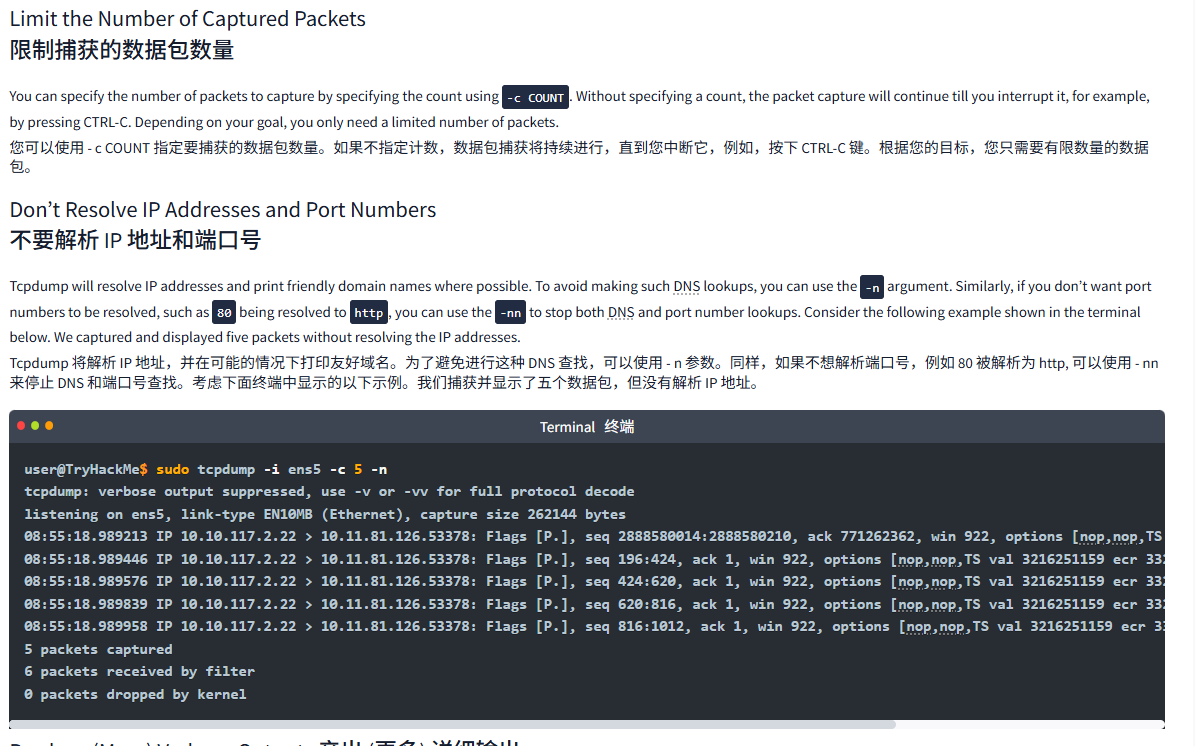
Tcpdump will resolve IP addresses and print friendly domain names where possible. To avoid making such DNS lookups, you can use the -n argument. Similarly, if you don't want port numbers to be resolved, such as 80 being resolved to http, you can use the -nn to stop both DNS and port number lookups. Consider the following example shown in the terminal below. We captured and displayed five packets without resolving the IP addresses.
Tcpdump 将解析 IP 地址,并在可能的情况下打印友好域名。为了避免进行这种 DNS 查找,可以使用 - n 参数。同样,如果不想解析端口号,例如 80 被解析为 http, 可以使用 - nn 来停止 DNS 和端口号查找。考虑下面终端中显示的以下示例。我们捕获并显示了五个数据包,但没有解析 IP 地址。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ sudo tcpdump -i ens5 -c 5 -n
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode
listening on ens5, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 262144 bytes
08:55:18.989213 IP 10.10.117.2.22 > 10.11.81.126.53378: Flags [P.], seq 2888580014:2888580210, ack 771262362, win 922, options [nop,nop,TS val 3216251159 ecr 33295823], length 196
08:55:18.989446 IP 10.10.117.2.22 > 10.11.81.126.53378: Flags [P.], seq 196:424, ack 1, win 922, options [nop,nop,TS val 3216251159 ecr 33295823], length 228
08:55:18.989576 IP 10.10.117.2.22 > 10.11.81.126.53378: Flags [P.], seq 424:620, ack 1, win 922, options [nop,nop,TS val 3216251159 ecr 33295823], length 196
08:55:18.989839 IP 10.10.117.2.22 > 10.11.81.126.53378: Flags [P.], seq 620:816, ack 1, win 922, options [nop,nop,TS val 3216251159 ecr 33295823], length 196
08:55:18.989958 IP 10.10.117.2.22 > 10.11.81.126.53378: Flags [P.], seq 816:1012, ack 1, win 922, options [nop,nop,TS val 3216251159 ecr 33295823], length 196
5 packets captured
6 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernelProduce (More) Verbose Output产出 (更多) 详细输出
If you want to print more details about the packets, you can use -v to produce a slightly more verbose output. According to the Tcpdump manual page (man tcpdump), the addition of -v will print "the time to live, identification, total length and options in an IP packet" among other checks. The -vv will produce more verbose output; the -vvv will provide even more verbosity; check the manual page for details.
如果你想打印更多关于数据包的详细信息,可以使用 - v 来产生稍微详细一些的输出。根据 Tcpdump 手册页 (man tcpdump), 添加 - v 将在其他检查中打印 "IP 数据包的生存时间、身份、总长度和选项"。-vv 将产生更详细的输出;-vvv 将提供更多详细信息;请查看手册页了解详细信息。
Summary and Examples总结和示例
The table below provides a summary of the command line options that we covered.
下表提供了我们讨论的命令行选项的总结。
|------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Command | Explanation 解释 |
| tcpdump -i INTERFACE | Captures packets on a specific network interface 在特定网络接口上捕获数据包 |
| tcpdump -w FILE | Writes captured packets to a file 将捕获的数据包写入文件 |
| tcpdump -r FILE | Reads captured packets from a file 从文件中读取捕获的数据包 |
| tcpdump -c COUNT | Captures a specific number of packets 捕获特定数量的数据包 |
| tcpdump -n | Don't resolve IP addresses不解析 IP 地址 |
| tcpdump -nn | Don't resolve IP addresses and don't resolve protocol numbers 不解析 IP 地址和协议编号 |
| tcpdump -v | Verbose display; verbosity can be increased with -vv and -vvv 详细显示;可以使用 - vv 和 - vvv 来增加详细性 |
Consider the following examples:考虑以下示例:
tcpdump -i eth0 -c 50 -vcaptures and displays 50 packets by listening on theeth0interface, which is a wired Ethernet, and displays them verbosely.
Tcpdump -i eth0 -c 50 -v 通过侦听 eth0 接口 (一种有线以太网) 捕获并显示 50 个数据包,并详细显示它们。tcpdump -i wlo1 -w data.pcapcaptures packets by listening on thewlo1interface (the WiFi interface) and writes the packets todata.pcap. It will continue till the user interrupts the capture by pressing CTRL-C.
Tcpdump -i wlo1 -w data.pcap 通过侦听 wlo1 接口 (WiFi 接口) 捕获数据包,并将数据包写入 data.pcap。该过程将持续进行,直到用户按 CTRL-C 中断捕获。tcpdump -i any -nncaptures packets on all interfaces and displays them on screen without domain name or protocol resolution.
Tcpdump -i any -nn 捕获所有接口上的数据包,并将其显示在屏幕上,而不需要域名或协议解析。
问题
答案
Task3 Filtering Expressions 过滤表达式
图片版

Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ sudo tcpdump host example.com -w http.pcap
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v[v]... for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes
16:49:02.482295 IP 192.168.139.132.49480 > 93.184.215.14.http: Flags [S], seq 3330895816, win 32120, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 621343956 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0
16:49:02.635087 IP 93.184.215.14.http > 192.168.139.132.49480: Flags [S.], seq 2231582859, ack 3330895817, win 64240, options [mss 1460], length 0
16:49:02.635125 IP 192.168.139.132.49480 > 93.184.215.14.http: Flags [.], ack 1, win 32120, length 0
16:49:02.635491 IP 192.168.139.132.49480 > 93.184.215.14.http: Flags [P.], seq 1:131, ack 1, win 32120, length 130: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1
16:49:02.635580 IP 93.184.215.14.http > 192.168.139.132.49480: Flags [.], ack 131, win 64240, length 0
[...]
^C
13 packets captured
25 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel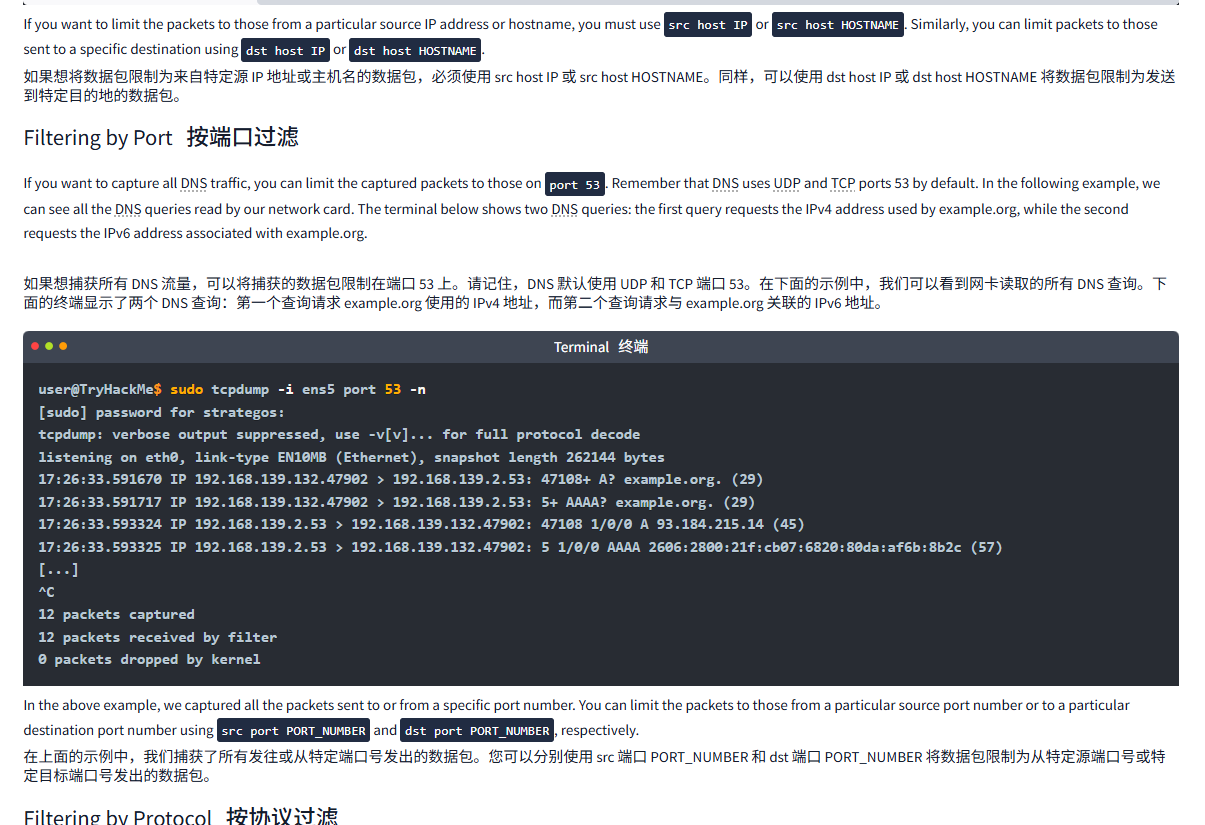
文字版
Although you can run tcpdump without providing any filtering expressions, this won't be useful. Just like in a social gathering, you don't try to listen to everyone at the same time; you would rather give your attention to a specific person or conversation. Considering the number of packets seen by our network card, it is impossible to see everything at once; we need to be specific and capture what we are interested in inspecting.
虽然你可以运行 tcpdump 而不提供任何过滤表达式,但这将是无用的。就像在社交聚会中一样,你不会试图同时倾听所有人;你更愿意将注意力集中在特定的人或对话上。考虑到我们的网卡看到的数据包数量,不可能一次性看到所有内容;我们需要具体化并捕捉我们感兴趣的内容。
Filtering by Host主机筛选
Let's say you are only interested in IP packets exchanged with your network printer or a specific game server. You can easily limit the captured packets to this host using host IP or host HOSTNAME. In the terminal below, we capture all the packets exchanged with example.com and save them to http.pcap. It is important to note that capturing packets requires you to be logged-in as root or to use sudo.
假设你只对与网络打印机或特定游戏服务器交换的 IP 数据包感兴趣。你可以使用主机 IP 或主机主机名轻松地将捕获的数据包限制到这个主机。在下面的终端中,我们捕获与 example.com 交换的所有数据包,并将其保存到 http.pcap。需要注意的是,捕获数据包需要你以 root 身份登录或使用 sudo。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ sudo tcpdump host example.com -w http.pcap
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v[v]... for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes
16:49:02.482295 IP 192.168.139.132.49480 > 93.184.215.14.http: Flags [S], seq 3330895816, win 32120, options [mss 1460,sackOK,TS val 621343956 ecr 0,nop,wscale 7], length 0
16:49:02.635087 IP 93.184.215.14.http > 192.168.139.132.49480: Flags [S.], seq 2231582859, ack 3330895817, win 64240, options [mss 1460], length 0
16:49:02.635125 IP 192.168.139.132.49480 > 93.184.215.14.http: Flags [.], ack 1, win 32120, length 0
16:49:02.635491 IP 192.168.139.132.49480 > 93.184.215.14.http: Flags [P.], seq 1:131, ack 1, win 32120, length 130: HTTP: GET / HTTP/1.1
16:49:02.635580 IP 93.184.215.14.http > 192.168.139.132.49480: Flags [.], ack 131, win 64240, length 0
[...]
^C
13 packets captured
25 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernelIf you want to limit the packets to those from a particular source IP address or hostname, you must use src host IP or src host HOSTNAME. Similarly, you can limit packets to those sent to a specific destination using dst host IP or dst host HOSTNAME.
如果想将数据包限制为来自特定源 IP 地址或主机名的数据包,必须使用 src host IP 或 src host HOSTNAME。同样,可以使用 dst host IP 或 dst host HOSTNAME 将数据包限制为发送到特定目的地的数据包。
Filtering by Port按端口过滤
If you want to capture all DNS traffic, you can limit the captured packets to those on port 53. Remember that DNS uses UDP and TCP ports 53 by default. In the following example, we can see all the DNS queries read by our network card. The terminal below shows two DNS queries: the first query requests the IPv4 address used by example.org, while the second requests the IPv6 address associated with example.org.
如果想捕获所有 DNS 流量,可以将捕获的数据包限制在端口 53 上。请记住,DNS 默认使用 UDP 和 TCP 端口 53。在下面的示例中,我们可以看到网卡读取的所有 DNS 查询。下面的终端显示了两个 DNS 查询:第一个查询请求 example.org 使用的 IPv4 地址,而第二个查询请求与 example.org 关联的 IPv6 地址。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ sudo tcpdump -i ens5 port 53 -n
[sudo] password for strategos:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v[v]... for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes
17:26:33.591670 IP 192.168.139.132.47902 > 192.168.139.2.53: 47108+ A? example.org. (29)
17:26:33.591717 IP 192.168.139.132.47902 > 192.168.139.2.53: 5+ AAAA? example.org. (29)
17:26:33.593324 IP 192.168.139.2.53 > 192.168.139.132.47902: 47108 1/0/0 A 93.184.215.14 (45)
17:26:33.593325 IP 192.168.139.2.53 > 192.168.139.132.47902: 5 1/0/0 AAAA 2606:2800:21f:cb07:6820:80da:af6b:8b2c (57)
[...]
^C
12 packets captured
12 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernelIn the above example, we captured all the packets sent to or from a specific port number. You can limit the packets to those from a particular source port number or to a particular destination port number using src port PORT_NUMBER and dst port PORT_NUMBER, respectively.
在上面的示例中,我们捕获了所有发往或从特定端口号发出的数据包。您可以分别使用 src 端口 PORT_NUMBER 和 dst 端口 PORT_NUMBER 将数据包限制为从特定源端口号或特定目标端口号发出的数据包。
Filtering by Protocol按协议过滤
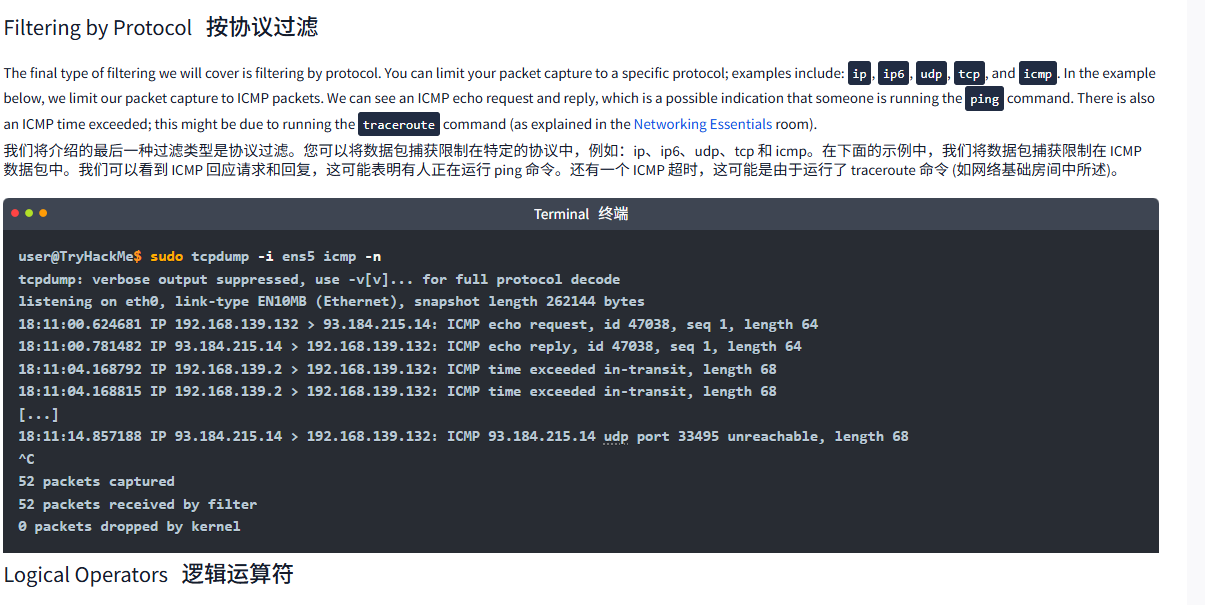
The final type of filtering we will cover is filtering by protocol. You can limit your packet capture to a specific protocol; examples include: ip, ip6, udp, tcp, and icmp. In the example below, we limit our packet capture to ICMP packets. We can see an ICMP echo request and reply, which is a possible indication that someone is running the ping command. There is also an ICMP time exceeded; this might be due to running the traceroute command (as explained in the Networking Essentials room).
我们将介绍的最后一种过滤类型是协议过滤。您可以将数据包捕获限制在特定的协议中,例如:ip、ip6、udp、tcp 和 icmp。在下面的示例中,我们将数据包捕获限制在 ICMP 数据包中。我们可以看到 ICMP 回应请求和回复,这可能表明有人正在运行 ping 命令。还有一个 ICMP 超时,这可能是由于运行了 traceroute 命令 (如网络基础房间中所述)。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ sudo tcpdump -i ens5 icmp -n
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v[v]... for full protocol decode
listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes
18:11:00.624681 IP 192.168.139.132 > 93.184.215.14: ICMP echo request, id 47038, seq 1, length 64
18:11:00.781482 IP 93.184.215.14 > 192.168.139.132: ICMP echo reply, id 47038, seq 1, length 64
18:11:04.168792 IP 192.168.139.2 > 192.168.139.132: ICMP time exceeded in-transit, length 68
18:11:04.168815 IP 192.168.139.2 > 192.168.139.132: ICMP time exceeded in-transit, length 68
[...]
18:11:14.857188 IP 93.184.215.14 > 192.168.139.132: ICMP 93.184.215.14 udp port 33495 unreachable, length 68
^C
52 packets captured
52 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernelLogical Operators逻辑运算符
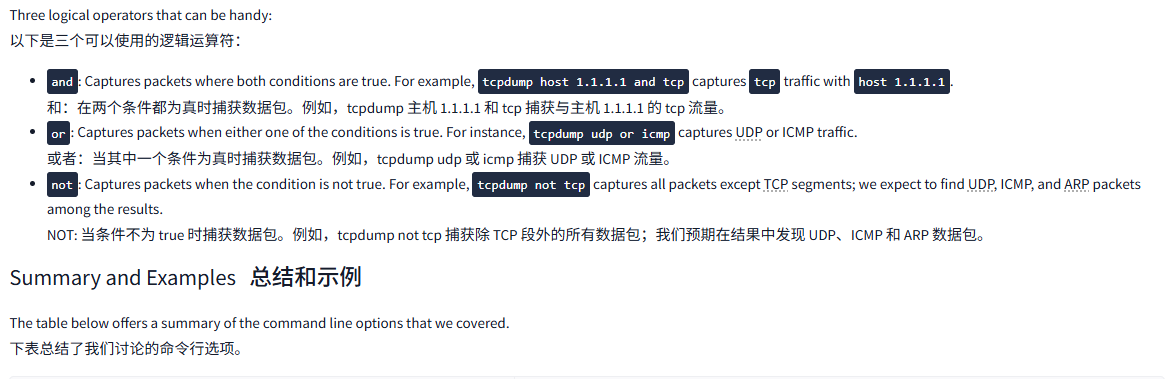
Three logical operators that can be handy:
以下是三个可以使用的逻辑运算符:
and: Captures packets where both conditions are true. For example,tcpdump host 1.1.1.1 and tcpcapturestcptraffic withhost 1.1.1.1.
和:在两个条件都为真时捕获数据包。例如,tcpdump 主机 1.1.1.1 和 tcp 捕获与主机 1.1.1.1 的 tcp 流量。or: Captures packets when either one of the conditions is true. For instance,tcpdump udp or icmpcaptures UDP or ICMP traffic.
或者:当其中一个条件为真时捕获数据包。例如,tcpdump udp 或 icmp 捕获 UDP 或 ICMP 流量。not: Captures packets when the condition is not true. For example,tcpdump not tcpcaptures all packets except TCP segments; we expect to find UDP, ICMP, and ARP packets among the results.
NOT: 当条件不为 true 时捕获数据包。例如,tcpdump not tcp 捕获除 TCP 段外的所有数据包;我们预期在结果中发现 UDP、ICMP 和 ARP 数据包。
Summary and Examples总结和示例
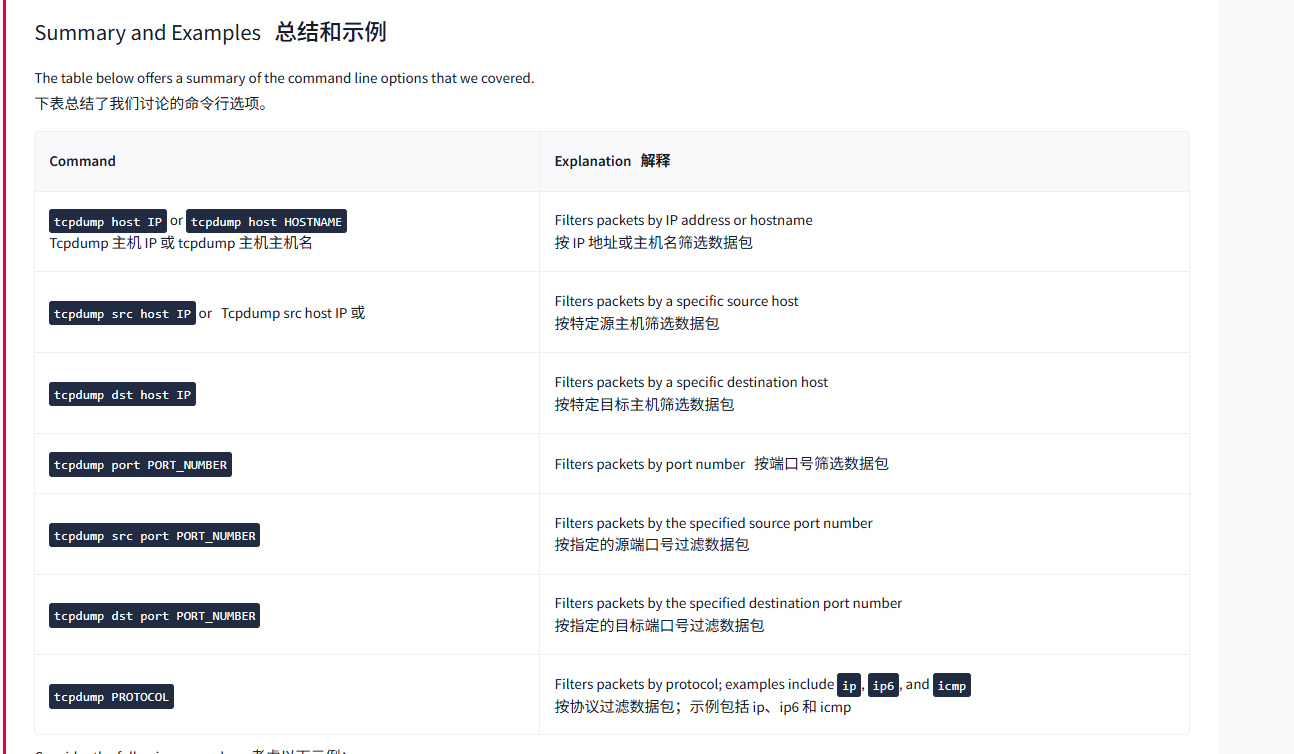
The table below offers a summary of the command line options that we covered.
下表总结了我们讨论的命令行选项。
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Command | Explanation 解释 |
| tcpdump host IP or tcpdump host HOSTNAME Tcpdump 主机 IP 或 tcpdump 主机主机名 | Filters packets by IP address or hostname 按 IP 地址或主机名筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump src host IP orTcpdump src host IP 或 | Filters packets by a specific source host 按特定源主机筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump dst host IP | Filters packets by a specific destination host 按特定目标主机筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump port PORT_NUMBER | Filters packets by port number按端口号筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump src port PORT_NUMBER | Filters packets by the specified source port number 按指定的源端口号过滤数据包 |
| tcpdump dst port PORT_NUMBER | Filters packets by the specified destination port number 按指定的目标端口号过滤数据包 |
| tcpdump PROTOCOL | Filters packets by protocol; examples include ip, ip6, and icmp 按协议过滤数据包;示例包括 ip、ip6 和 icmp |
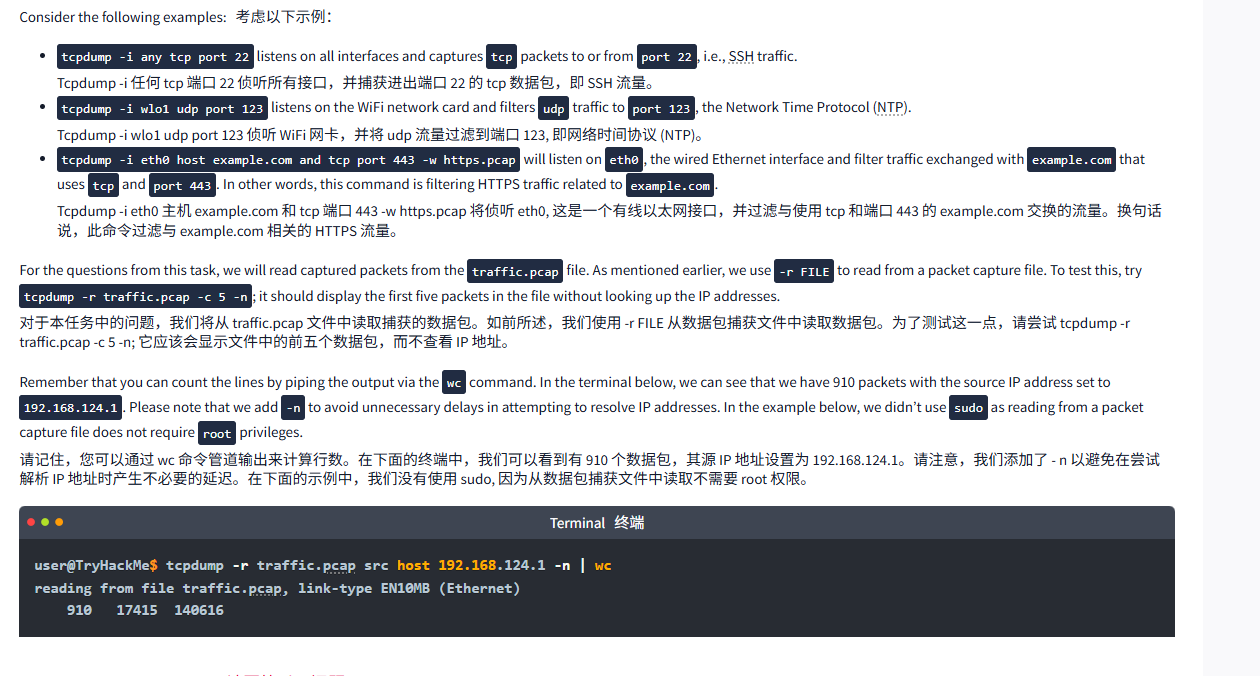
Consider the following examples:考虑以下示例:
tcpdump -i any tcp port 22listens on all interfaces and capturestcppackets to or fromport 22, i.e., SSH traffic.
Tcpdump -i 任何 tcp 端口 22 侦听所有接口,并捕获进出端口 22 的 tcp 数据包,即 SSH 流量。tcpdump -i wlo1 udp port 123listens on the WiFi network card and filtersudptraffic toport 123, the Network Time Protocol (NTP).
Tcpdump -i wlo1 udp port 123 侦听 WiFi 网卡,并将 udp 流量过滤到端口 123, 即网络时间协议 (NTP)。tcpdump -i eth0 host example.com and tcp port 443 -w https.pcapwill listen oneth0, the wired Ethernet interface and filter traffic exchanged withexample.comthat usestcpandport 443. In other words, this command is filtering HTTPS traffic related toexample.com.
Tcpdump -i eth0 主机 example.com 和 tcp 端口 443 -w https.pcap 将侦听 eth0, 这是一个有线以太网接口,并过滤与使用 tcp 和端口 443 的 example.com 交换的流量。换句话说,此命令过滤与 example.com 相关的 HTTPS 流量。
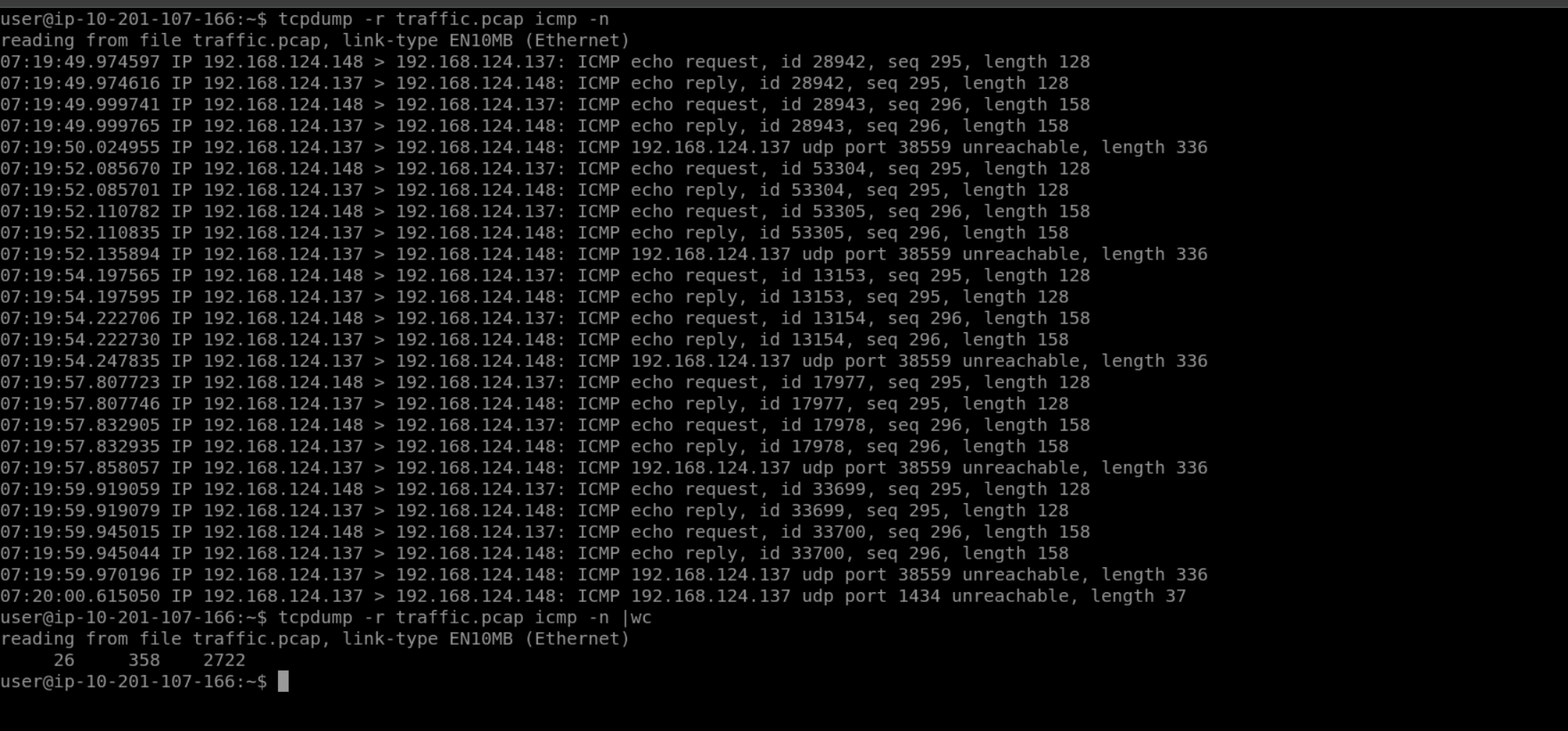
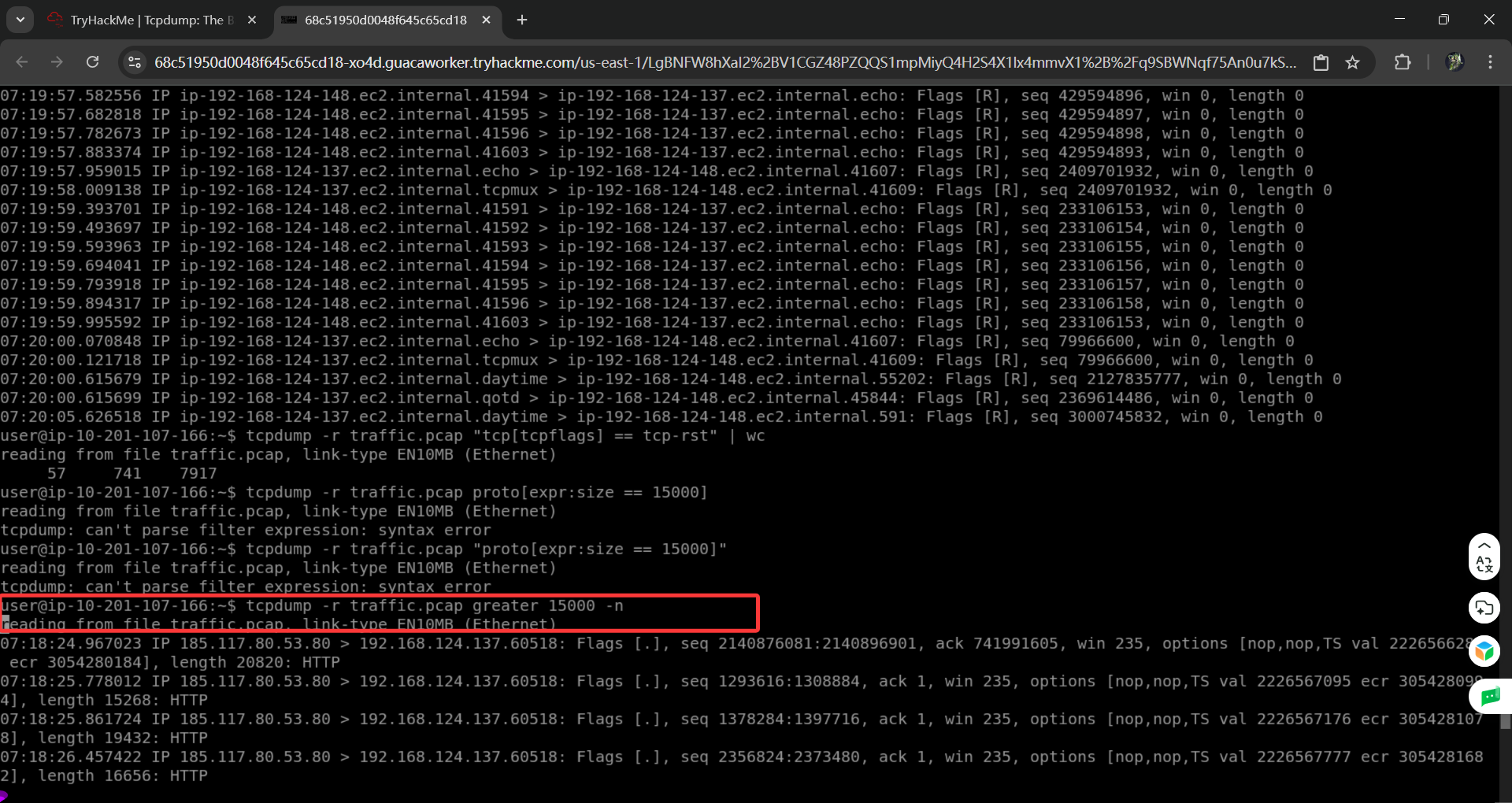
For the questions from this task, we will read captured packets from the traffic.pcap file. As mentioned earlier, we use -r FILE to read from a packet capture file. To test this, try tcpdump -r traffic.pcap -c 5 -n; it should display the first five packets in the file without looking up the IP addresses.
对于本任务中的问题,我们将从 traffic.pcap 文件中读取捕获的数据包。如前所述,我们使用 -r FILE 从数据包捕获文件中读取数据包。为了测试这一点,请尝试 tcpdump -r traffic.pcap -c 5 -n; 它应该会显示文件中的前五个数据包,而不查看 IP 地址。
Remember that you can count the lines by piping the output via the wc command. In the terminal below, we can see that we have 910 packets with the source IP address set to 192.168.124.1. Please note that we add -n to avoid unnecessary delays in attempting to resolve IP addresses. In the example below, we didn't use sudo as reading from a packet capture file does not require root privileges.
请记住,您可以通过 wc 命令管道输出来计算行数。在下面的终端中,我们可以看到有 910 个数据包,其源 IP 地址设置为 192.168.124.1。请注意,我们添加了 - n 以避免在尝试解析 IP 地址时产生不必要的延迟。在下面的示例中,我们没有使用 sudo, 因为从数据包捕获文件中读取不需要 root 权限。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r traffic.pcap src host 192.168.124.1 -n | wc
reading from file traffic.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet)
910 17415 140616问题
答案

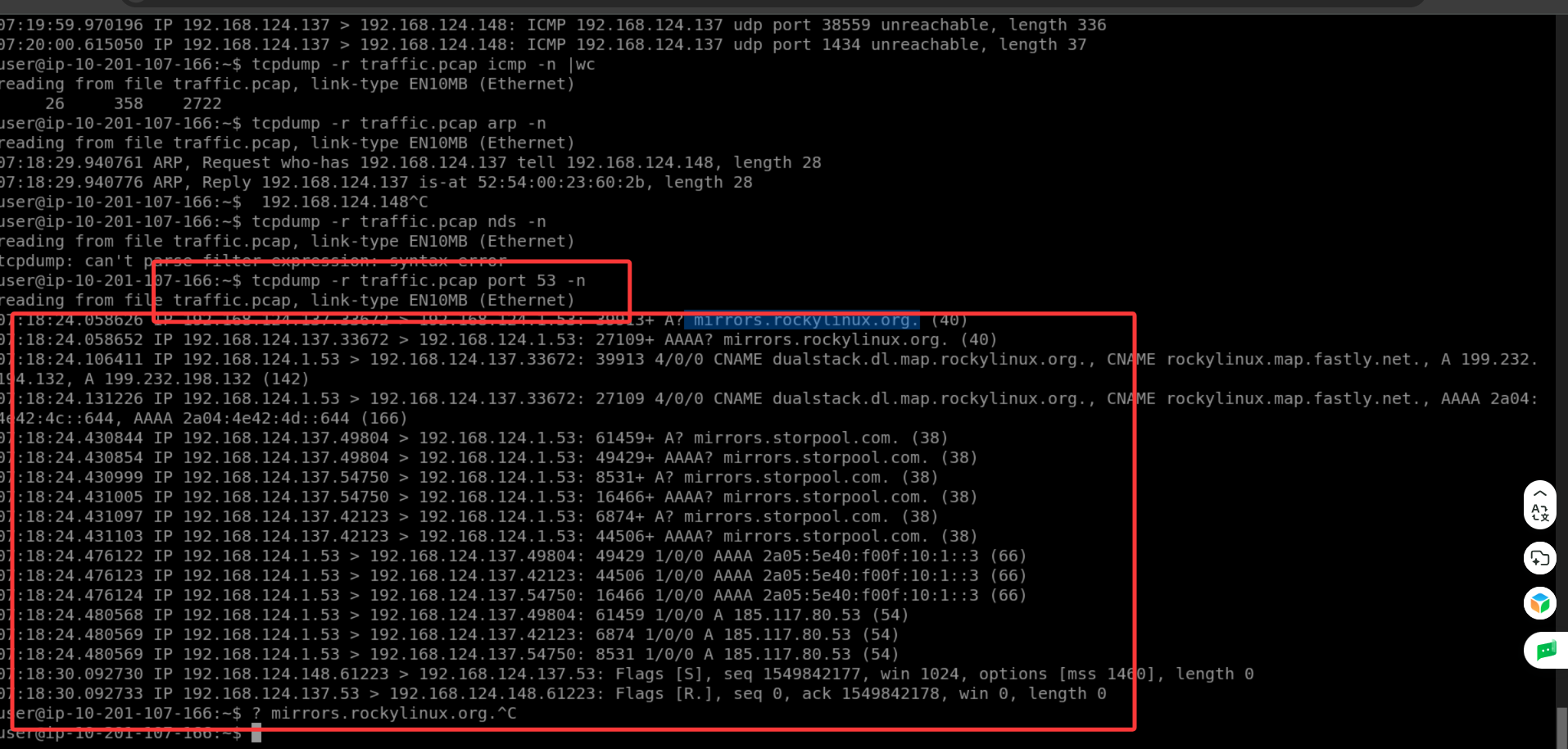
Task4 Advanced Filtering 高级过滤
图片版


文字版
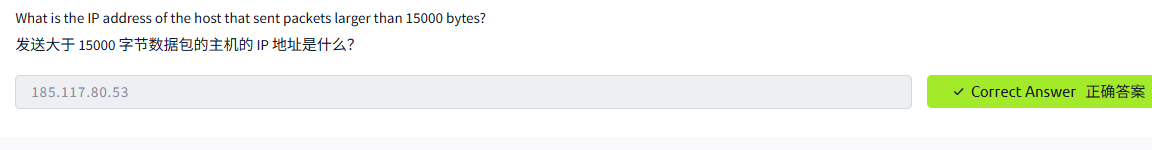
There are many more ways to filter packets. After all, in any real-life situation, we would need to filter through thousands or even millions of packets. It is indispensable to be able to express the exact packets to display. For example, we can limit the displayed packets to those smaller or larger than a certain length:
过滤数据包的方法有很多种。毕竟,在现实生活中的任何情况下,我们都需要过滤数千甚至数百万个数据包。能够准确地表达要显示的数据包是不可或缺的。例如,我们可以将显示的数据包限制为那些小于或大于一定长度的数据包:
greater LENGTH: Filters packets that have a length greater than or equal to the specified length
更长的长度:过滤长度大于或等于指定长度的数据包less LENGTH: Filters packets that have a length less than or equal to the specified length
较短长度:过滤长度小于或等于指定长度的数据包。
We recommend you check the pcap-filter manual page by issuing the command man pcap-filter; however, for the purposes of this room, we will focus on one advanced option that allows you to filter packets based on the TCP flags. Understanding the TCP flags will make it easy to build on this knowledge and master more advanced filtering techniques.
我们建议您通过发出命令 man pcap-filter 来检查 pcap-filter 手册页;然而,出于本节的目的,我们将重点介绍一个高级选项,该选项允许您根据 TCP 标志过滤数据包。了解 TCP 标志将使您更容易基于这些知识并掌握更高级的过滤技术。
Binary Operations二进制操作
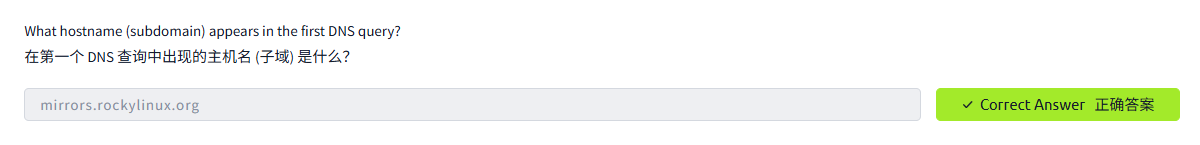
Before proceeding, it is worth visiting binary operations. A binary operation works on bits, i.e., zeroes and ones. An operation takes one or two bits and returns one bit. Let's explain in more depth and consider the following three binary operations: &, |, and !.
在继续之前,值得访问二元运算。二元运算处理位,即 0 和 1。一个运算取 1 或 2 位并返回 1 位。让我们更深入地解释,并考虑以下三个二元运算:&、| 和!
& (And) takes two bits and returns 0 unless both inputs are 1, as shown in the table below.
&(And) 取两位并返回 0, 除非两个输入都是 1, 如下表所示。
|----------------------|----------------------|--------------------------------------------|
| Input 1 输入 1 | Input 2 输入 2 | Input1 **&**Input 2 输入 1 和输入 2 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
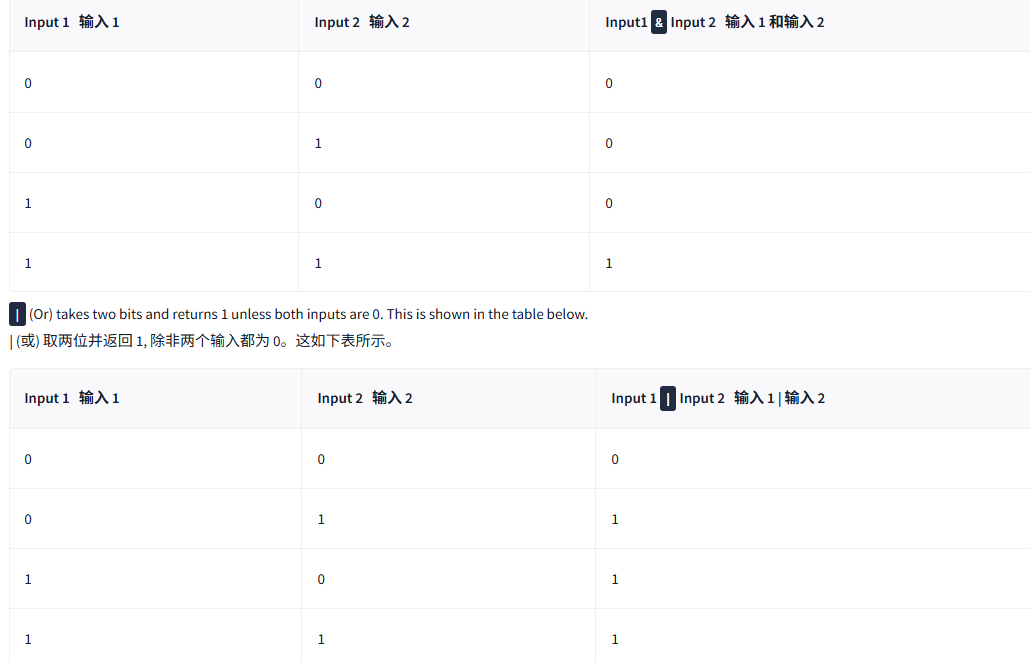
| (Or) takes two bits and returns 1 unless both inputs are 0. This is shown in the table below.
| (或) 取两位并返回 1, 除非两个输入都为 0。这如下表所示。
|----------------------|----------------------|-----------------------------------------------|
| Input 1 输入 1 | Input 2 输入 2 | Input 1 **|**Input 2 输入 1 | 输入 2 |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
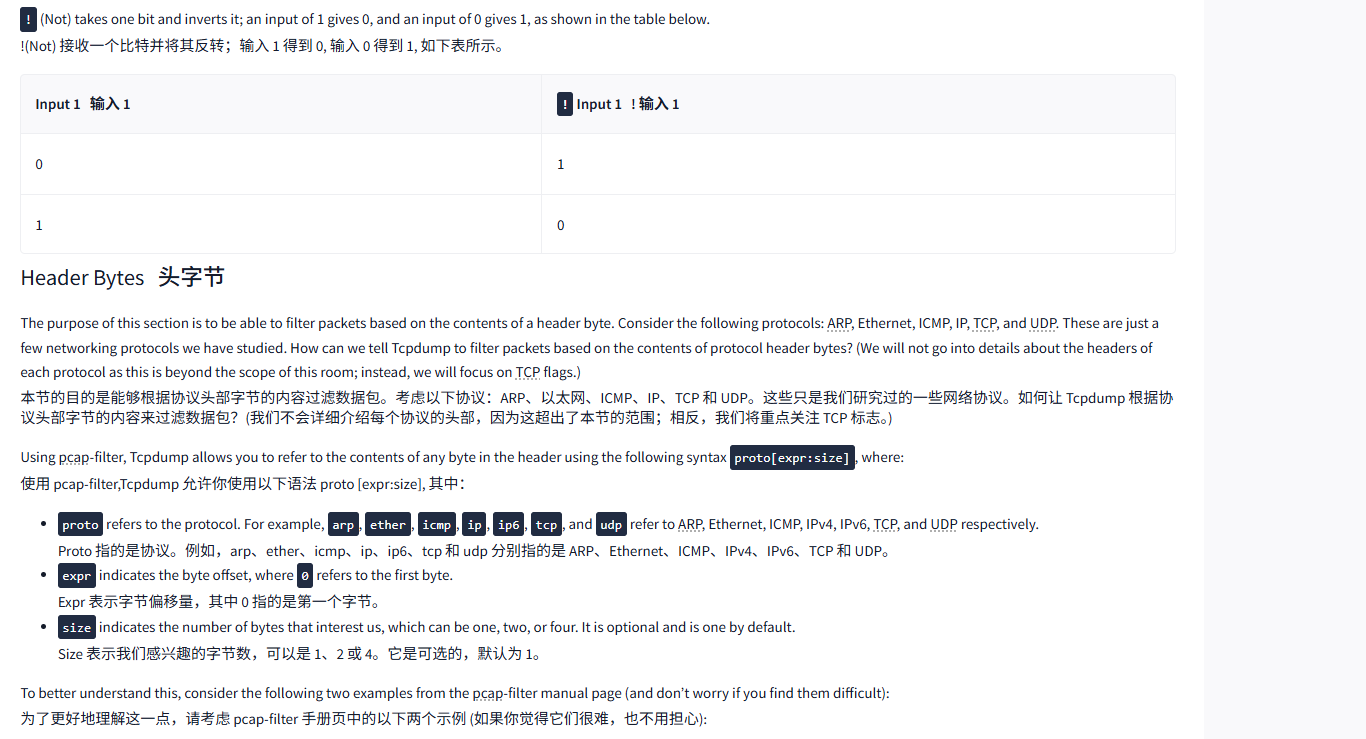
! (Not) takes one bit and inverts it; an input of 1 gives 0, and an input of 0 gives 1, as shown in the table below.
!(Not) 接收一个比特并将其反转;输入 1 得到 0, 输入 0 得到 1, 如下表所示。
|----------------------|-----------------------------|
| Input 1 输入 1 | **!**Input 1 ! 输入 1 |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Header Bytes头字节
The purpose of this section is to be able to filter packets based on the contents of a header byte. Consider the following protocols: ARP, Ethernet, ICMP, IP, TCP, and UDP. These are just a few networking protocols we have studied. How can we tell Tcpdump to filter packets based on the contents of protocol header bytes? (We will not go into details about the headers of each protocol as this is beyond the scope of this room; instead, we will focus on TCP flags.)
本节的目的是能够根据协议头部字节的内容过滤数据包。考虑以下协议:ARP、以太网、ICMP、IP、TCP 和 UDP。这些只是我们研究过的一些网络协议。如何让 Tcpdump 根据协议头部字节的内容来过滤数据包?(我们不会详细介绍每个协议的头部,因为这超出了本节的范围;相反,我们将重点关注 TCP 标志。)
Using pcap-filter, Tcpdump allows you to refer to the contents of any byte in the header using the following syntax proto[expr:size], where:
使用 pcap-filter,Tcpdump 允许你使用以下语法 proto [expr:size], 其中:
protorefers to the protocol. For example,arp,ether,icmp,ip,ip6,tcp, andudprefer to ARP, Ethernet, ICMP, IPv4, IPv6, TCP, and UDP respectively.
Proto 指的是协议。例如,arp、ether、icmp、ip、ip6、tcp 和 udp 分别指的是 ARP、Ethernet、ICMP、IPv4、IPv6、TCP 和 UDP。exprindicates the byte offset, where0refers to the first byte.
Expr 表示字节偏移量,其中 0 指的是第一个字节。sizeindicates the number of bytes that interest us, which can be one, two, or four. It is optional and is one by default.
Size 表示我们感兴趣的字节数,可以是 1、2 或 4。它是可选的,默认为 1。
To better understand this, consider the following two examples from the pcap-filter manual page (and don't worry if you find them difficult):
为了更好地理解这一点,请考虑 pcap-filter 手册页中的以下两个示例 (如果你觉得它们很难,也不用担心):
-
ether[0] & 1 != 0takes the first byte in the Ethernet header and the decimal number 1 (i.e.,0000 0001in binary) and applies the&(the And binary operation). It will return true if the result is not equal to the number 0 (i.e.,0000 0000). The purpose of this filter is to show packets sent to a multicast address. A multicast Ethernet address is a particular address that identifies a group of devices intended to receive the same data.Ether [0] & 1 != 0 取以太网报头中的第一个字节和十进制数 1 (即二元运算中的 0000 0001), 并应用 &(And 二元运算)。如果结果不等于 0 (即 0000 0000), 则返回 true。此过滤器的目的是显示发送到多播地址的数据包。多播以太网地址是一个特定的地址,用于标识一组旨在接收相同数据的设备。
-
ip[0] & 0xf != 5takes the first byte in the IP header and compares it with the hexadecimal number F (i.e.,0000 1111in binary). It will return true if the result is not equal to the (decimal) number 5 (i.e.,0000 0101in binary). The purpose of this filter is to catch all IP packets with options.
Ip [0] & 0xf ! = 5 取 IP 报头中的第一个字节,并将其与十六进制数 F (即二进制中的 0000 1111) 进行比较。如果结果不等于 (十进制) 数 5 (即二进制中的 00000 0101), 则返回 true。这个过滤器的目的是捕获所有带有选项的 IP 数据包。
Don't worry if you find the above two examples complex. We included them so you know what you can achieve with this; however, fully understanding the above examples is not necessary to finish this task. Instead, we will focus on filtering TCP packets based on the set TCP flags.
如果你觉得上面两个例子很复杂,不用担心。我们包含它们是为了让你知道你可以通过它们实现什么;然而,完全理解上面的例子并不是完成这项任务的必要条件。相反,我们将专注于根据设置的 TCP 标志过滤 TCP 数据包。
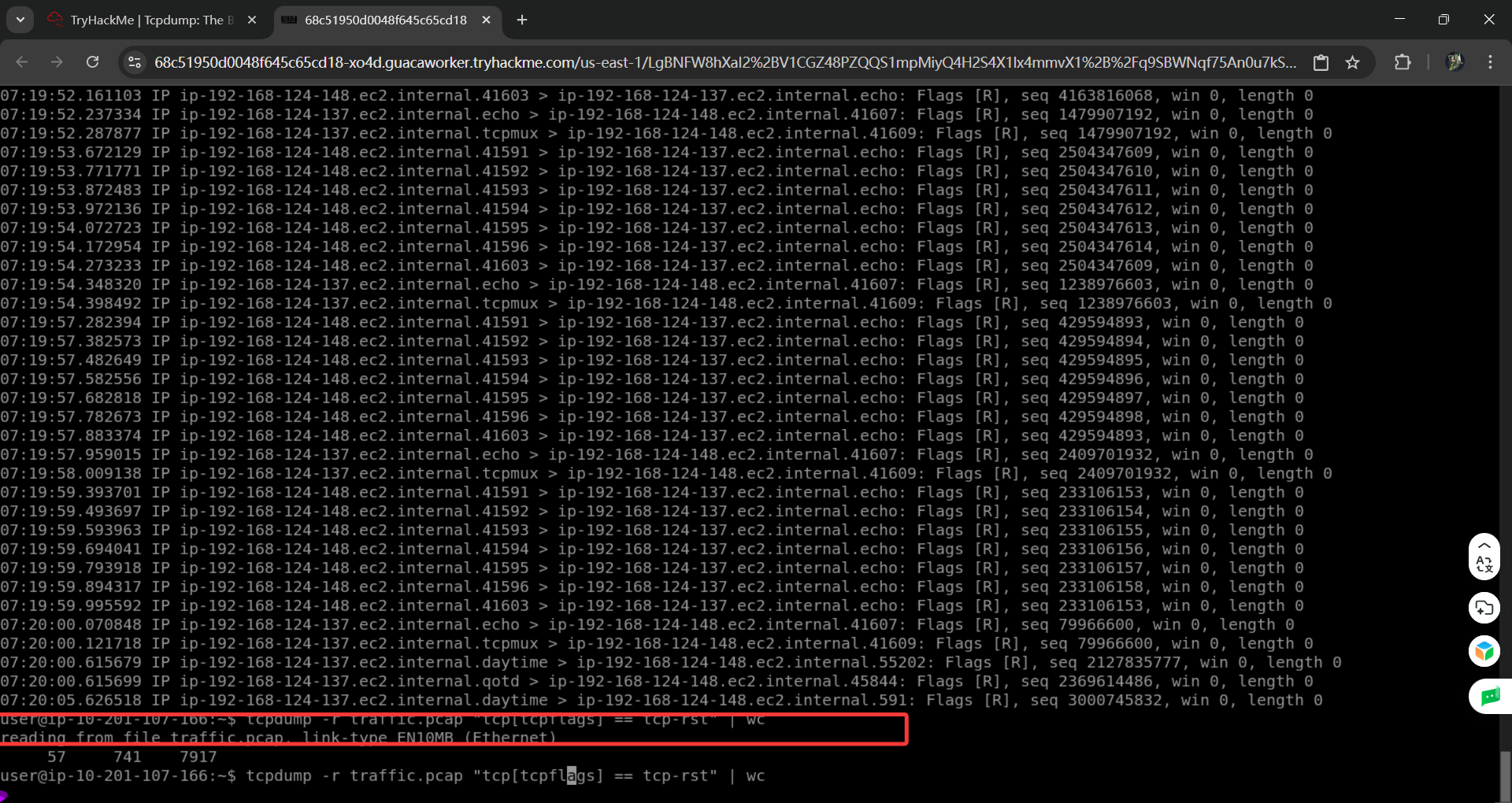
You can use tcp[tcpflags] to refer to the TCP flags field. The following TCP flags are available to compare with:
可以使用 tcp [tcpflags] 来引用 TCP 标志字段。以下 TCP 标志可以与之进行比较:
tcp-synTCP SYN (Synchronize)Tcp-syn TCP SYN (同步)tcp-ackTCP ACK (Acknowledge)Tcp-ACK TCP ACK (确认)tcp-finTCP FIN (Finish)Tcp-fin TCP FIN (完成)tcp-rstTCP RST (Reset)Tcp-rst TCP RST (重置)tcp-pushTCP PushTcp-push TCP 推送
Based on the above, we can write:
基于上述内容,我们可以这样写:
tcpdump "tcp[tcpflags] == tcp-syn"to capture TCP packets with only the SYN (Synchronize) flag set, while all the other flags are unset.
Tcpdump"tcp [tcpflags] == tcp-syn" 用于捕获只设置了 SYN (Synchronize) 标志的 TCP 数据包,而其他所有标志都未设置。tcpdump "tcp[tcpflags] & tcp-syn != 0"to capture TCP packets with at least the SYN (Synchronize) flag set.
Tcpdump"tcp [tcpflags] & tcp-syn != 0" 用于捕获至少设置了 SYN (Synchronize) 标志的 TCP 数据包。tcpdump "tcp[tcpflags] & (tcp-syn|tcp-ack) != 0"to capture TCP packets with at least the SYN (Synchronize) or ACK (Acknowledge) flags set.
Tcpdump"tcp [tcpflags] & (tcp-syn|tcp-ack) != 0" 用于捕获至少设置了 SYN (Synchronize) 或 ACK (Acknowledge) 标志的 TCP 数据包。
You can write your own filter depending on what you are looking for.
你可以根据需要编写自己的过滤器。
问题
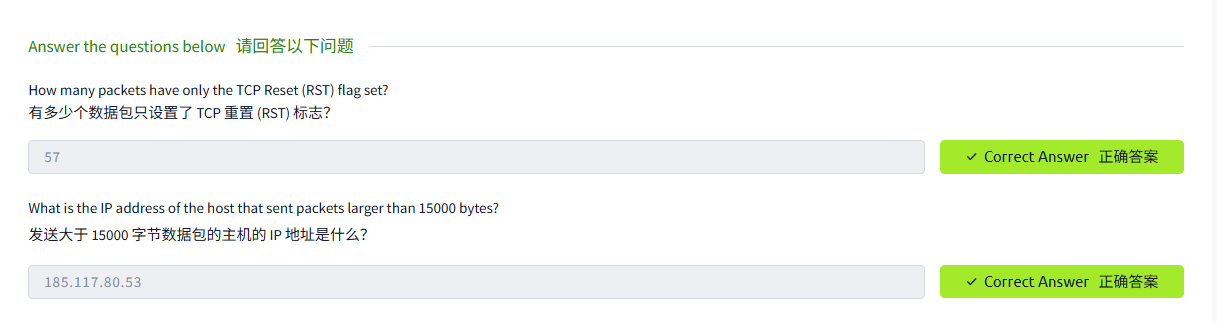
答案
Task5 Displaying Packets显示数据包
文字版
Tcpdump is a rich program with many options to customize how the packets are printed and displayed. We have selected to cover the following five options:
Tcpdump 是一个丰富的程序,有许多选项可以自定义数据包的打印和显示方式。我们选择了以下五个选项:
-q: Quick output; print brief packet information
-q: 快速输出;打印简短的数据包信息-e: Print the link-level header
-e: 打印链路级别的报头-A: Show packet data in ASCII
-A: 以 ASCII 格式显示数据包数据-xx: Show packet data in hexadecimal format, referred to as hex
-xx: 以十六进制格式显示数据包数据,称为十六进制-X: Show packet headers and data in hex and ASCII
-X: 以十六进制和 ASCII 格式显示报文头和数据
To demonstrate how the above options manipulate the output, we will first display two captured packets without using any additional arguments.
为了演示上述选项如何操作输出,我们将首先显示两个捕获的数据包,而不使用任何额外的参数。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r TwoPackets.pcap
reading from file TwoPackets.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144
18:59:59.979771 IP 104.18.12.149.https > g5000.45248: Flags [P.], seq 2695955324:2695955349, ack 2856007037, win 16, options [nop,nop,TS val 412758285 ecr 3959057198], length 25
18:59:59.980574 IP g5000.45248 > 104.18.12.149.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:30, ack 25, win 2175, options [nop,nop,TS val 3959057384 ecr 412758285], length 29Brief Packet Information简要数据包信息
If you prefer shorter output lines, you can opt for "quick" output with -q. The following example shows the timestamp, along with the source and destination IP addresses and source and destination port numbers.
如果您更喜欢较短的输出行,可以使用 - q 选择 "快速" 输出。以下示例显示了时间戳,以及源和目标 IP 地址以及源和目标端口号。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r TwoPackets.pcap -q
reading from file TwoPackets.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144
18:59:59.979771 IP 104.18.12.149.https > g5000.45248: tcp 25
18:59:59.980574 IP g5000.45248 > 104.18.12.149.https: tcp 29Displaying Link-Level Header显示链路级别报头
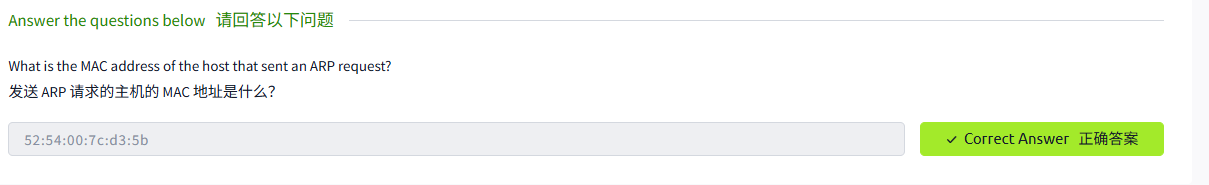
If you are on an Ethernet or WiFi network and want to include the MAC addresses in Tcpdump output, all you need to do is to add -e. This is convenient when you are learning how specific protocols, such as ARP and DHCP function. It can also help you track the source of any unusual packets on your network.
如果你在以太网或 WiFi 网络上,并且想要在 Tcpdump 输出中包含 MAC 地址,你所需要做的就是添加 - e。当你学习如何使用特定协议 (如 ARP 和 DHCP 功能) 时,这很方便。它还可以帮助你跟踪网络上任何不寻常数据包的来源。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r TwoPackets.pcap -e
reading from file TwoPackets.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144
18:59:59.979771 44:df:65:d8:fe:6c (oui Unknown) > 02:83:1e:40:5d:17 (oui Unknown), ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 91: 104.18.12.149.https > g5000.45248: Flags [P.], seq 2695955324:2695955349, ack 2856007037, win 16, options [nop,nop,TS val 412758285 ecr 3959057198], length 25
18:59:59.980574 02:83:1e:40:5d:17 (oui Unknown) > 44:df:65:d8:fe:6c (oui Unknown), ethertype IPv4 (0x0800), length 95: g5000.45248 > 104.18.12.149.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:30, ack 25, win 2175, options [nop,nop,TS val 3959057384 ecr 412758285], length 29Displaying Packets as ASCII将数据包显示为 ASCII
ASCII stands for American Standard Code for Information Interchange; ASCII codes represent text. In other words, you can expect -A to display all the bytes mapped to English letters, numbers, and symbols.
ASCII 代表美国信息交换标准码;ASCII 码代表文本。换句话说,你可以期望 - A 显示所有映射到英文字母、数字和符号的字节。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r TwoPackets.pcap -A
reading from file TwoPackets.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144
18:59:59.979771 IP 104.18.12.149.https > g5000.45248: Flags [P.], seq 2695955324:2695955349, ack 2856007037, win 16, options [nop,nop,TS val 412758285 ecr 3959057198], length 25
E..M..@.5..)h.....BY.......|.;5}...........
..1...k......j.3.2.....&9a.....-L
18:59:59.980574 IP g5000.45248 > 104.18.12.149.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:30, ack 25, win 2175, options [nop,nop,TS val 3959057384 ecr 412758285], length 29
E..Ql.@.@.VV..BYh........;5}...............
..k...1.......1.y.&VC<#._J$..z...D#.`Displaying Packets in Hexadecimal Format以十六进制格式显示数据包
ASCII format works well when the packet contents are plain-text English. It won't work if the contents have undergone encryption or even compression. Furthermore, it won't work for languages that don't use the English alphabet. Hence, we need another way to display the packet contents regardless of format. Being 8 bits, any octet can be displayed as two hexadecimal digits. (Each hexadecimal digit represents 4 bits.) To display the packets in hexadecimal format, we must add -xx as shown in the terminal below.
ASCII 格式在数据包内容为纯文本英文时效果良好。如果内容经过加密甚至压缩,它就无法正常工作。此外,它也不适用于不使用英文字母的语言。因此,我们需要另一种方式来显示数据包内容,而不管其格式如何。作为 8 位数,任何八位数都可以显示为两个十六进制数字。(每个十六进制数字代表 4 位。) 要以十六进制格式显示数据包,我们必须添加 - xx, 如下面的终端所示。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r TwoPackets.pcap -xx
reading from file TwoPackets.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144
18:59:59.979771 IP 104.18.12.149.https > g5000.45248: Flags [P.], seq 2695955324:2695955349, ack 2856007037, win 16, options [nop,nop,TS val 412758285 ecr 3959057198], length 25
0x0000: 0283 1e40 5d17 44df 65d8 fe6c 0800 4500
0x0010: 004d fbd8 4000 3506 d229 6812 0c95 c0a8
0x0020: 4259 01bb b0c0 a0b1 037c aa3b 357d 8018
0x0030: 0010 f905 0000 0101 080a 189a 310d ebfa
0x0040: 6b2e 1703 0300 146a 8f33 1832 e6a2 fb99
0x0050: eb26 3961 dad4 1611 152d 4c
18:59:59.980574 IP g5000.45248 > 104.18.12.149.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:30, ack 25, win 2175, options [nop,nop,TS val 3959057384 ecr 412758285], length 29
0x0000: 44df 65d8 fe6c 0283 1e40 5d17 0800 4500
0x0010: 0051 6ca8 4000 4006 5656 c0a8 4259 6812
0x0020: 0c95 b0c0 01bb aa3b 357d a0b1 0395 8018
0x0030: 087f 17e0 0000 0101 080a ebfa 6be8 189a
0x0040: 310d 1703 0300 18f4 31fa 798d 2656 433c
0x0050: 2389 5f4a 24c2 fa7a 1496 8444 238e 60Adding -xx lets us see the packet octet by octet. In the example above, we can closely inspect the IP and TCP headers in addition to the packet contents.
添加 - xx 后,我们可以逐个八位数查看数据包的八位数。在上面的例子中,除了数据包内容外,我们还可以仔细检查 IP 和 TCP 报头。
Best of Both Worlds两全其美
If you would like to display the captured packets in hexadecimal and ASCII formats, Tcpdump makes it easy with the -X option.
如果你想以十六进制和 ASCII 格式显示捕获的数据包,Tcpdump 使用 - X 选项可以简化操作。
Terminal终端
user@TryHackMe$ tcpdump -r TwoPackets.pcap -X
reading from file TwoPackets.pcap, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144
18:59:59.979771 IP 104.18.12.149.https > g5000.45248: Flags [P.], seq 2695955324:2695955349, ack 2856007037, win 16, options [nop,nop,TS val 412758285 ecr 3959057198], length 25
0x0000: 4500 004d fbd8 4000 3506 d229 6812 0c95 E..M..@.5..)h...
0x0010: c0a8 4259 01bb b0c0 a0b1 037c aa3b 357d ..BY.......|.;5}
0x0020: 8018 0010 f905 0000 0101 080a 189a 310d ..............1.
0x0030: ebfa 6b2e 1703 0300 146a 8f33 1832 e6a2 ..k......j.3.2..
0x0040: fb99 eb26 3961 dad4 1611 152d 4c ...&9a.....-L
18:59:59.980574 IP g5000.45248 > 104.18.12.149.https: Flags [P.], seq 1:30, ack 25, win 2175, options [nop,nop,TS val 3959057384 ecr 412758285], length 29
0x0000: 4500 0051 6ca8 4000 4006 5656 c0a8 4259 E..Ql.@.@.VV..BY
0x0010: 6812 0c95 b0c0 01bb aa3b 357d a0b1 0395 h........;5}....
0x0020: 8018 087f 17e0 0000 0101 080a ebfa 6be8 ..............k.
0x0030: 189a 310d 1703 0300 18f4 31fa 798d 2656 ..1.......1.y.&V
0x0040: 433c 2389 5f4a 24c2 fa7a 1496 8444 238e C<#._J$..z...D#.
0x0050: 60Summary and Examples总结和示例
The table below provides a summary of the command line options that we covered.
下表提供了我们讨论的命令行选项的总结。
|---------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Command | Explanation 解释 |
| tcpdump -q | Quick and quite: brief packet information 快速且完整:简短的数据包信息 |
| tcpdump -e | Include MAC addresses包含 MAC 地址 |
| tcpdump -A | Print packets as ASCII encoding以 ASCII 编码格式打印数据包 |
| tcpdump -xx | Display packets in hexadecimal format以十六进制格式显示数据包 |
| tcpdump -X | Show packets in both hexadecimal and ASCII formats 以十六进制和 ASCII 格式显示数据包 |
问题
答案

Task6
总结
Summary and Examples总结和示例
The table below provides a summary of the command line options that we covered.
下表提供了我们讨论的命令行选项的总结。
|------------------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Command | Explanation 解释 |
| tcpdump -i INTERFACE | Captures packets on a specific network interface 在特定网络接口上捕获数据包 |
| tcpdump -w FILE | Writes captured packets to a file 将捕获的数据包写入文件 |
| tcpdump -r FILE | Reads captured packets from a file 从文件中读取捕获的数据包 |
| tcpdump -c COUNT | Captures a specific number of packets 捕获特定数量的数据包 |
| tcpdump -n | Don't resolve IP addresses不解析 IP 地址 |
| tcpdump -nn | Don't resolve IP addresses and don't resolve protocol numbers 不解析 IP 地址和协议编号 |
| tcpdump -v | Verbose display; verbosity can be increased with -vv and -vvv 详细显示;可以使用 - vv 和 - vvv 来增加详细性 |
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Command | Explanation 解释 |
| tcpdump host IP or tcpdump host HOSTNAME Tcpdump 主机 IP 或 tcpdump 主机主机名 | Filters packets by IP address or hostname 按 IP 地址或主机名筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump src host IP orTcpdump src host IP 或 | Filters packets by a specific source host 按特定源主机筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump dst host IP | Filters packets by a specific destination host 按特定目标主机筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump port PORT_NUMBER | Filters packets by port number按端口号筛选数据包 |
| tcpdump src port PORT_NUMBER | Filters packets by the specified source port number 按指定的源端口号过滤数据包 |
| tcpdump dst port PORT_NUMBER | Filters packets by the specified destination port number 按指定的目标端口号过滤数据包 |
| tcpdump PROTOCOL | Filters packets by protocol; examples include ip, ip6, and icmp 按协议过滤数据包;示例包括 ip、ip6 和 icmp |
|---------------|-------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| Command | Explanation 解释 |
| tcpdump -q | Quick and quite: brief packet information 快速且完整:简短的数据包信息 |
| tcpdump -e | Include MAC addresses包含 MAC 地址 |
| tcpdump -A | Print packets as ASCII encoding以 ASCII 编码格式打印数据包 |
| tcpdump -xx | Display packets in hexadecimal format以十六进制格式显示数据包 |
| tcpdump -X | Show packets in both hexadecimal and ASCII formats 以十六进制和 ASCII 格式显示数据包 |
greater LENGTH: Filters packets that have a length greater than or equal to the specified length
greater LENGTH:过滤长度大于或等于指定长度的数据包less LENGTH: Filters packets that have a length less than or equal to the specified length
less LENGTH:过滤长度小于或等于指定长度的数据包。