db.user.deleteOne({ "age" : 2828})的explain()输出结果如下,deleteOne执行的策略是DELETE>FETCH>IXSCAN,先按照FETCH>IXSCAN读取数据,再根据DELETE删除。
mongo/db/exec/delete.cpp的doWork,这个是DeleteStage获取自己儿子节点FetchStage,执行儿子节点FetchStage,FetchStage的doWork方法继续寻找自己儿子节点IndexScan,继续执行儿子节点IndexScan。DeleteStage获取到Document文档,继续调用collection()->deleteDocument()进行文档删除。
db.user.deleteOne({ "age" : 2828})核心类是DeleteStage,mongo/db/exec/delete.cpp的doWork,主要逻辑1、WriteUnitOfWork创建了一个写事务单元,这是 MongoDB 实现 ACID 特性的关键机制之一。在这个事务单元内的所有操作会被视为一个原子操作,要么全部成功提交,要么失败时全部回滚;2、调用集合的deleteDocument方法执行删除操作。getOpObserver()->onDelete通过 MongoDB 的 OpObserver 机制,在文档删除操作执行前触发自定义逻辑,是 MongoDB 提供的用于监控和扩展数据操作行为的重要接口,常见于数据库插件、审计工具或自定义业务逻辑的实现中
1、删除代码触发OpObserver者
mongo/db/catalog/collection_impl.cpp的deleteDocument代码
cpp
void CollectionImpl::deleteDocument(OperationContext* opCtx,
StmtId stmtId,
RecordId loc,
OpDebug* opDebug,
bool fromMigrate,
bool noWarn,
Collection::StoreDeletedDoc storeDeletedDoc) {
if (isCapped()) {
log() << "failing remove on a capped ns " << _ns;
uasserted(10089, "cannot remove from a capped collection");
return;
}
Snapshotted<BSONObj> doc = docFor(opCtx, loc);
getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()->aboutToDelete(opCtx, ns(), doc.value());
boost::optional<BSONObj> deletedDoc;
if (storeDeletedDoc == Collection::StoreDeletedDoc::On) {
deletedDoc.emplace(doc.value().getOwned());
}
int64_t keysDeleted;
_indexCatalog->unindexRecord(opCtx, doc.value(), loc, noWarn, &keysDeleted);
_recordStore->deleteRecord(opCtx, loc);
getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()->onDelete(
opCtx, ns(), uuid(), stmtId, fromMigrate, deletedDoc);
if (opDebug) {
opDebug->additiveMetrics.incrementKeysDeleted(keysDeleted);
}
}getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()->aboutToDelete(opCtx, ns(), doc.value());在删除前调用,此时文档还存在,可用于实现复制、审计等功能。
getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()->onDelete(opCtx, ns(), uuid(), stmtId, fromMigrate, deletedDoc);在删除后调用,可用于触发变更流 (Change Streams) 等功能。
在 MongoDB中,OpObserver(操作观察者)是一个核心接口,用于监听数据库的各种操作事件 。通过getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()获取的观察者实例注册了一系列与数据库操作相关的监听服务。mongo/db/op_observer.h定义代码如下:
cpp
namespace mongo {
struct InsertStatement;
class OperationContext;
namespace repl {
class OpTime;
} // namespace repl
/**
* Holds document update information used in logging.
*/
struct OplogUpdateEntryArgs {
CollectionUpdateArgs updateArgs;
NamespaceString nss;
CollectionUUID uuid;
OplogUpdateEntryArgs(CollectionUpdateArgs updateArgs, NamespaceString nss, CollectionUUID uuid)
: updateArgs(std::move(updateArgs)), nss(std::move(nss)), uuid(std::move(uuid)) {}
};
struct TTLCollModInfo {
Seconds expireAfterSeconds;
Seconds oldExpireAfterSeconds;
std::string indexName;
};
class OpObserver {
public:
enum class CollectionDropType {
// The collection is being dropped immediately, in one step.
kOnePhase,
// The collection is being dropped in two phases, by renaming to a drop pending collection
// which is registered to be reaped later.
kTwoPhase,
};
virtual ~OpObserver() = default;
virtual void onCreateIndex(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
CollectionUUID uuid,
BSONObj indexDoc,
bool fromMigrate) = 0;
virtual void onStartIndexBuild(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
CollectionUUID collUUID,
const UUID& indexBuildUUID,
const std::vector<BSONObj>& indexes,
bool fromMigrate) = 0;
virtual void onCommitIndexBuild(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
CollectionUUID collUUID,
const UUID& indexBuildUUID,
const std::vector<BSONObj>& indexes,
bool fromMigrate) = 0;
virtual void onAbortIndexBuild(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
CollectionUUID collUUID,
const UUID& indexBuildUUID,
const std::vector<BSONObj>& indexes,
const Status& cause,
bool fromMigrate) = 0;
virtual void onInserts(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
std::vector<InsertStatement>::const_iterator begin,
std::vector<InsertStatement>::const_iterator end,
bool fromMigrate) = 0;
virtual void onUpdate(OperationContext* opCtx, const OplogUpdateEntryArgs& args) = 0;
virtual void aboutToDelete(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
const BSONObj& doc) = 0;
virtual void onDelete(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
StmtId stmtId,
bool fromMigrate,
const boost::optional<BSONObj>& deletedDoc) = 0;
virtual void onInternalOpMessage(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
const boost::optional<UUID> uuid,
const BSONObj& msgObj,
const boost::optional<BSONObj> o2MsgObj) = 0;
void onOpMessage(OperationContext* opCtx, const BSONObj& msgObj) {
onInternalOpMessage(opCtx, {}, boost::none, msgObj, boost::none);
}
virtual void onCreateCollection(OperationContext* opCtx,
Collection* coll,
const NamespaceString& collectionName,
const CollectionOptions& options,
const BSONObj& idIndex,
const OplogSlot& createOpTime) = 0;
virtual void onCollMod(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
const BSONObj& collModCmd,
const CollectionOptions& oldCollOptions,
boost::optional<TTLCollModInfo> ttlInfo) = 0;
virtual void onDropDatabase(OperationContext* opCtx, const std::string& dbName) = 0;
virtual repl::OpTime onDropCollection(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& collectionName,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
std::uint64_t numRecords,
CollectionDropType dropType) = 0;
virtual void onDropIndex(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
const std::string& indexName,
const BSONObj& indexInfo) = 0;
virtual repl::OpTime preRenameCollection(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& fromCollection,
const NamespaceString& toCollection,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
OptionalCollectionUUID dropTargetUUID,
std::uint64_t numRecords,
bool stayTemp) = 0;
virtual void postRenameCollection(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& fromCollection,
const NamespaceString& toCollection,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
OptionalCollectionUUID dropTargetUUID,
bool stayTemp) = 0;
virtual void onRenameCollection(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& fromCollection,
const NamespaceString& toCollection,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
OptionalCollectionUUID dropTargetUUID,
std::uint64_t numRecords,
bool stayTemp) = 0;
virtual void onApplyOps(OperationContext* opCtx,
const std::string& dbName,
const BSONObj& applyOpCmd) = 0;
virtual void onEmptyCapped(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& collectionName,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid) = 0;
virtual void onUnpreparedTransactionCommit(
OperationContext* opCtx, const std::vector<repl::ReplOperation>& statements) = 0;
virtual void onPreparedTransactionCommit(
OperationContext* opCtx,
OplogSlot commitOplogEntryOpTime,
Timestamp commitTimestamp,
const std::vector<repl::ReplOperation>& statements) noexcept = 0;
virtual void onTransactionPrepare(OperationContext* opCtx,
const std::vector<OplogSlot>& reservedSlots,
std::vector<repl::ReplOperation>& statements) = 0;
virtual void onTransactionAbort(OperationContext* opCtx,
boost::optional<OplogSlot> abortOplogEntryOpTime) = 0;
...
virtual void onReplicationRollback(OperationContext* opCtx,
const RollbackObserverInfo& rbInfo) = 0;
struct Times;
protected:
class ReservedTimes;
};
struct OpObserver::Times {
static Times& get(OperationContext*);
std::vector<repl::OpTime> reservedOpTimes;
private:
friend OpObserver::ReservedTimes;
// Because `OpObserver`s are re-entrant, it is necessary to track the recursion depth to know
// when to actually clear the `reservedOpTimes` vector, using the `ReservedTimes` scope object.
int _recursionDepth = 0;
};
class OpObserver::ReservedTimes {
ReservedTimes(const ReservedTimes&) = delete;
ReservedTimes& operator=(const ReservedTimes&) = delete;
public:
explicit ReservedTimes(OperationContext* const opCtx);
~ReservedTimes();
const Times& get() const {
return _times;
}
private:
Times& _times;
};
} // namespace mongo2、OpObserver 注册的核心监听服务
2.1. 数据库操作监听
onCreateCollection/onCollMod/preRenameCollection/onRenameCollection/onDropCollection。监听集合创建、修改、重命名,删除动作。
2.2. 数据操作监听
onInsert:插入操作前后的回调,用于审计、权限控制或数据验证。onUpdate:更新操作前后的回调,可获取更新前和更新后的数据。aboutToDelete/onDelete:删除操作前后的回调(如用户之前代码中使用的场景)。
2.3. 事务与并发控制监听
onUnpreparedTransactionCommit/onPreparedTransactionCommit/onTransactionPrepare/onTransactionAbort:监听事务生命周期,支持分布式事务的跟踪和日志记录。
2.4. 索引与存储相关监听
onCreateIndex/onDropIndex:监听索引创建和删除事件,用于索引管理和元数据跟踪。onStartIndexBuild/onCommitIndexBuild/onAbortIndexBuild:监听索引构建过程,可用于监控长时间运行的索引操作。
2.5. 索引与存储相关监听
onDropDatabase:监听数据库删除事件
mongod启动db.cpp入口流程是:main-> mongoDbMain -> initAndListen -> _initAndListen; _initAndListen初始化OpObserverRegistry对象,OpObserverRegistry增加观察者OpObserverShardingImpl、AuthOpObserver...
mongo/db/db.cpp的_initAndListen观察者注册代码如下:
cpp
auto serviceContext = getGlobalServiceContext();
serviceContext->setFastClockSource(FastClockSourceFactory::create(Milliseconds(10)));
auto opObserverRegistry = std::make_unique<OpObserverRegistry>();
opObserverRegistry->addObserver(std::make_unique<OpObserverShardingImpl>());
opObserverRegistry->addObserver(std::make_unique<AuthOpObserver>());
if (serverGlobalParams.clusterRole == ClusterRole::ShardServer) {
opObserverRegistry->addObserver(std::make_unique<ShardServerOpObserver>());
} else if (serverGlobalParams.clusterRole == ClusterRole::ConfigServer) {
opObserverRegistry->addObserver(std::make_unique<ConfigServerOpObserver>());
}
setupFreeMonitoringOpObserver(opObserverRegistry.get());
serviceContext->setOpObserver(std::move(opObserverRegistry));常见OpObserver关系图如下:
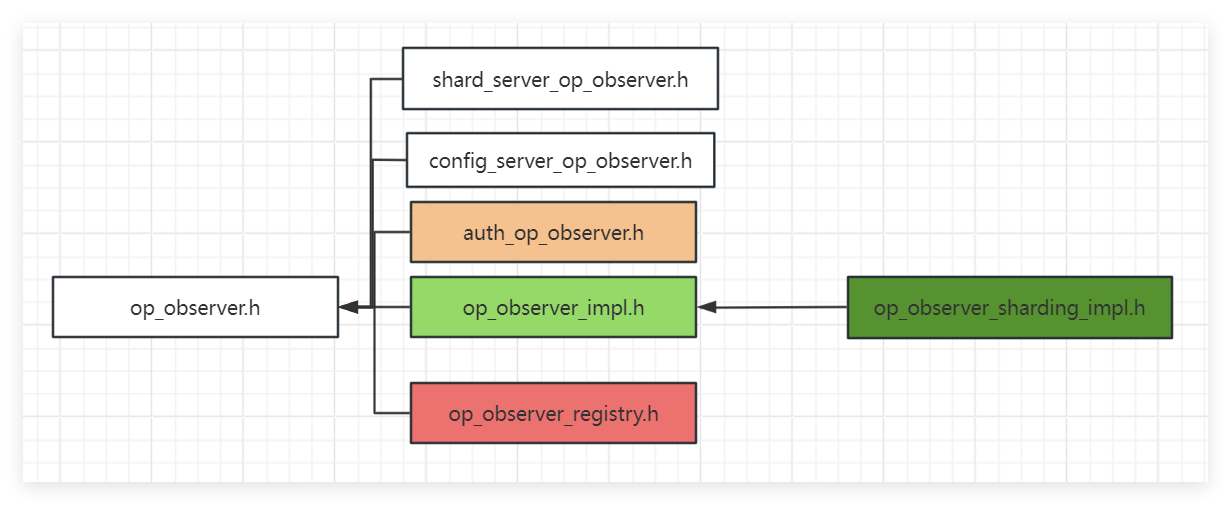
serviceContext->setOpObserver(std::move(opObserverRegistry));上面观察者注册的是OpObserverRegistry对象。
getGlobalServiceContext()->getOpObserver()获取的对象是OpObserverRegistry;
3、执行观察者****OpObserver 监听流程
mongo/db/op_observer_impl.cpp的代码如下:
cpp
void aboutToDelete(OperationContext* const opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
const BSONObj& doc) override {
ReservedTimes times{opCtx};
for (auto& o : _observers){
o->aboutToDelete(opCtx, nss, doc);
}
}
void onDelete(OperationContext* const opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
StmtId stmtId,
bool fromMigrate,
const boost::optional<BSONObj>& deletedDoc) override {
ReservedTimes times{opCtx};
for (auto& o : _observers)
o->onDelete(opCtx, nss, uuid, stmtId, fromMigrate, deletedDoc);
}MongoDB中OpObserverImpl类的onDelete方法实现,其主要功能是在删除操作发生时记录操作日志,并根据不同情况进行相应处理。/mongo/db/op_observer_impl.cpp中onDelete代码如下:
cpp
void OpObserverImpl::onDelete(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
StmtId stmtId,
bool fromMigrate,
const boost::optional<BSONObj>& deletedDoc) {
auto& documentKey = documentKeyDecoration(opCtx);
invariant(!documentKey.isEmpty());
std::cout<<"conca OpObserverImpl aboutToDelete...documentKey="<<documentKey<<std::endl;
auto txnParticipant = TransactionParticipant::get(opCtx);
const bool inMultiDocumentTransaction =
txnParticipant && opCtx->writesAreReplicated() && txnParticipant.transactionIsOpen();
OpTimeBundle opTime;
if (inMultiDocumentTransaction) {
...
} else {
std::cout<<"conca OpObserverImpl aboutToDelete...replLogDelete"<<std::endl;
opTime = replLogDelete(opCtx, nss, uuid, stmtId, fromMigrate, deletedDoc);
SessionTxnRecord sessionTxnRecord;
sessionTxnRecord.setLastWriteOpTime(opTime.writeOpTime);
sessionTxnRecord.setLastWriteDate(opTime.wallClockTime);
onWriteOpCompleted(opCtx, std::vector<StmtId>{stmtId}, sessionTxnRecord);
}
...
}inMultiDocumentTransaction代码块 如果是多文档事务的一部分,将删除操作添加到事务操作列表中
replLogDelete代码块非事务操作则直接记录删除操作到 oplog,并更新会话事务记录。replLogDelete代码是 MongoDB 中处理删除操作日志记录的核心函数,主要功能是将删除操作写入操作日志(oplog)。这个函数在分布式环境中非常重要,因为 oplog 是 MongoDB 复制集和分片集群实现数据一致性的基础。
/mongo/db/op_observer_impl.cpp中replLogDelete代码如下:
cpp
/**
* Write oplog entry(ies) for the delete operation.
*/
OpTimeBundle replLogDelete(OperationContext* opCtx,
const NamespaceString& nss,
OptionalCollectionUUID uuid,
StmtId stmtId,
bool fromMigrate,
const boost::optional<BSONObj>& deletedDoc) {
MutableOplogEntry oplogEntry;
oplogEntry.setNss(nss);
oplogEntry.setUuid(uuid);
repl::OplogLink oplogLink;
repl::appendRetryableWriteInfo(opCtx, &oplogEntry, &oplogLink, stmtId);
OpTimeBundle opTimes;
if (deletedDoc && opCtx->getTxnNumber()) {
std::cout<<"conca OpObserverImpl aboutToDelete...replLogDelete...getTxnNumber is not null"<<std::endl;
MutableOplogEntry noopEntry = oplogEntry;
noopEntry.setOpType(repl::OpTypeEnum::kNoop);
noopEntry.setObject(deletedDoc.get());
auto noteOplog = logOperation(opCtx, &noopEntry);
opTimes.prePostImageOpTime = noteOplog;
oplogLink.preImageOpTime = noteOplog;
}
oplogEntry.setOpType(repl::OpTypeEnum::kDelete);
oplogEntry.setObject(documentKeyDecoration(opCtx));
oplogEntry.setFromMigrateIfTrue(fromMigrate);
// oplogLink could have been changed to include preImageOpTime by the previous no-op write.
repl::appendRetryableWriteInfo(opCtx, &oplogEntry, &oplogLink, stmtId);
opTimes.writeOpTime = logOperation(opCtx, &oplogEntry);
opTimes.wallClockTime = oplogEntry.getWallClockTime();
return opTimes;
}if (deletedDoc && opCtx->getTxnNumber()) {}代码块:如果删除的文档存在且当前操作属于事务(有事务编号),创建一个特殊的 noop 类型操作日志,记录被删除文档的完整内容,这一步是为了支持 MongoDB 的变更流(Change Streams)和文档级别的回滚。
oplogEntry.setOpType(repl::OpTypeEnum::kDelete)代码块:记录删除操作:设置操作类型为 kDelete,设置删除的文档键documentKey(documentKeyDecoration(opCtx)值是{ _id: ObjectId('681dc7c924a18a334118bc27') }),调用 logOperation 函数将删除操作写入 oplog,返回操作时间(OpTime)和时钟时间。
4、oplog是MongoDB 实现复制集和分片集群的基础
/mongo/db/op_observer_impl.cpp中logOperation代码如下:
cpp
repl::OpTime logOperation(OperationContext* opCtx, MutableOplogEntry* oplogEntry) {
oplogEntry->setWallClockTime(getWallClockTimeForOpLog(opCtx));
auto& times = OpObserver::Times::get(opCtx).reservedOpTimes;
auto opTime = repl::logOp(opCtx, oplogEntry);
times.push_back(opTime);
return opTime;
}这段代码是 MongoDB 中将操作写入 oplog(操作日志)的核心函数之一。oplog 是 MongoDB 实现复制集和分片集群的基础,所有对数据的变更都会记录在这里,用于在副本之间同步数据。
-
设置操作时间戳:
- 获取当前操作的时钟时间(wall clock time)
- 将这个时间戳设置到 oplog 条目中
-
预留操作时间:
- 从操作上下文中获取
OpObserver::Times结构 - 这个结构包含一个
reservedOpTimes列表,用于记录操作的时间戳
- 从操作上下文中获取
-
写入操作日志:
- 调用
repl::logOp函数将 oplog 条目写入磁盘 - 这个函数会分配一个唯一的操作时间戳(OpTime)
- 调用
-
记录操作时间:
- 将分配的 OpTime 添加到预留时间列表中
- 返回这个 OpTime 给调用者