
大家好,我是花姐。经常有小伙伴问我:"股票的支撑位、压力位怎么找?有没有办法用 Python 程序自动算出来?"
之前我们讲了通过枢轴点、局部极值 2种方法来确定压力和支撑位置,今天我们来说说均线簇法确定压力和支撑位置。
开始前的准备
我这里用的行情数据源是 xtquant + miniQMT 。 后续示例里会用到一些常见的 Python 库:pandas, numpy, matplotlib,进阶部分还会涉及 scipy, sklearn。在实际运行代码之前,记得先把环境配置好:
bash
pip install pandas numpy matplotlib scipy scikit-learn xtquant这样就能避免因为依赖缺失导致的报错啦。
以下是一个基于xtquant + miniQMT获取股票行情的方法,后面的行情Dataframe数据都会通过这个方法来获取:
python
def get_hq(code,start_date='19900101',period='1d',dividend_type='front_ratio',count=-1):
'''
基于xtquant下载某个股票的历史行情
盘中运行最后一个K里存了最新的行情
period 1d 1w 1mon
dividend_type - 除权方式,用于K线数据复权计算,对tick等其他周期数据无效
none 不复权
front 前复权
back 后复权
front_ratio 等比前复权
back_ratio 等比后复权
'''
xtdata.enable_hello = False
xtdata.download_history_data(stock_code=code, period='1d',incrementally=True)
history_data = xtdata.get_market_data_ex(['open','high','low','close','volume','amount','preClose','suspendFlag'],[code],period=period,start_time=start_date,count=count,dividend_type=dividend_type)
print(history_data)
df = history_data[code]
df.index = pd.to_datetime(df.index.astype(str), format='%Y%m%d')
df['date'] = df.index
return df1. 由来与直观理解
在股市里,价格上涨或者下跌往往会遇到一些"阻力"或"支撑",这个概念大家可能听得多,但怎么量化呢?
于是就有了均线簇的概念:
- 我们把多条均线同时画在一张K线图上
- 当这些均线在某个价格区间聚集时,就形成了"均线簇"
- 均线簇的密集区往往对应压力位(价格上不去)或支撑位(价格不跌破)
直观理解:
- 想象几条橡皮筋同时捆在股票价格上方或下方,价格想突破或跌破时就像要拉开橡皮筋,会有阻力
- 这就是均线簇在做的事情:用过去价格的平均值,画出价格心理关口
2. 数学定义与原理
- 简单移动平均线(SMA)
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> S M A n ( t ) = 1 n ∑ i = 0 n − 1 P t − i SMA_n(t) = \frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=0}^{n-1} P_{t-i} </math>SMAn(t)=n1i=0∑n−1Pt−i
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> n n </math>n 是窗口大小(天数)
- <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> P t P_t </math>Pt 是第 <math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML"> t t </math>t 天的收盘价
- 均线簇的形成条件
- 当多条不同周期均线之间的价格差异非常小,比如5日、10日、20日、30日均线同时靠近同一个价格区间
- 数学上可以用均线标准差 或者均线最大最小差值来量化:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> MA_spread = max ( M A 1 , M A 2 , . . . , M A n ) − min ( M A 1 , M A 2 , . . . , M A n ) \text{MA\_spread} = \max(MA_1, MA_2, ..., MA_n) - \min(MA_1, MA_2, ..., MA_n) </math>MA_spread=max(MA1,MA2,...,MAn)−min(MA1,MA2,...,MAn)
- 当
MA_spread很小,说明均线聚集形成簇
原理:
- 均线簇反映了市场短中期均衡状态
- 多空力量在这个价格附近相对均衡
- 突破均线簇往往伴随成交量放大,是典型的趋势启动信号
3. 常用算法
- 简单聚合均线
- 选择5条或以上不同周期均线
- 计算均线最大最小差值
- 小于阈值时判定为均线簇
- 均线簇密度算法(进阶)
- 用均线标准差衡量密集度:
<math xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML" display="block"> MA_std = std ( M A 1 , M A 2 , . . . , M A n ) \text{MA\_std} = \text{std}(MA_1, MA_2, ..., MA_n) </math>MA_std=std(MA1,MA2,...,MAn)
- 标准差越小,均线聚集越密集
- 可以设置动态阈值,如过去20日均值的20%
- 支撑/压力判定
- 均线簇在股价上方 → 压力位
- 均线簇在股价下方 → 支撑位
4. 实战Python代码
均线簇 ≈ 市场在蓄力,方向不确定,但一旦突破,往往容易走出一波行情 🚀
4.1 使用简单聚合均线
计算思路
-
1 算均线 → 5日、10日、20日、30日、60日
-
2.判断是否簇 → 如果这些均线的最高值和最低值之间的差距小于价格的1%,就算是"簇"。
-
3.找第一个点 → 我们只想标记簇刚出现的时候(而不是整个簇区域)。
示例代码
python
from xtquant import xtdata
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mplfinance as mpf
def detect_ma_clusters(df, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60], price_col='close', threshold_pct=0.01):
"""
根据均线计算均线簇,并只返回连续簇的第一个点
"""
df = df.copy()
print(df)
# 1. 计算均线
for period in ma_periods:
df[f'MA_{period}'] = df[price_col].rolling(window=period).mean()
df = df.dropna(subset=[f'MA_{p}' for p in ma_periods])
print(df)
ma_cols = [f'MA_{p}' for p in ma_periods]
# 2. 计算均线最大最小值及差值
df['MA_max'] = df[ma_cols].max(axis=1)
df['MA_min'] = df[ma_cols].min(axis=1)
df['MA_spread'] = df['MA_max'] - df['MA_min']
# 3. 判断均线簇(相对价格)
df['Cluster'] = df['MA_spread'] / df[price_col] < threshold_pct
# 4. 只取连续簇的第一个值
# shift(1) 表示前一天的 Cluster 状态
df['Cluster_start'] = (df['Cluster'] & ~df['Cluster'].shift(1).fillna(False))
# 取出第一个点
cluster = df.loc[df['Cluster_start'], price_col]
return cluster
def draw_ma_clusters(df, cluster, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60]):
# mplfinance 要求 DataFrame 索引为日期,并包含 Open, High, Low, Close
mpf_data = df[['open','high','low','close','volume']].copy()
mpf_data.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(mpf_data.index)
apds = []
# 准备支撑位/压力位标记
cluster_y = np.full(len(mpf_data), np.nan)
# 填充支撑位/压力位对应价格
if len(cluster) > 0:
for date, price in cluster.items():
if date in mpf_data.index:
idx = mpf_data.index.get_loc(date)
cluster_y[idx] = price
apds.append(mpf.make_addplot(cluster_y, type='scatter', markersize=80, marker='^', color='black'))
mc = mpf.make_marketcolors(up='r', down='g', inherit=True)
s = mpf.make_mpf_style(marketcolors=mc,rc={'font.family': 'SimHei'})
mpf.plot(
mpf_data,
type='candle',
style=s,
title="K线及均线簇",
mav=ma_periods,
addplot=apds,
volume=True,
figsize=(14,7)
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
code = '600519.SH' # 贵州茅台
df = get_hq(code, start_date='20200101', period='1d', count=200)
cluster = detect_ma_clusters(df, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60])
draw_ma_clusters(df, cluster, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60])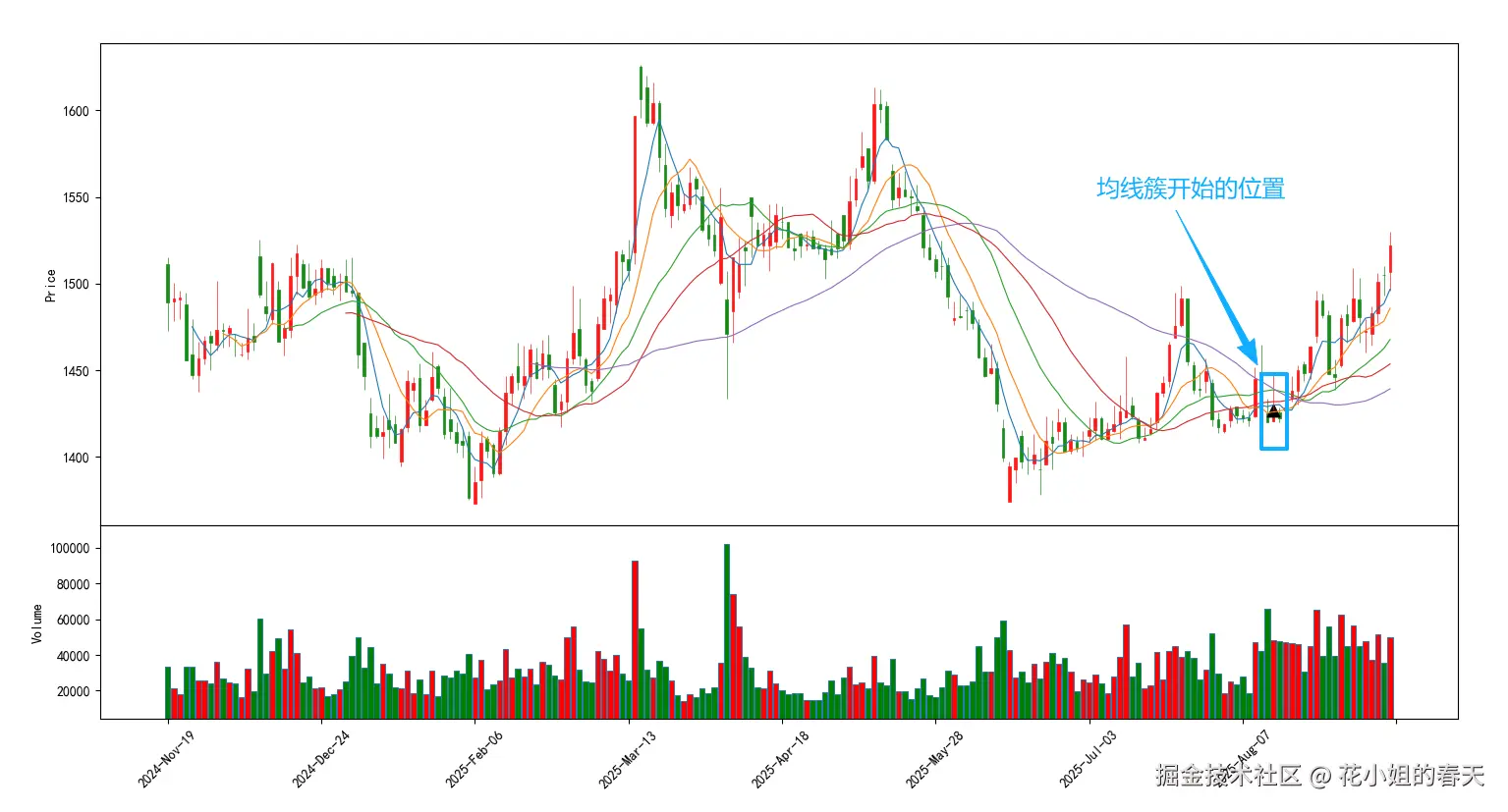
4.2 使用均线簇密度算法(进阶)
计算思路
-
计算不同周期的均线;
-
计算这些均线的标准差
MA_std; -
用动态阈值:
MA_std < rolling_mean(MA_std, 20) * factor来判定是否属于"均线簇"; -
依然只取连续簇的第一个点。
示例代码
python
from xtquant import xtdata
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mplfinance as mpf
def draw_ma_clusters(df, cluster, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60]):
# mplfinance 要求 DataFrame 索引为日期,并包含 Open, High, Low, Close
mpf_data = df[['open','high','low','close','volume']].copy()
mpf_data.index = pd.DatetimeIndex(mpf_data.index)
apds = []
# 准备支撑位/压力位标记
cluster_y = np.full(len(mpf_data), np.nan)
# 填充支撑位/压力位对应价格
# 支撑位绘制
if len(cluster) > 0:
for date, price in cluster.items():
if date in mpf_data.index:
idx = mpf_data.index.get_loc(date)
cluster_y[idx] = price
apds.append(mpf.make_addplot(cluster_y, type='scatter', markersize=80, marker='^', color='black'))
mc = mpf.make_marketcolors(up='r', down='g', inherit=True)
s = mpf.make_mpf_style(marketcolors=mc,rc={'font.family': 'SimHei'})
mpf.plot(
mpf_data,
type='candle',
style=s,
title="K线及均线簇",
mav=ma_periods,
addplot=apds,
volume=True,
figsize=(14,7)
)
def detect_ma_clusters_std(df, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60], price_col='close',
lookback=20, factor=0.2):
"""
基于均线标准差来检测均线簇,并只返回连续簇的第一个点
参数:
df : DataFrame,行情数据
ma_periods : list,均线周期
price_col : str,收盘价字段
lookback : int,动态阈值的回看窗口
factor : float,动态阈值因子(比如0.2表示20%)
"""
df = df.copy()
# 1. 计算均线
for period in ma_periods:
df[f'MA_{period}'] = df[price_col].rolling(window=period).mean()
df = df.dropna(subset=[f'MA_{p}' for p in ma_periods])
ma_cols = [f'MA_{p}' for p in ma_periods]
# 2. 计算均线标准差
df['MA_std'] = df[ma_cols].std(axis=1)
# 3. 计算动态阈值:过去 lookback 日 MA_std 均值 * factor
df['Threshold'] = df['MA_std'].rolling(window=lookback).mean() * factor
# 4. 判断均线簇
df['Cluster'] = df['MA_std'] < df['Threshold']
# 5. 只取连续簇的第一个点
df['Cluster_start'] = (df['Cluster'] & ~df['Cluster'].shift(1).fillna(False))
# 取出第一个点(收盘价作为簇的价格)
cluster = df.loc[df['Cluster_start'], price_col]
return cluster
if __name__ == "__main__":
code = '600519.SH' # 贵州茅台
df = get_hq(code, start_date='20200101', period='1d', count=200)
cluster = detect_ma_clusters_std(df, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60])
draw_ma_clusters(df, cluster, ma_periods=[5, 10, 20, 30, 60])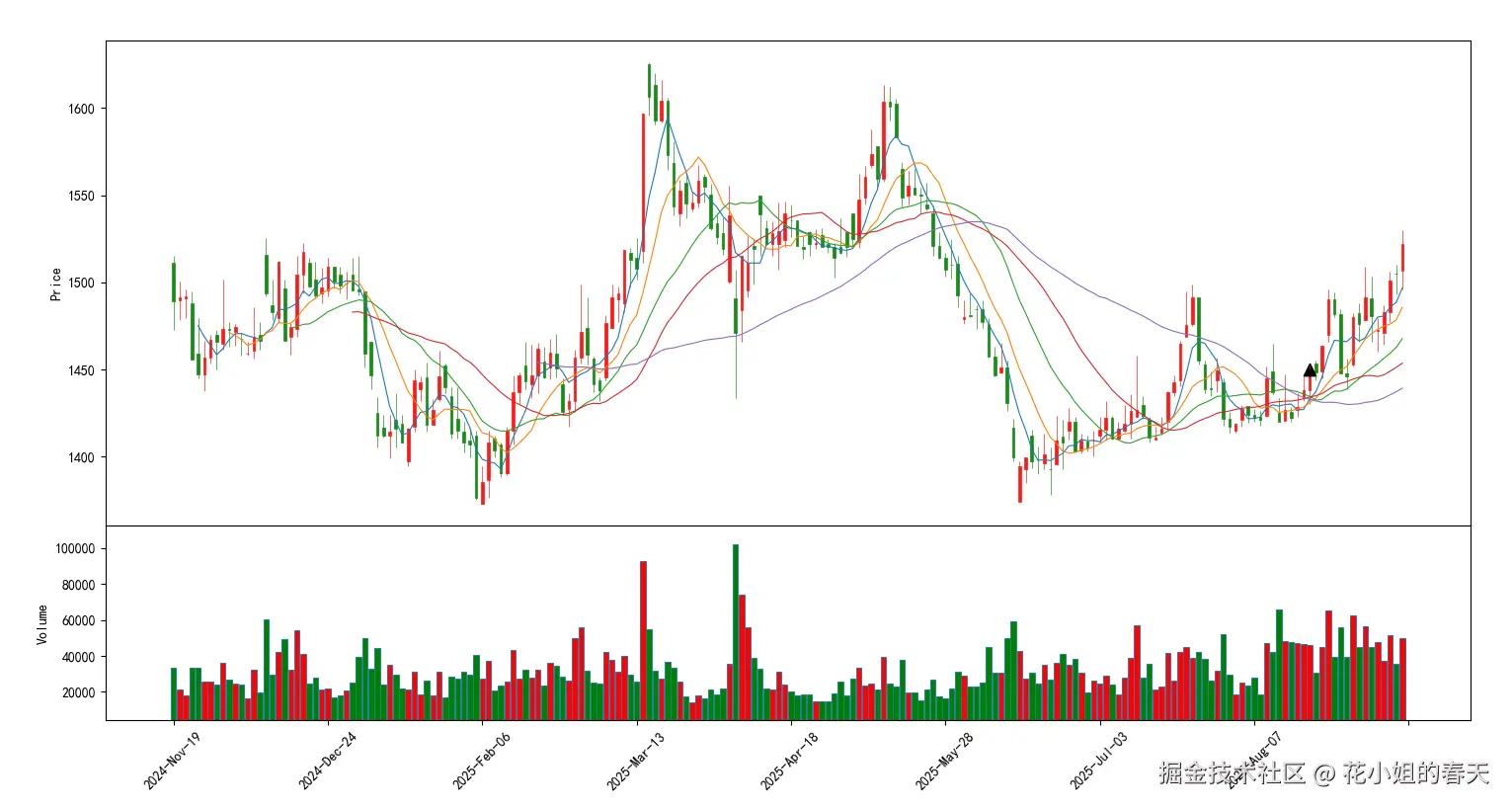
今天关于寻找股票支撑与压力位的均线簇法就写到这里了,更高级的用法有兴趣的朋友可以结合AI来自由探索,花姐这里只做简单科普抛砖引玉。
下一篇我们介绍通过斐波那契回撤寻找股票支撑与压力位。