驱动种类
| 字符设备 |
|---|
| 块设备 |
| 网络设备 |
编译到内核 或 编译成模块(.ko)
一:字符设备
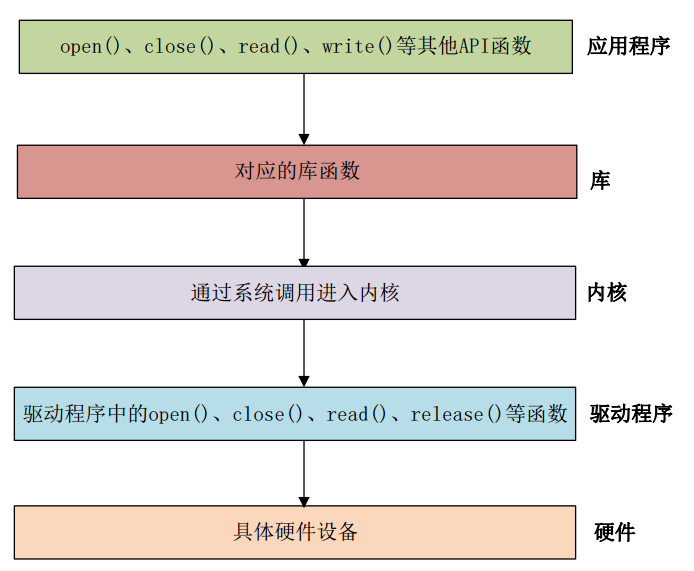
file_operations 的结构体
在 Linux 内核文件 include/linux/fs.h 中
c
struct file_operations {
struct module *owner;
loff_t (*llseek) (struct file *, loff_t, int);
ssize_t (*read) (struct file *, char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*write) (struct file *, const char __user *, size_t, loff_t *);
ssize_t (*read_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
ssize_t (*write_iter) (struct kiocb *, struct iov_iter *);
int (*iterate) (struct file *, struct dir_context *);
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *, struct poll_table_struct *);
long (*unlocked_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
long (*compat_ioctl) (struct file *, unsigned int, unsigned long);
int (*mmap) (struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*mremap)(struct file *, struct vm_area_struct *);
int (*open) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*flush) (struct file *, fl_owner_t id);
int (*release) (struct inode *, struct file *);
int (*fsync) (struct file *, loff_t, loff_t, int datasync);
int (*aio_fsync) (struct kiocb *, int datasync);
int (*fasync) (int, struct file *, int);
int (*lock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*sendpage) (struct file *, struct page *, int, size_t, loff_t *, int);
unsigned long (*get_unmapped_area)(struct file *, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long, unsigned long);
int (*check_flags)(int);
int (*flock) (struct file *, int, struct file_lock *);
ssize_t (*splice_write)(struct pipe_inode_info *, struct file *, loff_t *, size_t, unsigned int);
ssize_t (*splice_read)(struct file *, loff_t *, struct pipe_inode_info *, size_t, unsigned int);
int (*setlease)(struct file *, long, struct file_lock **, void **);
long (*fallocate)(struct file *file, int mode, loff_t offset,
loff_t len);
void (*show_fdinfo)(struct seq_file *m, struct file *f);
#ifndef CONFIG_MMU
unsigned (*mmap_capabilities)(struct file *);
#endif
};2.字符设备编写步骤
2.1驱动模块的入口和出口
c
module_init(led_init);
module_exit(led_exit);2.2字符设备注册与注销
register_chrdev 一次性注册了驱动的设备号、名字、和fops
__init *(void) & __exit *(void)函数实现
c
static int __init chrdevbase_init(void){
int retvalue = 0;
/* 注册字符设备驱动 */
retvalue = register_chrdev(CHRDEVBASE_MAJOR, CHRDEVBASE_NAME, &chrdevbase_fops);
if(retvalue < 0){
printk("chrdevbase driver register failed\r\n");
}
printk("chrdevbase init!\r\n");
return 0;
}
static void __exit chrdevbase_exit(void){
/* 注销字符设备驱动 */
unregister_chrdev(CHRDEVBASE_MAJOR, CHRDEVBASE_NAME);
printk("chrdevbase exit!\r\n");
}2.3添加 LICENSE 和作者信息
c
/*
* LICENSE和作者信息
*/
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
MODULE_AUTHOR("kai");2.4设备号分配
linux内核使用dev_t(types.h) 32位,高12位为主设备号,低20位为次设备号。
MDJPOR(dev_t)、MINOR、MKDEV(major,minor)
静态手动分配
有一些常用的设备号已经被 Linux 内核开发者给分配掉
了,具体分配的内容可以查看文档 Documentation/devices.txt。并不是说内核开发者已经分配掉
的主设备号我们就不能用了,具体能不能用还得看我们的硬件平台运行过程中有没有使用这个
主设备号,使用"cat /proc/devices"命令即可查看当前系统中所有已经使用了的设备号。
c
int register_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count, const char *name)
/*
参数 from 是要申请的起始设备号,也就是给定的设备号;参数 count 是要申请的数量,一
般都是一个;参数 name 是设备名字。
注销字符设备 之 后 要 释 放 掉 设 备 号 , 不 管 是 通 过 alloc_chrdev_region 函数还是
register_chrdev_region 函数申请的设备号,统一使用如下释放函数:
*/动态分配
c
int alloc_chrdev_region(dev_t *dev, unsigned baseminor, unsigned count, const char *name)
/*
dev:保存申请到的设备号。
baseminor:次设备号起始地址,alloc_chrdev_region 可以申请一段连续的多个设备号,这
些设备号的主设备号一样,但是次设备号不同,次设备号以 baseminor 为起始地址地址开始递
增。一般 baseminor 为 0,也就是说次设备号从 0 开始。
count:要申请的设备号数量。
name:设备名字。
*/释放
c
void unregister_chrdev_region(dev_t from, unsigned count)
/*
from:要释放的设备号。
count:表示从 from 开始,要释放的设备号数量。
*/2.5添加设备
实现设备的具体操作函数(file_operations )
register_chrdev 直接注册,参考2.2
cdev注册
在 Linux 中使用 cdev 结构体表示一个字符设备,cdev 结构体在 include/linux/cdev.h 文件中
c
struct cdev {
struct kobject kobj;
struct module *owner;
const struct file_operations *ops;
struct list_head list;
dev_t dev;
unsigned int count;
};
c
truct cdev test_cdev;
static const struct file_operations *_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
void cdev_init(struct cdev *cdev, const struct file_operations *fops)
int cdev_add(struct cdev *p, dev_t dev, unsigned count)
void cdev_del(struct cdev *p)//卸载驱动2.6创建设备节点
手动创建节点
bash
mknod /dev/chrdevbase c 200 0 创建节点 c字符型设备 200主设备号,0次设备号
ls /dev/chrdevbase -l"命令查看自动创建设备节点
mdev 机制
创建类
c
struct class *class_create (struct module *owner, const char *name)
void class_destroy(struct class *cls);创建设备
c
struct device *device_create(struct class *class,
struct device *parent,
dev_t devt,
void *drvdata,
const char *fmt, ...)
void device_destroy(struct class *class, dev_t devt)2.7驱动模块加载&卸载(linux加载)
bash
cp *.ko /lib/modules/4.1.15
depmod #depmod(depend module)可检测模块的相依性,供modprobe在安装模块时使用。
modprobe *.ko
lsmod#查看加载的ko
cat /proc/devices #查看所有驱动的设备号
bash
insmod **.ko#(只加载本身ko,不解决ko间的依赖关系)
modprobe #会解决ko之间的依赖关系
rmmod *.ko #卸载ko
modprobe -r *.ko #卸载依赖所有的ko2.8app调用
c
/* 打开驱动文件 */
fd = open(filename, O_RDWR);//filenme == /dev/chrdevbase
retvalue = read(fd, readbuf, 50);
retvalue = write(fd, writebuf, 50);
retvalue = close(fd);内核空间和应用空间内存访问
用户空间:32位系统中占用0~3GB,64位系统中占用低128T
内核空间:32位系统中占用3~4GB,64位系统中占用高128T
copy_from_user用于将数据从用户空间复制到内核空间:
copy_to_user用于将数据从内核空间复制到用户空间:
ioremap 函数用于获取指 定 物 理 地 址 空 间 对 应 的 虚 拟 地 址 空 间
iounmap 函数释放掉 ioremap 函数所做的映射
I/O 内存访问函数
使用 ioremap 函数将寄存器的物
理地址映射到虚拟地址以后,我们就可以直接通过指针访问这些地址,但是 Linux 内核不建议
这么做,而是推荐使用一组操作函数来对映射后的内存进行读写操作。
readb、readw 和 readl 这三个函数分别对应 8bit、16bit 和 32bit 读操作,参数 addr 就是要
读取写内存地址,返回值就是读取到的数据。
writeb、writew 和 writel 这三个函数分别对应 8bit、16bit 和 32bit 写操作,参数 value 是要
写入的数值,addr 是要写入的地址。