Ext系列文件系统
文章目录
- Ext系列文件系统
- 一、理解硬件
-
- [1.1 磁盘的物理结构](#1.1 磁盘的物理结构)
- [1.2 磁盘的存储结构](#1.2 磁盘的存储结构)
- [1.3 如何定位⼀个扇区呢?](#1.3 如何定位⼀个扇区呢?)
- [1.4 磁盘的逻辑结构](#1.4 磁盘的逻辑结构)
-
- [(1) 理解过程](#(1) 理解过程)
- [(2) 真实过程](#(2) 真实过程)
- [1.5 CHS && LBA 地址](#1.5 CHS && LBA 地址)
- 二、引入文件系统
-
- [2.1 引入"块"概念](#2.1 引入"块"概念)
- [2.2 引入"分区"概念](#2.2 引入"分区"概念)
- [2.3 引入"inode"概念](#2.3 引入"inode"概念)
- 三、ext2文件系统
-
- [3.1 宏观认识](#3.1 宏观认识)
- [3.2 Block Group](#3.2 Block Group)
- [3.3 块组内部构成](#3.3 块组内部构成)
-
- [3.3.1 超级块(Super Block)](#3.3.1 超级块(Super Block))
- [3.3.2 GDT(Group Descriptor Table)](#3.3.2 GDT(Group Descriptor Table))
- [3.3.3 位块图(Block Bitmap)](#3.3.3 位块图(Block Bitmap))
- [3.3.4 inode位图(Inode Bitmap)](#3.3.4 inode位图(Inode Bitmap))
- [3.3.5 i 节点表(Inode Table)](#3.3.5 i 节点表(Inode Table))
- [3.3.6 Date Block](#3.3.6 Date Block)
- [3.4 inode和datablock映射(弱化)](#3.4 inode和datablock映射(弱化))
- [3.5 目录与文件名](#3.5 目录与文件名)
- [3.6 路径解析](#3.6 路径解析)
- [3.7 路径缓存](#3.7 路径缓存)
- [3.8 挂载分区](#3.8 挂载分区)
- 四、软硬链接
-
- [4.1 硬链接](#4.1 硬链接)
- [4.2 软链接](#4.2 软链接)
- [4.3 软硬链接对比](#4.3 软硬链接对比)
- [4.4 软硬链接用途](#4.4 软硬链接用途)
一、理解硬件


1.1 磁盘的物理结构
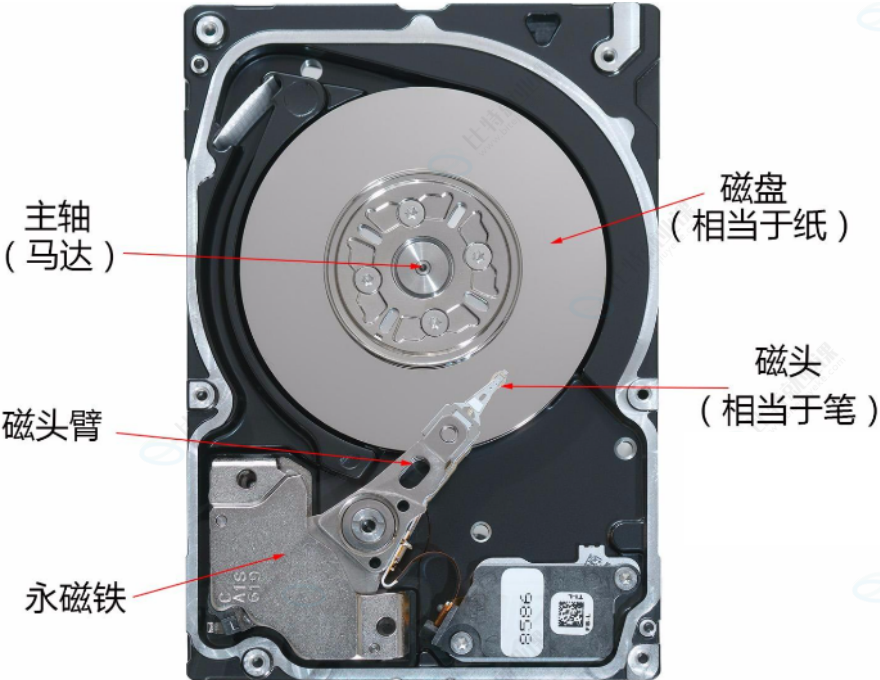
1.2 磁盘的存储结构
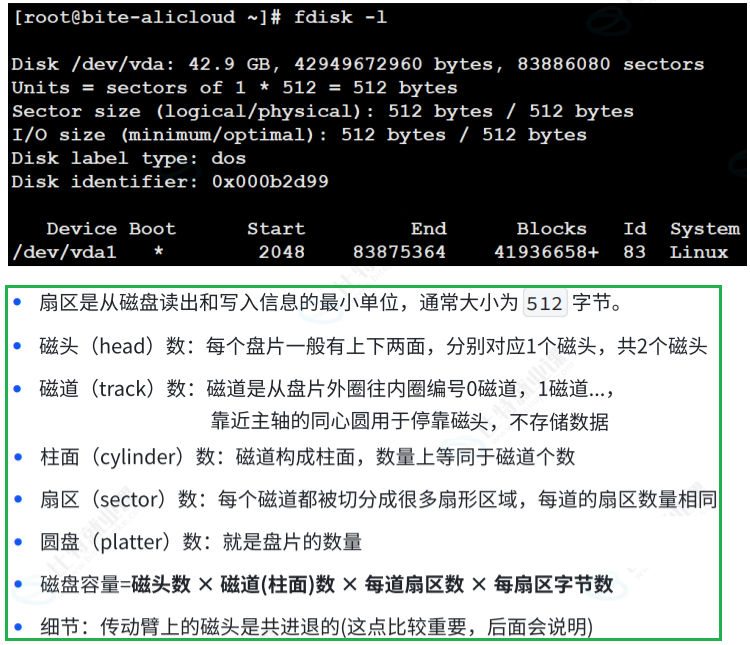
磁盘存储的基本单位是:扇区(512字节)
磁头在传动臂的带动下,共进退
磁盘写入的时候,是向柱面进行批量写入的
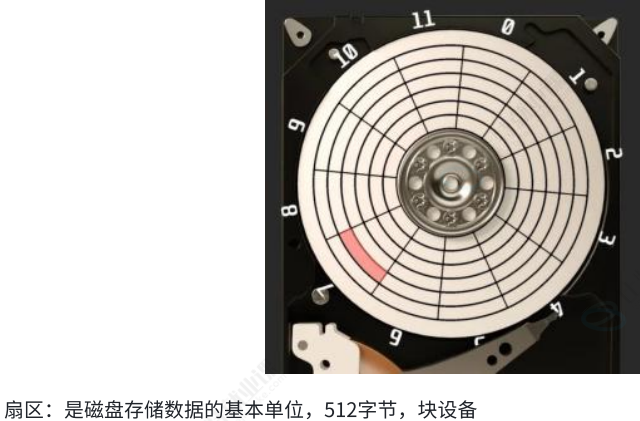

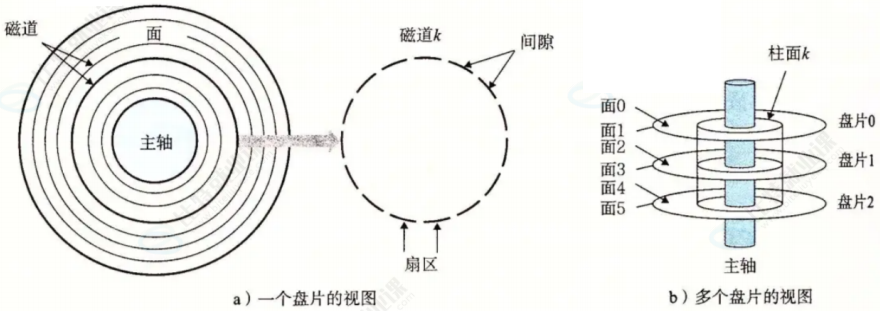

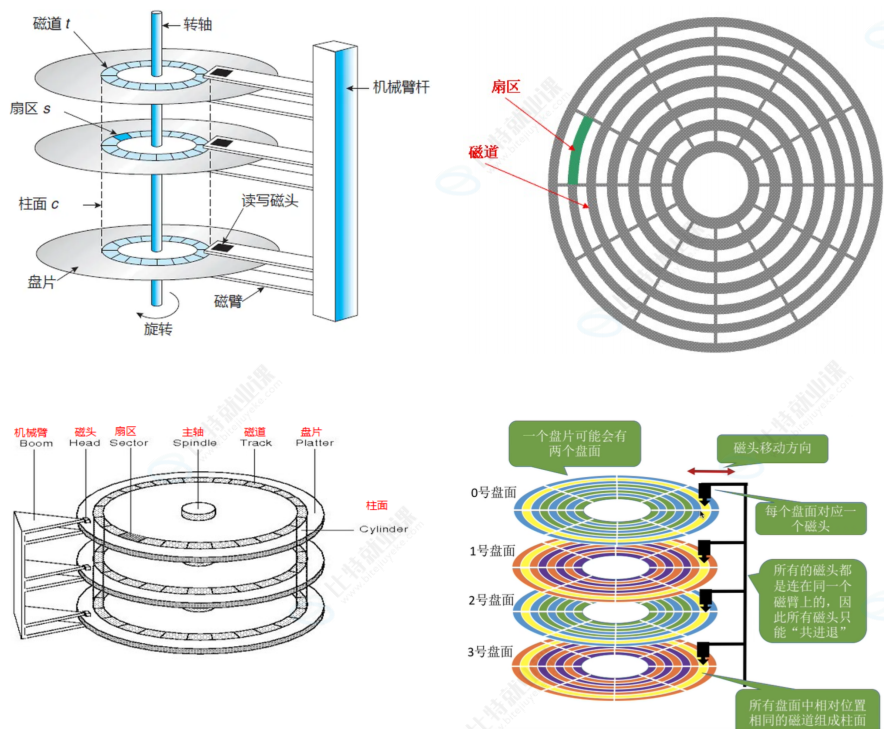
1.3 如何定位⼀个扇区呢?
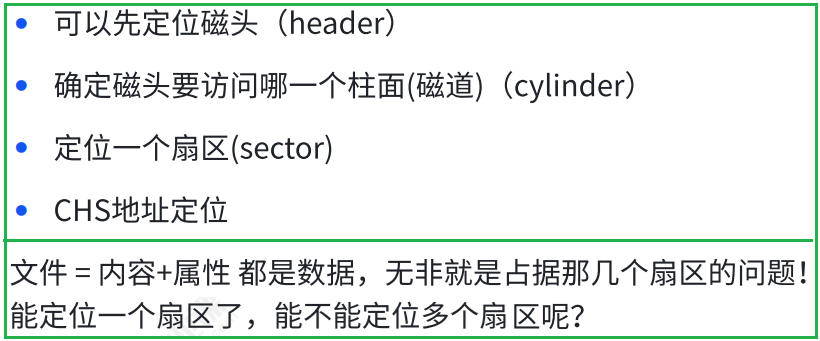

1.4 磁盘的逻辑结构
OS文件系统访问磁盘,不以扇区为单位,而是以块为单位,一般是4KB
(可以调整) , 连续八个扇区
(1) 理解过程
磁带上面可以存数据,我们可以把磁带拉直,形成线性结构
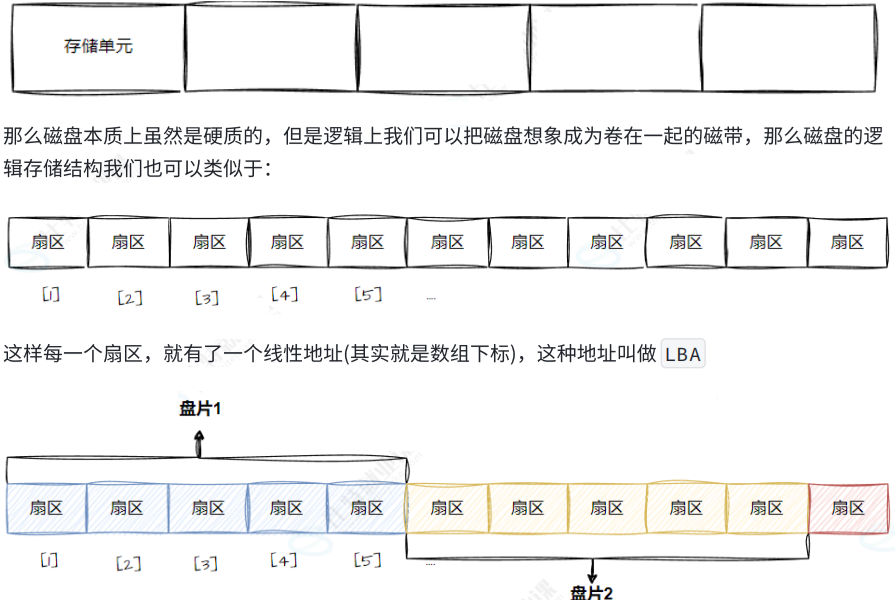
(2) 真实过程
一个细节:传动臂上的磁头是共进退的
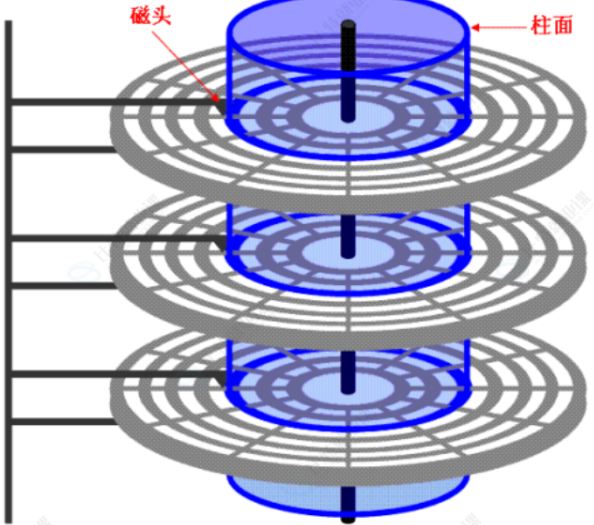


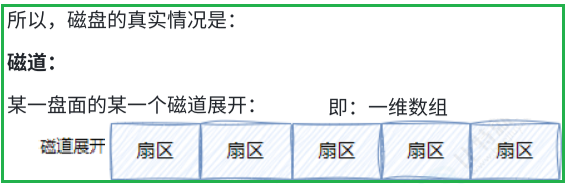
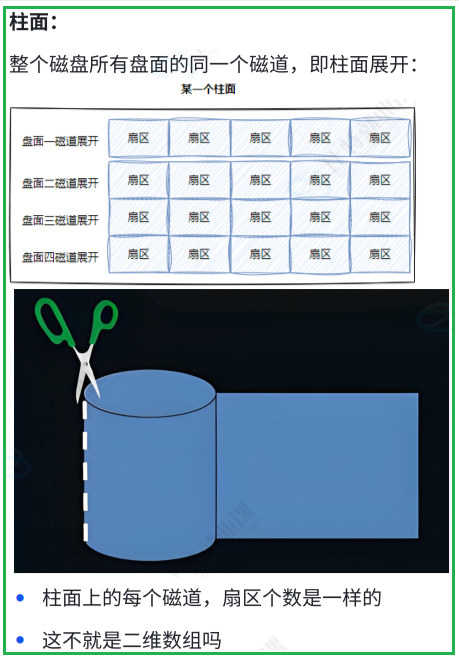

1.5 CHS && LBA 地址

二、引入文件系统
2.1 引入"块"概念
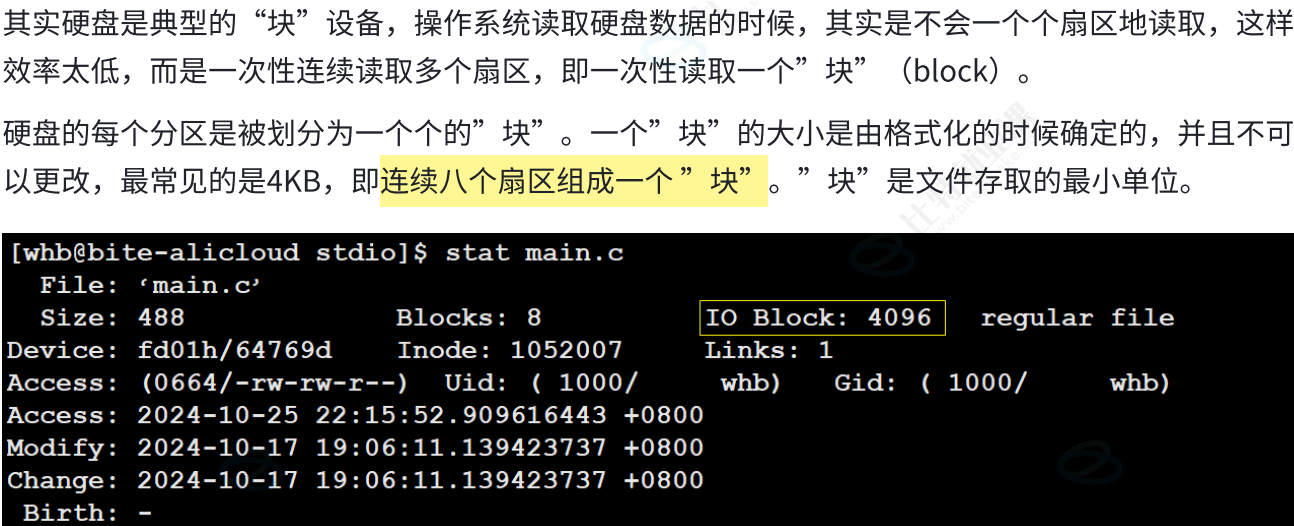

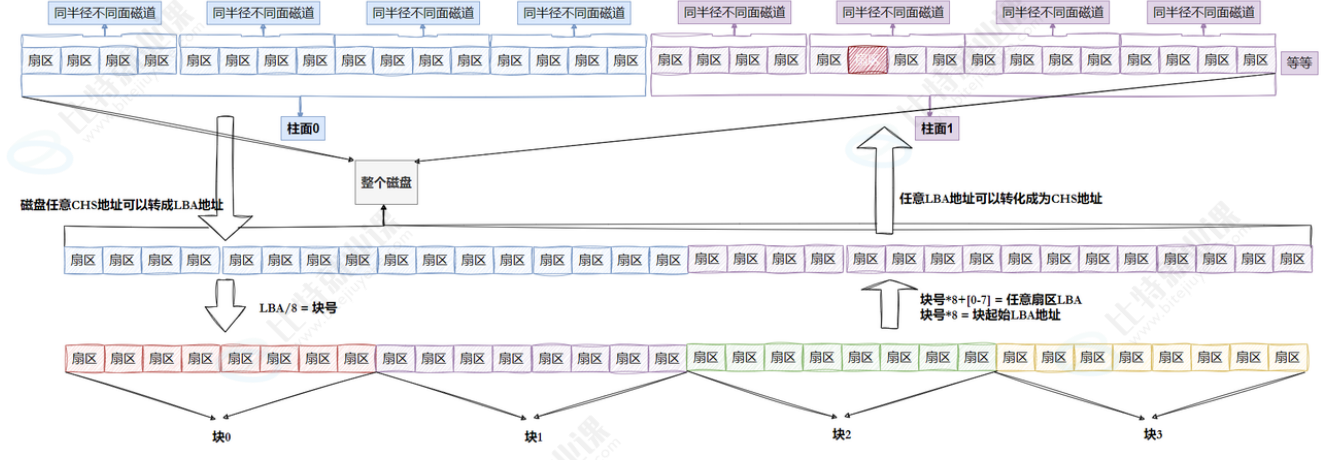
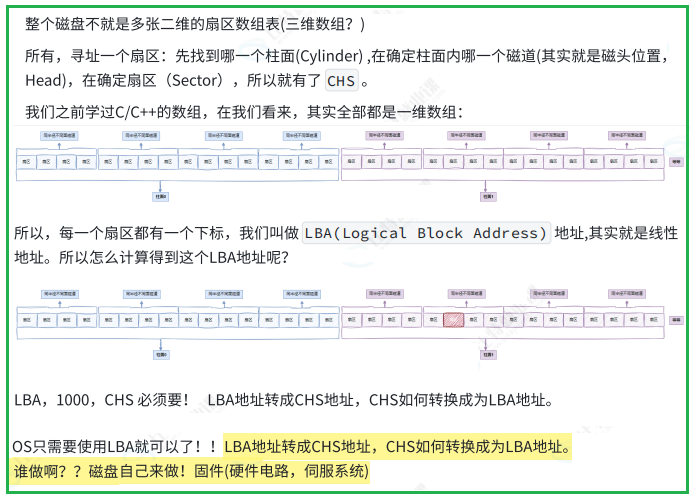
2.2 引入"分区"概念
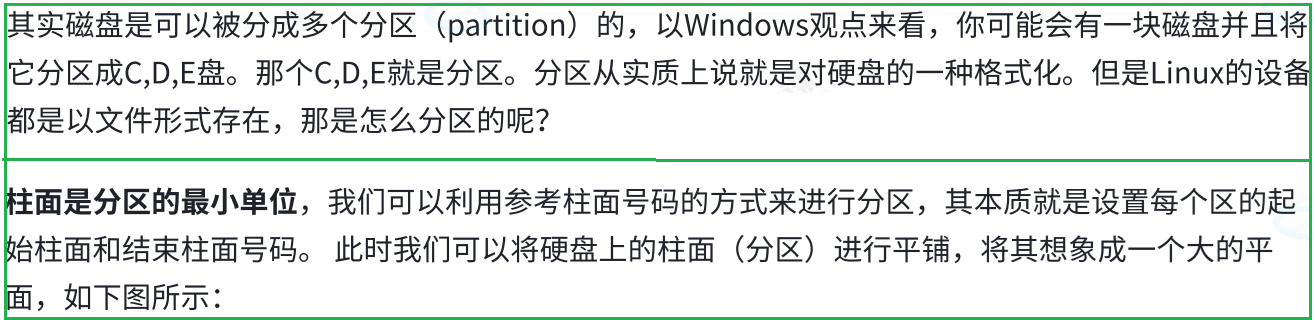
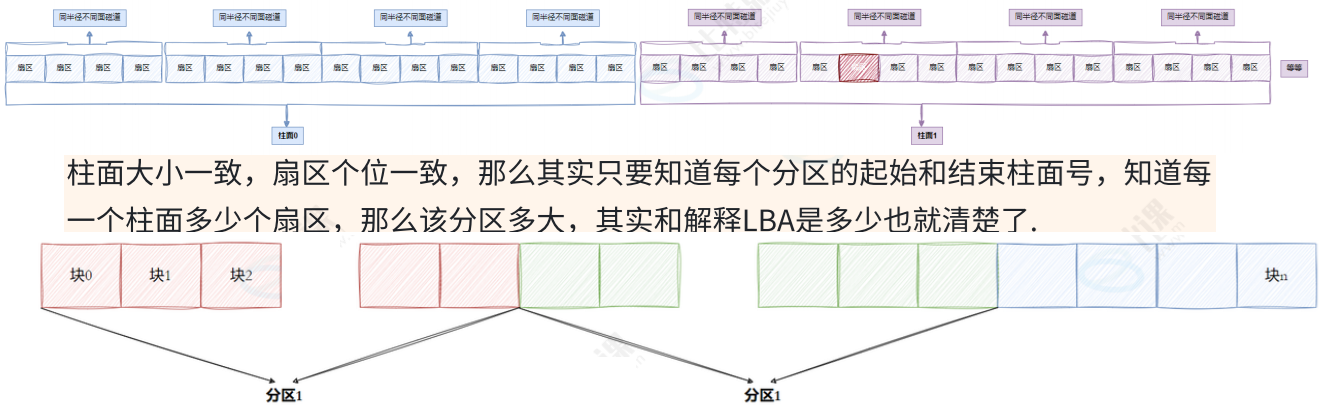
2.3 引入"inode"概念



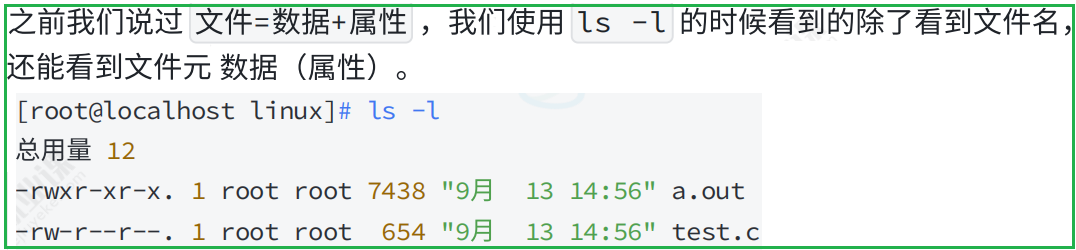

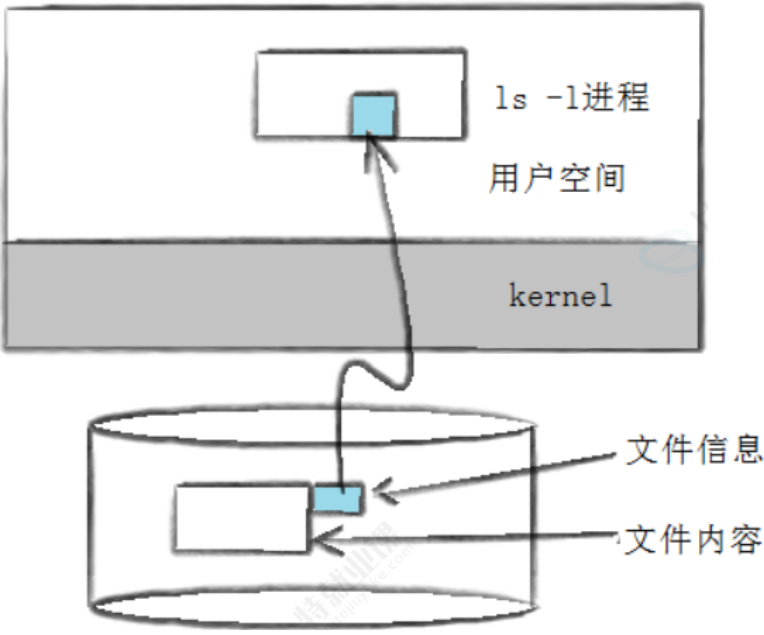
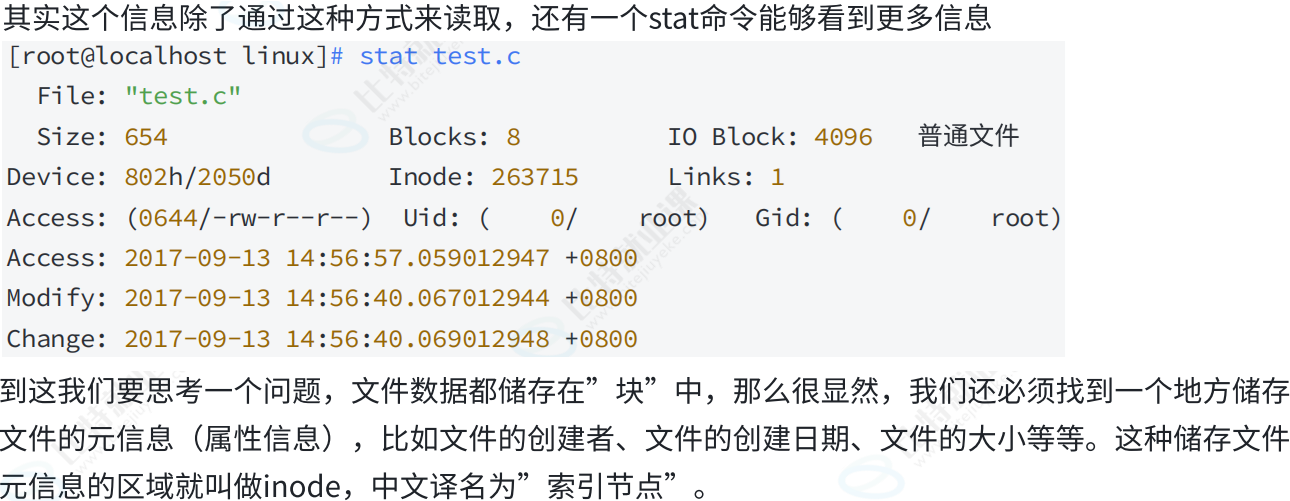
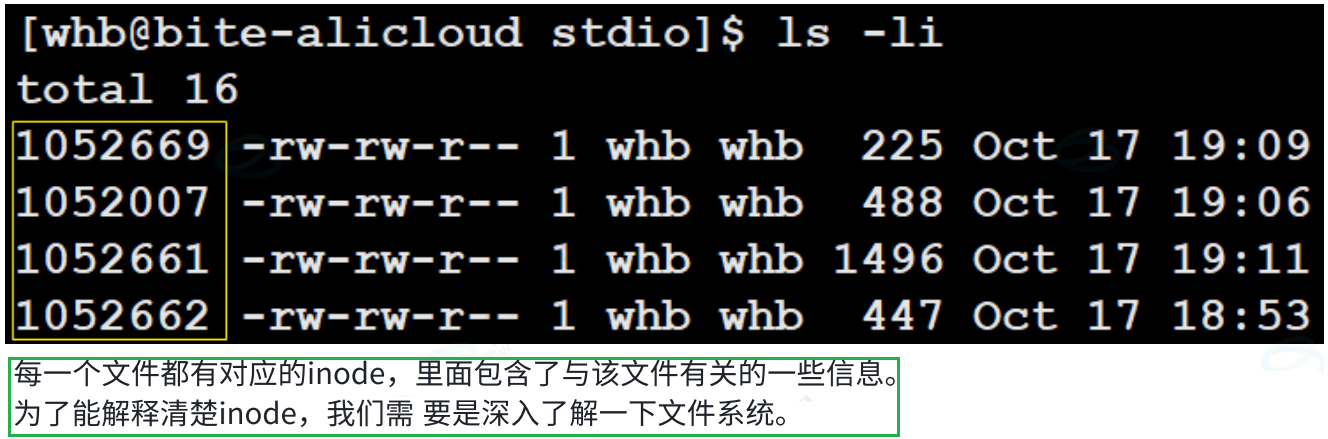

所以一个文件的属性inode长什么样子呢?
代码如下(示例):
c
/*
* Structure of an inode on the disk
*/
struct ext2_inode {
__le16 i_mode; /* File mode */
__le16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */
__le32 i_size; /* Size in bytes */
__le32 i_atime; /* Access time */
__le32 i_ctime; /* Creation time */
__le32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */
__le32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */
__le16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */
__le16 i_links_count; /* Links count */
__le32 i_blocks; /* Blocks count */
__le32 i_flags; /* File flags */
union {
struct {
__le32 l_i_reserved1;
} linux1;
struct {
__le32 h_i_translator;
} hurd1;
struct {
__le32 m_i_reserved1;
} masix1;
} osd1; /* OS dependent 1 */
__le32 i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers to blocks */
__le32 i_generation; /* File version (for NFS) */
__le32 i_file_acl; /* File ACL */
__le32 i_dir_acl; /* Directory ACL */
__le32 i_faddr; /* Fragment address */
union {
struct {
__u8 l_i_frag; /* Fragment number */
__u8 l_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */
__u16 i_pad1;
__le16 l_i_uid_high; /* these 2 fields */
__le16 l_i_gid_high; /* were reserved2[0] */
__u32 l_i_reserved2;
} linux2;
struct {
__u8 h_i_frag; /* Fragment number */
__u8 h_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */
__le16 h_i_mode_high;
__le16 h_i_uid_high;
__le16 h_i_gid_high;
__le32 h_i_author;
} hurd2;
struct {
__u8 m_i_frag; /* Fragment number */
__u8 m_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */
__u16 m_pad1;
__u32 m_i_reserved2[2];
} masix2;
} osd2; /* OS dependent 2 */
};
/*
* Constants relative to the data blocks
*/
#define EXT2_NDIR_BLOCKS 12
#define EXT2_IND_BLOCK EXT2_NDIR_BLOCKS
#define EXT2_DIND_BLOCK (EXT2_IND_BLOCK + 1)
#define EXT2_TIND_BLOCK (EXT2_DIND_BLOCK + 1)
#define EXT2_N_BLOCKS (EXT2_TIND_BLOCK + 1)
备注:EXT2_N_BLOCKS = 15三、ext2文件系统
3.1 宏观认识

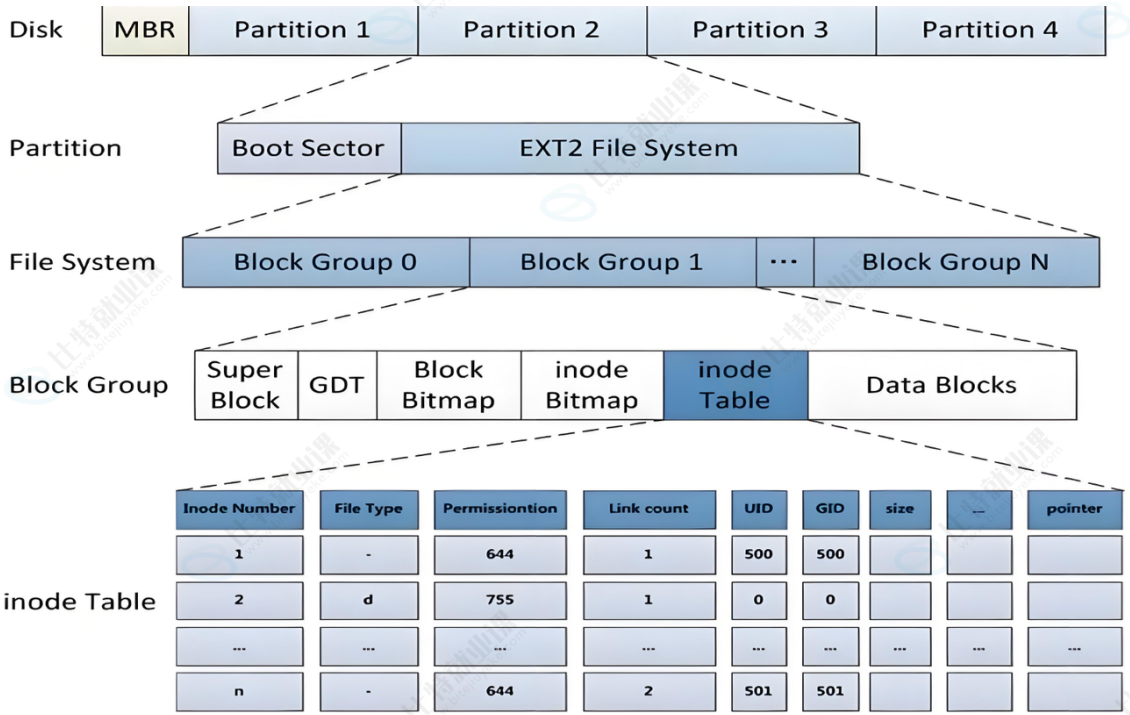

3.2 Block Group
ext2⽂件系统会根据分区的⼤⼩划分为数个Block Group。⽽每个Block Group都有着相同的结构组成。政府管理各区的例⼦
3.3 块组内部构成
3.3.1 超级块(Super Block)

代码如下(示例):
c
/*
* Structure of the super block
*/
struct ext2_super_block {
__le32 s_inodes_count; /* Inodes count */
__le32 s_blocks_count; /* Blocks count */
__le32 s_r_blocks_count; /* Reserved blocks count */
__le32 s_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */
__le32 s_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */
__le32 s_first_data_block; /* First Data Block */
__le32 s_log_block_size; /* Block size */
__le32 s_log_frag_size; /* Fragment size */
__le32 s_blocks_per_group; /* # Blocks per group */
__le32 s_frags_per_group; /* # Fragments per group */
__le32 s_inodes_per_group; /* # Inodes per group */
__le32 s_mtime; /* Mount time */
__le32 s_wtime; /* Write time */
__le16 s_mnt_count; /* Mount count */
__le16 s_max_mnt_count; /* Maximal mount count */
__le16 s_magic; /* Magic signature */
__le16 s_state; /* File system state */
__le16 s_errors; /* Behaviour when detecting errors */
__le16 s_minor_rev_level; /* minor revision level */
__le32 s_lastcheck; /* time of last check */
__le32 s_checkinterval; /* max. time between checks */
__le32 s_creator_os; /* OS */
__le32 s_rev_level; /* Revision level */
__le16 s_def_resuid; /* Default uid for reserved blocks */
__le16 s_def_resgid; /* Default gid for reserved blocks */
/*
* These fields are for EXT2_DYNAMIC_REV superblocks only.
*
* Note: the difference between the compatible feature set and
* the incompatible feature set is that if there is a bit set
* in the incompatible feature set that the kernel doesn't
* know about, it should refuse to mount the filesystem.
*
* e2fsck's requirements are more strict; if it doesn't know
* about a feature in either the compatible or incompatible
* feature set, it must abort and not try to meddle with
* things it doesn't understand...
*/
__le32 s_first_ino; /* First non-reserved inode */
__le16 s_inode_size; /* size of inode structure */
__le16 s_block_group_nr; /* block group # of this superblock */
__le32 s_feature_compat; /* compatible feature set */
__le32 s_feature_incompat; /* incompatible feature set */
__le32 s_feature_ro_compat; /* readonly-compatible feature set */
__u8 s_uuid[16]; /* 128-bit uuid for volume */
char s_volume_name[16]; /* volume name */
char s_last_mounted[64]; /* directory where last mounted */
__le32 s_algorithm_usage_bitmap; /* For compression */
/*
* Performance hints. Directory preallocation should only
* happen if the EXT2_COMPAT_PREALLOC flag is on.
*/
__u8 s_prealloc_blocks; /* Nr of blocks to try to preallocate*/
__u8 s_prealloc_dir_blocks; /* Nr to preallocate for dirs */
__u16 s_padding1;
/*
* Journaling support valid if EXT3_FEATURE_COMPAT_HAS_JOURNAL set.
*/
__u8 s_journal_uuid[16]; /* uuid of journal superblock */
__u32 s_journal_inum; /* inode number of journal file */
__u32 s_journal_dev; /* device number of journal file */
__u32 s_last_orphan; /* start of list of inodes to delete */
__u32 s_hash_seed[4]; /* HTREE hash seed */
__u8 s_def_hash_version; /* Default hash version to use */
__u8 s_reserved_char_pad;
__u16 s_reserved_word_pad;
__le32 s_default_mount_opts;
__le32 s_first_meta_bg; /* First metablock block group */
__u32 s_reserved[190]; /* Padding to the end of the block */
};3.3.2 GDT(Group Descriptor Table)

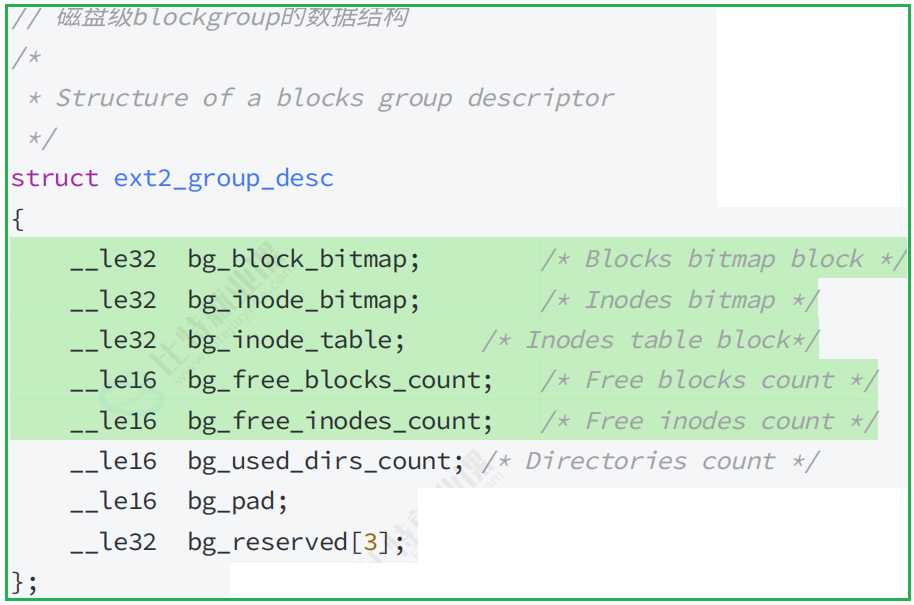
3.3.3 位块图(Block Bitmap)
Block Bitmap中记录着Data Block中哪个数据块已经被占⽤,
哪个数据块没有被占⽤
3.3.4 inode位图(Inode Bitmap)
每个bit表⽰⼀个inode是否空闲可⽤。
3.3.5 i 节点表(Inode Table)

3.3.6 Date Block

3.4 inode和datablock映射(弱化)

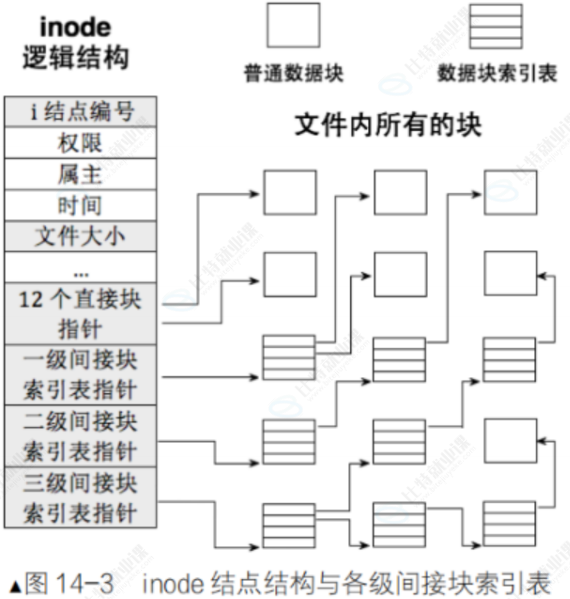

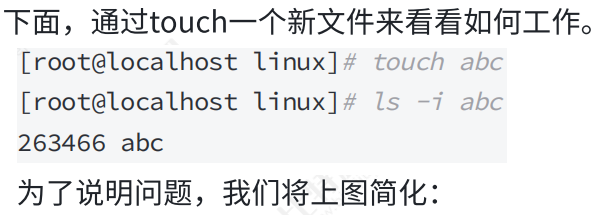
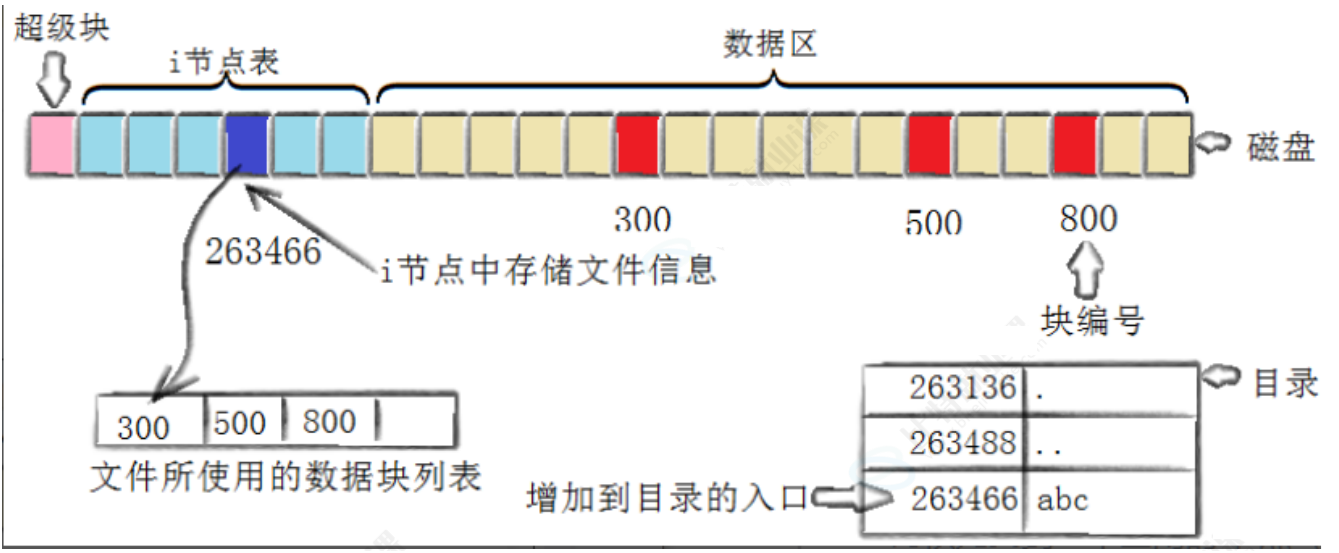
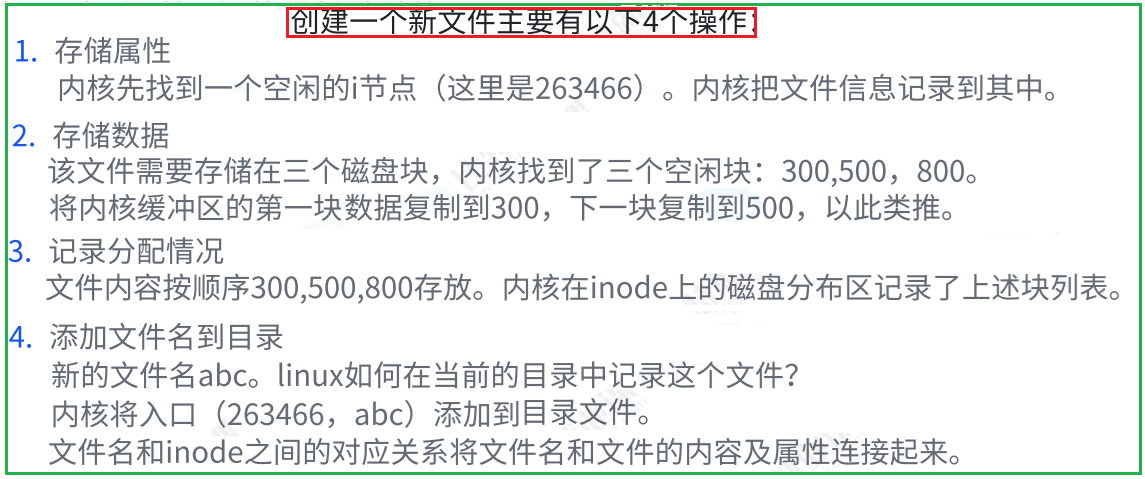
3.5 目录与文件名


3.6 路径解析

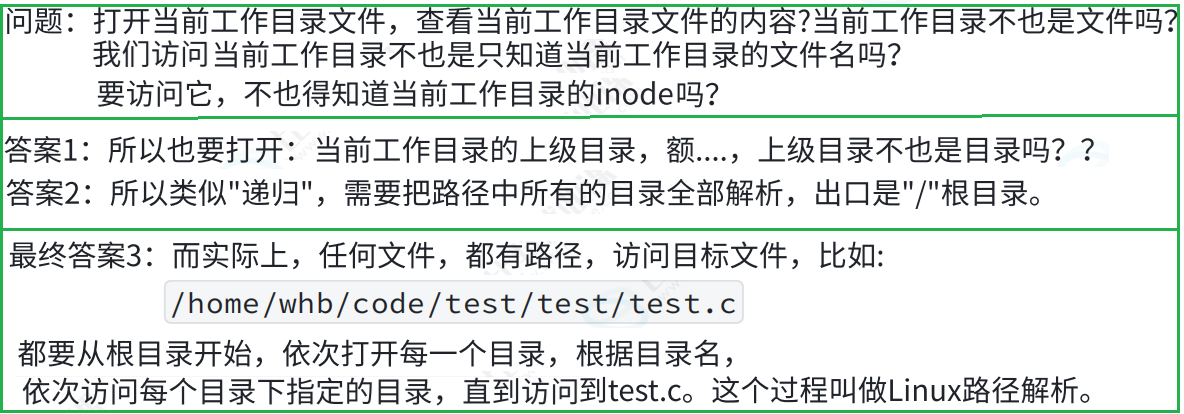

3.7 路径缓存

代码如下(示例):
c
代码块
struct dentry {
atomic_t d_count;
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
spinlock_t d_lock; /* per dentry lock */
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
* negative */
/*
* The next three fields are touched by __d_lookup. Place them here
* so they all fit in a cache line.
*/
struct hlist_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
/*
* d_child and d_rcu can share memory
*/
union {
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
} d_u;
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
struct list_head d_alias; /* inode alias list */
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
#ifdef CONFIG_PROFILING
struct dcookie_struct *d_cookie; /* cookie, if any */
#endif
int d_mounted;
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN_MIN]; /* small names */
};
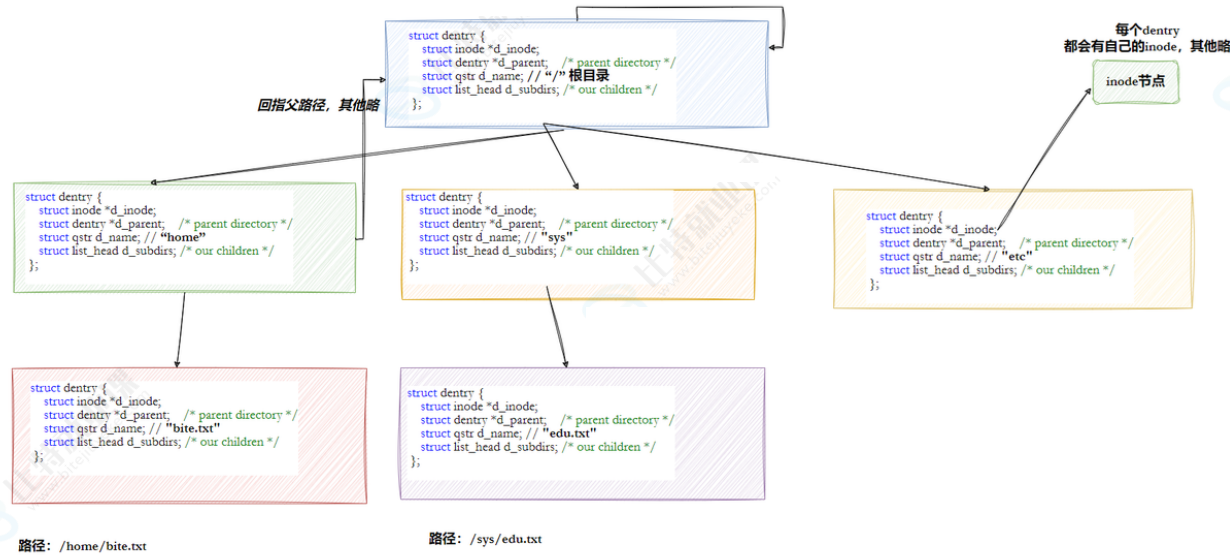
3.8 挂载分区




四、软硬链接


4.1 硬链接
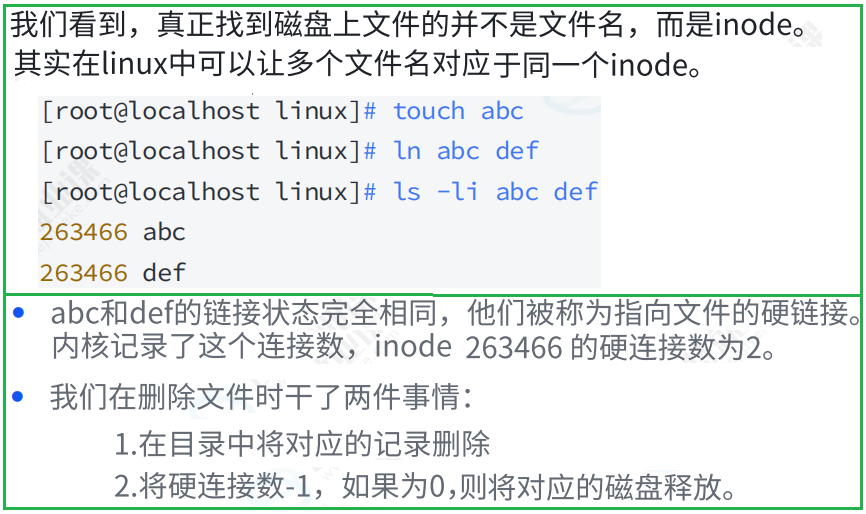
4.2 软链接

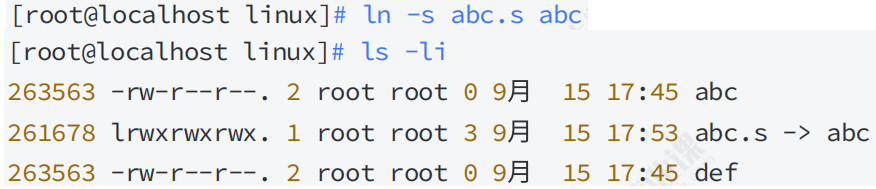
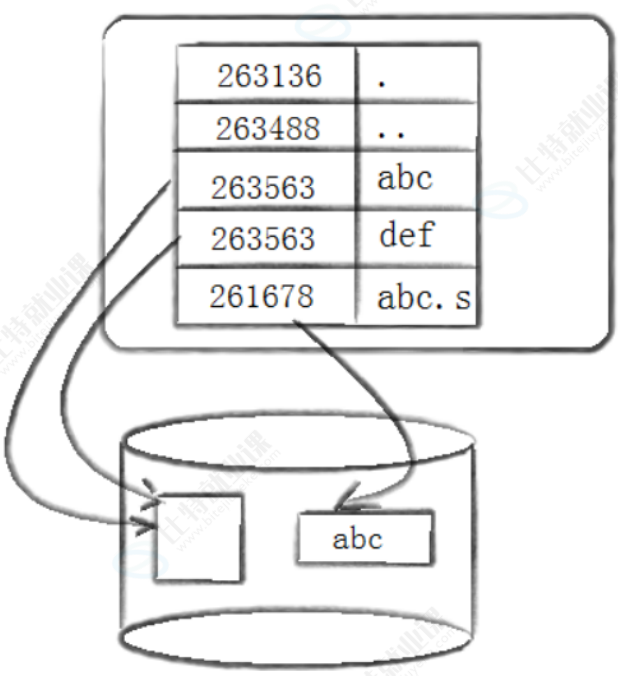

4.3 软硬链接对比

4.4 软硬链接用途
