python读取文件的常用操作
1、在Python中,为了实现数据和代码分离,我们通常将数据存储在外部文件中,然后在代码中读取。常见的文件格式包括:YAML、JSON、INI、XML、CSV等。
-
JSON: 广泛使用,适合复杂数据结构,易于读写和解析。
-
YAML: 更人类可读,支持注释,适合配置文件。
-
INI: 简单,适合简单的键值对配置。
-
XML: 结构严谨,但较繁琐,常用于旧式配置和数据交换。
-
CSV: 适合表格数据。
-
环境变量文件: 适合敏感数据(如密码)和部署配置。
-
纯文本: 适合非结构化数据。
-
Python文件: 灵活,但要注意安全,避免执行恶意代码。
1. JSON 文件
python
import json
def read_json(file_path):
"""读取JSON文件"""
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return json.load(file)
# 使用示例
config = read_json('config.json')
print(config['database']['host'])Python读取JSON文件的常用方式
读取json有有点要注意,是读取的json文件还是json数据。
json文件就是一个文件,里面是json格式,而 json数据,就是json格式的字符串。
1. 基础读取方法
- 方法1.1:使用
json.load()读取json文件
python
import json
with open('data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = json.load(file)
print(data)- 方法1.2:使用
json.loads()读取字符串
python
import json
# 从字符串读取
json_string = '{"name": "张三", "age": 30}'
data = json.loads(json_string)
print(data)
# 从文件读取字符串再解析
with open('data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
content = file.read()
data = json.loads(content)示例JSON文件 (config.json)
json
{
"database": {
"host": "localhost",
"port": 3306,
"username": "admin",
"password": "secret",
"name": "mydb"
},
"app": {
"name": "My Application",
"debug": true,
"max_connections": 100,
"version": 1.0,
"features": ["auth", "logging", "cache"]
},
"paths": {
"data_dir": "/var/data",
"log_file": "/var/log/app.log"
}
}基本读取代码
python
import json
# 方法1: 使用 json.load() 从文件读取
with open('config.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
config = json.load(file)
print(config)
print(f"配置类型: {type(config)}") # <class 'dict'>2. 完整的数据访问方法
python
import json
def read_json_file(file_path):
"""
读取JSON文件并返回解析后的数据
"""
try:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = json.load(file)
return data
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"文件 {file_path} 不存在")
return None
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSON解析错误: {e}")
return None
# 使用示例
config = read_json_file('config.json')
if config:
# 访问嵌套数据
db_host = config['database']['host']
db_port = config['database']['port']
app_name = config['app']['name']
debug_mode = config['app']['debug']
features = config['app']['features']
print(f"数据库主机: {db_host}")
print(f"数据库端口: {db_port}")
print(f"应用名称: {app_name}")
print(f"调试模式: {debug_mode}")
print(f"功能列表: {features}")
# 使用get方法安全访问(避免KeyError)
timeout = config['app'].get('timeout', 30) # 默认值30
print(f"超时时间: {timeout}")3. 高级用法和配置类
python
import json
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional
class JSONConfigManager:
"""JSON配置文件管理器"""
def __init__(self, config_path: str):
self.config_path = Path(config_path)
self._data = None
self._load_config()
def _load_config(self):
"""加载配置文件"""
if not self.config_path.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(f"配置文件不存在: {self.config_path}")
try:
with open(self.config_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
self._data = json.load(file)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
raise ValueError(f"JSON文件格式错误: {e}")
def get(self, key_path: str, default: Any = None) -> Any:
"""
使用点号分隔的路径获取配置值
Args:
key_path: 例如 'database.host'
default: 默认值
"""
keys = key_path.split('.')
value = self._data
try:
for key in keys:
value = value[key]
return value
except (KeyError, TypeError):
return default
def get_section(self, section: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取整个章节的配置"""
return self._data.get(section, {})
def get_all(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""获取所有配置"""
return self._data.copy()
def reload(self):
"""重新加载配置文件"""
self._load_config()
# 使用示例
config_mgr = JSONConfigManager('config.json')
# 使用点号路径访问
db_host = config_mgr.get('database.host')
app_name = config_mgr.get('app.name')
debug_mode = config_mgr.get('app.debug')
first_feature = config_mgr.get('app.features.0') # 访问数组元素
print(f"数据库主机: {db_host}")
print(f"应用名称: {app_name}")
print(f"调试模式: {debug_mode}")
print(f"第一个功能: {first_feature}")
# 获取整个章节
database_config = config_mgr.get_section('database')
print("数据库配置:", database_config)4. 处理复杂JSON结构
复杂JSON示例 (data.json)
json
{
"users": [
{
"id": 1,
"name": "张三",
"email": "zhangsan@example.com",
"preferences": {
"theme": "dark",
"language": "zh-CN"
}
},
{
"id": 2,
"name": "李四",
"email": "lisi@example.com",
"preferences": {
"theme": "light",
"language": "en-US"
}
}
],
"metadata": {
"total_count": 2,
"page": 1,
"per_page": 10
}
}读取复杂结构
python
import json
with open('data.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
data = json.load(file)
# 处理数组和嵌套对象
users = data['users']
for user in users:
print(f"用户: {user['name']}")
print(f" 邮箱: {user['email']}")
print(f" 主题: {user['preferences']['theme']}")
print(f" 语言: {user['preferences']['language']}")
# 处理元数据
metadata = data['metadata']
print(f"总记录数: {metadata['total_count']}")2. YAML 文件
python
import yaml
def read_yaml(file_path):
"""读取YAML文件"""
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return yaml.safe_load(file)
# 使用示例
config = read_yaml('config.yaml')yaml.safe_load(file) 返回的数据类型取决于YAML文件的内容结构,它会将YAML结构映射到对应的Python数据类型。
- 读取这个ymal文件后, 会根据里面内容和结构,识别成对应的值。首先看缩量,没有缩量顶在最前面的如果有 - 整个符号,就识别成一个列表,如果 都是 是 A:B 这种,就识别成了 字典格式。如果两个都有,就识别成了列表。如果只有一个数据,就识别成了字母或者数字这种。
- 正常用的多的还是字典类型。这样方便读取
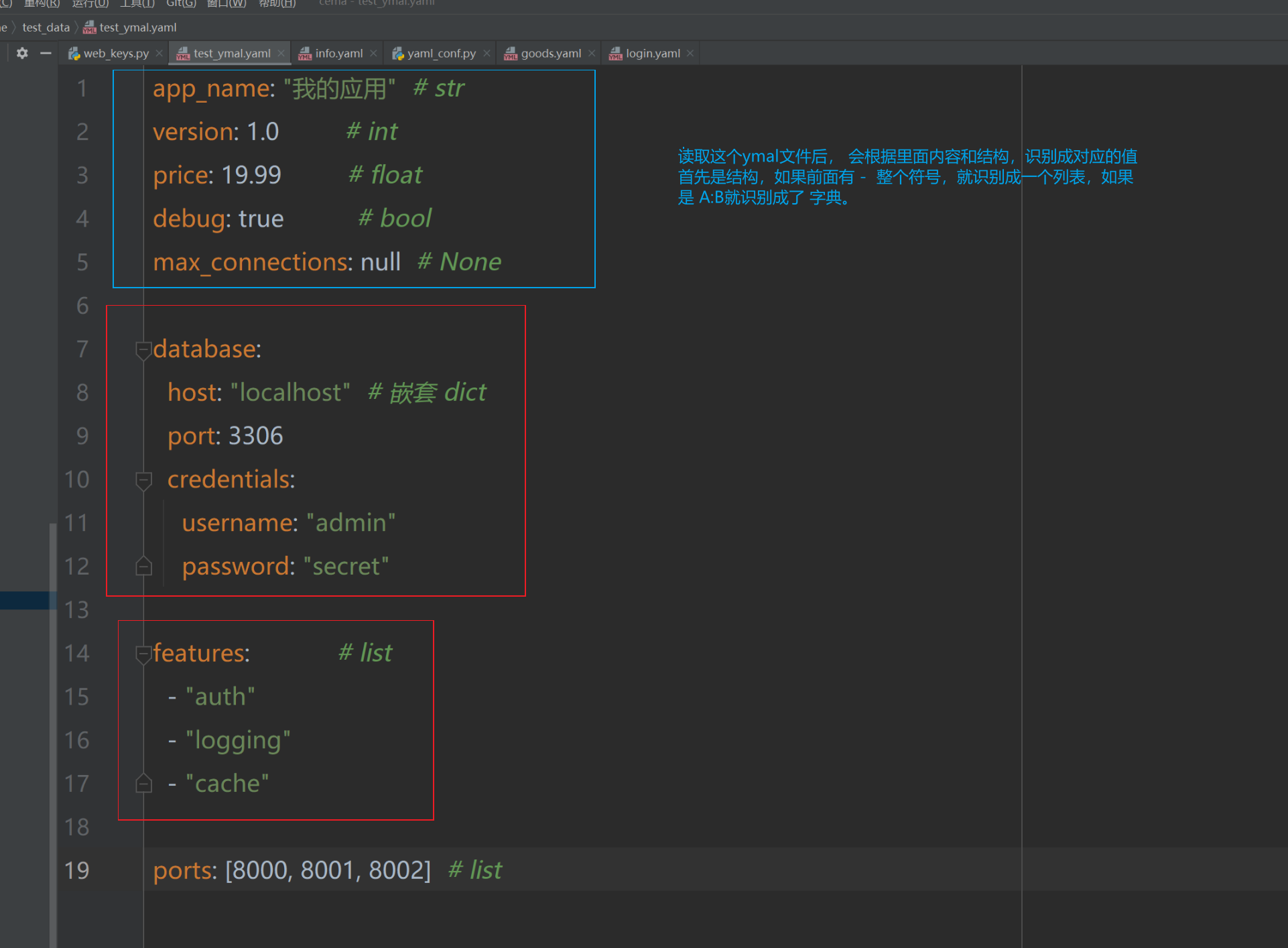
以下是详细的对应关系:
2.1 基本数据类型映射
| YAML 类型 | Python 类型 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 字符串 | str |
"hello" → "hello" |
| 整数 | int |
42 → 42 |
| 浮点数 | float |
3.14 → 3.14 |
| 布尔值 | bool |
true/false → True/False |
| 空值 | NoneType |
null/~ → None |
2.2. 集合数据类型映射
| YAML 结构 | Python 类型 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| 对象/字典 | dict |
{key: value} → dict |
| 数组/列表 | list |
[item1, item2] → list |
2.3. 实际示例
示例 YAML 文件:
yaml
# config.yaml
app_name: "我的应用" # str
version: 1.0 # int
price: 19.99 # float
debug: true # bool
max_connections: null # None
database:
host: "localhost" # 嵌套 dict
port: 3306
credentials:
username: "admin"
password: "secret"
features: # list
- "auth"
- "logging"
- "cache"
ports: [8000, 8001, 8002] # list读取和类型检查:
python
import yaml
from typing import Any, Dict, List
with open('config.yaml', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
config = yaml.safe_load(file)
# 检查各个字段的类型
print(f"整个配置类型: {type(config)}") # <class 'dict'>
print(f"app_name 类型: {type(config['app_name'])}") # <class 'str'>
print(f"version 类型: {type(config['version'])}") # <class 'int'>
print(f"price 类型: {type(config['price'])}") # <class 'float'>
print(f"debug 类型: {type(config['debug'])}") # <class 'bool'>
print(f"max_connections 类型: {type(config['max_connections'])}") # <class 'NoneType'>
print(f"database 类型: {type(config['database'])}") # <class 'dict'>
print(f"features 类型: {type(config['features'])}") # <class 'list'>
print(f"ports 类型: {type(config['ports'])}") # <class 'list'>
# 访问嵌套数据
print(f"数据库主机: {config['database']['host']}") # localhost
print(f"用户名: {config['database']['credentials']['username']}") # admin
print(f"第一个特性: {config['features'][0]}") # auth2.4. 类型注解的最佳实践
为了代码的清晰性和类型安全,建议使用类型注解:
python
from typing import TypedDict, List, Optional
class DatabaseConfig(TypedDict):
host: str
port: int
credentials: Dict[str, str]
class AppConfig(TypedDict):
app_name: str
version: int
price: float
debug: bool
max_connections: Optional[int]
database: DatabaseConfig
features: List[str]
ports: List[int]
def load_config(file_path: str) -> AppConfig:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
config: AppConfig = yaml.safe_load(file)
return config
# 使用类型注解的配置
config: AppConfig = load_config('config.yaml')2.5. 处理复杂情况
多文档 YAML:
yaml
-
name: "文档1"
data: [1, 2, 3]
-
name: "文档2"
data: [4, 5, 6]上面这种读取后,就是一个列表里面套两个字典的类型。
python
with open('multi_doc.yaml', 'r') as file:
documents = list(yaml.safe_load_all(file))
# documents 类型: List[Dict[str, Any]]
print(f"文档数量: {len(documents)}") # 2
print(f"第一个文档类型: {type(documents[0])}") # <class 'dict'>总结
yaml.safe_load(file) 返回的类型规则:
- 最外层通常是
dict(最常见的情况) - 也可能是
list、str、int、float、bool、None - 嵌套结构保持对应的 Python 类型映射
- 使用类型注解可以提高代码的可读性和安全性
- 对于复杂项目,建议定义
TypedDict来描述配置结构
在实际使用中,绝大多数YAML配置文件都会返回 dict 类型,因为YAML通常用于表示键值对配置信息。
3. Python读取INI文件的常用方式
python
import configparser
def read_ini(file_path):
"""读取INI配置文件"""
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(file_path, encoding='utf-8')
return config
# 使用示例
config = read_ini('config.ini')
db_host = config.get('database', 'host')
db_port = config.getint('database', 'port')在Python中读取INI文件,最常用的是使用标准库中的 configparser 模块。以下是详细的使用方法:
1. 基本读取方法
示例INI文件 (config.ini)
ini
[database]
host = localhost
port = 3306
username = admin
password = secret
name = mydb
[app]
name = My Application
debug = True
max_connections = 100
version = 1.0
[paths]
data_dir = /var/data
log_file = /var/log/app.log基本读取代码
python
import configparser
# 创建配置解析器
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
# 读取INI文件
config.read('config.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 获取所有章节
sections = config.sections()
print("所有章节:", sections) # 输出: ['database', 'app', 'paths']
# 检查章节是否存在
if config.has_section('database'):
print("database章节存在")
# 获取特定章节的所有选项
options = config.options('database')
print("database选项:", options) # 输出: ['host', 'port', 'username', 'password', 'name']
# 获取键值对
items = config.items('database')
print("database键值对:", dict(items))2. 获取配置值的方法
python
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('config.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 方法1: 直接获取(返回字符串)
db_host = config['database']['host']
print(f"数据库主机: {db_host}") # localhost
# 方法2: 使用get方法(可指定默认值)
db_port = config.get('database', 'port')
print(f"数据库端口: {db_port}") # 3306
# 方法3: 获取特定类型的值
debug_mode = config.getboolean('app', 'debug')
max_conn = config.getint('app', 'max_connections')
version = config.getfloat('app', 'version')
print(f"调试模式: {debug_mode}, 类型: {type(debug_mode)}") # True, <class 'bool'>
print(f"最大连接数: {max_conn}, 类型: {type(max_conn)}") # 100, <class 'int'>
print(f"版本号: {version}, 类型: {type(version)}") # 1.0, <class 'float'>
# 方法4: 带默认值的获取
timeout = config.get('app', 'timeout', fallback=30)
print(f"超时时间: {timeout}") # 30 (使用默认值)3. 处理带插值的INI文件
INI文件支持变量插值:
ini
[paths]
home = /home/user
bin_dir = %(home)s/bin
config_dir = %(home)s/.config
python
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read('config_with_vars.ini', encoding='utf-8')
# 获取带插值的配置
bin_dir = config.get('paths', 'bin_dir')
print(f"二进制目录: {bin_dir}") # 输出: /home/user/bin
# 禁用插值(获取原始值)
config_no_interp = configparser.ConfigParser(interpolation=None)
config_no_interp.read('config_with_vars.ini', encoding='utf-8')
bin_dir_raw = config_no_interp.get('paths', 'bin_dir')
print(f"原始值: {bin_dir_raw}") # 输出: %(home)s/bin4. 完整的使用示例
python
import configparser
import os
from typing import Any
def load_ini_config(file_path: str) -> dict:
"""
加载INI配置文件并返回字典格式的配置
Args:
file_path: INI文件路径
Returns:
包含所有配置的字典
"""
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"配置文件不存在: {file_path}")
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(file_path, encoding='utf-8')
result = {}
for section in config.sections():
result[section] = {}
for key, value in config.items(section):
# 尝试转换为适当的数据类型
result[section][key] = _convert_value(value)
return result
def _convert_value(value: str) -> Any:
"""将字符串值转换为适当的数据类型"""
if value.lower() in ('true', 'yes', 'on', '1'):
return True
elif value.lower() in ('false', 'no', 'off', '0'):
return False
elif value.isdigit():
return int(value)
elif _is_float(value):
return float(value)
else:
return value
def _is_float(value: str) -> bool:
"""检查字符串是否可以转换为浮点数"""
try:
float(value)
return True
except ValueError:
return False
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
try:
config = load_ini_config('config.ini')
# 访问配置
db_config = config['database']
app_config = config['app']
print("数据库配置:")
for key, value in db_config.items():
print(f" {key}: {value} ({type(value).__name__})")
print("\n应用配置:")
for key, value in app_config.items():
print(f" {key}: {value} ({type(value).__name__})")
except FileNotFoundError as e:
print(f"错误: {e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"读取配置时出错: {e}")INI文件适合简单的配置场景,对于复杂的嵌套结构,YAML或JSON可能是更好的选择。
4. 环境变量文件 (.env)
python
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
# 加载.env文件
load_dotenv()
# 读取环境变量
db_host = os.getenv('DB_HOST')
api_key = os.getenv('API_KEY')5. Python 配置文件 (.py)
python
# config.py
DATABASE = {
'host': 'localhost',
'port': 3306,
'user': 'admin'
}
APP_CONFIG = {
'debug': True,
'secret_key': 'your-secret-key'
}
python
# main.py
import config
db_host = config.DATABASE['host']
debug_mode = config.APP_CONFIG['debug']6. XML 文件
python
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def read_xml(file_path):
"""读取XML文件"""
tree = ET.parse(file_path)
root = tree.getroot()
return root
# 使用示例
root = read_xml('config.xml')
for child in root:
print(f"{child.tag}: {child.text}")7. CSV 文件
python
import csv
def read_csv(file_path):
"""读取CSV文件"""
data = []
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
reader = csv.DictReader(file)
for row in reader:
data.append(row)
return data
# 使用示例
users = read_csv('users.csv')
for user in users:
print(user['name'], user['email'])8. 综合配置管理类
python
import os
import json
import yaml
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Any, Dict
class ConfigManager:
"""统一的配置管理器"""
def __init__(self, config_dir='config'):
self.config_dir = Path(config_dir)
self._cache = {}
def load_config(self, filename: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""根据文件扩展名自动选择加载方式"""
if filename in self._cache:
return self._cache[filename]
file_path = self.config_dir / filename
if not file_path.exists():
raise FileNotFoundError(f"配置文件不存在: {file_path}")
suffix = file_path.suffix.lower()
if suffix == '.json':
data = self._load_json(file_path)
elif suffix in ['.yaml', '.yml']:
data = self._load_yaml(file_path)
elif suffix == '.ini':
data = self._load_ini(file_path)
else:
raise ValueError(f"不支持的配置文件格式: {suffix}")
self._cache[filename] = data
return data
def _load_json(self, file_path: Path) -> Dict[str, Any]:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return json.load(file)
def _load_yaml(self, file_path: Path) -> Dict[str, Any]:
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return yaml.safe_load(file)
def _load_ini(self, file_path: Path) -> Dict[str, Any]:
import configparser
config = configparser.ConfigParser()
config.read(file_path, encoding='utf-8')
data = {}
for section in config.sections():
data[section] = dict(config.items(section))
return data
def get(self, filename: str, key: str, default=None):
"""获取特定配置值"""
config = self.load_config(filename)
keys = key.split('.')
value = config
for k in keys:
value = value.get(k, {})
return value if value != {} else default
# 使用示例
config_mgr = ConfigManager('config')
# 读取数据库配置
db_config = config_mgr.load_config('database.yaml')
# 或获取特定值
db_host = config_mgr.get('database.yaml', 'database.host')9. 环境特定的配置
python
import os
from typing import Dict, Any
class EnvironmentConfig:
"""环境特定的配置管理"""
def __init__(self):
self.env = os.getenv('APP_ENV', 'development')
self.configs = self._load_environment_configs()
def _load_environment_configs(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""加载环境配置"""
base_config = self._load_config('config/base.yaml')
env_config = self._load_config(f'config/{self.env}.yaml')
# 合并配置,环境配置覆盖基础配置
return self._deep_merge(base_config, env_config)
def _load_config(self, file_path: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
"""加载单个配置文件"""
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file:
return yaml.safe_load(file) or {}
def _deep_merge(self, base: Dict, override: Dict) -> Dict:
"""深度合并字典"""
result = base.copy()
for key, value in override.items():
if (key in result and isinstance(result[key], dict)
and isinstance(value, dict)):
result[key] = self._deep_merge(result[key], value)
else:
result[key] = value
return result
def get(self, key: str, default=None):
"""获取配置值"""
keys = key.split('.')
value = self.configs
for k in keys:
value = value.get(k, {})
return value if value != {} else default
# 使用示例
config = EnvironmentConfig()
db_config = config.get('database')
debug_mode = config.get('app.debug')最佳实践建议
- 按环境分离:开发、测试、生产环境使用不同配置
- 敏感信息保护:密码、密钥等使用环境变量或密钥管理服务
- 配置验证:读取后验证必要配置项是否存在
- 类型安全:确保配置值的类型正确
- 默认值:为可选配置提供合理的默认值
- 文档化:为配置文件提供说明文档
选择哪种方式取决于项目需求、团队熟悉度和部署环境。对于现代Python项目,推荐使用YAML + 环境变量的组合方式。