在人工智能领域,多模态学习正成为解决复杂问题的关键技术。本文将深入探讨多模态分类的概念、应用场景,并通过完整代码示例展示如何实现一个图文结合的分类系统。
什么是多模态分类?
多模态分类是指利用多种不同类型的数据(如图像、文本、音频等)共同完成分类任务的方法。与单一模态相比,多模态方法能够捕捉更丰富的信息,提高分类的准确性和鲁棒性。
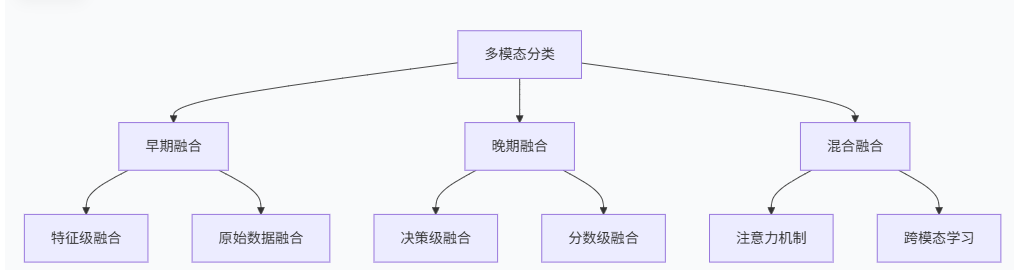
多模态分类的主要类型
多模态分类的优势
-
信息互补性:不同模态提供互补信息
-
鲁棒性增强:当某一模态数据缺失或质量较差时,其他模态可以弥补
-
性能提升:通常比单模态方法获得更好的分类效果
-
更接近人类认知:人类天然使用多感官信息理解世界
实战:图文多模态分类系统
下面我们将构建一个结合图像和文本的多模态分类模型,用于商品分类任务。
环境准备
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision.models as models
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from PIL import Image
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from transformers import BertModel, BertTokenizer
import os
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
import seaborn as sns数据预处理
python
class MultimodalDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, image_dir, csv_file, transform=None, max_length=128):
self.data = pd.read_csv(csv_file)
self.image_dir = image_dir
self.transform = transform
self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
self.max_length = max_length
self.label_map = {'electronics': 0, 'clothing': 1, 'books': 2, 'home': 3}
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
item = self.data.iloc[idx]
# 图像处理
img_path = os.path.join(self.image_dir, item['image_path'])
image = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB')
if self.transform:
image = self.transform(image)
# 文本处理
text = str(item['description'])
encoding = self.tokenizer(
text,
truncation=True,
padding='max_length',
max_length=self.max_length,
return_tensors='pt'
)
# 标签
label = self.label_map[item['category']]
return {
'image': image,
'input_ids': encoding['input_ids'].flatten(),
'attention_mask': encoding['attention_mask'].flatten(),
'label': torch.tensor(label, dtype=torch.long)
}
# 数据变换
transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
])多模态模型架构
python
class MultimodalClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, text_feature_dim=768, image_feature_dim=1000, hidden_dim=512, dropout=0.3):
super(MultimodalClassifier, self).__init__()
# 图像分支 - 使用预训练的ResNet
self.image_encoder = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
self.image_encoder.fc = nn.Linear(self.image_encoder.fc.in_features, image_feature_dim)
# 文本分支 - 使用预训练的BERT
self.text_encoder = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
self.text_projection = nn.Linear(text_feature_dim, text_feature_dim)
# 融合层
self.fusion = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(image_feature_dim + text_feature_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim // 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim // 2, num_classes)
)
# 注意力机制(可选)
self.attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(
embed_dim=image_feature_dim + text_feature_dim,
num_heads=8,
dropout=dropout
)
def forward(self, image, input_ids, attention_mask):
# 图像特征提取
image_features = self.image_encoder(image)
# 文本特征提取
text_outputs = self.text_encoder(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
text_features = text_outputs.last_hidden_state[:, 0, :] # [CLS] token
text_features = self.text_projection(text_features)
# 特征融合
combined_features = torch.cat([image_features, text_features], dim=1)
# 应用注意力(可选)
combined_features = combined_features.unsqueeze(0)
attended_features, _ = self.attention(combined_features, combined_features, combined_features)
combined_features = attended_features.squeeze(0)
# 分类
output = self.fusion(combined_features)
return output
# 初始化模型
device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
model = MultimodalClassifier(num_classes=4).to(device)
print(f"模型参数量: {sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters()):,}")训练过程
python
def train_model(model, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer, num_epochs=10):
train_losses = []
val_accuracies = []
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 训练阶段
model.train()
running_loss = 0.0
for batch in train_loader:
images = batch['image'].to(device)
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(device)
labels = batch['label'].to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
outputs = model(images, input_ids, attention_mask)
loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
# 验证阶段
model.eval()
correct = 0
total = 0
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in val_loader:
images = batch['image'].to(device)
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(device)
labels = batch['label'].to(device)
outputs = model(images, input_ids, attention_mask)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
total += labels.size(0)
correct += (predicted == labels).sum().item()
epoch_loss = running_loss / len(train_loader)
epoch_accuracy = 100 * correct / total
train_losses.append(epoch_loss)
val_accuracies.append(epoch_accuracy)
print(f'Epoch [{epoch+1}/{num_epochs}], Loss: {epoch_loss:.4f}, Accuracy: {epoch_accuracy:.2f}%')
return train_losses, val_accuracies
# 训练配置
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=2e-5, weight_decay=1e-4)
# 开始训练
train_losses, val_accuracies = train_model(
model, train_loader, val_loader, criterion, optimizer, num_epochs=15
)可视化训练过程
python
def plot_training_history(train_losses, val_accuracies):
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(15, 5))
# 损失曲线
ax1.plot(train_losses, label='Training Loss')
ax1.set_title('Training Loss Over Epochs')
ax1.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax1.set_ylabel('Loss')
ax1.legend()
ax1.grid(True)
# 准确率曲线
ax2.plot(val_accuracies, label='Validation Accuracy', color='orange')
ax2.set_title('Validation Accuracy Over Epochs')
ax2.set_xlabel('Epoch')
ax2.set_ylabel('Accuracy (%)')
ax2.legend()
ax2.grid(True)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
plot_training_history(train_losses, val_accuracies)模型评估
python
def evaluate_model(model, test_loader):
model.eval()
all_predictions = []
all_labels = []
with torch.no_grad():
for batch in test_loader:
images = batch['image'].to(device)
input_ids = batch['input_ids'].to(device)
attention_mask = batch['attention_mask'].to(device)
labels = batch['label'].to(device)
outputs = model(images, input_ids, attention_mask)
_, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
all_predictions.extend(predicted.cpu().numpy())
all_labels.extend(labels.cpu().numpy())
# 分类报告
print("Classification Report:")
print(classification_report(all_labels, all_predictions,
target_names=['electronics', 'clothing', 'books', 'home']))
# 混淆矩阵
cm = confusion_matrix(all_labels, all_predictions)
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
sns.heatmap(cm, annot=True, fmt='d', cmap='Blues',
xticklabels=['electronics', 'clothing', 'books', 'home'],
yticklabels=['electronics', 'clothing', 'books', 'home'])
plt.title('Confusion Matrix')
plt.xlabel('Predicted')
plt.ylabel('Actual')
plt.show()
evaluate_model(model, test_loader)单样本预测
python
def predict_single_sample(model, image_path, description, transform, label_map_inv):
model.eval()
# 处理图像
image = Image.open(image_path).convert('RGB')
image_tensor = transform(image).unsqueeze(0).to(device)
# 处理文本
tokenizer = BertTokenizer.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
encoding = tokenizer(
description,
truncation=True,
padding='max_length',
max_length=128,
return_tensors='pt'
)
input_ids = encoding['input_ids'].to(device)
attention_mask = encoding['attention_mask'].to(device)
with torch.no_grad():
output = model(image_tensor, input_ids, attention_mask)
probabilities = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)
predicted_class = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).item()
confidence = torch.max(probabilities).item()
# 可视化结果
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(12, 5))
# 显示图像
ax1.imshow(image)
ax1.set_title(f'Predicted: {label_map_inv[predicted_class]}\nConfidence: {confidence:.2f}')
ax1.axis('off')
# 显示概率分布
classes = list(label_map_inv.values())
probabilities = probabilities.cpu().numpy()[0]
ax2.barh(classes, probabilities)
ax2.set_xlabel('Probability')
ax2.set_title('Class Probabilities')
ax2.set_xlim(0, 1)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return label_map_inv[predicted_class], confidence
# 反向标签映射
label_map_inv = {0: 'electronics', 1: 'clothing', 2: 'books', 3: 'home'}
# 测试预测
predicted_class, confidence = predict_single_sample(
model,
'test_image.jpg',
'This is a modern smartphone with high-resolution camera and long battery life',
transform,
label_map_inv
)多模态分类的挑战与解决方案
主要挑战
-
模态对齐:不同模态数据的时间或空间对齐问题
-
缺失模态:如何处理部分模态数据缺失的情况
-
计算复杂度:多模态模型通常需要更多计算资源
-
数据不平衡:不同模态数据质量和数量不一致
解决方案
python
# 处理缺失模态的示例
class RobustMultimodalClassifier(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes, dropout=0.3):
super().__init__()
# 图像编码器
self.image_encoder = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
self.image_encoder.fc = nn.Linear(self.image_encoder.fc.in_features, 512)
# 文本编码器
self.text_encoder = BertModel.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased')
self.text_projection = nn.Linear(768, 512)
# 模态缺失处理
self.image_missing_proj = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(512))
self.text_missing_proj = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(512))
# 分类器
self.classifier = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(1024, 512),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(dropout),
nn.Linear(512, num_classes)
)
def forward(self, image=None, input_ids=None, attention_mask=None):
# 处理图像模态(支持缺失)
if image is not None:
image_features = self.image_encoder(image)
else:
batch_size = input_ids.size(0) if input_ids is not None else 1
image_features = self.image_missing_proj.unsqueeze(0).repeat(batch_size, 1)
# 处理文本模态(支持缺失)
if input_ids is not None:
text_outputs = self.text_encoder(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask)
text_features = text_outputs.last_hidden_state[:, 0, :]
text_features = self.text_projection(text_features)
else:
batch_size = image.size(0) if image is not None else 1
text_features = self.text_missing_proj.unsqueeze(0).repeat(batch_size, 1)
# 特征融合
combined_features = torch.cat([image_features, text_features], dim=1)
output = self.classifier(combined_features)
return output应用场景
多模态分类在以下领域有广泛应用:
-
电子商务:商品分类、推荐系统
-
医疗诊断:结合医学影像和临床报告
-
自动驾驶:融合摄像头、激光雷达和地图数据
-
社交媒体:内容分类和情感分析
-
智能客服:结合语音、文本和上下文信息
总结
多模态分类代表了人工智能发展的重要方向,它通过整合多种信息源,使模型能够更全面地理解复杂现实世界。本文通过完整的代码示例展示了如何构建一个图文多模态分类系统,涵盖了数据预处理、模型架构、训练策略和评估方法。
随着技术的不断发展,多模态学习将在更多领域发挥重要作用,推动人工智能向更智能、更人性化的方向发展。
进一步学习资源: