摘要
本文介绍了Python系统类库json的几种用法,包含解析、转换、读取、写入、过滤,让我们看代码。
前提条件
- 导入类库
javascript
import json
from datetime import datetime- 设置文件编码utf-8
代码示例
1. 打开 JSON 文件
kotlin
try:
with open('data1.json', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print(data) # 解析后的数据,输出: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York', 'hobbies': ['reading', 'traveling', 'gaming']}
print(type(data)) # 数据类型,输出: <class 'dict'>
except FileNotFoundError:
print("错误:文件未找到,请检查路径是否正确。")
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSON 解析错误:{e}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"未知错误:{e}")2.将 Python 字典或列表转换回 JSON 字符串
sql
dict_data = {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York', 'hobbies': ['reading', 'traveling', 'gaming']} #字典
list_data = ["reading", "cycling", "hiking"] #列表
#格式化打印
"""输出:
{
"age": 30,
"city": "New York",
"hobbies": [
"reading",
"traveling",
"gaming"
],
"name": "John"
}
[
"reading",
"cycling",
"hiking"
]
"""
print(json.dumps(dict_data, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=True, indent=4))
print(json.dumps(list_data, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=True, indent=4))
#压缩打印
#输出: {"age": 30, "city": "New York", "hobbies": ["reading", "traveling", "gaming"], "name": "John"}
#输出: ["reading", "cycling", "hiking"]
print(json.dumps(dict_data, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=True))
print(json.dumps(list_data, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=True))3.写入 JSON 数据到新文件
python
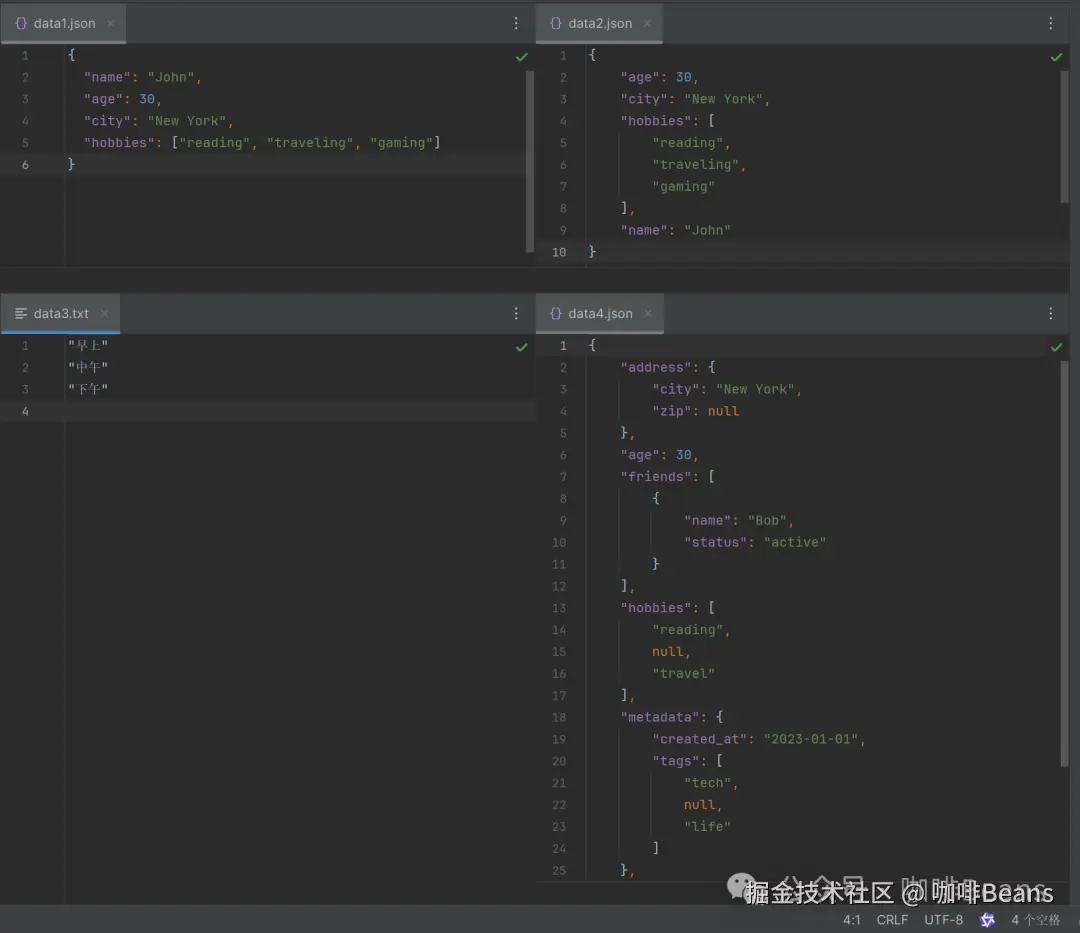
with open('data2.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(data, f, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=True, indent=4)4.JSON逐行写入文件
python
data_list = ['早上','中午','下午']
with open('data3.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for item in data_list:
f.write(json.dumps(item, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
# 读取 JSON Lines 文件
with open('data3.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in f:
item = json.loads(line)
print(item)
"""输出:
早上
中午
下午
"""5.处理嵌套数据
python
json_str = {
"name": "Alice",
"age": "30",
"hobbies": ["reading", "null", "travel"],
"address": {"city": "New York", "zip": "null"},
"friends": [{"name": "Bob", "status": "active"}],
"metadata": {"created_at": "2023-01-01T12:00:00", "tags": ["tech", "null", "life"]}
}
def process_nested(data):
if isinstance(data, dict):
for key, value in data.items():
data[key] = process_nested(value)
elif isinstance(data, list):
for i, item in enumerate(data):
data[i] = process_nested(item)
elif isinstance(data, str):
# 示例:将字符串 "null" 替换为 None
if data.lower() == "null":
return None
# 将字符串形式的数字转换为整数或浮点数
try:
return int(data)
except ValueError:
try:
return float(data)
except ValueError:
pass
try:
dt = datetime.fromisoformat(data)
return dt.date().isoformat()
except ValueError:
pass
return data
#JSON中,空值必须用null表示(小写),而不是其他语言中的None、nil或undefined
#Python的json模块遵循这一规范,因此在序列化时会将Python的None转换为JSON的 null
cleaned_data = process_nested(json_str)
with open('data4.json', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(cleaned_data, f, ensure_ascii=False, sort_keys=True, indent=4)6.过滤 JSON 数据
css
json_data = {
"name": "Alice",
"age": "30",
"hobbies": ["reading", "null", "travel"],
"address": {"city": "New York", "zip": "null"},
"friends": [{"name": "Bob", "status": "active"}],
"metadata": {"created_at": "2023-01-01T12:00:00", "tags": ["tech", "null", "life"]}
}
filtered_data = {key: value for key, value in json_data.items() if key in ['name', 'age']}
print(filtered_data) # 输出: {'name': 'Alice', 'age': '30'}- 结果展示
总结
以上我们了解了Python系统类库json的几种用法,包含解析、转换、读取、写入、过滤,环绕dumps、dump、loads、load这几个方法展开。
关注公众号:咖啡Beans
在这里,我们专注于软件技术的交流与成长,分享开发心得与笔记,涵盖编程、AI、资讯、面试等多个领域。无论是前沿科技的探索,还是实用技巧的总结,我们都致力于为大家呈现有价值的内容。期待与你共同进步,开启技术之旅。