我们知道android虚拟机的heap内存默认是512MB,android高版本的内存大约是这样子,android低版本内存大约是这样子,
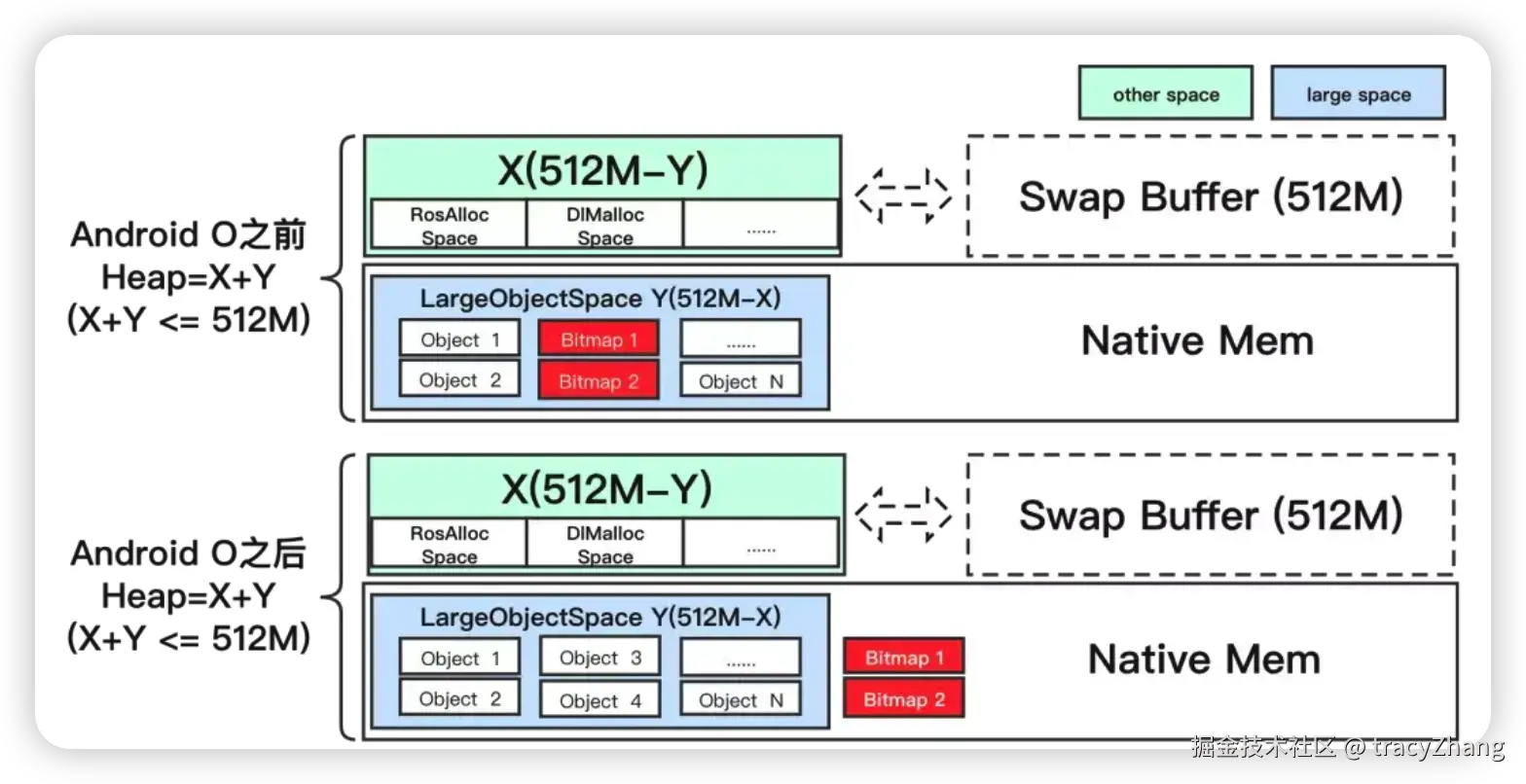
一个显著的点是,android高版本中的bitmap从java堆中移到native中,只有一个java对象和native的bitmap绑定,最终释放的时候通过
NativeAllocationRegistry机制实现java层bitmap释放时候同步回收对应的native对象,原理见这篇文章 juejin.cn/post/748575... NativeAllocationRegistry----通过绑定Java对象辅助回收native对象内存的机制 那么低版本的bitmap 是不是可以改造一下,直接从native分配呢?答案肯定是可以的。
1 低版本bitmap分配的原理
我们使用BitmapFactory decode一张图片时候,
xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
static jobject nativeDecodeStream(JNIEnv* env, jobject clazz, jobject is,
jbyteArray storage,jobject padding, jobject options) {
jobject bitmap = NULL;
std::unique_ptr<SkStream> stream(CreateJavaInputStreamAdaptor(env, is, storage));
if (stream.get()) {
std::unique_ptr<SkStreamRewindable> bufferedStream(
SkFrontBufferedStream::Create(stream.release(),
SkCodec::MinBufferedBytesNeeded()));
SkASSERT(bufferedStream.get() != NULL);
bitmap = doDecode(env, bufferedStream.release(), padding, options);
}
return bitmap;
}xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
static jobject doDecode(JNIEnv* env, SkStreamRewindable* stream, jobject padding, jobject options) {
// ------ 省略
SkBitmap::HeapAllocator heapAllocator;
SkBitmap::Allocator* decodeAllocator;
if (javaBitmap != nullptr && willScale) {
// This will allocate pixels using a HeapAllocator, since there will be an extra
// scaling step that copies these pixels into Java memory. This allocator
// also checks that the recycled javaBitmap is large enough.
decodeAllocator = &scaleCheckingAllocator;
} else if (javaBitmap != nullptr) {
decodeAllocator = &recyclingAllocator;
} else if (willScale) {
// This will allocate pixels using a HeapAllocator, since there will be an extra
// scaling step that copies these pixels into Java memory.
decodeAllocator = &heapAllocator;
} else {
decodeAllocator = &javaAllocator;
}
SkBitmap decodingBitmap;
if (!decodingBitmap.setInfo(bitmapInfo) ||
!decodingBitmap.tryAllocPixels(decodeAllocator, colorTable)) {
// SkAndroidCodec should recommend a valid SkImageInfo, so setInfo()
// should only only fail if the calculated value for rowBytes is too
// large.
// tryAllocPixels() can fail due to OOM on the Java heap, OOM on the
// native heap, or the recycled javaBitmap being too small to reuse.
return nullptr;
}
// Use SkAndroidCodec to perform the decode.
SkAndroidCodec::AndroidOptions codecOptions;
codecOptions.fZeroInitialized = (decodeAllocator == &javaAllocator) ?
SkCodec::kYes_ZeroInitialized : SkCodec::kNo_ZeroInitialized;
codecOptions.fColorPtr = colorPtr;
codecOptions.fColorCount = colorCount;
codecOptions.fSampleSize = sampleSize;
SkCodec::Result result = codec->getAndroidPixels(decodeInfo, decodingBitmap.getPixels(),
decodingBitmap.rowBytes(), &codecOptions);
// 省略-----
}1.1 分配java内存
我们看这步,构建了一个SkBitmap对象,并且分配内存,使用的decodeAllocator为javaAllocator
c++
SkBitmap decodingBitmap;
if (!decodingBitmap.setInfo(bitmapInfo) ||
!decodingBitmap.tryAllocPixels(decodeAllocator, colorTable))xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
bool SkBitmap::tryAllocPixels(Allocator* allocator, SkColorTable* ctable) {
HeapAllocator stdalloc;
if (nullptr == allocator) {
allocator = &stdalloc;
}
return allocator->allocPixelRef(this, ctable);
}xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
bool JavaPixelAllocator::allocPixelRef(SkBitmap* bitmap, SkColorTable* ctable) {
JNIEnv* env = vm2env(mJavaVM);
mStorage = GraphicsJNI::allocateJavaPixelRef(env, bitmap, ctable);
return mStorage != nullptr;
}
android::Bitmap* GraphicsJNI::allocateJavaPixelRef(JNIEnv* env, SkBitmap* bitmap,
SkColorTable* ctable) {
const SkImageInfo& info = bitmap->info();
if (info.colorType() == kUnknown_SkColorType) {
doThrowIAE(env, "unknown bitmap configuration");
return NULL;
}
size_t size;
if (!computeAllocationSize(*bitmap, &size)) {
return NULL;
}
// we must respect the rowBytes value already set on the bitmap instead of
// attempting to compute our own.
const size_t rowBytes = bitmap->rowBytes();
jbyteArray arrayObj = (jbyteArray) env->CallObjectMethod(gVMRuntime,
gVMRuntime_newNonMovableArray,
gByte_class, size);
if (env->ExceptionCheck() != 0) {
return NULL;
}
SkASSERT(arrayObj);
jbyte* addr = (jbyte*) env->CallLongMethod(gVMRuntime, gVMRuntime_addressOf, arrayObj);
if (env->ExceptionCheck() != 0) {
return NULL;
}
SkASSERT(addr);
android::Bitmap* wrapper = new android::Bitmap(env, arrayObj, (void*) addr,
info, rowBytes, ctable);
wrapper->getSkBitmap(bitmap);
// since we're already allocated, we lockPixels right away
// HeapAllocator behaves this way too
bitmap->lockPixels();
return wrapper;
}这里通过newNonMovableArray分配java内存,而且是一个不能移动的Array
c++
jbyteArray arrayObj = (jbyteArray) env->CallObjectMethod(gVMRuntime,
gVMRuntime_newNonMovableArray,
gByte_class, size);xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
static jobject VMRuntime_newNonMovableArray(JNIEnv* env, jobject, jclass javaElementClass,
jint length) {
ScopedFastNativeObjectAccess soa(env);
if (UNLIKELY(length < 0)) {
ThrowNegativeArraySizeException(length);
return nullptr;
}
mirror::Class* element_class = soa.Decode<mirror::Class*>(javaElementClass);
if (UNLIKELY(element_class == nullptr)) {
ThrowNullPointerException("element class == null");
return nullptr;
}
Runtime* runtime = Runtime::Current();
mirror::Class* array_class =
runtime->GetClassLinker()->FindArrayClass(soa.Self(), &element_class);
if (UNLIKELY(array_class == nullptr)) {
return nullptr;
}
gc::AllocatorType allocator = runtime->GetHeap()->GetCurrentNonMovingAllocator();
mirror::Array* result = mirror::Array::Alloc<true>(soa.Self(), array_class, length,
array_class->GetComponentSizeShift(),
allocator);
return soa.AddLocalReference<jobject>(result);
}最终通过 AllocObjectWithAllocator在java 堆里分配了一个java 的array对象
c++
template <bool kIsInstrumented, bool kFillUsable>
inline Array* Array::Alloc(Thread* self, Class* array_class, int32_t component_count,
size_t component_size_shift, gc::AllocatorType allocator_type) {
DCHECK(allocator_type != gc::kAllocatorTypeLOS);
DCHECK(array_class != nullptr);
DCHECK(array_class->IsArrayClass());
DCHECK_EQ(array_class->GetComponentSizeShift(), component_size_shift);
DCHECK_EQ(array_class->GetComponentSize(), (1U << component_size_shift));
size_t size = ComputeArraySize(component_count, component_size_shift);
#ifdef __LP64__
// 64-bit. No size_t overflow.
DCHECK_NE(size, 0U);
#else
// 32-bit.
if (UNLIKELY(size == 0)) {
self->ThrowOutOfMemoryError(StringPrintf("%s of length %d would overflow",
PrettyDescriptor(array_class).c_str(),
component_count).c_str());
return nullptr;
}
#endif
gc::Heap* heap = Runtime::Current()->GetHeap();
Array* result;
if (!kFillUsable) {
SetLengthVisitor visitor(component_count);
result = down_cast<Array*>(
heap->AllocObjectWithAllocator<kIsInstrumented, true>(self, array_class, size,
allocator_type, visitor));
} else {
SetLengthToUsableSizeVisitor visitor(component_count,
DataOffset(1U << component_size_shift).SizeValue(),
component_size_shift);
result = down_cast<Array*>(
heap->AllocObjectWithAllocator<kIsInstrumented, true>(self, array_class, size,
allocator_type, visitor));
}
if (kIsDebugBuild && result != nullptr && Runtime::Current()->IsStarted()) {
array_class = result->GetClass(); // In case the array class moved.
CHECK_EQ(array_class->GetComponentSize(), 1U << component_size_shift);
if (!kFillUsable) {
CHECK_EQ(result->SizeOf(), size);
} else {
CHECK_GE(result->SizeOf(), size);
}
}
return result;
}1.2 获取java内存中地址
我们再来看这一步
c++
jbyte* addr = (jbyte*) env->CallLongMethod(gVMRuntime, gVMRuntime_addressOf,
arrayObj);这一步是获取刚创建的array在内存中的地址,我们看下gVMRuntime_addressOf的实现
xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
static jlong VMRuntime_addressOf(JNIEnv* env, jobject, jobject javaArray) {
if (javaArray == nullptr) {
// Most likely allocation failed
return 0;
}
ScopedFastNativeObjectAccess soa(env);
mirror::Array* array = soa.Decode<mirror::Array*>(javaArray);
if (!array->IsArrayInstance()) {
ThrowIllegalArgumentException("not an array");
return 0;
}
if (Runtime::Current()->GetHeap()->IsMovableObject(array)) {
ThrowRuntimeException("Trying to get address of movable array object");
return 0;
}
return reinterpret_cast<uintptr_t>(
array->GetRawData(array->GetClass()->GetComponentSize(), 0));
}xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
void* GetRawData(size_t component_size, int32_t index)
SHARED_REQUIRES(Locks::mutator_lock_) {
intptr_t data = reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>(this) + DataOffset(component_size).Int32Value() +
+ (index * component_size);
return reinterpret_cast<void*>(data);
}
inline MemberOffset Array::DataOffset(size_t component_size) {
DCHECK(IsPowerOfTwo(component_size)) << component_size;
size_t data_offset = RoundUp(OFFSETOF_MEMBER(Array, first_element_), component_size);
DCHECK_EQ(RoundUp(data_offset, component_size), data_offset)
<< "Array data offset isn't aligned with component size";
return MemberOffset(data_offset);
}我们看下array对象的在内存中布局
c++
// array对象的父类Object// The Class representing the type of the object.
HeapReference<Class> klass_;
// Monitor and hash code information.
uint32_t monitor_;
// array对象本身
// The number of array elements.
int32_t length_;
// Marker for the data (used by generated code)
uint32_t first_element_[0];这一步是获取刚创建的array在内存中的地址, 实际上是获取的首元素first_element_的地址,
| 字段 | 值 |
|---|---|
| 类引用(klass_) | |
| 锁状态(monitor_) | |
| 数组长度(length_) | |
| 首元素地址 | ← first_element_[0] |
1.3 构建native层的Bitmap,并且将地址赋值给SkBitmap
c++
android::Bitmap* wrapper = new android::Bitmap(env, arrayObj, (void*) addr,
info, rowBytes, ctable);
wrapper->getSkBitmap(bitmap);
// since we're already allocated, we lockPixels right away
// HeapAllocator behaves this way too
bitmap->lockPixels();这里构建了native的Bitmap,并且将之前的地址等信息赋值给了mPixelRef
xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
Bitmap::Bitmap(JNIEnv* env, jbyteArray storageObj, void* address,
const SkImageInfo& info, size_t rowBytes, SkColorTable* ctable)
: mPixelStorageType(PixelStorageType::Java) {
env->GetJavaVM(&mPixelStorage.java.jvm);
mPixelStorage.java.jweakRef = env->NewWeakGlobalRef(storageObj);
mPixelStorage.java.jstrongRef = nullptr;
mPixelRef.reset(new WrappedPixelRef(this, address, info, rowBytes, ctable));
// Note: this will trigger a call to onStrongRefDestroyed(), but
// we want the pixel ref to have a ref count of 0 at this point
mPixelRef->unref();
}xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
void Bitmap::getSkBitmap(SkBitmap* outBitmap) {
assertValid();
android::AutoMutex _lock(mLock);
// Safe because mPixelRef is a WrappedPixelRef type, otherwise rowBytes()
// would require locking the pixels first.
outBitmap->setInfo(mPixelRef->info(), mPixelRef->rowBytes());
outBitmap->setPixelRef(refPixelRefLocked())->unref();
outBitmap->setHasHardwareMipMap(hasHardwareMipMap());
}注意这步outBitmap->setPixelRef(refPixelRefLocked())->unref(); 是将刚才native的mPixelRef 赋值给了SkBitmap
xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
SkPixelRef* SkBitmap::setPixelRef(SkPixelRef* pr, int dx, int dy) {
#ifdef SK_DEBUG
if (pr) {
if (kUnknown_SkColorType != fInfo.colorType()) {
const SkImageInfo& prInfo = pr->info();
SkASSERT(fInfo.width() <= prInfo.width());
SkASSERT(fInfo.height() <= prInfo.height());
SkASSERT(fInfo.colorType() == prInfo.colorType());
switch (prInfo.alphaType()) {
case kUnknown_SkAlphaType:
SkASSERT(fInfo.alphaType() == kUnknown_SkAlphaType);
break;
case kOpaque_SkAlphaType:
case kPremul_SkAlphaType:
SkASSERT(fInfo.alphaType() == kOpaque_SkAlphaType ||
fInfo.alphaType() == kPremul_SkAlphaType);
break;
case kUnpremul_SkAlphaType:
SkASSERT(fInfo.alphaType() == kOpaque_SkAlphaType ||
fInfo.alphaType() == kUnpremul_SkAlphaType);
break;
}
}
}
#endif
if (pr) {
const SkImageInfo& info = pr->info();
fPixelRefOrigin.set(SkTPin(dx, 0, info.width()),
SkTPin(dy, 0, info.height()));
} else {
// ignore dx,dy if there is no pixelref
fPixelRefOrigin.setZero();
}
if (fPixelRef != pr) {
this->freePixels();
SkASSERT(nullptr == fPixelRef);
SkSafeRef(pr);
fPixelRef = pr;
this->updatePixelsFromRef();
}
SkDEBUGCODE(this->validate();)
return pr;
}
void SkBitmap::updatePixelsFromRef() const {
if (fPixelRef) {
if (fPixelLockCount > 0) {
SkASSERT(fPixelRef->isLocked());
void* p = fPixelRef->pixels();
if (p) {
p = (char*)p
+ fPixelRefOrigin.fY * fRowBytes
+ fPixelRefOrigin.fX * fInfo.bytesPerPixel();
}
fPixels = p;
fColorTable = fPixelRef->colorTable();
} else {
SkASSERT(0 == fPixelLockCount);
fPixels = nullptr;
fColorTable = nullptr;
}
}
}1.4 将图片信息写入SKBitmap对应的内存里
c++
SkCodec::Result result = codec->getAndroidPixels(
decodeInfo,
decodingBitmap.getPixels(),
decodingBitmap.rowBytes(),
&codecOptions
);xrefandroid.com/android-7.0...
c++
SkCodec::Result SkAndroidCodec::getAndroidPixels(
const SkImageInfo& info,
void* pixels,
size_t rowBytes,
const AndroidOptions* options
) {
if (!pixels) {
return SkCodec::kInvalidParameters;
}
if (rowBytes < info.minRowBytes()) {
return SkCodec::kInvalidParameters;
}
AndroidOptions defaultOptions;
if (!options) {
options = &defaultOptions;
}
else if (options->fSubset) {
if (!is_valid_subset(*options->fSubset, fInfo.dimensions())) {
return SkCodec::kInvalidParameters;
}
if (SkIRect::MakeSize(fInfo.dimensions()) == *options->fSubset) {
// The caller wants the whole thing, rather than a subset. Modify
// the AndroidOptions passed to onGetAndroidPixels to not specify
// a subset.
defaultOptions = *options;
defaultOptions.fSubset = nullptr;
options = &defaultOptions;
}
}
return this->onGetAndroidPixels(
info,
pixels,
rowBytes,
*options
);
}最终找到合适的图片的Codec去加载到void* pixels,也就是刚才分配的java array对应的heap内存上。
2 高版本bitmap分配的原理
我们直接简化,看下关键步骤即可
c++
// 分配内存
bool SkBitmap::tryAllocPixels(Allocator* allocator) {
HeapAllocator stdalloc;
if (nullptr == allocator) {
allocator = &stdalloc;
}
return allocator->allocPixelRef(this);
}
// 分配内存
static sk_sp<Bitmap> allocateBitmap(SkBitmap* bitmap, AllocPixelRef alloc) {
const SkImageInfo& info = bitmap->info();
if (info.colorType() == kUnknown_SkColorType) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("unknown bitmap configuration");
return nullptr;
}
size_t size;
// we must respect the rowBytes value already set on the bitmap instead of
// attempting to compute our own.
const size_t rowBytes = bitmap->rowBytes();
if (!Bitmap::computeAllocationSize(rowBytes, bitmap->height(), &size)) {
return nullptr;
}
auto wrapper = alloc(size, info, rowBytes);
if (wrapper) {
wrapper->getSkBitmap(bitmap);
}
return wrapper;
}
// 分配内存
bool HeapAllocator::allocPixelRef(SkBitmap* bitmap) {
mStorage = android::Bitmap::allocateHeapBitmap(bitmap);
return !!mStorage;
}
// 真正分配内存,直接分配一个native内存
sk_sp<Bitmap> Bitmap::allocateHeapBitmap(size_t size, const SkImageInfo& info, size_t rowBytes) {
void* addr = calloc(size, 1);
if (!addr) {
return nullptr;
}
return sk_sp<Bitmap>(new Bitmap(addr, size, info, rowBytes));
}
// 绑定native内存和SkBitmap
void Bitmap::getSkBitmap(SkBitmap* outBitmap) {
#ifdef __ANDROID__ // Layoutlib does not support hardware acceleration
if (isHardware()) {
outBitmap->allocPixels(mInfo);
uirenderer::renderthread::RenderProxy::copyHWBitmapInto(this, outBitmap);
return;
}
#endif
outBitmap->setInfo(mInfo, rowBytes());
outBitmap->setPixelRef(sk_ref_sp(this), 0, 0);
}
// 绑定native内存和SkBitmap
void SkBitmap::setPixelRef(sk_sp<SkPixelRef> pr, int dx, int dy) {
#ifdef SK_DEBUG
if (pr) {
if (kUnknown_SkColorType != this->colorType()) {
SkASSERT(dx >= 0 && this->width() + dx <= pr->width());
SkASSERT(dy >= 0 && this->height() + dy <= pr->height());
}
}
#endif
fPixelRef = kUnknown_SkColorType != this->colorType() ? std::move(pr) : nullptr;
void* p = nullptr;
size_t rowBytes = this->rowBytes();
// ignore dx,dy if there is no pixelref
if (fPixelRef) {
rowBytes = fPixelRef->rowBytes();
// TODO(reed): Enforce that PixelRefs must have non-null pixels.
p = fPixelRef->pixels();
if (p) {
p = (char*)p + dy * rowBytes + dx * this->bytesPerPixel();
}
}
fPixmap.reset(fPixmap.info(), p, rowBytes);
SkDEBUGCODE(this->validate());
}3流程对比
| 特性 | 低版本方案 | 高版本方案 |
|---|---|---|
| 存储位置 | Java堆(非移动数组) | Native堆 |
| 分配成本 | JNI调用+GC压力 | 直接系统调用 |
| 内存管理 | GC回收+手动释放 | 引用计数+自动回收 |
| 最大优势 | 兼容性好 | 突破Java堆限制 |
| 典型问题 | 容易OOM | 需要处理Native OOM |
4 方案实现
源码地址 github.com/PTrainbow/N...
c++
/**
* addressOf 代理
*
* 判断当前是否需要 hook(是来自 allocateJavaPixelRefProxy 的调用)
* 申请 native 内存,修改 fake array
* 此时 fake array 为:
* | kclass_ | uint32_t monitor_ | size(Java 层真实申请的大小) | magic number | global ref | native byte[] pointer |
*
* @param env
* @param obj
* @param javaArray
* @return
*/
jlong addressOfProxy(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj, jbyteArray javaArray) {
// LOGE("call addressOfProxy");
if (pthread_getspecific(canHook) == nullptr) {
// LOGE("call addressOfProxy origin! bitmap allocate null");
return ((AddressOfType) addressOfOrigin)(env, obj, javaArray);
}
// LOGE("do addressOfProxy hook!");
pthread_setspecific(canHook, nullptr);
jlong addr = ((AddressOfType) addressOfOrigin)(env, obj, javaArray);
bool isNativeBitmap = addr != 0 && *(int32_t *) addr == magicNum;
if (isNativeBitmap) {
jint bitmapSize = *(int32_t *) (addr - sizeof(int32_t));
// LOGE("native bitmap malloc");
void *bitmap = calloc(bitmapSize, 1);
registerNativeAllocation(env, bitmapSize);
*(void **) (addr + sizeof(int) + sizeof(jobject)) = bitmap;
addr = reinterpret_cast<jlong>(bitmap);
}
return addr;
}
/**
* newNonMovableArray 代理
*
* 判断当前是否需要 hook(是来自 allocateJavaPixelRefProxy 的调用)
* 构造 fake array,global ref 存储
* 此时 fake array 为:
* | kclass_ | uint32_t monitor_ | size(Java 层真实申请的大小) | magic number | global ref | nullptr |
*
* @param env
* @param obj
* @param javaElementClass
* @param bitmapSize
* @return
*/
jbyteArray newNonMovableArrayProxy(JNIEnv *env, jobject obj, jclass javaElementClass,
jint bitmapSize) {
// LOGE("call newNonMovableArrayProxy");
if (pthread_getspecific(canHook) == nullptr || addressOfOrigin == nullptr) {
// LOGE("call newNonMovableArray origin! bitmap is null");
return ((NewNonMovableArrayType) newNonMovableArrayOrigin)(env, obj, javaElementClass, bitmapSize);
}
int fakeArraySize = fakeArrSelfLen;
jbyteArray fakeArray = ((NewNonMovableArrayType) newNonMovableArrayOrigin)(env, obj,
javaElementClass,
fakeArraySize);
// LOGE("do newNonMovableArrayProxy hook");
jobject globalRef = env->NewGlobalRef(fakeArray);
jlong fakeAddr = ((AddressOfType) addressOfOrigin)(env, VMRuntime, fakeArray);
*(int32_t *) (fakeAddr - sizeof(int)) = bitmapSize;
*(int32_t *) (fakeAddr) = magicNum;
*(jobject *) (fakeAddr + sizeof(int)) = globalRef;
if (bitmapSize != env->GetArrayLength(fakeArray)) {
return ((NewNonMovableArrayType) newNonMovableArrayOrigin)(env, obj, javaElementClass,
bitmapSize);
} else {
return fakeArray;
}
}
void deleteWeakGlobalRefProxy(JNIEnv *env, jweak obj) {
if (env->IsSameObject(obj, nullptr) || addressOfOrigin == nullptr) {
((DeleteWeakGlobalRefType) deleteWeakGlobalRefOrigin)(env, obj);
return;
}
jlong addr = 0;
if (env->IsInstanceOf(obj, byteClazz)) {
addr = ((AddressOfType) addressOfOrigin)(env, VMRuntime, obj);
}
if (addr != 0 && *(int32_t *) (addr) == magicNum) {
jobject globalRef = *(jobject *) (addr + sizeof(int));
void *bitmap = *(void **) (addr + sizeof(int) + sizeof(jobject));
int realBitmapSize = *(int *) (addr - sizeof(int));
*(int32_t *) (addr - sizeof(int)) = fakeArrSelfLen;
env->DeleteGlobalRef(globalRef);
if (bitmap != nullptr) {
// LOGE("native bitmap free");
free(bitmap);
registerNativeFree(env, realBitmapSize);
}
}
((DeleteWeakGlobalRefType) deleteWeakGlobalRefOrigin)(env, obj);
}
void* allocateJavaPixelRefProxy(JNIEnv *env, void *param1, void *param2) {
pthread_setspecific(canHook, (void *) (1));
return ((AllocateJavaPixelRefType)allocateJavaPixelRefOrigin)(env, param1, param2);
}