前言:以下使用是基于与string和vector部分较不常见的使用(少部分经常使用的未列举),还有部分可看list - C++ Reference来阅读文档
构造函数(Construct list)

cpp
//打印函数
template<class Contain>
void Print(const Contain& con)
{
for (auto& e : con)
{
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
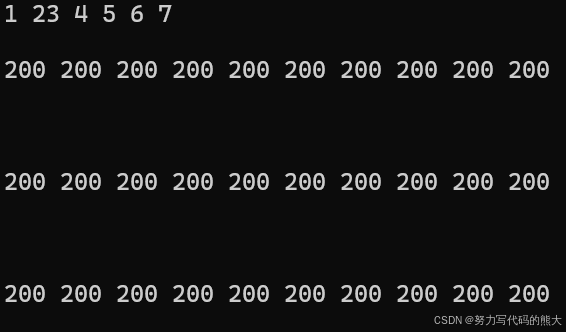
list<int> l1{ 1, 23, 4, 5, 6, 7 };//内存池构造
Print(l1);
list<int> l2(10, 200);//构造10个相同200
Print(l2);
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
list<int> l3(l2.begin(), l2.end());//按l2迭代器构造
Print(l3);
cout << endl;
cout << endl;
list<int> l4(l3);//拷贝l3
Print(l4);
}
元素访问( Element access )
front
说明:访问首元素元素

cpp
void test02()
{
list<int> l1{ 1, 23, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
cout << l1.front() << endl;//返回头元素
}back
说明:访问末尾元素

cpp
void test02()
{
list<int> l1{ 1, 23, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
cout << l1.back() << endl;//返回尾部元素
}
修饰(Modifiers)
assign
说明:将list类的实例化对象替换未一个新的list初始化对象

cpp
//assign
list<int> l2{ 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
cout << "assign前:";
Print(l2);
//l2.assign(l1.begin()+1, l1.end());//error这是一个例子,双向迭代器不能支持+-操作,一般能实现的只有随机迭代器
//l2.assign(l1.begin(), l1.end());//这是可以的
l2.assign(10, 1000);
cout << "assign后:";
Print(l2); 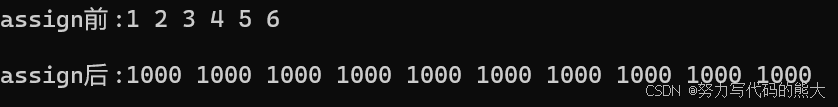
关于迭代器可以参考这个博客List迭代器和模拟(迭代器的模拟)-CSDN博客。
push_front
说明:在链表第一个结点头插

cpp
//push_front
list<int> l3{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "push_front前:";
Print(l3);
cout << "push_front后:";
l3.push_front(10000);
Print(l3);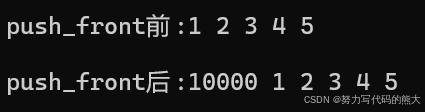
pop_front
说明:删除链表第一个元素结点
cpp
//pop_front
l3.pop_front();
cout << "pop_front后:";
Print(l3);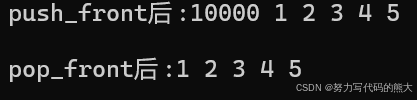
push_back和pop_back
说明:push_back在链表尾部插入结点;pop_back删除尾部结点
cpp
//push_back和pop_back
list<int> l4{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "push_back前:";
Print(l4);
l4.push_back(10000);
cout << "push_back后";
Print(l4);
cout << "pop_back后:";
l4.pop_back();
Print(l4);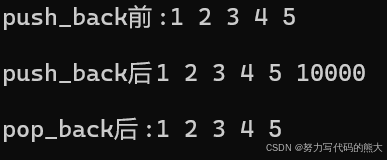
insert
说明:在任意位置插入结点

cpp
list<int> l5{ 1,2,3,4,5 };
cout << "insert前:";
Print(l5);
l5.insert(l5.begin(), 10000);//同理被迭代器限制,不能加加(解决办法就是在调用之前使用一个变量存储迭代器然后++\--操作达到想要的指向地址)
cout << "insert后:";
Print(l5);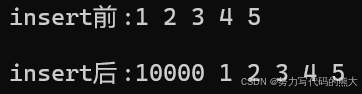
erase
说明:在任意位置删除结点

cpp
cout << "erase后:";
l5.erase(l5.begin());
Print(l5);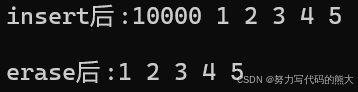
数据操作(Operations)
remove
说明:删除所有数据未val的结点

cpp
//remove删除所有val数据
list<int> l2{ 1,2,2,2,2,2,10,20,30,30 };
cout << "remove前:";
Print(l2);
cout << "remove后:";
l2.remove(2);
Print(l2);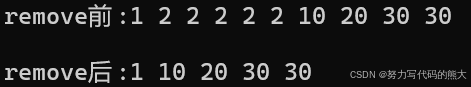
unique
说明:删除重复的元素

cpp
//unique删除重复的数
list<int> l3{ 1,2,2,2,2,2,10,20,30,30 };
cout << "删除重复前:";
Print(l3);
l3.unique();
cout << "删除重复后:";
Print(l3);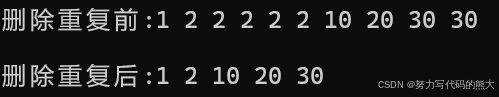
sort
说明:排序未有序序列(升序)

cpp
list<int> l4{ 20,10,30,40,70,50,80,60 };
list<int> l5{ 100,500,300,600,200,900,400 };
l4.sort();
l5.sort();merge
说明:合并有序链表(一般需要和sort使用)

cpp
//merge合并到调用merge的链表中(内部必须是有序序列,所以在使用之前都要使用sort函数)
list<int> l4{ 20,10,30,40,70,50,80,60 };
list<int> l5{ 100,500,300,600,200,900,400 };
l4.sort();
l5.sort();
cout << "merge前:";
Print(l4);
cout << "merge后:";
l4.merge(l5);
Print(l4);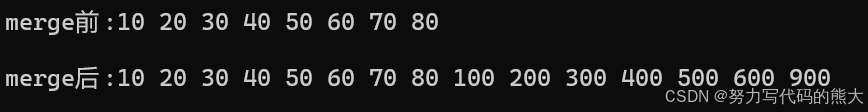
reserve
说明:对链表进行逆置处理
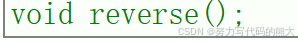
cpp
//reverse逆置
list<int> l6{ 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,0 };
cout << "逆置前:";
Print(l6);
l6.reverse();
cout << "逆置后:";
Print(l6);
splice
说明:拼接2个list链表

cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
int main() {
std::list<int> l1 = {1, 2, 3};
std::list<int> l2 = {4, 5};
l1.splice(l1.begin(), l2);
std::cout << "list l1 after splice operation: ";
for (auto ele : l1) std::cout << ele << " ";
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "list l2 after splice operation: ";
std::cout << "l2.size is: " << l2.size() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
拼接后会使得被拼接的链表结点清除。
解释一下文档中第二个和第三个,第二个是从pos位置拼接从另一个list的i位置开始
第三个是从pos位置拼接从另一个list的迭代器拼接。
