目录
一、数据获取
通过爬虫获取图片数据。
import requests
import re
import os
import time
headers = {'User-Agent':'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/84.0.4147.125 Safari/537.36'}
name = input('您要爬取什么图片')
num = 0
num_1 = 0
num_2 = 0
x = input('您要爬取几张呢?,输入1等于60张图片。')
list_1 = []
for i in range(int(x)):
name_1 = os.getcwd()
name_2 = os.path.join(name_1,'图片')
url = 'https://image.baidu.com/search/flip?tn=baiduimage&ie=utf-8&word='+name+'&pn='+str(i*30)
res = requests.get(url,headers=headers)
htlm_1 = res.content.decode()
a = re.findall('"objURL":"(.*?)",',htlm_1)
if not os.path.exists(name_2):
os.makedirs(name_2)
for b in a:
try:
b_1 = re.findall('https:(.*?)&',b)
b_2 = ''.join(b_1)
if b_2 not in list_1:
num = num +1
img = requests.get(b)
f = open(os.path.join(name_1,'图片',name+str(num)+'.png'),'ab')
print('---------正在下载第'+str(num)+'张图片----------')
f.write(img.content)
f.close()
list_1.append(b_2)
elif b_2 in list_1:
num_1 = num_1 + 1
continue
except Exception as e:
print('---------第'+str(num)+'张图片无法下载----------')
num_2 = num_2 +1
continue
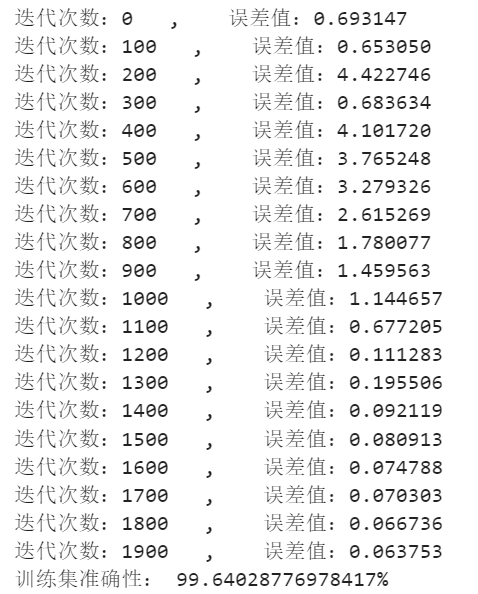
print('下载完成,总共下载{}张,成功下载:{}张,重复下载:{}张,下载失败:{}张'.format(num+num_1+num_2,num,num_1,num_2))
结果:
二、数据处理与数据集制作
本次学习,通过逻辑回归识别猪的图片。通过网络爬虫分别爬取猪,猫,狗的图片,来做是否是猪的预测。
(1)数据处理:
-
手动筛除一些图片
-
图片标准化 长度宽度为64*64
(2)标准化代码
from PIL import Image
import os
## 说明:输入原始图像路径和新建图像文件夹名称 默认修改出长度宽度为64*64
def stdimage(pathorg,name,pathnew=None,width=64,length=64):
#检查文件是否建立
if pathnew == None: # 如果没有手动创建
tage = os.path.exists(os.getcwd()+'\\'+name) #检查一下是否属实
if not tage: #没有整个新文件夹
os.mkdir(os.getcwd()+"\\"+name) #创建文件夹,name
image_path = os.getcwd()+"\\"+name+"\\"
else:#已经手动创建
tage = os.path.exists(pathnew+"\\"+name)
if not tage:
path = os.getcwd()
os.mkdir(path+"\\"+name)
image_path = path +"\\"+name+"\\"
## 开始处理
i = 1# 从一开始
list_name = os.listdir(pathorg) #获取图片名称列表
for item in list_name:
#检查是否有图片
tage = os.path.exists(pathorg+str(i)+'.png')
if not tage:
image = Image.open(pathorg+'\\'+item)
std = image.resize((width,length),Image.ANTIALIAS)
## 模式为RGB
if not std.mode == "RGB":
std = std.convert('RGB')
std.save(image_path+str(i)+'.png')
i+=1(3)数据集制作
将图片数据制作成pyh5数据来保存,方便使用和共享。
首先将标准化好的图片变为numpy数组。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import os
# 创建图片的numpy数组。
# 输入图片的path然后for循环建立rgb图片数组。
def creatdata(path):
im_name_list = os.listdir(path)
all_data =[]
for item in im_name_list:
try:
all_data.append(plt.imread(path+'\\'+item).tolist())
except:
print(item+" open error ")
return all_data
data = creatdata(r"F:\JupyterLab\CNN\stdimage")再将data数据保存到pyh5文件中
import h5py
import numpy as np
# 准备数据
a = np.zeros((112, 1)) # 假设这是训练集的标签为0的数据
b = np.ones((166, 1)) # 假设这是训练集的标签为1的数据
c = np.vstack((a, b)) # 合并标签数据
# 假设 data 是训练集的特征数据
# data = ... # 你需要定义 data,例如 data = np.random.rand(278, 64, 64, 3)
# 类别名称
d = np.array([['nopig'], ['pig']], dtype=h5py.string_dtype())
# 写入 HDF5 文件
with h5py.File("train_pig.h5", "w") as f:
f.create_dataset("train_set_x", data=data) # 确保 data 已定义
f.create_dataset("train_set_y", data=c)
f.create_dataset("classes_list", data=d)三、逻辑回归
(1)加载数据
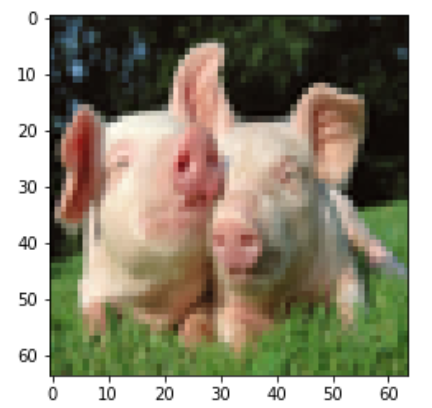
将我们制作好的数据取出来,并且可视化。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import h5py
import numpy as np
train_data = h5py.File("train_pig.h5","r")
train_set_x_orig = np.array(train_data['train_set_x'][:])
train_set_y_orig = np.array(train_data['train_set_y'][:])
classes = np.array(train_data["classes_lsit"][:])
train_set_y_orig=train_set_y_orig.reshape((1,train_set_y_orig.shape[0]))
def plot_data(a):
plt.imshow(train_set_x_orig[a])
plot_data(1)
plot_data(118)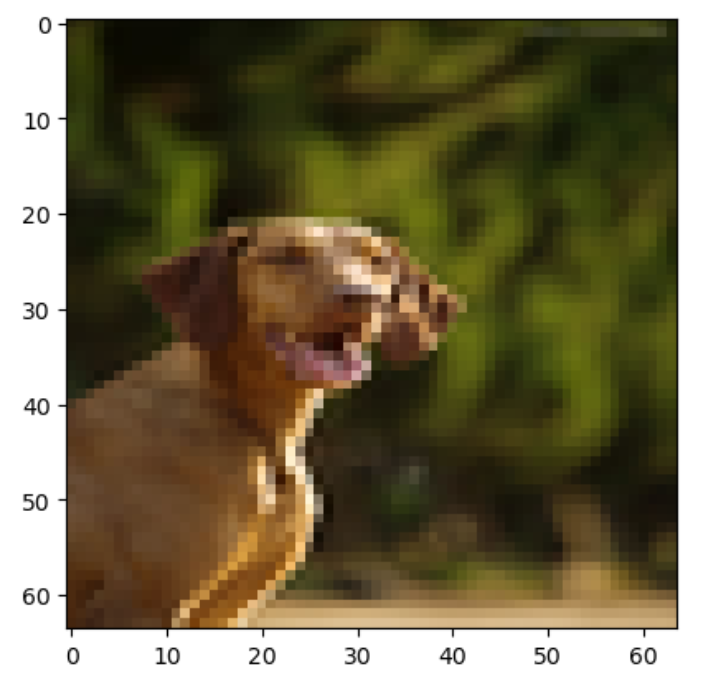

(2)训练集
train_set_x_f = train_set_x_orig.reshape(train_set_x_orig.shape[0],-1).T(3)逻辑回归
准备好搭建的基本函数和方法
def sigmod(z):
s= 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
return s
def cast_TD(w,b,X,Y):
"""
实现前向和后向传播的成本函数及其梯度。
参数:
w - 权重,大小不等的数组(num_px * num_px * 3,1)
b - 偏差,一个标量
X - 矩阵类型为(num_px * num_px * 3,训练数量)
Y - 真正的“标签”矢量(如果非猫则为0,如果是猫则为1),矩阵维度为(1,训练数据数量)
返回:
cost- 逻辑回归的负对数似然成本
dw - 相对于w的损失梯度,因此与w相同的形状
db - 相对于b的损失梯度,因此与b的形状相同
"""
m = X.shape[1]
##正向传播
## j的定义式
A = sigmod(np.dot(w.T,X)+b)
cost = (-1/m)*np.sum(Y * np.log(A)+(1-Y)*(np.log(1-A)))
## 反向传播
## 计算dw,db
dw = (1/m)*np.dot(X,(A-Y).T)
db = (1/m)*np.sum(A-Y)
assert(dw.shape == w.shape)
assert(db.dtype == float)
cost = np.squeeze(cost)
assert(cost.shape == ())
grade = {
"dw" : dw,
"db" : db
}
return (grade , cost)
def changew(w , b , X , Y , times , alpha , print_cost = False):
"""
此函数通过运行梯度下降算法来优化w和b
参数:
w - 权重,大小不等的数组(num_px * num_px * 3,1)
b - 偏差,一个标量
X - 维度为(num_px * num_px * 3,训练数据的数量)的数组。
Y - 真正的“标签”矢量(如果非猫则为0,如果是猫则为1),矩阵维度为(1,训练数据的数量)
times - 优化循环的迭代次数
alpha - 梯度下降更新规则的学习率
print_cost - 每100步打印一次损失值
返回:
params - 包含权重w和偏差b的字典
grads - 包含权重和偏差相对于成本函数的梯度的字典
成本 - 优化期间计算的所有成本列表,将用于绘制学习曲线。
提示:
我们需要写下两个步骤并遍历它们:
1)计算当前参数的成本和梯度,使用propagate()。
2)使用w和b的梯度下降法则更新参数。
"""
costs = []
## 开始迭代
for i in range(times):
grads,cost =cast_TD(w,b,X,Y)
dw = grads["dw"]
db = grads["db"]
w= w - alpha*dw
b = b - alpha*db
if i % 100 == 0:
costs.append(cost)
if(print_cost) and (i%100==0):
print("迭代次数:%i , 误差值:%f" % (i,cost))
p = {
"w":w,
"b":b
}
grads = {
"dw":dw,
"db":db
}
return (p,grads,costs)
def initnet(a):
w = np.zeros(shape = (a,1))
b= 0
assert(w.shape == (a,1))
assert(isinstance(b,float) or isinstance(b,int))
return (w,b)
def yuce(w,b,X):
"""
使用学习逻辑回归参数logistic (w,b)预测标签是0还是1,
参数:
w - 权重,大小不等的数组(num_px * num_px * 3,1)
b - 偏差,一个标量
X - 维度为(num_px * num_px * 3,训练数据的数量)的数据
返回:
Y_prediction - 包含X中所有图片的所有预测【0 | 1】的一个numpy数组(向量)
"""
m = X.shape[1]
Yyuce = np.zeros((1,m)) #设置一个矩阵来存放预测值
w = w.reshape(X.shape[0],1)
A = sigmod(np.dot(w.T,X)+b)
for i in range(A.shape[1]):
Yyuce[0,i] = 1 if A[0,i]> 0.5 else 0
assert(Yyuce.shape == (1,m))
return Yyuce
def logitic(X_train,Y_train,times=2000,alpha = 0.1,print_cost = False):
"""
通过调用之前实现的函数来构建逻辑回归模型
参数:
X_train - numpy的数组,维度为(num_px * num_px * 3,m_train)的训练集
Y_train - numpy的数组,维度为(1,m_train)(矢量)的训练标签集
X_test - numpy的数组,维度为(num_px * num_px * 3,m_test)的测试集
Y_test - numpy的数组,维度为(1,m_test)的(向量)的测试标签集
times - 表示用于优化参数的迭代次数的超参数
alpha - 表示logitic()更新规则中使用的学习速率的超参数
print_cost - 设置为true以每100次迭代打印成本
返回:
res - 包含有关模型信息的字典。
"""
w , b = initnet(X_train.shape[0])
p,grads,costs = changew(w,b,X_train,Y_train,times,alpha,print_cost)
w , b = p["w"],p["b"]
# 预测,检查模型的可靠性
Yyuce_train = yuce(w,b,X_train)
# 打印准确性
print("训练集准确性:",format(100 - np.mean(np.abs(Y_train-Yyuce_train))*100)+"%")
d = {
"costs":costs, # 作图时候可以使用代价,看代价的变化
"Yyuce_train":Yyuce_train,
"w":w,
"b":b,
"alpha":alpha,
"times":times
}
return d开始使用
d = logitic(train_set_x_f,train_set_y_orig,times = 2000,alpha = 0.01,print_cost=True)
costs = np.squeeze(d['costs'])
plt.plot(costs)
plt.ylabel('cost')
plt.xlabel('times')
plt.title("Alpha = "+ str(d["alpha"]))
plt.show()结果