项目概述
本项目是一个基于 wxPython 开发的桌面应用程序,用于将图片和文字描述组合生成精美的 PDF 小说。它解决了创作者需要将图文内容快速整理成电子书的需求,特别适合绘本、图文小说、摄影作品集等场景。
C:\pythoncode\new\novel_pdf_generator (1).py
核心功能
- 批量导入和管理图片
- 为图片添加场景描述
- 支持一段文字对应多张图片
- 智能布局算法,将文字和配图显示在同一页
- 自动生成带封面的 PDF 文件
技术架构
依赖库分析
python
import wx # GUI框架
import json # 数据持久化
import os # 文件系统操作
from pathlib import Path # 路径处理
from reportlab.lib.pagesizes import A4 # PDF页面尺寸
from reportlab.pdfgen import canvas # PDF画布
from reportlab.lib.utils import ImageReader # 图片读取
from reportlab.pdfbase import pdfmetrics # 字体管理
from reportlab.pdfbase.ttfonts import TTFont # TrueType字体
from PIL import Image # 图片处理
import math # 数学计算技术栈选择理由:
- wxPython:跨平台GUI框架,原生界面风格,性能优秀
- ReportLab:强大的PDF生成库,支持精确的页面控制
- Pillow (PIL):图片处理标准库,用于图片缩放和格式转换
- JSON:轻量级数据格式,便于项目保存和加载
核心数据结构
ImageItem 类
python
class ImageItem:
"""图片项数据类"""
def __init__(self, path, description="", group_id=None):
self.path = path # 图片文件路径
self.description = description # 场景描述文字
self.group_id = group_id # 分组ID(相同ID表示同一组)设计思路:
- 使用
group_id实现多张图片共享同一段描述的功能 - 通过时间戳生成唯一ID,避免冲突
- 简洁的数据结构便于序列化为JSON
GUI 界面设计
布局结构
程序采用左右分栏布局:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 小说名称输入框 │
├──────────────┬──────────────────────────┤
│ 左侧区域 │ 右侧区域 │
│ ┌────────┐ │ ┌──────────────────┐ │
│ │操作按钮│ │ │ 图片预览区域 │ │
│ ├────────┤ │ └──────────────────┘ │
│ │图片列表│ │ ┌──────────────────┐ │
│ │ │ │ │ 场景描述输入 │ │
│ │ │ │ └──────────────────┘ │
│ │ │ │ [图片数量] [操作按钮] │
│ └────────┘ │ │
└──────────────┴──────────────────────────┘关键UI组件
1. 标题输入区
python
title_sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.HORIZONTAL)
title_label = wx.StaticText(panel, label='小说名称:')
self.title_text = wx.TextCtrl(panel, size=(300, -1))用于输入小说标题,会显示在PDF封面页。
2. 图片列表框
python
self.image_listbox = wx.ListBox(panel, style=wx.LB_SINGLE)- 使用
wx.LB_SINGLE单选模式 - 动态显示文件名和描述预览
- 绑定点击事件触发图片预览
3. 图片预览区
python
self.image_preview = wx.StaticBitmap(panel, size=(450, 350))
self.image_preview.SetBackgroundColour(wx.Colour(240, 240, 240))使用 StaticBitmap 组件显示选中的图片,设置灰色背景便于识别。
4. 分组控制
python
self.group_spin = wx.SpinCtrl(panel, value='1', min=1, max=50, initial=1)SpinCtrl 数字调节器,用户可以指定当前描述对应的图片数量(1-50张)。
核心功能实现
1. 图片管理
批量添加文件夹
python
def on_add_folder(self, event):
"""添加文件夹中的所有图片"""
dlg = wx.DirDialog(self, "选择图片文件夹")
if dlg.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
folder_path = dlg.GetPath()
image_extensions = ('.jpg', '.jpeg', '.png', '.bmp', '.gif')
for file in sorted(os.listdir(folder_path)):
if file.lower().endswith(image_extensions):
full_path = os.path.join(folder_path, file)
self.add_image_item(full_path)
self.update_listbox()
dlg.Destroy()关键点:
- 使用
sorted()确保文件按名称排序 lower().endswith()不区分大小写匹配扩展名- 必须调用
dlg.Destroy()释放对话框资源
单张/多张添加
python
def on_add_image(self, event):
"""添加单张图片"""
wildcard = "图片文件 (*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.png;*.bmp;*.gif)|*.jpg;*.jpeg;*.png;*.bmp;*.gif"
dlg = wx.FileDialog(self, "选择图片", wildcard=wildcard,
style=wx.FD_OPEN | wx.FD_MULTIPLE)
if dlg.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
paths = dlg.GetPaths() # 获取多个路径
for path in paths:
self.add_image_item(path)
self.update_listbox()
dlg.Destroy()使用 wx.FD_MULTIPLE 标志支持多选,GetPaths() 返回路径列表。
2. 图片预览功能
python
def show_preview(self, image_path):
"""显示图片预览"""
try:
img = Image.open(image_path)
# 调整图片大小以适应预览区域
preview_size = (450, 350)
img.thumbnail(preview_size, Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
# 转换为wx.Bitmap
width, height = img.size
wx_img = wx.Image(width, height)
wx_img.SetData(img.convert("RGB").tobytes())
bitmap = wx.Bitmap(wx_img)
self.image_preview.SetBitmap(bitmap)
except Exception as e:
wx.MessageBox(f"无法加载图片:{str(e)}", "错误", wx.OK | wx.ICON_ERROR)技术细节:
thumbnail()方法保持宽高比缩放LANCZOS重采样算法提供最佳缩放质量- PIL Image → wx.Image → wx.Bitmap 的转换链
- 必须转换为RGB模式(去除Alpha通道)
3. 图片顺序调整
上移实现
python
def on_move_up(self, event):
"""上移图片"""
selection = self.image_listbox.GetSelection()
if selection > 0:
# Python交换语法
self.image_items[selection], self.image_items[selection-1] = \
self.image_items[selection-1], self.image_items[selection]
self.update_listbox()
self.image_listbox.SetSelection(selection-1)设计要点:
- 检查边界条件(不能上移第一项)
- 使用Python优雅的元组解包交换
- 更新后保持选中状态
4. 描述分组功能
python
def on_save_description(self, event):
"""保存描述到当前及后续指定数量的图片"""
selection = self.image_listbox.GetSelection()
if selection != wx.NOT_FOUND:
description = self.description_text.GetValue()
group_count = self.group_spin.GetValue()
# 生成唯一的组ID
import time
group_id = int(time.time() * 1000) # 毫秒级时间戳
# 为当前及后续图片设置相同的描述和组ID
for i in range(selection, min(selection + group_count, len(self.image_items))):
self.image_items[i].description = description
self.image_items[i].group_id = group_id
self.update_listbox()
self.save_to_json()
wx.MessageBox(f"描述已保存到 {group_count} 张图片!", "提示", wx.OK | wx.ICON_INFORMATION)核心逻辑:
- 生成毫秒级时间戳作为唯一组ID
- 从选中位置开始,连续设置指定数量的图片
- 使用
min()防止越界 - 相同
group_id的图片会在PDF中显示在同一页
5. 数据持久化
保存到JSON
python
def save_to_json(self):
"""保存所有数据到JSON"""
data = {
'novel_title': self.title_text.GetValue(),
'images': []
}
for item in self.image_items:
data['images'].append({
'path': item.path,
'description': item.description,
'group_id': item.group_id
})
json_path = 'novel_data.json'
with open(json_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
json.dump(data, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=2)JSON结构示例:
json
{
"novel_title": "时光旅行者",
"images": [
{
"path": "/path/to/image1.jpg",
"description": "主角在未来城市中醒来",
"group_id": 1696834567890
},
{
"path": "/path/to/image2.jpg",
"description": "主角在未来城市中醒来",
"group_id": 1696834567890
}
]
}从JSON加载
python
def on_load_json(self, event):
"""从JSON加载数据"""
wildcard = "JSON文件 (*.json)|*.json"
dlg = wx.FileDialog(self, "选择JSON文件", wildcard=wildcard, style=wx.FD_OPEN)
if dlg.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
json_path = dlg.GetPath()
try:
with open(json_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
data = json.load(f)
self.image_items.clear()
if 'novel_title' in data:
self.title_text.SetValue(data['novel_title'])
for img_data in data.get('images', []):
if os.path.exists(img_data['path']): # 验证文件存在
item = ImageItem(
img_data['path'],
img_data.get('description', ''),
img_data.get('group_id')
)
self.image_items.append(item)
self.update_listbox()
wx.MessageBox("JSON文件加载成功!", "提示", wx.OK | wx.ICON_INFORMATION)
except Exception as e:
wx.MessageBox(f"加载JSON失败:{str(e)}", "错误", wx.OK | wx.ICON_ERROR)
dlg.Destroy()安全性考虑:
- 检查文件路径是否存在
- 使用
get()方法提供默认值 - 完整的异常处理机制
PDF生成核心算法
1. PDF创建流程
python
def create_pdf(self, pdf_path):
"""创建PDF文件"""
c = canvas.Canvas(pdf_path, pagesize=A4)
page_width, page_height = A4
# 注册中文字体
try:
pdfmetrics.registerFont(TTFont('SimSun', 'simsun.ttc'))
font_name = 'SimSun'
except:
try:
pdfmetrics.registerFont(TTFont('SimSun', '/System/Library/Fonts/STHeiti Light.ttc'))
font_name = 'SimSun'
except:
font_name = 'Helvetica'
# 创建封面页
if self.novel_title:
c.setFont(font_name, 36)
title_width = c.stringWidth(self.novel_title, font_name, 36)
c.drawString((page_width - title_width) / 2, page_height / 2, self.novel_title)
c.showPage()
# 按组处理内容...字体处理策略:
- 优先尝试Windows字体(simsun.ttc)
- 其次尝试macOS字体(STHeiti)
- 最后回退到默认字体(Helvetica)
- 使用
stringWidth()计算文字宽度实现居中
2. 图片分组处理
python
# 按组处理图片
processed_indices = set()
for i, item in enumerate(self.image_items):
if i in processed_indices:
continue
# 收集同组的图片
if item.group_id is not None:
group_images = [img for j, img in enumerate(self.image_items)
if img.group_id == item.group_id]
for j, img in enumerate(self.image_items):
if img.group_id == item.group_id:
processed_indices.add(j)
else:
group_images = [item]
processed_indices.add(i)
# 在一页中显示文字和所有配图
self.draw_content_page(c, item.description, group_images,
page_width, page_height, font_name)
c.showPage()算法解析:
- 使用
set记录已处理的图片索引,避免重复处理 - 通过
group_id识别同组图片 - 列表推导式高效收集同组图片
- 每组内容调用
draw_content_page()渲染到一页
3. 智能布局算法
这是整个项目最复杂也最精彩的部分:
python
def draw_content_page(self, c, description, images, page_width, page_height, font_name):
"""在一页中绘制文字描述和配图"""
margin = 40
usable_width = page_width - 2 * margin
usable_height = page_height - 2 * margin
current_y = page_height - margin
# 1. 绘制文字描述
if description:
c.setFont(font_name, 12)
lines = self.wrap_text(description, usable_width - 10, c, font_name, 12)
for line in lines:
current_y -= 18
c.drawString(margin + 5, current_y, line)
current_y -= 20 # 文字和图片之间的间距
# 2. 计算剩余空间
remaining_height = current_y - margin
if len(images) == 0:
return
num_images = len(images)
# 3. 根据图片数量选择布局策略
if num_images == 1:
# 单张图片:居中显示
self.draw_single_image(c, images[0].path, margin, margin,
usable_width, remaining_height)
elif num_images == 2:
# 两张图片:并排显示
img_width = (usable_width - 20) / 2
for idx, img in enumerate(images):
x = margin + idx * (img_width + 20)
self.draw_single_image(c, img.path, x, margin,
img_width, remaining_height)
elif num_images == 3:
# 三张图片:动态布局
if remaining_height > usable_width * 0.8:
# 空间充足:上1下2布局
top_height = remaining_height * 0.5
bottom_height = remaining_height * 0.45
self.draw_single_image(c, images[0].path, margin,
margin + bottom_height + 20,
usable_width, top_height)
img_width = (usable_width - 20) / 2
for idx, img in enumerate(images[1:]):
x = margin + idx * (img_width + 20)
self.draw_single_image(c, img.path, x, margin,
img_width, bottom_height)
else:
# 空间不足:三张并排
img_width = (usable_width - 40) / 3
for idx, img in enumerate(images):
x = margin + idx * (img_width + 20)
self.draw_single_image(c, img.path, x, margin,
img_width, remaining_height)
elif num_images == 4:
# 四张图片:2x2网格
img_width = (usable_width - 20) / 2
img_height = (remaining_height - 20) / 2
positions = [
(0, 1), (1, 1), # 上排
(0, 0), (1, 0) # 下排
]
for idx, img in enumerate(images):
col, row = positions[idx]
x = margin + col * (img_width + 20)
y = margin + row * (img_height + 20)
self.draw_single_image(c, img.path, x, y, img_width, img_height)
else:
# 5张及以上:自动网格布局
cols = min(3, num_images)
rows = math.ceil(num_images / cols)
img_width = (usable_width - (cols - 1) * 15) / cols
img_height = (remaining_height - (rows - 1) * 15) / rows
for idx, img in enumerate(images):
row = idx // cols
col = idx % cols
x = margin + col * (img_width + 15)
y = margin + (rows - 1 - row) * (img_height + 15)
self.draw_single_image(c, img.path, x, y, img_width, img_height)布局策略详解:
单图布局(1张)
┌─────────────────┐
│ 文字描述 │
├─────────────────┤
│ │
│ [单张大图] │
│ │
└─────────────────┘充分利用剩余空间,图片居中显示。
双图布局(2张)
┌─────────────────┐
│ 文字描述 │
├────────┬────────┤
│ │ │
│ [图1] │ [图2] │
│ │ │
└────────┴────────┘左右并排,平分空间。
三图布局(3张)
根据剩余空间自适应:
空间充足时(高度 > 宽度 * 0.8):
┌─────────────────┐
│ 文字描述 │
├─────────────────┤
│ [图片1] │
├────────┬────────┤
│ [图2] │ [图3] │
└────────┴────────┘空间不足时:
┌─────────────────┐
│ 文字描述 │
├─────┬─────┬─────┤
│[图1]│[图2]│[图3]│
└─────┴─────┴─────┘四图布局(4张)
┌─────────────────┐
│ 文字描述 │
├────────┬────────┤
│ [图1] │ [图2] │
├────────┼────────┤
│ [图3] │ [图4] │
└────────┴────────┘标准2x2网格。
多图布局(5+张)
┌──────────────────────┐
│ 文字描述 │
├──────┬──────┬────────┤
│[图1] │[图2] │ [图3] │
├──────┼──────┼────────┤
│[图4] │[图5] │ [图6] │
└──────┴──────┴────────┘自动计算网格(最多3列),向上取整行数。
4. 单图绘制函数
python
def draw_single_image(self, c, image_path, x, y, max_width, max_height):
"""在指定位置绘制单张图片"""
try:
img = Image.open(image_path)
img_width, img_height = img.size
# 计算缩放比例(保持宽高比)
scale = min(max_width / img_width, max_height / img_height)
new_width = img_width * scale
new_height = img_height * scale
# 居中对齐
x_centered = x + (max_width - new_width) / 2
y_centered = y + (max_height - new_height) / 2
c.drawImage(image_path, x_centered, y_centered,
width=new_width, height=new_height)
except Exception as e:
print(f"绘制图片 {image_path} 时出错:{str(e)}")关键算法:
scale = min(width_ratio, height_ratio)确保图片不超出边界- 居中算法:
centered = start + (available - actual) / 2 - 异常处理确保单张图片失败不影响整体生成
5. 文字换行算法
python
def wrap_text(self, text, max_width, canvas_obj, font_name, font_size):
"""文字换行"""
lines = []
paragraphs = text.split('\n')
for para in paragraphs:
if not para.strip():
lines.append('')
continue
current_line = ""
for char in para:
test_line = current_line + char
if canvas_obj.stringWidth(test_line, font_name, font_size) < max_width:
current_line = test_line
else:
if current_line:
lines.append(current_line)
current_line = char
if current_line:
lines.append(current_line)
return lines算法特点:
- 支持段落(
\n)保留 - 逐字符测量宽度,精确换行
- 使用
stringWidth()考虑不同字符宽度(中英文混排) - 空段落保留为空行
性能优化与最佳实践
1. 内存管理
python
# 使用 thumbnail 而非 resize
img.thumbnail(preview_size, Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)thumbnail() 直接修改原对象,比 resize() 返回新对象更节省内存。
2. 资源释放
python
dlg = wx.FileDialog(...)
if dlg.ShowModal() == wx.ID_OK:
# 处理逻辑
dlg.Destroy() # 必须显式销毁wxPython 对话框必须手动销毁,否则会内存泄漏。
3. 异常处理
所有文件操作和图片处理都包裹在 try-except 中,确保程序稳定性。
4. 用户体验优化
- 操作后立即提供反馈(MessageBox)
- 保持选中状态(移动后重新选中)
- 列表显示描述预览(快速识别)
可能的扩展功能
1. 图片编辑
- 添加滤镜效果
- 裁剪和旋转
- 亮度、对比度调整
2. 文字排版
- 支持富文本(粗体、斜体)
- 自定义字体和字号
- 段落对齐方式
3. 模板系统
python
templates = {
'simple': {'margin': 40, 'font_size': 12},
'elegant': {'margin': 60, 'font_size': 14},
'compact': {'margin': 20, 'font_size': 10}
}4. 批量处理
- 支持多个项目
- 项目间快速切换
- 批量导出
5. 云端同步
- 项目保存到云端
- 多设备协同编辑
- 版本控制
常见问题与解决方案
问题1:中文字体不显示
原因: 系统缺少中文字体或路径错误
解决方案:
python
# 添加更多字体路径
font_paths = [
'simsun.ttc', # Windows
'/System/Library/Fonts/STHeiti Light.ttc', # macOS
'/usr/share/fonts/truetype/wqy/wqy-microhei.ttc' # Linux
]
for path in font_paths:
try:
pdfmetrics.registerFont(TTFont('SimSun', path))
font_name = 'SimSun'
break
except:
continue问题2:图片过大导致内存溢出
解决方案: 在加载前预处理图片
python
def optimize_image(image_path, max_size=(2000, 2000)):
img = Image.open(image_path)
img.thumbnail(max_size, Image.Resampling.LANCZOS)
return img问题3:PDF文件过大
解决方案: 压缩图片质量
python
# 保存为JPEG并降低质量
img.save(temp_path, 'JPEG', quality=85, optimize=True)
c.drawImage(temp_path, ...)运行结果
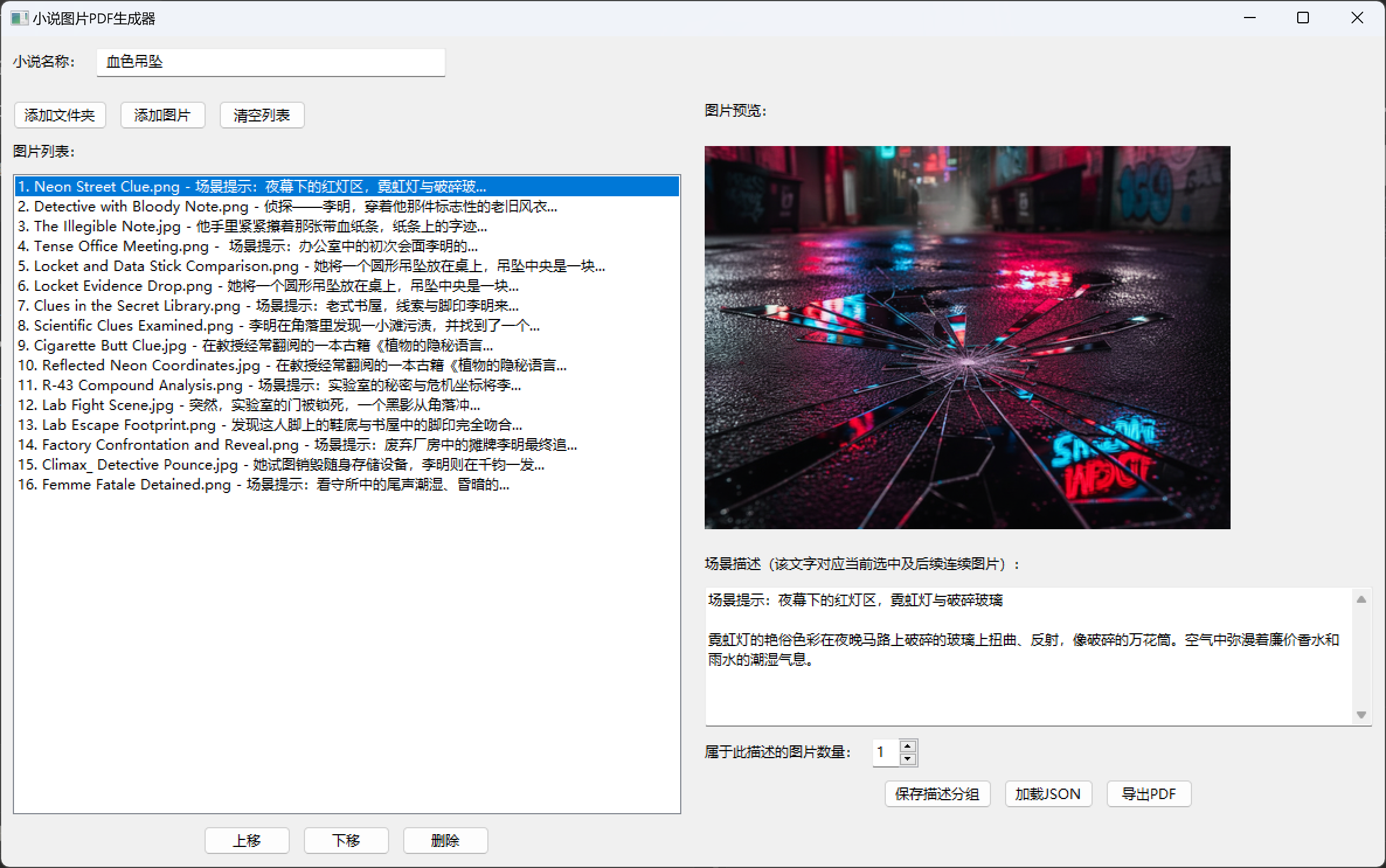
pdf结果