MyBatis Mapper配置解析深度解密:XML与注解的双重解析引擎
「MyBatis Mapper解析内核揭秘:XMLMapperBuilder与MapperAnnotationBuilder的双重解析机制深度剖析」
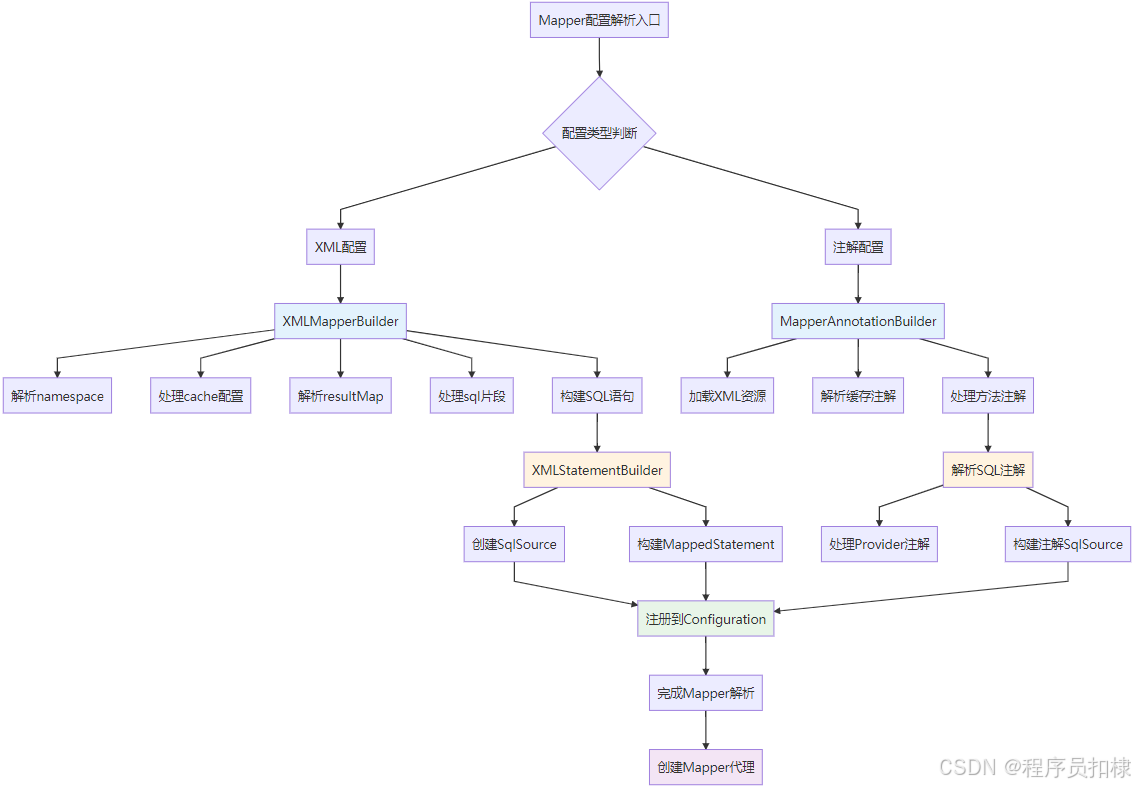
Mapper配置解析:MyBatis的核心生命力
在MyBatis的整体架构中,Mapper配置解析是整个框架最为核心和复杂的部分。它承担着将开发者定义的接口和SQL映射转化为可执行代码的重任。理解
XMLMapperBuilder和MapperAnnotationBuilder的工作原理,就等于掌握了MyBatis的灵魂所在。
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
免费获取源码。
更多内容敬请期待。如有需要可以联系作者免费送
更多源码定制,项目修改,项目二开可以联系作者
点击可以进行搜索(每人免费送一套代码):千套源码目录(点我)
2025元旦源码免费送(点我)
我们常常在当下感到时间慢,觉得未来遥远,但一旦回头看,时间已经悄然流逝。对于未来,尽管如此,也应该保持一种从容的态度,相信未来仍有许多可能性等待着我们。
XMLMapperBuilder:XML配置的解析引擎
解析入口与初始化过程
XMLMapperBuilder是处理Mapper XML文件的核心类,其构造过程体现了资源定位和依赖注入的设计思想:
java
public class XMLMapperBuilder extends BaseBuilder {
public XMLMapperBuilder(InputStream inputStream, Configuration configuration,
String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
this(configuration, new XPathParser(inputStream, true, configuration.getVariables(),
new XMLMapperEntityResolver()), resource, sqlFragments);
}
private XMLMapperBuilder(Configuration configuration, XPathParser parser,
String resource, Map<String, XNode> sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.resource = resource;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
}
}关键组件解析:
-
XPathParser:基于XPath的XML解析器,负责将XML转换为DOM树
-
MapperBuilderAssistant:构建助手,负责具体的Mapper组件构建
-
sqlFragments :SQL片段缓存,支持
<sql>标签的重用
核心解析流程分析
parse()方法是XMLMapperBuilder的入口点,它按照固定的顺序解析Mapper文件的各个部分:
java
public void parse() {
// 检查是否已经加载过该资源,避免重复解析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析mapper根节点
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 标记资源已加载
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 绑定Mapper接口
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
// 处理未解析的ResultMap和CacheRef
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}configurationElement()方法体现了XML配置的完整解析顺序:
java
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 1. 解析namespace
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 2. 解析cache-ref
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
// 3. 解析cache(二级缓存配置)
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
// 4. 解析resultMap(结果映射)
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("resultMap"));
// 5. 解析sql(可重用的SQL片段)
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("sql"));
// 6. 解析CRUD语句(最核心的部分)
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select"),
context.evalNodes("insert"),
context.evalNodes("update"),
context.evalNodes("delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" +
resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}SQL语句解析的深度机制
buildStatementFromContext()方法负责处理具体的SQL语句节点,这是MyBatis最核心的功能:
java
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser =
new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// 解析单个SQL语句节点
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 处理解析依赖问题
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}XMLStatementBuilder.parseStatementNode()的关键步骤:
java
public void parseStatementNode() {
// 1. 获取语句属性
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
// 2. 验证databaseId匹配
if (!databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace())) {
return;
}
// 3. 解析各种属性
Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");
Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");
String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");
String parameterType = context.getStringAttribute("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveClass(parameterType);
String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");
String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");
String lang = context.getStringAttribute("lang");
String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");
// 4. 解析SQL命令类型
String nodeName = context.getNode().getNodeName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
// 5. 判断是否为Select语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("flushCache", !isSelect);
boolean useCache = context.getBooleanAttribute("useCache", isSelect);
// 6. 解析SQL源
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);
// 7. 构建MappedStatement
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType,
/* 其他参数... */);
}MapperAnnotationBuilder:注解配置的解析引擎
注解解析的架构设计
MapperAnnotationBuilder专门处理基于注解的Mapper配置,它采用了一种完全不同的解析策略:
java
public class MapperAnnotationBuilder {
private final Configuration configuration;
private final MapperBuilderAssistant assistant;
private final Class<?> type;
public MapperAnnotationBuilder(Configuration configuration, Class<?> type) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.assistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, type.getName());
this.type = type;
}
public void parse() {
String resource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".java (best guess)";
// 检查资源是否已加载
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 解析注解配置
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
// 解析接口方法
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
}注解解析的核心逻辑
parseStatement()方法是注解解析的核心,它需要处理各种SQL注解:
java
void parseStatement(Method method) {
// 获取方法参数类型
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
// 获取语言驱动
LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
// 解析SQL注解
SqlSource sqlSource = getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(method, parameterTypeClass, languageDriver);
if (sqlSource == null) {
return;
}
// 解析其他注解属性
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = getSqlCommandType(method);
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
// 解析Options注解
Options options = method.getAnnotation(Options.class);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
// 构建MappedStatement
assistant.addMappedStatement(
mappedStatementId,
sqlSource,
sqlCommandType,
/* 其他参数... */
);
}多注解支持的实现机制
MyBatis支持多种SQL注解,每种注解都有特定的解析逻辑:
java
private SqlSource getSqlSourceFromAnnotations(Method method,
Class<?> parameterType,
LanguageDriver languageDriver) {
try {
// 检查@Select注解
Class<? extends Annotation> sqlAnnotationType = getSqlAnnotationType(method);
Class<? extends Annotation> sqlProviderAnnotationType = getSqlProviderAnnotationType(method);
if (sqlAnnotationType != null) {
if (sqlProviderAnnotationType != null) {
throw new BindingException("You cannot supply both a static SQL and SqlProvider method.");
}
// 解析静态SQL注解
Annotation sqlAnnotation = method.getAnnotation(sqlAnnotationType);
final String[] strings = (String[]) sqlAnnotation.getClass()
.getMethod("value").invoke(sqlAnnotation);
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(strings, parameterType, languageDriver);
} else if (sqlProviderAnnotationType != null) {
// 解析SQL Provider注解
return buildSqlSourceFromSqlProvider(method, languageDriver);
}
return null;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Could not find value method on SQL annotation. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}支持的注解类型包括:
-
@Select,@Insert,@Update,@Delete:静态SQL注解 -
@SelectProvider,@InsertProvider,@UpdateProvider,@DeleteProvider:动态SQL提供者 -
@Options:语句选项配置 -
@ResultMap:结果映射引用 -
@ResultType:结果类型指定
双重解析机制的协同工作
XML与注解的优先级处理
MyBatis允许同时使用XML和注解配置,框架需要处理两者的优先级和冲突:
java
public void parse() {
// 先尝试加载XML配置
String resource = type.getName().replace('.', '/') + ".xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
if (inputStream != null) {
// 如果存在XML配置,优先使用XML
XMLMapperBuilder xmlParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream,
assistant.getConfiguration(), resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
xmlParser.parse();
} else {
// 否则使用注解配置
parseAnnotation();
}
}冲突解决策略
当XML和注解配置冲突时,MyBatis采用明确的解决策略:
-
同名校验:相同的方法名在XML和注解中不能重复定义
-
XML优先:如果同时存在,XML配置会覆盖注解配置
-
运行时验证:在Mapper注册阶段进行完整性检查
解析过程中的高级特性
延迟解析机制
MyBatis采用延迟解析策略来处理配置间的依赖关系:
java
private void parsePendingResultMaps() {
Collection<ResultMapResolver> incompleteResultMaps =
configuration.getIncompleteResultMaps();
synchronized (incompleteResultMaps) {
Iterator<ResultMapResolver> iter = incompleteResultMaps.iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
try {
iter.next().resolve();
iter.remove();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
// 仍然无法解析,继续等待
}
}
}
}碎片化SQL的管理
<sql>片段的解析和管理体现了代码复用的设计思想:
java
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
sqlElement(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
sqlElement(list, null);
}
private void sqlElement(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
String databaseId = context.getStringAttribute("databaseId");
String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");
id = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
if (databaseIdMatchesCurrent(id, databaseId, requiredDatabaseId)) {
// 缓存SQL片段供后续使用
sqlFragments.put(id, context);
}
}
}性能优化与缓存策略
解析结果缓存
为了避免重复解析,MyBatis实现了多级缓存机制:
java
public class Configuration {
// 已加载的资源缓存
protected final Set<String> loadedResources = new HashSet<>();
// Mapper注册表缓存
protected final Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers = new HashMap<>();
// MappedStatement缓存
protected final Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements =
new StrictMap<>("Mapped Statements collection");
// 缓存配置
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new StrictMap<>("Caches collection");
}懒加载与按需解析
MyBatis采用懒加载策略,只有在真正使用时才进行完整解析:
java
public class MapperRegistry {
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory =
(MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 动态代理创建Mapper实例
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}总结
XMLMapperBuilder和MapperAnnotationBuilder共同构成了MyBatis Mapper配置解析的双重引擎,它们分别针对不同的配置风格提供了完整的解决方案。通过深入分析这两个核心类的实现,我们可以学到:
-
架构设计智慧:如何设计可扩展的解析器架构
-
代码复用策略:通过Builder模式实现复杂对象的逐步构建
-
异常处理机制:优雅处理解析过程中的依赖和异常
-
性能优化思想:通过缓存和懒加载提升框架性能
理解这些底层机制,不仅有助于我们更好地使用MyBatis,更能提升我们的系统设计能力和代码质量意识。这种从使用者到理解者的转变,是每个开发者技术成长的重要里程碑。
🥂(❁´◡`❁)您的点赞👍➕评论📝➕收藏⭐是作者创作的最大动力🤞
💖📕🎉🔥 支持我:点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝欢迎留言讨论
🔥🔥🔥(源码 + 调试运行 + 问题答疑)
🔥🔥🔥 有兴趣可以联系我。文末有免费源码
💖学习知识需费心,
📕整理归纳更费神。
🎉源码免费人人喜,
🔥码农福利等你领!💖常来我家多看看,
📕网址:扣棣编程** ,
🎉感谢支持常陪伴,
🔥点赞关注别忘记!**💖山高路远坑又深,
📕大军纵横任驰奔,
🎉谁敢横刀立马行?
🔥唯有点赞+关注成!
往期文章推荐:
基于Springboot + vue实现的学生宿舍信息管理系统
免费获取宠物商城源码--SpringBoot+Vue宠物商城网站系统
【2025小年源码免费送】