目录
[4.1 什么是序列化和反序列](#4.1 什么是序列化和反序列)
[4.3 为什么不使用Java自带的序列化(Serializable)](#4.3 为什么不使用Java自带的序列化(Serializable))
[4.4 如何使用Hadoop的序列化和反序列化](#4.4 如何使用Hadoop的序列化和反序列化)
[5.1 准备工作](#5.1 准备工作)
[5.2 客户端提交作业](#5.2 客户端提交作业)
[5.3 切片数量计算(重点)](#5.3 切片数量计算(重点))
[5.4 Map阶段源码分析](#5.4 Map阶段源码分析)
[5.4.3 runNewMapper()方法分析](#5.4.3 runNewMapper()方法分析)
[5.4.4 mapper、inputFormat和input对象的创建](#5.4.4 mapper、inputFormat和input对象的创建)
[5.4.5 initialize方法源码分析](#5.4.5 initialize方法源码分析)
[5.4.6 run(mapperContext)](#5.4.6 run(mapperContext))
[5.4.9 有Reduce时out对象创建](#5.4.9 有Reduce时out对象创建)
[5.4.10 分区](#5.4.10 分区)
[5.4.13 排序比较器](#5.4.13 排序比较器)
[5.4.14 没有Reduce时out对象创建](#5.4.14 没有Reduce时out对象创建)
[5.5 Reduce阶段源码分析](#5.5 Reduce阶段源码分析)
4.1 什么是序列化和反序列
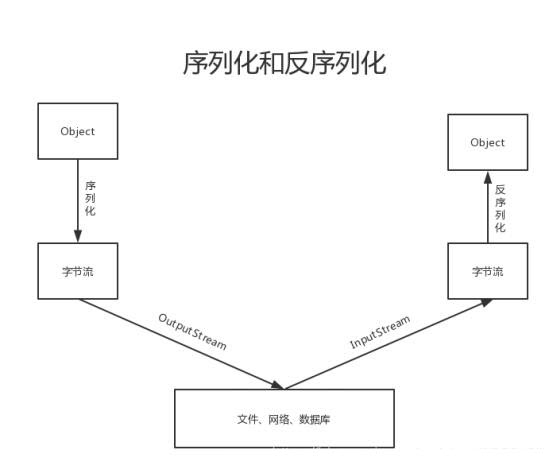
序列化定义:就是把内存中的对象,转换为字节序列,以便于存储到磁盘或网络传输,此过程被称为序列化。
反序列化定义:将字节序列或磁盘中的持久化字节数据,转换为内存中的对象的过程。
##4.2 hadoop为什么需要序列化和反序列化
数据经过mapper 任务的处理后,会产生溢出文件,这些文件会被保存到磁盘上。mapper任务完成后,reducer会通过http get的方式从mapper端拷贝对应分区的数据,中间需要经过网络传输。需要做持久化(存盘)或网络传输,这中间就需要做数据的序列化和反序列操作
4.3 为什么不使用Java自带的序列化(Serializable)
Java的序列化是一个偏重量序列化,一个对象被序列化后,会带有很多的额外的信息,比如各种校验信息、继承体系、Header,从而导致体积较大。又由于hadoop处理的数据量一般都比较大,所以该方式不利于数据的传输。
Hadoop序列化的特点:
- 紧凑:节省存储空间
- 快捷:读写数据的额外开销比较小
- 可扩展型更强:可以随着通讯协议升级而升级。
- 跨语言:支持多语言的交互。
4.4 如何使用Hadoop的序列化和反序列化
hadoop为基本的数据类型提供的对应的序列化和反序列化功能的类。如下图所示:
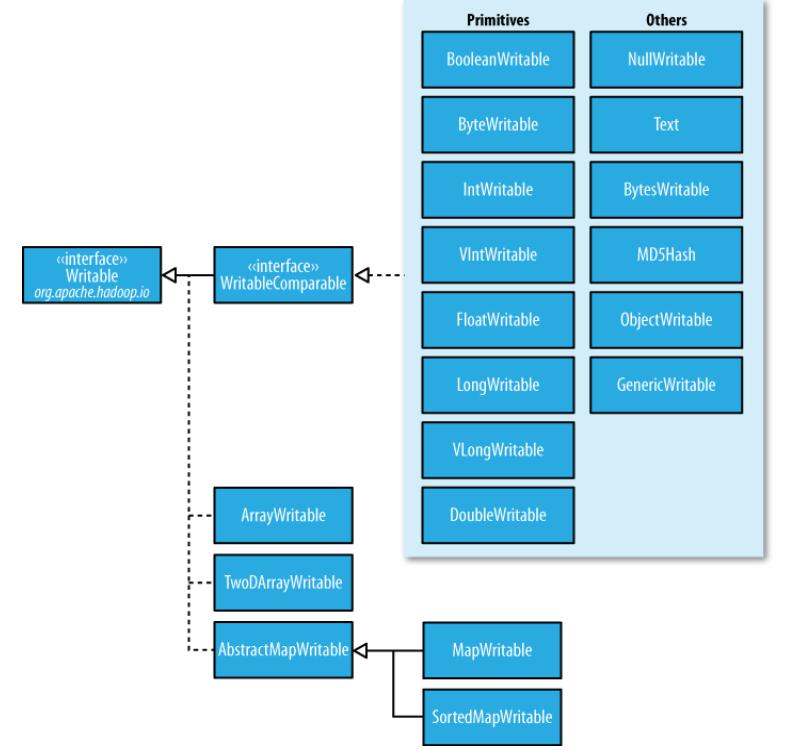
| Java类型 | Hadoop Writable类型 |
|---|---|
| Byte | ByteWritable |
| Int | IntWritable |
| Long | LongWritable |
| Float | FloatWritable |
| Double | DoubleWritable |
| Boolean | BooleanWritable |
| String | Text |
| Map | MapWritable |
| Array | ArrayWritable |
| Null | NullWritable |
有些时候这些基本的类不能满足我们的开发需求,需要自定义类,那么这些自定义的类如何实现序列化和反序列化呢?
具体实现的步骤如下:
-
实现Writable接口
-
预置一个空的构造函数,这是因为在发序列化时会被调用的
java
public Xxx(){
super();
}- 重写序列化的方法
java
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException{
out.writeInt(age);
out.writeLong(xx);
....
}重写反序列化的方法
java
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException{
age = in.readInt();
xx = in.readLong();
....
}-
顺序一定要保持一致,先序列化的谁,一定要先反序列化谁。
-
重写类的toString()方法
-
如果该类需要作为Mapper的key中使用,还需要实现Comparable接口,这是因为Shuffle过程中需要对Mapper的key做排序。
#五、MapReduce源码分析
5.1 准备工作
- 在WCMapper类中的map方法的首行添加如下代码:
java
Thread.sleep(99999999);-
重新打jar包
-
上传到hadoop集群中,重新运行
java
yarn jar wc.jar com.itbaizhan.WCDriver /wordcount/input /wordcount/output3在hadoop集群中的任何节点上执行如下命令
java
[root@node2 ~]# hdfs dfs -ls -R /tmp/hadoop-yarn/
drwx------ - root supergroup 0 2021-10-29 03:49 /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging/job_1635443832663_0002下载文件夹/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging/job_1635443832663_0002
java
[root@node2 ~]# hdfs dfs -get /tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging/job_1635443832663_0002-
从该节点的/root目录下下载到windows系统的桌面上,内容列表如下
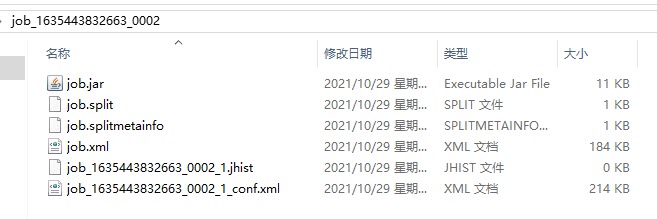
job.jar:作业的jar包
job.xml:当前作业的参数的配置文件
job.split和job.splitmetainfo:当前作业的逻辑切片的相关信息文件
-
将job.xml拷贝到wordcount项目的根目录,然后进行格式化(目的:方便查看参数),使用Ctrl+Alt+L进行格式化。
-
配置信息的来源:
默认配置信息:
一部分来源于MRJobConfig接口
一部分来至于*-default.xml文件
自定义的信息:
一部分来至于xxx-site.xml文件
一部分来至于我们通过程序设置的参数
5.2 客户端提交作业
- 点击WCDriver类中的waitForCompletion方法
java
boolean result = job.waitForCompletion(true);
//或者
job.waitForCompletion(true);waitForCompletion方法的内容如下:
java
/**提交作业并等待作业的完成
* Submit the job to the cluster and wait for it to finish.
* @param verbose print the progress to the user:
* @return true if the job succeeded
* @throws IOException thrown if the communication with the
* <code>JobTracker</code> is lost
*/
public boolean waitForCompletion(boolean verbose
) throws IOException, InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
if (state == JobState.DEFINE) {
submit();//提交作业
}
if (verbose) {//true会调用 monitorAndPrintJob();
//打印作业的进度的相关日志
monitorAndPrintJob();
} else {
//每隔5000ms指定的时间判断作业是否完成
// get the completion poll interval from the client.
int completionPollIntervalMillis =
Job.getCompletionPollInterval(cluster.getConf());
while (!isComplete()) {
try {
Thread.sleep(completionPollIntervalMillis);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
}
}
}
return isSuccessful();
}monitorAndPrintJob方法源码分析
java
/**
* Monitor a job and print status in real-time as progress is made and tasks
* fail.
* @return true if the job succeeded
* @throws IOException if communication to the JobTracker fails
*/
public boolean monitorAndPrintJob()
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String lastReport = null;
Job.TaskStatusFilter filter;
//获取作业的配置文件对象
Configuration clientConf = getConfiguration();
filter = Job.getTaskOutputFilter(clientConf);
//获取作业的id
JobID jobId = getJobID();
//输出作业Id
LOG.info("Running job: " + jobId);
int eventCounter = 0;
boolean profiling = getProfileEnabled();
IntegerRanges mapRanges = getProfileTaskRange(true);
IntegerRanges reduceRanges = getProfileTaskRange(false);
//每隔1000ms判断一次作业是否完成
int progMonitorPollIntervalMillis =
Job.getProgressPollInterval(clientConf);
/* make sure to report full progress after the job is done */
boolean reportedAfterCompletion = false;
boolean reportedUberMode = false;
while (!isComplete() || !reportedAfterCompletion) {
if (isComplete()) {
reportedAfterCompletion = true;
} else {
//休眠1000ms
Thread.sleep(progMonitorPollIntervalMillis);
}
if (status.getState() == JobStatus.State.PREP) {
continue;
}
if (!reportedUberMode) {
reportedUberMode = true;
LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " running in uber mode : " + isUber());
}
String report =
(" map " + StringUtils.formatPercent(mapProgress(), 0)+
" reduce " +
StringUtils.formatPercent(reduceProgress(), 0));
//本次报告的执行进度和上次报告的进度不同才会打印
if (!report.equals(lastReport)) {
LOG.info(report);
lastReport = report;
}
TaskCompletionEvent[] events =
getTaskCompletionEvents(eventCounter, 10);
eventCounter += events.length;
printTaskEvents(events, filter, profiling, mapRanges, reduceRanges);
}
boolean success = isSuccessful();
//输出作业的最终执行信息
if (success) {
LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " completed successfully");
} else {
LOG.info("Job " + jobId + " failed with state " + status.getState() +
" due to: " + status.getFailureInfo());
}
//相关计数器信息的处理
Counters counters = getCounters();
if (counters != null) {
LOG.info(counters.toString());
}
return success;
}submit()方法分析(在waitForCompletion方法中点击submit()进入)
java
/**
* Submit the job to the cluster and return immediately.
* @throws IOException
*/
public void submit()
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
setUseNewAPI();
connect();
final JobSubmitter submitter =
getJobSubmitter(cluster.getFileSystem(), cluster.getClient());
status = ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<JobStatus>() {
public JobStatus run() throws IOException, InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
//进行作业的提交
return submitter.submitJobInternal(Job.this, cluster);
}
});
state = JobState.RUNNING;
LOG.info("The url to track the job: " + getTrackingURL());
}- submitJobInternal()方法提交作业(从submit()方法进入的)
java
/**
* Internal method for submitting jobs to the system.The job submission process involves:
* 1.Checking the input and output specifications of the job.
检查作业的输入输出路径
* 2.Computing the {@link InputSplit}s for the job.
计算作业的切片信息
* 3.Setup the requisite accounting information for the
* {@link DistributedCache} of the job, if necessary.
如果需要,给分布式缓存设置比较的计数器
* 4.Copying the job's jar and configuration to the map-reduce system
* directory on the distributed file-system.
将jar包、配置文件、切片信息等提交到hdfs上map-reduce系统目录
* 5.Submitting the job to the <code>JobTracker</code> and optionally
* monitoring it's status.
将作业提交给JobTracker(hadoop1.x)/ResourceManager(hadoop2.x+),并可选的监控作业的状态。
* @param job the configuration to submit
* @param cluster the handle to the Cluster
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* @throws InterruptedException
* @throws IOException
*/
JobStatus submitJobInternal(Job job, Cluster cluster)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException {
//验证作业的输出路径
//validate the jobs output specs
checkSpecs(job);
Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
addMRFrameworkToDistributedCache(conf);
//作业的相关文件(jar,xml,split等)提交到路径
Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(cluster, conf);
//configure the command line options correctly on the submitting dfs
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
if (ip != null) {
submitHostAddress = ip.getHostAddress();
submitHostName = ip.getHostName();
conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOST,submitHostName);
conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOSTADDR,submitHostAddress);
}
JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID();
job.setJobID(jobId);
Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString());
JobStatus status = null;
try {
conf.set(MRJobConfig.USER_NAME,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getShortUserName());
conf.set("hadoop.http.filter.initializers",
"org.apache.hadoop.yarn.server.webproxy.amfilter.AmFilterInitializer");
conf.set(MRJobConfig.MAPREDUCE_JOB_DIR, submitJobDir.toString());
LOG.debug("Configuring job " + jobId + " with " + submitJobDir
+ " as the submit dir");
// get delegation token for the dir
TokenCache.obtainTokensForNamenodes(job.getCredentials(),
new Path[] { submitJobDir }, conf);
populateTokenCache(conf, job.getCredentials());
// generate a secret to authenticate shuffle transfers
if (TokenCache.getShuffleSecretKey(job.getCredentials()) == null) {
KeyGenerator keyGen;
try {
keyGen = KeyGenerator.getInstance(SHUFFLE_KEYGEN_ALGORITHM);
keyGen.init(SHUFFLE_KEY_LENGTH);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
throw new IOException("Error generating shuffle secret key", e);
}
SecretKey shuffleKey = keyGen.generateKey();
TokenCache.setShuffleSecretKey(shuffleKey.getEncoded(),
job.getCredentials());
}
if (CryptoUtils.isEncryptedSpillEnabled(conf)) {
conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.MR_AM_MAX_ATTEMPTS, 1);
LOG.warn("Max job attempts set to 1 since encrypted intermediate" +
"data spill is enabled");
}
copyAndConfigureFiles(job, submitJobDir);
Path submitJobFile = JobSubmissionFiles.getJobConfPath(submitJobDir);
// Create the splits for the job
LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + jtFs.makeQualified(submitJobDir));
int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir);
conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.NUM_MAPS, maps);
LOG.info("number of splits:" + maps);
int maxMaps = conf.getInt(MRJobConfig.JOB_MAX_MAP,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_JOB_MAX_MAP);
if (maxMaps >= 0 && maxMaps < maps) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("The number of map tasks " + maps +
" exceeded limit " + maxMaps);
}
// write "queue admins of the queue to which job is being submitted"
// to job file.
String queue = conf.get(MRJobConfig.QUEUE_NAME,
JobConf.DEFAULT_QUEUE_NAME);
AccessControlList acl = submitClient.getQueueAdmins(queue);
conf.set(toFullPropertyName(queue,
QueueACL.ADMINISTER_JOBS.getAclName()), acl.getAclString());
// removing jobtoken referrals before copying the jobconf to HDFS
// as the tasks don't need this setting, actually they may break
// because of it if present as the referral will point to a
// different job.
TokenCache.cleanUpTokenReferral(conf);
if (conf.getBoolean(
MRJobConfig.JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS_ENABLED,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS_ENABLED)) {
// Add HDFS tracking ids
ArrayList<String> trackingIds = new ArrayList<String>();
for (Token<? extends TokenIdentifier> t :
job.getCredentials().getAllTokens()) {
trackingIds.add(t.decodeIdentifier().getTrackingId());
}
conf.setStrings(MRJobConfig.JOB_TOKEN_TRACKING_IDS,
trackingIds.toArray(new String[trackingIds.size()]));
}
// Set reservation info if it exists
ReservationId reservationId = job.getReservationId();
if (reservationId != null) {
conf.set(MRJobConfig.RESERVATION_ID, reservationId.toString());
}
// Write job file to submit dir
writeConf(conf, submitJobFile);
//
// Now, actually submit the job (using the submit name)
//
printTokens(jobId, job.getCredentials());
status = submitClient.submitJob(
jobId, submitJobDir.toString(), job.getCredentials());
if (status != null) {
return status;
} else {
throw new IOException("Could not launch job");
}
} finally {
if (status == null) {
LOG.info("Cleaning up the staging area " + submitJobDir);
if (jtFs != null && submitJobDir != null)
jtFs.delete(submitJobDir, true);
}
}
}分析job资源提交的hdfs上的路径(选学)
入口:
java
//前置路径
Path jobStagingArea = JobSubmissionFiles.getStagingDir(cluster, conf);
//configure the command line options correctly on the submitting dfs
InetAddress ip = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
if (ip != null) {
submitHostAddress = ip.getHostAddress();
submitHostName = ip.getHostName();
conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOST,submitHostName);
conf.set(MRJobConfig.JOB_SUBMITHOSTADDR,submitHostAddress);
}
JobID jobId = submitClient.getNewJobID();
job.setJobID(jobId);
//提交作业相关文件的hdfs上具体路径
Path submitJobDir = new Path(jobStagingArea, jobId.toString());前置路径:
java
public static Path getStagingDir(Cluster cluster, Configuration conf)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
UserGroupInformation user = UserGroupInformation.getLoginUser();
//cluster:集群对象, conf:配置文件对象, user:当前用户 root
return getStagingDir(cluster, conf, user);
}
public static Path getStagingDir(Cluster cluster, Configuration conf,
UserGroupInformation realUser) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//获取对应前置路径
Path stagingArea = cluster.getStagingAreaDir();
FileSystem fs = stagingArea.getFileSystem(conf);
UserGroupInformation currentUser = realUser.getCurrentUser();
try {
....
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
//在hdfs创建对应的目录
fs.mkdirs(stagingArea, new FsPermission(JOB_DIR_PERMISSION));
}
return stagingArea;
}
public static Path getStagingAreaDir(Configuration conf, String user) {
return new Path(conf.get("yarn.app.mapreduce.am.staging-dir", "/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging") + "/" + user + "/" + ".staging");
}获取到前置路径如下:/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging
所以最终路径为:/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging/jobId
5.3 切片数量计算(重点)
- 程序入口JobSubmitter类中的submitJobInternal方法的198行开始
java
JobStatus submitJobInternal(Job job, Cluster cluster)
throws ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException, IOException {
// Create the splits for the job 198行
LOG.debug("Creating splits at " + jtFs.makeQualified(submitJobDir));
//写切片信息文件到/tmp/hadoop-yarn/staging/root/.staging/jobId下,并返回切片的数量
int maps = writeSplits(job, submitJobDir);
//使用切片数量作为MapTask任务的数量,所以说有几个切片就对应几个MapTask
conf.setInt(MRJobConfig.NUM_MAPS, maps);
LOG.info("number of splits:" + maps);
}- 切片计算调用的哪个方法进行计算的?
java
private int writeSplits(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext job,
Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException,InterruptedException,
ClassNotFoundException {
JobConf jConf = (JobConf)job.getConfiguration();
int maps;
if (jConf.getUseNewMapper()) {
//hadoop2.x+ 调用该方法进行前切片的计算
maps = writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir);
} else {
//hadoop1.x使用的切片计算的方法
maps = writeOldSplits(jConf, jobSubmitDir);
}
return maps;
}分析writeNewSplits(job, jobSubmitDir)方法,研究切片计算的细节。
java
private <T extends InputSplit>
int writeNewSplits(JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException,
InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
//确定InputFormat类使用是? 通过这个类就可以知道如何截取的切片
InputFormat<?, ?> input =
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getInputFormatClass(), conf);
//切片的计算逻辑
List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job);
//array数组中保存是InputSplit对象,也就是切片对象
T[] array = (T[]) splits.toArray(new InputSplit[splits.size()]);
// sort the splits into order based on size, so that the biggest
// go first 对数组中的切片对象进行排序
Arrays.sort(array, new SplitComparator());
//向指定的目录下写切片信息 job.split和job.splitmetainfo
JobSplitWriter.createSplitFiles(jobSubmitDir, conf,
jobSubmitDir.getFileSystem(conf), array);
//array数组的长度就是切片的数量(MapTask的数量)
return array.length;
}由于input对象时抽象类InputFormat声明的,点入getSplits方法时,是一个抽象方法:
java
public abstract class InputFormat<K, V> {
public abstract
List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
} 选中方法名getSplits,然后Ctrl+Alt+B,弹出如下界面:
-
确定InputFormat类是哪个?
Ctrl+点击 步骤3中job.getInputFormatClass()进行类的确定
java
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException;选择getInputFormatClass(),Ctrl+Alt+B->选择JobContextImpl类中的代码:
java
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
//INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR = "mapreduce.job.inputformat.class"
return (Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
}点击conf.getClass()
java
public Class<?> getClass(String name, Class<?> defaultValue) {
String valueString = getTrimmed(name);
if (valueString == null)
return defaultValue;
try {
return getClassByName(valueString);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}如果如上方法代码后发现:如果之前指定过mapreduce.job.inputformat.class 对应的format类使用自己指定的,如果没有指定过使用默认的TextInputFormat。
-
进入TextInputFormat类,
点击、或 Ctrl+Shift+R->输入TextInputFormat,进入:
java
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input;
...
import com.google.common.base.Charsets;
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public class TextInputFormat extends FileInputFormat<LongWritable, Text> {
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
}
@Override
protected boolean isSplitable(JobContext context, Path file) {
final CompressionCodec codec =
new CompressionCodecFactory(context.getConfiguration()).getCodec(file);
if (null == codec) {
return true;
}
return codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec;
}
}-
进入后发现该类父类为FileInputFormat类,该类对getSplits方法进行了重写。
-
进入FileInputFormat类,阅读它的getSplits方法:
-
block块是物理上进行的切割,而切片是逻辑上的概念,切片需要确定以下几点:
A. 是哪个文件的切片
B.切片从哪里开始(相对原文件的偏移量)
C.切片在哪个主机上
D.切片的大小
java
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch().start();
//被用于计算切片的大小 minsize=max(1,0)=1 maxsize=Long.MAX_VALUE
long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job));
long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job);
// generate splits
List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>();
List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job);
boolean ignoreDirs = !getInputDirRecursive(job)
&& job.getConfiguration().getBoolean(INPUT_DIR_NONRECURSIVE_IGNORE_SUBDIRS, false);
//输入路径有些时候是目录,下面有多个被处理的文件,所以需要遍历
for (FileStatus file: files) {
if (ignoreDirs && file.isDirectory()) {
continue;
}
//获取对应文件的对象
Path path = file.getPath();
//获取文件的总大小
long length = file.getLen();
//表示如果指定的输入路径下的文件大小为0(为空文件),不进行分析。
if (length != 0) {
BlockLocation[] blkLocations;
if (file instanceof LocatedFileStatus) {
blkLocations = ((LocatedFileStatus) file).getBlockLocations();
} else {
FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration());
blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length);
}
if (isSplitable(job, path)) {
//获取block块的大小,hadoop2.x+默认是128MB,hadoop1.x默认64MB
long blockSize = file.getBlockSize();
//计算的切片的大小minsize=1 maxsize=Long.MAX_VALUE blockSize=128*1024*1024
long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize);
/*protected long computeSplitSize(long blockSize, long minSize,
long maxSize) {
//所以计算之后splitSize默认=blockSize=128MB,一个block块对应split切片
return Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize));
}
*/
/* 如果调整切片的大小:
1.设置为256MB: 只需要将minSize设置256*1024*1024B
conf.set(FileInputFormat.SPLIT_MINSIZE,"268435456");//256MB
2.设置为64MB: 只需要将maxSize设置为64*1024*1024
conf.set(FileInputFormat.SPLIT_MAXSIZE,"67108864");//64MB
*/
//首先将文件的大小赋值给bytesRemaining(表示的是剩余可切的文件大小)
long bytesRemaining = length;
//SPLIT_SLOP=1.1
while (((double) bytesRemaining)/splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, splitSize,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
bytesRemaining -= splitSize;
}
if (bytesRemaining != 0) {
int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length-bytesRemaining);
splits.add(makeSplit(path, length-bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining,
blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts(),
blkLocations[blkIndex].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else { // not splitable
//如果文件不可切,将整个文件作为一个切片对象添加到splits集合中
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
// Log only if the file is big enough to be splitted
if (length > Math.min(file.getBlockSize(), minSize)) {
LOG.debug("File is not splittable so no parallelization "
+ "is possible: " + file.getPath());
}
}
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0].getHosts(),
blkLocations[0].getCachedHosts()));
}
} else {
//Create empty hosts array for zero length files
splits.add(makeSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0]));
}
}
// Save the number of input files for metrics/loadgen
job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size());
sw.stop();
if (LOG.isDebugEnabled()) {
LOG.debug("Total # of splits generated by getSplits: " + splits.size()
+ ", TimeTaken: " + sw.now(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
return splits;
}如何修改使用的InputFormat类?
默认使用是TextInputFormat,如何修改?
java
private <T extends InputSplit>
int writeNewSplits(JobContext job, Path jobSubmitDir) throws IOException,
InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
Configuration conf = job.getConfiguration();
InputFormat<?, ?> input =
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getInputFormatClass(), conf);
List<InputSplit> splits = input.getSplits(job);
} 点击:getInputFormatClass()方法,进入JobContext接口中:
java
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException;选中getInputFormatClass()方法,Ctrl+Alt+B,选中JobContextImpl
java
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
}通过conf对象从配置文件中找常量INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR对应的字符串mapreduce.job.inputformat.class为key的值,如果没有设置过,则使用默认的TextInputFormat。
修改的话有两种方式:
java
//方式一:常用的方式
job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class);
//方式二:不常用
conf.set("mapreduce.job.inputformat.class","org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.KeyValueTextInputFormat");5.4 Map阶段源码分析

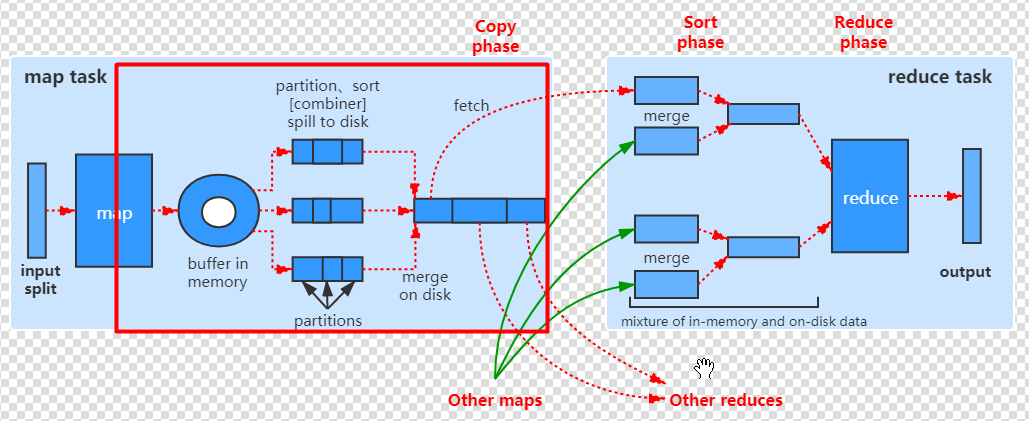
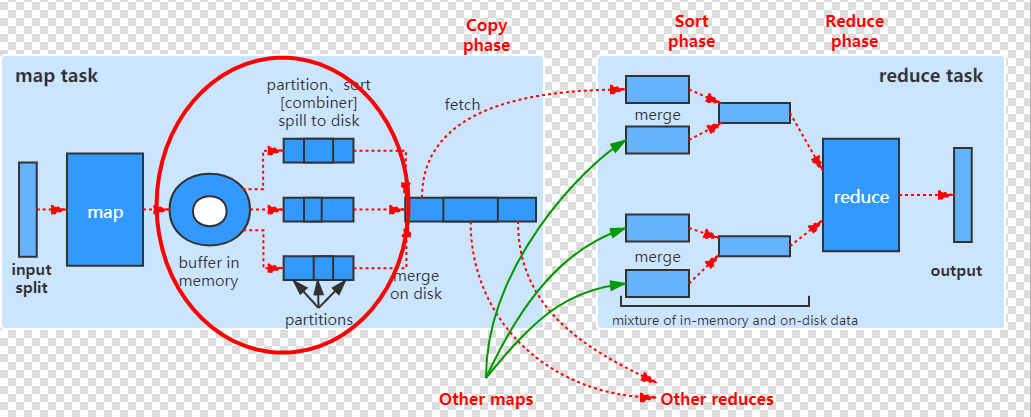
从切片读取数据,给map方法,map方法输出的键值对写到环形缓冲区,关注以下内容:
- 在写到环形缓冲区之前计算分区号
- 环形缓冲区排序后溢写到map端本地磁盘,可能会有合并的过程,3
- 可以设置环形缓冲区大小和阈值
- 排序所使用的算法:默认是快排,可以设置
- 可以自定义key和value
- 排序比较器可以自定义
- 可以设置Combiner类
###5.4.1 源码从哪里看?
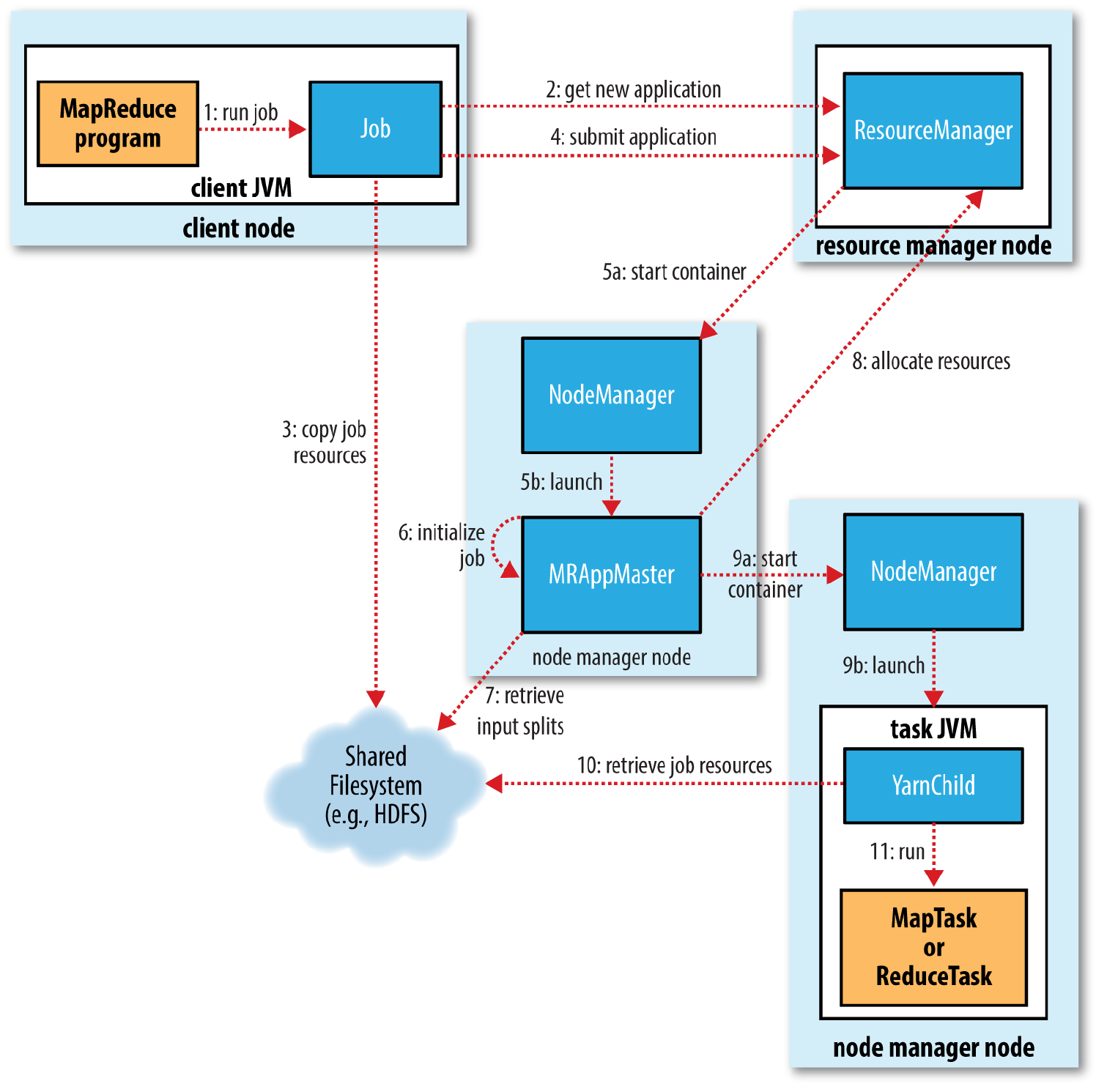
从上图可知,MapTask入口从YarnChild类开始,在IDEA中Ctrl+Shift+R->YarnChild->main()->174行开始阅读。
Ctrl+Alt+<- :返回到上一个位置
Ctrl+Alt+->:回到下一个位置
java
childUGI.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() throws Exception {
// use job-specified working directory
setEncryptedSpillKeyIfRequired(taskFinal);
FileSystem.get(job).setWorkingDirectory(job.getWorkingDirectory());
taskFinal.run(job, umbilical); // run the task Ctrl+单击该run()方法
return null;
}
});5.4.2 runNewMapper()方法引入
进入Task.java类的run()方法:
java
public abstract void run(JobConf job, TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException;选中run()方法之后Ctrl+Alt+B->选中MapTask ->run()方法中。
java
public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
this.umbilical = umbilical;
//如果为MapTask,则继续
if (isMapTask()) {
// If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map
// phase will govern the entire attempt's progress.
//获取ReduceTask的数量
if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {//后续没有reduce任务
mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f);
} else {//后续有reduce任务
// If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be
// split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%).
mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f);
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f);
}
}
TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical);
//获取是否使用新版的MapperApi
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper();
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// check if it is a cleanupJobTask
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (useNewApi) {//hadoop2.x+使用
runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
} else {//hadoop1.x使用
runOldMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter);
}
done(umbilical, reporter);
}5.4.3 runNewMapper()方法分析
java
private <INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job,
final TaskSplitIndex splitIndex,
final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
// make a task context so we can get the classes
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext =
new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,
getTaskID(),
reporter);
// make a mapper 创建Mapper对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);
// make the input format
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);
// rebuild the input split
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null;
split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()),
splitIndex.getStartOffset());
LOG.info("Processing split: " + split);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null;
// get an output object
if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) {
output =
new NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
} else {
output = new NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter);
}
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>
mapContext =
new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(),
input, output,
committer,
reporter, split);
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context
mapperContext =
new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext(
mapContext);
try {
//初始化input对象
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);
//运行mapper任务,调用自定义的Mapper类覆写的map方法
mapper.run(mapperContext);
mapPhase.complete();
//设置任务的当前阶段:排序
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.SORT);
//更新任务的状态
statusUpdate(umbilical);
//input对象的关闭与置空
input.close();
input = null;
//output对象的关闭与置空
output.close(mapperContext);
output = null;
} finally {
closeQuietly(input);
closeQuietly(output, mapperContext);
}
}5.4.4 mapper、inputFormat和input对象的创建
1. Mapper对象如何创建的?
java
// make a mapper 创建Mapper对象
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job);点击进入getMapperClass()方法中->JobContext接口中:
java
public Class<? extends Mapper<?,?,?,?>> getMapperClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException;选中getMapperClass()之后Ctrl+Alt+B->JobContextImpl:
java
public Class<? extends Mapper<?,?,?,?>> getMapperClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class<? extends Mapper<?,?,?,?>>)
conf.getClass(MAP_CLASS_ATTR, Mapper.class);
}去配置文件中查找MAP_CLASS_ATTR常量对应(mapreduce.job.map.class)的自定义的Mapper类,如果找到则使用自定义的Mapper类,如果找不到使用Mapper.class。
使用mapreduce.job.map.class去job.xml中查找对应的Mapper类:
java
<property>
<name>mapreduce.job.map.class</name>
<value>com.itbaizhan.WCMapper</value>
<final>false</final>
<source>programmatically</source>
</property>对应的自定义的Mapper类就是com.itbaizhan.WCMapper。对应的设置代码就是在WCDriver类中:
java
job.setMapperClass(WCMapper.class);
//也就是:
/**
* Set the {@link Mapper} for the job.
* @param cls the <code>Mapper</code> to use
* @throws IllegalStateException if the job is submitted
*/
public void setMapperClass(Class<? extends Mapper> cls
) throws IllegalStateException {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
conf.setClass(MAP_CLASS_ATTR, cls, Mapper.class);
}思考:为什么在WCDriver类设置好Mapper类之后可以在MapTask中直接使用?设置和使用谁先谁后?
参考答案:WCDriver在客户端执行的,搞定一切配置信息之后,才会提交作业,只有提交作业之后才开始运行MapTask.
2. inputFormat对象如何创建的?
java
// make the input format
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat =
(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job);taskContext.getInputFormatClass()->JobContext接口中:
java
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException;选择getInputFormatClass() 后Ctrl+Alt+B->选择JobContextImpl
java
public Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>> getInputFormatClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class<? extends InputFormat<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(INPUT_FORMAT_CLASS_ATTR, TextInputFormat.class);
}如果设置过使用自定义的InputFormat类,没有指定就使用TextInputFormat。可以通过如下方式设置:
java
job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class);默认使用的就是TextInputFormat类。
3. input对象如何创建的?
java
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input =
new NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>
(split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext);点击NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE>()
java
NewTrackingRecordReader(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<K, V> inputFormat,
TaskReporter reporter,
org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext)
throws InterruptedException, IOException {
this.reporter = reporter;
this.inputRecordCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_INPUT_RECORDS);
this.fileInputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(FileInputFormatCounter.BYTES_READ);
List <Statistics> matchedStats = null;
if (split instanceof org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit) {
matchedStats = getFsStatistics(((org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileSplit) split)
.getPath(), taskContext.getConfiguration());
}
fsStats = matchedStats;
long bytesInPrev = getInputBytes(fsStats);
//inputFormat默认是TextInputFormat对象创建的,createRecordReader()来至TextInputFormat
this.real = inputFormat.createRecordReader(split, taskContext);
long bytesInCurr = getInputBytes(fsStats);
fileInputByteCounter.increment(bytesInCurr - bytesInPrev);
}选择inputFormat.createRecordReader(split, taskContext),点击:进入InputFormat中:
java
public abstract
RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context
) throws IOException, InterruptedException;TextInputFormat类的createRecordReader():
java
@Override
public RecordReader<LongWritable, Text>
createRecordReader(InputSplit split,
TaskAttemptContext context) {
String delimiter = context.getConfiguration().get(
"textinputformat.record.delimiter");
byte[] recordDelimiterBytes = null;
if (null != delimiter)
recordDelimiterBytes = delimiter.getBytes(Charsets.UTF_8);
return new LineRecordReader(recordDelimiterBytes);
} 最终实现的是LineRecordReader(行读取器)。
5.4.5 initialize方法源码分析
点击MapTask类的runNewMapper()方法的798行:
java
input.initialize(split, mapperContext);进入到RecordReader抽象类中:
javapublic abstract void initialize(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context ) throws IOException, InterruptedException;
选中initialize方法,然后Ctrl+Alt+B->LineRecordReader类的initialize()方法中:
java
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit,
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit;
Configuration job = context.getConfiguration();
this.maxLineLength = job.getInt(MAX_LINE_LENGTH, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
//起始偏移量=切片的起始偏移量
start = split.getStart();
//结束偏移量=起始偏移量+切片的大小 单位:B
end = start + split.getLength();
//获取切片对应文件的Path路径的对象
final Path file = split.getPath();
// open the file and seek to the start of the split
//获取分布式文件系统对象
final FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job);
//打开文件进行读取
fileIn = fs.open(file);
CompressionCodec codec = new CompressionCodecFactory(job).getCodec(file);
if (null!=codec) {
isCompressedInput = true;
decompressor = CodecPool.getDecompressor(codec);
if (codec instanceof SplittableCompressionCodec) {
final SplitCompressionInputStream cIn =
((SplittableCompressionCodec)codec).createInputStream(
fileIn, decompressor, start, end,
SplittableCompressionCodec.READ_MODE.BYBLOCK);
in = new CompressedSplitLineReader(cIn, job,
this.recordDelimiterBytes);
start = cIn.getAdjustedStart();
end = cIn.getAdjustedEnd();
filePosition = cIn;
} else {
//如果start不等于:说明当前MapTask处理的切片不是对应文件的第一个切片,存在行被切断的问题
if (start != 0) {
// So we have a split that is only part of a file stored using
// a Compression codec that cannot be split.
throw new IOException("Cannot seek in " +
codec.getClass().getSimpleName() + " compressed stream");
}
in = new SplitLineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn,
decompressor), job, this.recordDelimiterBytes);
filePosition = fileIn;
}
} else {//当前MapTask处理是对应文件的第一个切片,不存在行被切断的风险
fileIn.seek(start);
in = new UncompressedSplitLineReader(
fileIn, job, this.recordDelimiterBytes, split.getLength());
filePosition = fileIn;
}
// If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record
// because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in
// next() method.
//如果start!=0,第一行不处理,
if (start != 0) {
start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start));
}
this.pos = start;
}从第二个切片开始,都放弃第一行的处理,那么Map任务处理的时候,就不存在断行的问题了。每个切片对应的Map任务都会向后多读取一行并进行处理。
5.4.6 run(mapperContext)
点击MapTask类的runNewMapper()方法的799行:
java
mapper.run(mapperContext);Ctrl+单击run方法,进入Mapper类的run方法中:
java
public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//自定义的Mapper类也可以覆写setup(context)和cleanup(context)方法,
//一个Map任务这两个方法都会执行一次。
setup(context);
try {
while (context.nextKeyValue()) {//是否还有未处理的内容
//调用自定义的Mapper类(比如WCMapper类)中的map方法
map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context);
}
} finally {
cleanup(context);
}
}###5.4.7 nextKeyValue()方法:
点击context.nextKeyValue()方法,进入到接口TaskInputOutputContext中:
java
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException;选中方法nextKeyValue()->Ctrl+Alt+B->MapContextImpl类的nextKeyValue()方法:
java
@Override
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException {
return reader.nextKeyValue();
}点击:reader.nextKeyValue()->RecodeReader类中:
java
public abstract
boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException;选中nextKeyValue()->LineRecordReader的nextKeyValue()方法:
java
//判断是否还存在未处理的键值对
//LineRecordReader类的注释:Treats keys as offset in file and value as line
//key是偏移量
//value:当前行的内容
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException {
if (key == null) {
key = new LongWritable();
}
key.set(pos);
if (value == null) {
value = new Text();
}
int newSize = 0;
// We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper
// split limit i.e. (end - 1)
while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) {
if (pos == 0) {
newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark();
} else {
//读取当前行的内容赋值给value
newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos));
//将偏移量改变
pos += newSize;
}
if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) {
break;
}
// line too long. try again
LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " +
(pos - newSize));
}
if (newSize == 0) {
key = null;
value = null;
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}LineRecordReader类的中getCurrentKey()和getCurrentValue():
java
@Override
public LongWritable getCurrentKey() {
return key;
}
@Override
public Text getCurrentValue() {
return value;
}接着调用自定义Mapper类中的map方法:
java
//文本中的每一行内容调用一次map方法
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(99999999);
if(value!=null) {
//value就是读取到的当前行中的内容,并将之转换为字符串
String lineContenct = value.toString();
//将字符串进行处理:先去掉两端的空格,然后在按照空格进行切分
String[] words = lineContenct.trim().split(" ");
//遍历数组,逐一进行输出
for(String word:words){
//将word内容封装到keyOut中
keyOut.set(word);
//将kv对输出
context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
}
}
}5.4.8 out对象如何创建
自定义的WCMapper类的map方法,将kv对输出时使用:context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
context如何来的?从run(Context context)传递过来的,也就是:mapper.run(mapperContext)
接下来分析mapperContext从何而来?
MapTask类的runNewMapper方法中:
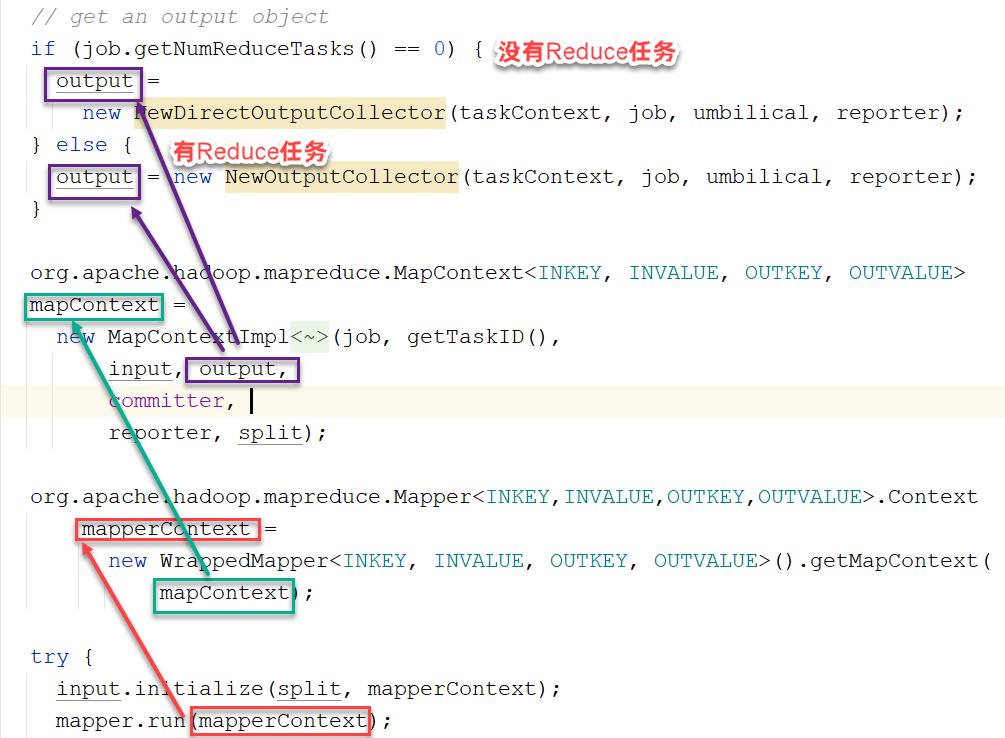
设置输出:如果作业只有map任务没有reduce任务,则直接通过NewDirectOutputCollector写到HDFS上。如果有reduce任务,通过NewOutputCollector写到圆形缓冲区中。
5.4.9 有Reduce时out对象创建
通过NewOutputCollector写到圆形缓冲区中。
java
NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
JobConf job,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//涉及到后续的圆形缓冲区,稍后讲:
collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
//获取reducer任务的数量,作为分区数量,所以分区和reduce任务一对一。
partitions = jobContext.getNumReduceTasks();
if (partitions > 1) {//有2个或2个以上的分区
//创建分区对象
partitioner = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>)
ReflectionUtils.newInstance(jobContext.getPartitionerClass(), job);
} else {//=1,直接返回 0
partitioner = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner<K,V>() {
@Override
public int getPartition(K key, V value, int numPartitions) {
return partitions - 1;
}
};
}
}5.4.10 分区
如果reduce任务数量大于1,也就是分区数量大于1,调用jobContext.getPartitionerClass()来获取分区类的Class对象。单击getPartitionerClass()->JobContext接口中:
java
public Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>> getPartitionerClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException;Ctrl+Alt+B->JobContextImpl:
java
public Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>> getPartitionerClass()
throws ClassNotFoundException {
return (Class<? extends Partitioner<?,?>>)
conf.getClass(PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR, HashPartitioner.class);
}获取PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR常量的值mapreduce.job.partitioner.class,该字符串去job.xml找它对应的value值。如果没有定义,则使用默认的HashPartitioner类作为分区类。
java
/** Partition keys by their {@link Object#hashCode()}. */
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}默认的分区的逻辑是,使用key的hashCode值%reduce任务数(也是分区总数) 求余数。
如何设置自定义的分区类:
java
job.setPartitionerClass(WCPartitioner.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(4);setPartitionerClass()方法的代码:
java
public void setPartitionerClass(Class<? extends Partitioner> cls
) throws IllegalStateException {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
conf.setClass(PARTITIONER_CLASS_ATTR, cls,
Partitioner.class);
}自定义分区类如何定义:
java
//自定义分区类的key,value的类型,要分别对应Mapper输出的key和value的类型
//自定义的分区列一定要继承Partitioner类,并覆写getPartition方法
//分区的原则:避免数据倾斜的出现
public class WCPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> {
//abcdefghi jklmnopqr stuvwzyz 其他的
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, IntWritable value, int numPartitions) {
//key转换为字符串
String word = key.toString();
char ch = word.charAt(0);
if(ch>='a'&&ch<='i'){
return 0;
}else if(ch>='j'&&ch<='r'){
return 1;
}else if(ch>='s'&&ch<='z'){
return 2;
}else{
return 3;
}
}
}###5.4.11 圆形缓冲区引入
如果有reduce任务,通过NewOutputCollector写到圆形缓冲区中。所以自定义Mapper类在执行context.write(xx)方法时调用的就是NewOutputCollector类中的write方法:
java
@Override
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//将(key,value,partitin)缩写(k,v,p)
collector.collect(key, value,
partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions));
}放回到构造方法中:
java
NewOutputCollector(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.JobContext jobContext,
JobConf job,
TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical,
TaskReporter reporter
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//涉及到后续的圆形缓冲区,稍后讲:
collector = createSortingCollector(job, reporter);
......
}点击createSortingCollector方法:
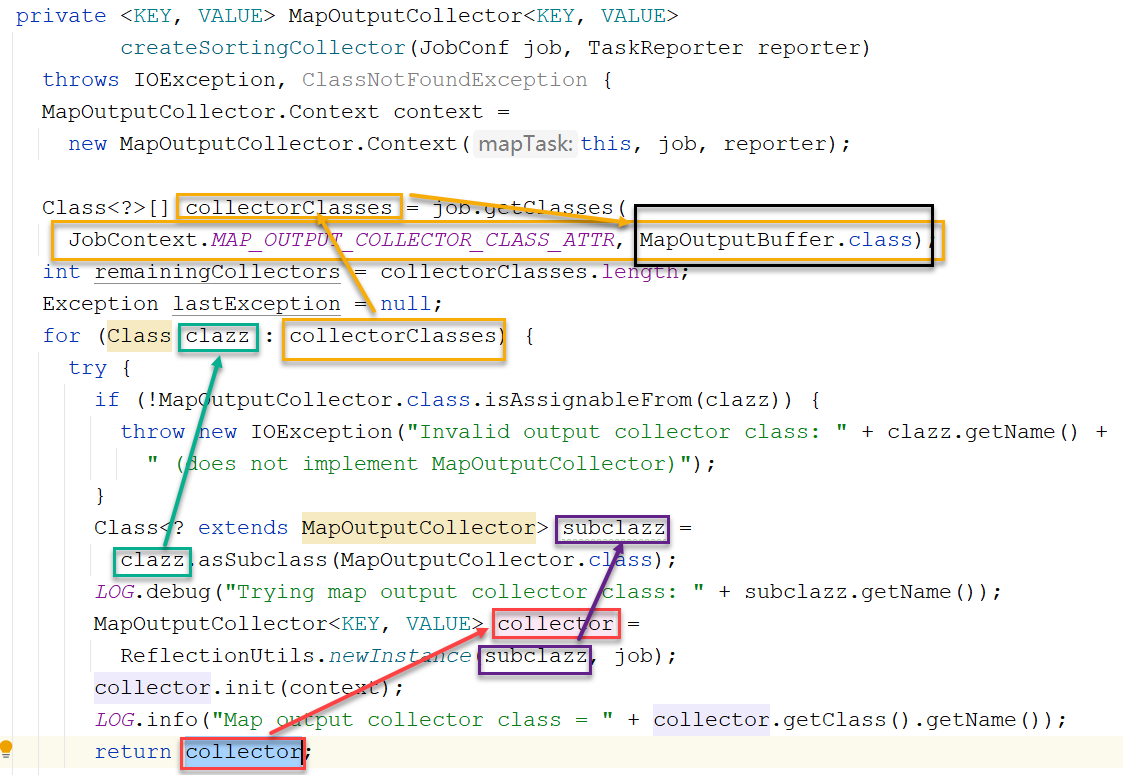
所以该collector就是找MAP_OUTPUT_COLLECTOR_CLASS_ATTR对应的配置的类,如果没有配置则使用默认的MapOutputBuffer类来创建对象。MapOutputBuffer就是圆形缓冲区的类。
###5.4.12 collector.init方法
点击MapTask类中的createSortingCollector()->单击collector.init(context);
java
public interface MapOutputCollector<K, V> {
public void init(Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
}选中init方法,Ctrl+Alt+B->选择MapOutputBuffer类:
java
public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
job = context.getJobConf();
reporter = context.getReporter();
mapTask = context.getMapTask();
mapOutputFile = mapTask.getMapOutputFile();
sortPhase = mapTask.getSortPhase();
spilledRecordsCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.SPILLED_RECORDS);
//获取分区的数量也就是reduce的数量
partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks();
rfs = ((LocalFileSystem)FileSystem.getLocal(job)).getRaw();
//sanity checks 阈值默认 0.8
//MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT = "mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent"
final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
//圆形缓冲区的大小100MB
//IO_SORT_MB = "mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb"
//DEFAULT_IO_SORT_MB = 100;
final int sortmb = job.getInt(MRJobConfig.IO_SORT_MB,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_IO_SORT_MB);
indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT,
INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT);
if (spillper > (float)1.0 || spillper <= (float)0.0) {
throw new IOException("Invalid \"" + JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT +
"\": " + spillper);
}
if ((sortmb & 0x7FF) != sortmb) {
throw new IOException(
"Invalid \"" + JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + "\": " + sortmb);
}
//MAP_SORT_CLASS = "map.sort.class" 如果配置了该参数对应的类,则使用它进行排序
//如果没有设置过,使用默认的QuickSort(快排)
sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass(
MRJobConfig.MAP_SORT_CLASS, QuickSort.class,
IndexedSorter.class), job);
// buffers and accounting 100变为二进制,然后向左位移20,
int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20;
maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE;
//定义一个字节数组,存放圆形缓冲区中的(k,v,p)对
//圆形缓冲区本质上是默认长度为100MB一个字节数组,通过一定的算法实现逻辑上的圆形缓存区的效果。
kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage];
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asIntBuffer();
setEquator(0);
bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator;
kvstart = kvend = kvindex;
maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA;
softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper);
bufferRemaining = softLimit;
LOG.info(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + ": " + sortmb);
LOG.info("soft limit at " + softLimit);
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "; length = " + maxRec);
// k/v serialization 排序比较器
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
//mapper类输出key的类型
keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
//mapper类输出value的类型
valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass();
serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job);
keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass);
keySerializer.open(bb);
valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass);
valSerializer.open(bb);
// output counters 计算器 字节数、记录数等
mapOutputByteCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_BYTES);
mapOutputRecordCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_MATERIALIZED_BYTES);
// compression 压缩处理
if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) {
Class<? extends CompressionCodec> codecClass =
job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class);
codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job);
} else {
codec = null;
}
// combiner 类相关
final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS);
combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(),
combineInputCounter,
reporter, null);
if (combinerRunner != null) {
final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector = null;
}
spillInProgress = false;
//MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS = "mapreduce.map.combine.minspills"
//如果配置文件中配置了就使用配置的值,没有配置默认为3个。
minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3);
//启动一个名称为SpillThread守护线程,进行写溢出文件
spillThread.setDaemon(true);
spillThread.setName("SpillThread");
spillLock.lock();
try {
//启动线程
spillThread.start();
while (!spillThreadRunning) {
spillDone.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
if (sortSpillException != null) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize",
sortSpillException);
}
}
java
public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
job = context.getJobConf();
reporter = context.getReporter();
mapTask = context.getMapTask();
mapOutputFile = mapTask.getMapOutputFile();
sortPhase = mapTask.getSortPhase();
spilledRecordsCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.SPILLED_RECORDS);
//获取分区的数量也就是reduce的数量
partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks();
rfs = ((LocalFileSystem)FileSystem.getLocal(job)).getRaw();
//sanity checks 阈值默认 0.8
//MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT = "mapreduce.map.sort.spill.percent"
final float spillper =
job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8);
//圆形缓冲区的大小100MB
//IO_SORT_MB = "mapreduce.task.io.sort.mb"
//DEFAULT_IO_SORT_MB = 100;
final int sortmb = job.getInt(MRJobConfig.IO_SORT_MB,
MRJobConfig.DEFAULT_IO_SORT_MB);
indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT,
INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT);
if (spillper > (float)1.0 || spillper <= (float)0.0) {
throw new IOException("Invalid \"" + JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT +
"\": " + spillper);
}
if ((sortmb & 0x7FF) != sortmb) {
throw new IOException(
"Invalid \"" + JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + "\": " + sortmb);
}
//MAP_SORT_CLASS = "map.sort.class" 如果配置了该参数对应的类,则使用它进行排序
//如果没有设置过,使用默认的QuickSort(快排)
sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass(
MRJobConfig.MAP_SORT_CLASS, QuickSort.class,
IndexedSorter.class), job);
// buffers and accounting 100变为二进制,然后向左位移20,
int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20;
maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE;
//定义一个字节数组,存放圆形缓冲区中的(k,v,p)对
//圆形缓冲区本质上是默认长度为100MB一个字节数组,通过一定的算法实现逻辑上的圆形缓存区的效果。
kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage];
bufvoid = kvbuffer.length;
kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer)
.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder())
.asIntBuffer();
setEquator(0);
bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator;
kvstart = kvend = kvindex;
maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA;
softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper);
bufferRemaining = softLimit;
LOG.info(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + ": " + sortmb);
LOG.info("soft limit at " + softLimit);
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "; length = " + maxRec);
// k/v serialization 排序比较器
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();
//mapper类输出key的类型
keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
//mapper类输出value的类型
valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass();
serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job);
keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass);
keySerializer.open(bb);
valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass);
valSerializer.open(bb);
// output counters 计算器 字节数、记录数等
mapOutputByteCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_BYTES);
mapOutputRecordCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_MATERIALIZED_BYTES);
// compression 压缩处理
if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) {
Class<? extends CompressionCodec> codecClass =
job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class);
codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job);
} else {
codec = null;
}
// combiner 类相关
final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS);
combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(),
combineInputCounter,
reporter, null);
if (combinerRunner != null) {
final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter =
reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job);
} else {
combineCollector = null;
}
spillInProgress = false;
//MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS = "mapreduce.map.combine.minspills"
//如果配置文件中配置了就使用配置的值,没有配置默认为3个。
minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3);
//启动一个名称为SpillThread守护线程,进行写溢出文件
spillThread.setDaemon(true);
spillThread.setName("SpillThread");
spillLock.lock();
try {
//启动线程
spillThread.start();
while (!spillThreadRunning) {
spillDone.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
if (sortSpillException != null) {
throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize",
sortSpillException);
}
}5.4.13 排序比较器
点击MapTask类中的createSortingCollector()->单击collector.init(context);
java
public interface MapOutputCollector<K, V> {
public void init(Context context
) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException;
}选中init方法,Ctrl+Alt+B->选择MapOutputBuffer类1018行:
java
comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator();点击getOutputKeyComparator()方法:
java
public RawComparator getOutputKeyComparator() {
//获取KEY_COMPARATOR对应排序比较器,如果有获取出来,没有的话返回null
Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass = getClass(
JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR, null, RawComparator.class);
//如果设置过排序比较器,则通过反射创建对应类的对象
if (theClass != null)
return ReflectionUtils.newInstance(theClass, this);
//如果没有设置过,通过如下方式获取对应key的类中的自带的一个比较器,比如Text类。
return WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), this);
}如何设置排序比较器?
java
job.setSortComparatorClass(WCSortComparator.class);点击如上方法:
java
public void setSortComparatorClass(Class<? extends RawComparator> cls
) throws IllegalStateException {
ensureState(JobState.DEFINE);
conf.setOutputKeyComparatorClass(cls);
}点击setOutputKeyComparatorClass(cls)方法:
java
public void setOutputKeyComparatorClass(Class<? extends RawComparator> theClass) {
setClass(JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR,
theClass, RawComparator.class);
}JobContext.KEY_COMPARATOR就是获取是使用到的常量,来找它对应的value。
如果没有设置排序比较器,如何从Key对应的类中找比较器?
常见的Key对应的类如Text、LongWritable等。
Ctrl+Shift+R->Text.java
java
//在Text类内部定义的比较器的类Comparator
//1.继承WritableComparator抽象类
public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator {
//2.添加一个无参数的构造方法
public Comparator() {
//3.通过super(Text.class) 调用父类的构造方法,并传递外部类Text.class
super(Text.class);
}
/*4.根据需要覆写父类的比较的方法
也可以覆写其他的方法,比如:
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
return a.compareTo(b);
}
*/
@Override
public int compare(byte[] b1, int s1, int l1,
byte[] b2, int s2, int l2) {
int n1 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b1[s1]);
int n2 = WritableUtils.decodeVIntSize(b2[s2]);
return compareBytes(b1, s1+n1, l1-n1, b2, s2+n2, l2-n2);
}
}
//5.注册比较器的类
static {
// register this comparator
WritableComparator.define(Text.class, new Comparator());
}Ctrl+点击 如上的define(),查看如何注册的比较器。
java
private static final ConcurrentHashMap<Class, WritableComparator> comparators
= new ConcurrentHashMap<Class, WritableComparator>();
public static void define(Class c, WritableComparator comparator) {
comparators.put(c, comparator);
}读取Key对应类注册的比较器的实例:
java
WritableComparator.get(getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class), Ctrl+单击如上的get方法
java
public static WritableComparator get(
Class<? extends WritableComparable> c, Configuration conf) {
WritableComparator comparator = comparators.get(c);
if (comparator == null) {
// force the static initializers to run
forceInit(c);
// look to see if it is defined now
comparator = comparators.get(c);
// if not, use the generic one
if (comparator == null) {
comparator = new WritableComparator(c, conf, true);
}
}
// Newly passed Configuration objects should be used.
ReflectionUtils.setConf(comparator, conf);
return comparator;
}就从我们注册是存入的Map中获取的:comparators.get(c)。
comparator在哪里使用的?
Ctrl+Shift+R->SpillThread->run()方法->sortAndSpill():
java
sorter.sort(MapOutputBuffer.this, mstart, mend, reporter)Ctrl+单击 sort()
java
void sort(IndexedSortable s, int l, int r, Progressable rep);Ctrl+Alt+B->QuickSort类:
java
public void sort(final IndexedSortable s, int p, int r,
final Progressable rep) {
sortInternal(s, p, r, rep, getMaxDepth(r - p));
}
private static void sortInternal(final IndexedSortable s, int p, int r,
final Progressable rep, int depth) {
if (null != rep) {
rep.progress();
}
while (true) {
if (r-p < 13) {
for (int i = p; i < r; ++i) {
for (int j = i; j > p && s.compare(j-1, j) > 0; --j) {
s.swap(j, j-1);
}
}
return;
}
......
}compare()->IndexedSortable接口的compare()方法->Ctrl+Alt+B->MapOutputBuffer类的compare方法:
java
public int compare(final int mi, final int mj) {
final int kvi = offsetFor(mi % maxRec);
final int kvj = offsetFor(mj % maxRec);
final int kvip = kvmeta.get(kvi + PARTITION);
final int kvjp = kvmeta.get(kvj + PARTITION);
// sort by partition
if (kvip != kvjp) {
return kvip - kvjp;
}
// sort by key 就使用到了comparator比较器对象
return comparator.compare(kvbuffer,
kvmeta.get(kvi + KEYSTART),
kvmeta.get(kvi + VALSTART) - kvmeta.get(kvi + KEYSTART),
kvbuffer,
kvmeta.get(kvj + KEYSTART),
kvmeta.get(kvj + VALSTART) - kvmeta.get(kvj + KEYSTART));
}5.4.14 没有Reduce时out对象创建
直接通过NewDirectOutputCollector写到HDFS上
MapTask类的runNewMapper方法中:

MapTask->NewDirectOutputCollector->write()方法:
java
public void write(K key, V value)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
reporter.progress();
long bytesOutPrev = getOutputBytes(fsStats);
out.write(key, value);
long bytesOutCurr = getOutputBytes(fsStats);
fileOutputByteCounter.increment(bytesOutCurr - bytesOutPrev);
mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1);
}分析out对象来源?
java
NewDirectOutputCollector(MRJobConfig jobContext,
JobConf job, TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical, TaskReporter reporter)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException {
this.reporter = reporter;
mapOutputRecordCounter = reporter
.getCounter(TaskCounter.MAP_OUTPUT_RECORDS);
fileOutputByteCounter = reporter
.getCounter(FileOutputFormatCounter.BYTES_WRITTEN);
List<Statistics> matchedStats = null;
if (outputFormat instanceof org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat) {
matchedStats = getFsStatistics(org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat
.getOutputPath(taskContext), taskContext.getConfiguration());
}
fsStats = matchedStats;
long bytesOutPrev = getOutputBytes(fsStats);
out = outputFormat.getRecordWriter(taskContext);
long bytesOutCurr = getOutputBytes(fsStats);
fileOutputByteCounter.increment(bytesOutCurr - bytesOutPrev);
}点击getRecordWriter()->Ctrl+Alt+B->MapFileOutputFormat
java
public RecordWriter<WritableComparable<?>, Writable> getRecordWriter(
TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
Configuration conf = context.getConfiguration();
CompressionCodec codec = null;
CompressionType compressionType = CompressionType.NONE;
if (getCompressOutput(context)) {
// find the kind of compression to do
compressionType = SequenceFileOutputFormat.getOutputCompressionType(context);
// find the right codec
Class<?> codecClass = getOutputCompressorClass(context,
DefaultCodec.class);
codec = (CompressionCodec) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, conf);
}
Path file = getDefaultWorkFile(context, "");
//将内容直接写入HDFS文件系统中
FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(conf);
// ignore the progress parameter, since MapFile is local
final MapFile.Writer out =
new MapFile.Writer(conf, fs, file.toString(),
context.getOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class),
context.getOutputValueClass().asSubclass(Writable.class),
compressionType, codec, context);
return new RecordWriter<WritableComparable<?>, Writable>() {
public void write(WritableComparable<?> key, Writable value)
throws IOException {
out.append(key, value);
}
public void close(TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException {
out.close();
}
};
}5.5 Reduce阶段源码分析
###5.5.1 概述
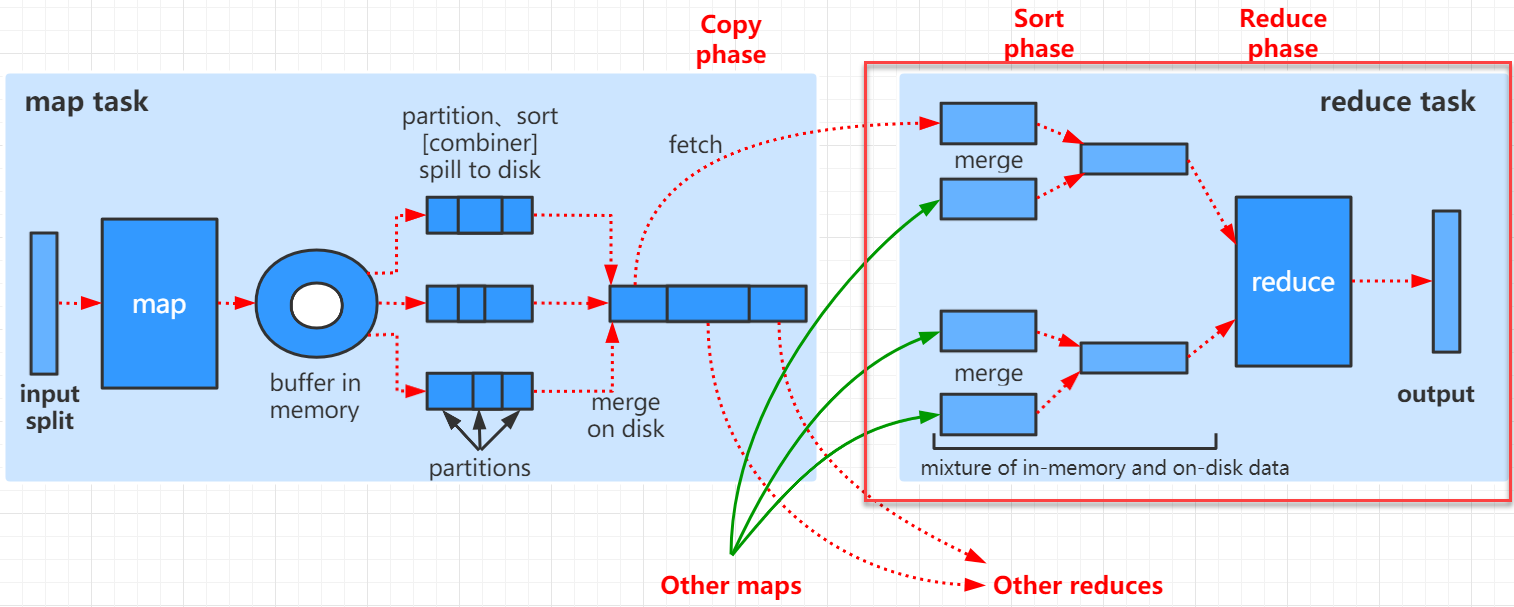
阅读源码需要解决以下问题:
- 默认启动5个线程去完成MapTask任务的节点上分别抓取数据。
- 通过什么方式去Map端抓取数据的http或https get?
- 如何进行分组的?
- reduce端的二次排序是如何进行的?
分析ReduceTask类的run方法:
java
public void run(JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical)
throws IOException, InterruptedException, ClassNotFoundException {
job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping());
if (isMapOrReduce()) {
//copy:从完成MapTask的Map端的节点中拷贝处理过的数据
copyPhase = getProgress().addPhase("copy");
//排序
sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort");
//reduce处理
reducePhase = getProgress().addPhase("reduce");
}
// start thread that will handle communication with parent
TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical);
boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewReducer();
//初始化处理
initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi);
// check if it is a cleanupJobTask
if (jobCleanup) {
runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (jobSetup) {
runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
if (taskCleanup) {
runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter);
return;
}
// Initialize the codec
codec = initCodec();
RawKeyValueIterator rIter = null;
ShuffleConsumerPlugin shuffleConsumerPlugin = null;
//combinerClass获取
Class combinerClass = conf.getCombinerClass();
CombineOutputCollector combineCollector =
(null != combinerClass) ?
new CombineOutputCollector(reduceCombineOutputCounter, reporter, conf) : null;
Class<? extends ShuffleConsumerPlugin> clazz =
job.getClass(MRConfig.SHUFFLE_CONSUMER_PLUGIN, Shuffle.class, ShuffleConsumerPlugin.class);
shuffleConsumerPlugin = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(clazz, job);
LOG.info("Using ShuffleConsumerPlugin: " + shuffleConsumerPlugin);
ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context shuffleContext =
new ShuffleConsumerPlugin.Context(getTaskID(), job, FileSystem.getLocal(job), umbilical,
super.lDirAlloc, reporter, codec,
combinerClass, combineCollector,
spilledRecordsCounter, reduceCombineInputCounter,
shuffledMapsCounter,
reduceShuffleBytes, failedShuffleCounter,
mergedMapOutputsCounter,
taskStatus, copyPhase, sortPhase, this,
mapOutputFile, localMapFiles);
//Shuffle插件初始化
shuffleConsumerPlugin.init(shuffleContext);
//Shuffle插件执行
rIter = shuffleConsumerPlugin.run();
// free up the data structures
mapOutputFilesOnDisk.clear();
sortPhase.complete(); // sort is complete
setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.REDUCE);
statusUpdate(umbilical);
Class keyClass = job.getMapOutputKeyClass();
Class valueClass = job.getMapOutputValueClass();
//分组比较器
RawComparator comparator = job.getOutputValueGroupingComparator();
if (useNewApi) {//hadoop2.x+ 使用
runNewReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
} else {//hadoop1.x 使用
runOldReducer(job, umbilical, reporter, rIter, comparator,
keyClass, valueClass);
}
shuffleConsumerPlugin.close();
done(umbilical, reporter);
}