力扣104.二叉树的最大深度
一、题目分析
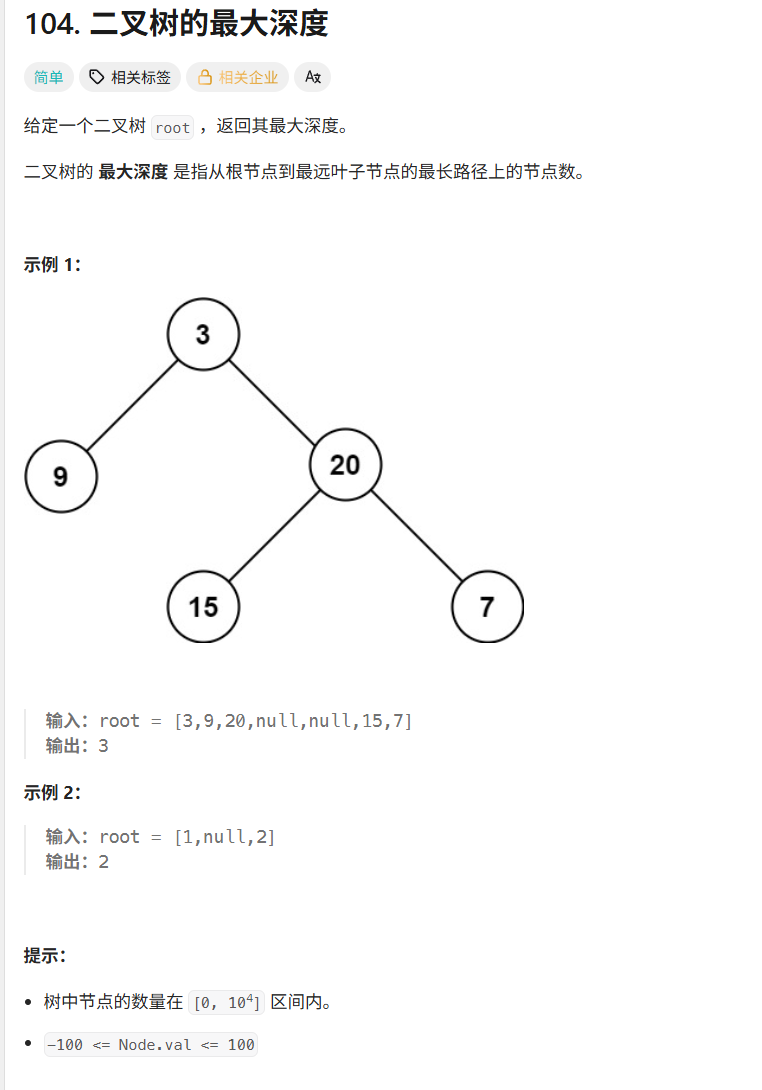
题目:
给定一棵二叉树的根节点 root,返回它的最大深度。
最大深度定义为:从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数量。
输入输出示例:
| 输入 | 输出 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
[3,9,20,null,null,15,7] |
3 |
最长路径是 3 → 20 → 7 |
[1,null,2] |
2 |
最长路径是 1 → 2 |
数据范围:
- 节点个数在
[0, 10^4] - 节点值在
[-100, 100]
二、解法一:递归(深度优先)
思路:
- 若树为空,深度为 0。
- 否则,最大深度等于左右子树深度的最大值 + 1。
- 是最经典、最自然的思路。
java
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}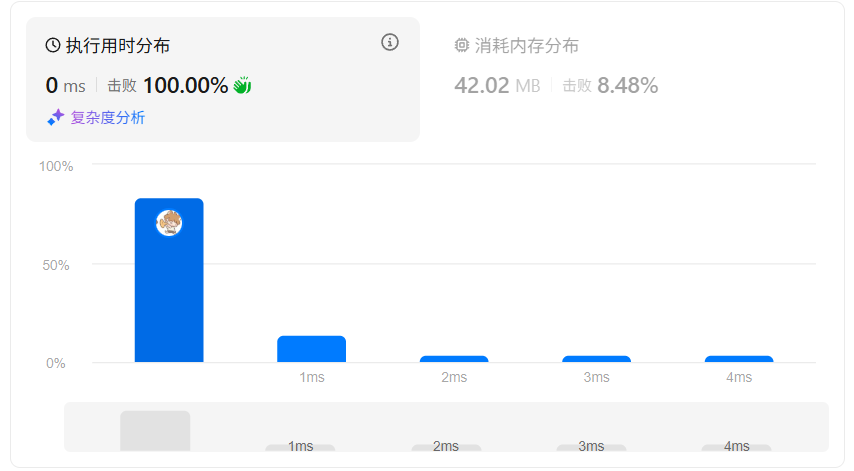
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点遍历一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(h),h 为树的高度(最坏情况下退化为 O(n))。
三、解法二:层序遍历(BFS)
思路:
- 用队列逐层遍历,每遍历一层深度 +1。
- 最终层数即为最大深度。
java
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
int depth = 0;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) queue.offer(node.left);
if (node.right != null) queue.offer(node.right);
}
depth++;
}
return depth;
}
}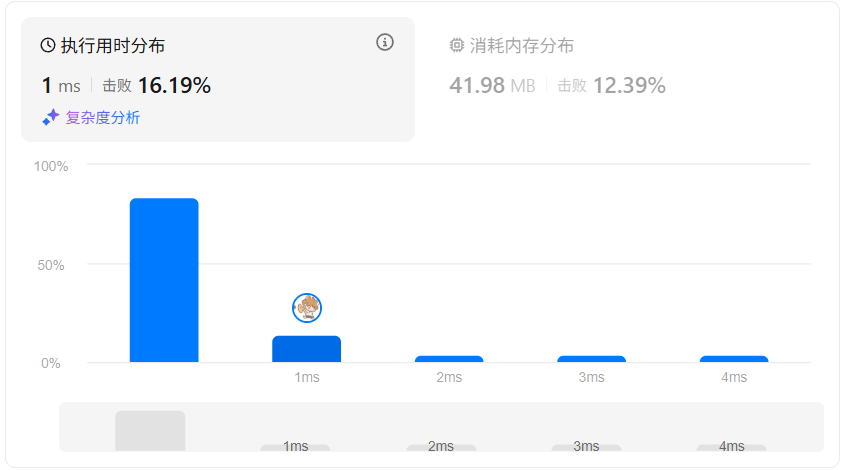
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n),每个节点进出队各一次。
- 空间复杂度:O(n),队列最多同时容纳一层节点。
四、解法三:显式栈(DFS 迭代版)
思路:
- 用栈模拟递归过程,栈中保存节点及其当前深度。
- 每次出栈时更新最大深度。
java
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Stack<TreeNode> nodeStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> depthStack = new Stack<>();
nodeStack.push(root);
depthStack.push(1);
int maxDepth = 0;
while (!nodeStack.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeStack.pop();
int depth = depthStack.pop();
maxDepth = Math.max(maxDepth, depth);
if (node.left != null) {
nodeStack.push(node.left);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
}
if (node.right != null) {
nodeStack.push(node.right);
depthStack.push(depth + 1);
}
}
return maxDepth;
}
}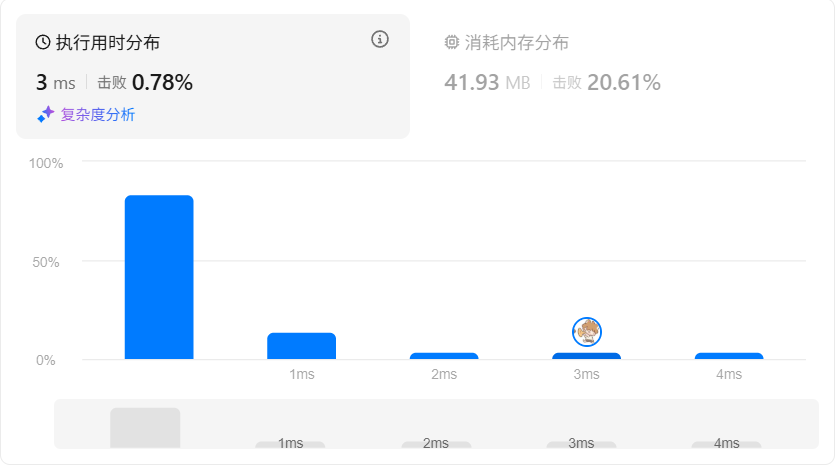
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度:O(n)
- 空间复杂度:O(n)
五、方法比较
| 方法 | 思路 | 是否递归 | 是否按层遍历 | 空间复杂度 | 优点 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 递归 | 自顶向下计算 | ✅ | ❌ | O(h) | 代码简洁直观 |
| BFS | 队列层序遍历 | ❌ | ✅ | O(n) | 层数一目了然 |
| 显式栈 DFS | 手动栈模拟递归 | ❌ | ❌ | O(n) | 控制过程灵活 |