Human Activity Recognition Using Smartphones Dataset
Dataset : Dataset for this project is downloaded from course website using link below https://d396qusza40orc.cloudfront.net/getdata%2Fprojectfiles%2FUCI%20HAR%20Dataset.zip
Source: The data linked to from the course website represent data collected from the accelerometers from the Samsung Galaxy S smartphone. A full description is available at the site where the data was obtained: http://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Human+Activity+Recognition+Using+Smartphones
Data Set Information:
这些数据是从30名年龄在19岁到48岁之间的志愿者身上收集的,这些志愿者将智能手机绑在腰间,进行6项标准活动中的一项,通过开发的手机软件记录运动数据。同时记录每个执行活动的志愿者的视频,后期根据这些视频和传感器数据进行手动标记所属运动类别(类似剪辑视频中的音画同步)。执行的六项活动如下:
Walking;Walking Upstairs;Walking Downstairs;Sitting;Standing;Laying;
选择30名年龄在19-48岁之间的志愿者作为研究对象。记录的运动数据是来自智能手机(特别是三星Galaxy S II)的x、y和z加速度计数据(线性加速度)和陀螺仪数据(角速度),采样频率为 50Hz(每秒50个数据点)。每名志愿者进行两次活动序列,第一次在设备位于腰间左侧,第二次测试时,智能手机由用户自己按喜好放置。
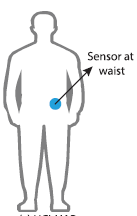
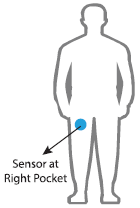
For each record in the dataset it is provided:
- Triaxial acceleration from the accelerometer (total acceleration) and the estimated body acceleration.
- Triaxial Angular velocity from the gyroscope.
- A 561-feature vector with time and frequency domain variables.
- Its activity label.
- An identifier of the subject who carried out the experiment.
Reference:
- Davide Anguita, Alessandro Ghio, Luca Oneto, Xavier Parra and Jorge L. Reyes-Ortiz. Human Activity Recognition on Smartphones using a Multiclass Hardware-Friendly Support Vector Machine. International Workshop of Ambient Assisted Living (IWAAL 2012). Vitoria-Gasteiz, Spain. Dec 2012
(1)dataset 介绍
|------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| test:测试集数据; | 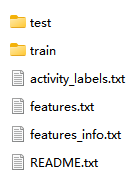 |
|
| train:训练集数据; |  |
|
| activity_labels.txt:活动的真实标签(6个); |  |
|
| features.txt:特征工程的特征; |  |
|
| features_info.txt:特征工程处理说明; |  |
|
| |  |
|
使用噪声滤波器对加速度计进行预处理。将数据分割成2.56秒(128个数据点)的固定窗口,重叠50%。将加速度计数据分为重力(总)和人体运动分量。
(1)使用中值滤波器和截止频率为 20Hz的三阶低通Butter-worth滤波器对这些信号进行了预处理,以降低噪声。 该速率足以捕获人体运动,因为其能量的99%包含在15Hz以下。
(2)巴特沃斯低通滤波器将具有重力和人体运动成分的加速度信号分离为人体加速度和重力。 假定重力仅具有低频分量,因此从实验中我们发现,对于恒定重力信号,0.3Hz是最佳转折频率。
将特征工程应用于窗口数据,并提供具有这些经过特征工程的数据。从每个窗口中提取了人类活动识别领域中常用的一些时间和频率特征。结果是一个561元素的特征向量。数据集根据受试者的数据分为训练集(70%)和测试集(30%),例如,训练21名受试者,测试9名受试者。
(2)以train文件夹为例,展开叙述:
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| X_train.txt:未经处理的原始数据,这个不用,可以不关心; y_train.txt:活动类别标签(数字1-6表示),shape为(7352,1);说明:注意这里的标签是从1开始表示第一类,而one-hot编码是从0开始,注意编码的时候要减去1!这个在以后的建模过程中会遇到,先说明一下。 subject train.txt:将训练集的每一个样本与志愿者编号(1-30)对应,即给每条样本记录属于哪位志愿者做标识,shape为(7352,1); | 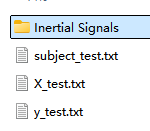 |
|
(3)以Inertial Signals
原始数据中有3个主要的类型: total acceleration, body acceleration, and body gyroscope. 每一类有3个维度,也就是说一个时间步有9个变量。此外,每组数据都被划分为2.65秒(128个时间步)的带重叠的窗口。这样每一行就有128*9(1152)个特征,相比于特征工程后的561个特征,显得有些冗余。
|-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| body_acc_x_train.txt、body_acc_y_train.txt、body_acc_z_train.txt:三轴的加速度数据; body_gyro_x_train.txt、body_gyro_y_train.txt、body_gyro_z_train.txt:三轴的陀螺仪数据(角速度); total_acc_x_train.txt、total_acc_y_train.txt、total_acc_z_train.txt:三轴的重力加速度数据; |  |
|
网络模型
UCI-HAR数据集深度剖析:训练仿真与可视化解读-CSDN博客
WISDM Smartphone and Smartwatch Activity and Biometrics Dataset
人体活动识别(HAR)是一种使用人工智能(AI)从智能手表等活动记录设备产生的原始数据中识别人类活动的方法。 当人们执行某种动作时,人们佩戴的传感器(智能手表、手环、专用设备等)就会产生信号。
数据集地址:
代码:
human action recognition-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56618414/article/details/141817309LSTM+CNN处理时序数据_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56618414/article/details/141817309LSTM+CNN处理时序数据_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
导入库
python
from pandas import read_csv, unique
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
from scipy.stats import mode
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix, ConfusionMatrixDisplay
from tensorflow import stack
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers import Dense, GlobalAveragePooling1D, BatchNormalization, MaxPool1D, Reshape, Activation
from keras.layers import Conv1D, LSTM
from keras.callbacks import ModelCheckpoint, EarlyStopping
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")数据集加载和可视化
python
def read_data(filepath):
df = read_csv(filepath, header=None, names=['user-id',
'activity',
'timestamp',
'X',
'Y',
'Z'])
## removing ';' from last column and converting it to float
##在 Z 列中移除了分号(;)
df['Z'].replace(regex=True, inplace=True, to_replace=r';', value=r'')
##将这一列的数据转换为浮点数
df['Z'] = df['Z'].apply(convert_to_float)
# df.dropna(axis=0, how='any', inplace=True)
return df
def convert_to_float(x):
##转化为float64
try:
return np.float64(x)
except:
return np.nan
df = read_data('Dataset/WISDM_ar_v1.1/WISDM_ar_v1.1_raw.txt')
df数据类别分析可视化
python
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
plt.xlabel('Activity Type')
plt.ylabel('Training examples ')
df['activity'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar',
title='Training examples by Activity Types')
plt.show()##不同活动类型的训练样本数
plt.figure(figsize=(15, 5))
plt.xlabel('User')
plt.ylabel('Training examples')
df['user-id'].value_counts().plot(kind='bar',
title='Training examples by user')
plt.show()##不同活动类型的训练样本数现在我将收集的三个轴上的加速度计数据进行可视化。
python
def axis_plot(ax, x, y, title):
ax.plot(x, y, 'r')##绘制绘制 x 和 y 数据点,并使用红色('r')线条
ax.set_title(title)
ax.xaxis.set_visible(False)##隐藏x轴
##设置x轴和y轴的范围
ax.set_ylim([min(y) - np.std(y), max(y) + np.std(y)])
ax.set_xlim([min(x), max(x)])
ax.grid(True)
for activity in df['activity'].unique():##遍历每种活动类型
limit = df[df['activity'] == activity][:180]##取前180个
fig, (ax0, ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=3, sharex=True, figsize=(15, 10))
axis_plot(ax0, limit['timestamp'], limit['X'], 'x-axis')
axis_plot(ax1, limit['timestamp'], limit['Y'], 'y-axis')
axis_plot(ax2, limit['timestamp'], limit['Z'], 'z-axis')
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2)
fig.suptitle(activity)
plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.9)
plt.show()数据预处理
数据预处理是一项非常重要的任务,它使我们的模型能够更好的利用我们的原始数据。这里将使用的数据预处理方法有:
标签编码
线性插值
数据分割
归一化
时间序列分割
独热编码
标签编码
由于模型不能接受非数字标签作为输入,我们将在另一列中添加' activity '列的编码标签,并将其命名为' activityEncode '。标签被转换成如下所示的数字标签(这个标签是我们要预测的结果标签)
Downstairs [0]
Jogging [1]
Sitting [2]
Standing [3]
Upstairs [4]
Walking [5]
python
label_encode = LabelEncoder()
df['activityEncode'] = label_encode.fit_transform(df['activity'].values.ravel())
df
##将数据框 df 中的 activity 列中的活动类型转换为数字编码,并将结果存储在一个新的列 activityEncode 中线性插值
利用线性插值可以避免采集过程中出现NaN的数据丢失的问题。它将通过插值法填充缺失的值。虽然在这个数据集中只有一个NaN值,但为了我们的展示,还是需要实现它。
human action recognition-CSDN博客![]() https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56618414/article/details/141817309
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_56618414/article/details/141817309