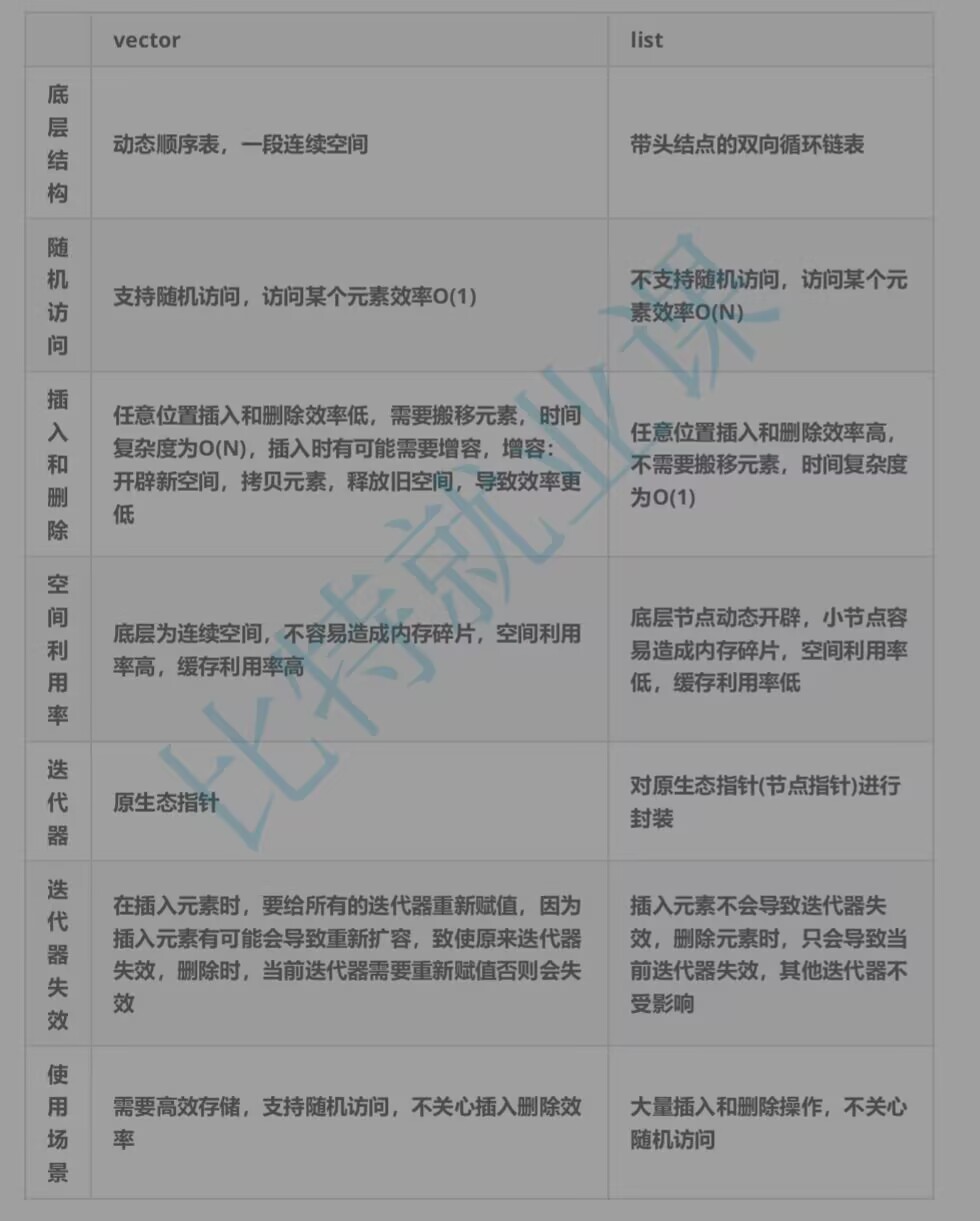
1.list的介绍与使用
list是环状双向串行的,有prev,next结点。
cpp
list(size_type n,const value_type& val=value_type())
n个val值元素构造
list() 构建空的list
list(const list& x) 拷贝构造函数
list(inputlterator first,inputlterator last)
用(first,last)区间中的元素构造list
List iterator
begin()+end() 返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器
rbegin()+rend() 返回end位置+返回begin位置
list的迭代器是双向迭代器,不是随机迭代器,不支持[]随机访问
empty 检测list是否为空,是返回true,否返回false
size 返回list有效节点的个数
front 返回list第一个节点中值的引用
back 返回list最后一个节点中值的引用
push_front 在list首元素前插入值为val的节点
pop_front 删除list第一个节点
push_back 在尾部插入值为val的节点
pop_back 删除list最后一个元素
insert 在list position位置插入值为val的节点
erase 删除list position位置的元素
swap 交换list中2个元素
clear 清空list中的有效元素list的迭代器也会失效,类似于指针,迭代器失效即迭代器指向的节点无效,该节点被删除了,list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,在list中插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效,只有在删除时会失效,erase,失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他没事。
cpp
// 链表节点类(声明与实现合并)
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
T _val;
ListNode<T>* _pPre;
ListNode<T>* _pNext;
// 构造函数
ListNode(const T& val = T())
: _val(val)
, _pPre(nullptr)
, _pNext(nullptr)
{}
};
// 链表迭代器类(声明与实现合并)
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
PNode _pNode;
// 构造函数
ListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr) : _pNode(pNode) {}
ListIterator(const Self& l) : _pNode(l._pNode) {}
// 解引用操作
Ref operator*() { return _pNode->_val; }
Ptr operator->() { return &(_pNode->_val); }
// 前置++
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return *this;
}
// 后置++
Self operator++(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
_pNode = _pNode->_pNext;
return temp;
}
// 前置--
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return *this;
}
// 后置--
Self operator--(int)
{
Self temp(*this);
_pNode = _pNode->_pPre;
return temp;
}
// 比较操作
bool operator!=(const Self& l) const { return _pNode != l._pNode; }
bool operator==(const Self& l) const { return _pNode == l._pNode; }
};
// 链表主体类(声明与实现合并)
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
public:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;
public:
// 构造函数:创建空链表(仅头节点)
list()
{
_pHead = new Node;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
}
// 填充构造:n个值为value的节点
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
_pHead = new Node;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
// 迭代器区间构造
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
_pHead = new Node;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
// 拷贝构造
list(const list<T>& l)
{
_pHead = new Node;
_pHead->_pPre = _pHead;
_pHead->_pNext = _pHead;
const_iterator it = l.begin();
while (it != l.end())
{
push_back(*it);
++it;
}
}
// 赋值运算符
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}
// 析构函数
~list()
{
clear();
delete _pHead;
_pHead = nullptr;
}
// 迭代器 begin/end
iterator begin() { return iterator(_pHead->_pNext); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_pHead); }
const_iterator begin() const { return const_iterator(_pHead->_pNext); }
const_iterator end() const { return const_iterator(_pHead); }
// 容量操作
size_t size() const
{
size_t count = 0;
const_iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
++count;
++it;
}
return count;
}
bool empty() const { return _pHead->_pNext == _pHead; }
// 元素访问
T& front()
{
if (empty()) throw std::out_of_range("list is empty");
return _pHead->_pNext->_val;
}
const T& front() const
{
if (empty()) throw std::out_of_range("list is empty");
return _pHead->_pNext->_val;
}
T& back()
{
if (empty()) throw std::out_of_range("list is empty");
return _pHead->_pPre->_val;
}
const T& back() const
{
if (empty()) throw std::out_of_range("list is empty");
return _pHead->_pPre->_val;
}
// 元素修改
void push_back(const T& val) { insert(end(), val); }
void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }
void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); }
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
// 在pos前插入节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
PNode newNode = new Node(val);
PNode posNode = pos._pNode;
newNode->_pPre = posNode->_pPre;
newNode->_pNext = posNode;
posNode->_pPre->_pNext = newNode;
posNode->_pPre = newNode;
return iterator(newNode);
}
// 删除pos位置节点
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
if (pos == end()) throw std::invalid_argument("cannot erase end iterator");
PNode posNode = pos._pNode;
PNode nextNode = posNode->_pNext;
posNode->_pPre->_pNext = nextNode;
nextNode->_pPre = posNode->_pPre;
delete posNode;
return iterator(nextNode);
}
// 清空所有节点
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
// 交换两个链表
void swap(list<T>& l) { std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead); }
private:
PNode _pHead; // 头节点(哨兵节点)
};
cpp
// 反向迭代器模板(适配器)
// Iterator:正向迭代器类型;Ref:引用类型;Ptr:指针类型
template<class Iterator, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct Reverse_iterator {
typedef Reverse_iterator<Iterator, Ref, Ptr> Self;
Iterator _it; // 存储正向迭代器
// 构造函数:用正向迭代器初始化
Reverse_iterator(Iterator it) : _it(it) {}
// 解引用:反向迭代器的*实际访问正向迭代器的前一个元素
Ref operator*() const {
Iterator tmp = _it; // 拷贝当前正向迭代器
--tmp; // 指向前一个元素
return *tmp; // 返回前一个元素的引用
}
// 箭头操作符:返回前一个元素的指针
Ptr operator->() const {
return &(operator*()); // 复用*操作
}
// 前置++:反向迭代器向前移动(对应正向迭代器向后移动)
Self& operator++() {
--_it; // 正向迭代器--,反向迭代器实际向前走
return *this;
}
// 前置--:反向迭代器向后移动(对应正向迭代器向前移动)
Self& operator--() {
++_it; // 正向迭代器++,反向迭代器实际向后走
return *this;
}
// 不等比较:判断两个反向迭代器是否不同
bool operator!=(const Self& other) const {
return _it != other._it;
}2.list与vector对比