❀保持低旋律节奏->个人主页
文章目录
栈和队列
1.1stack的介绍
官方文档❀stack介绍
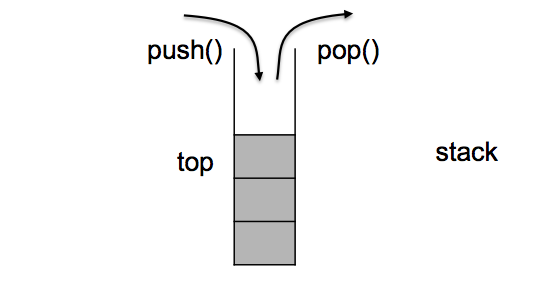
1.2stack的函数使用
| 函数说明 | 接口说明 | 参数说明 | 返回类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| stack() | 构造空栈 | 无参 | none |
| empty() | 检测stack是否为空 | 无参 | bool |
| size() | 返回stack中元素的个数 | 无参 | size_type |
| top() | 返回栈顶元素的引用 | 无参 | 栈顶元素 |
| push() | 将元素val压入stack中 | const value_type& val或value_type&& val | none |
| pop() | 将stack中尾部元素弹出 | 无参 | none |
2.1queue介绍
queue
官方文档❀queue介绍
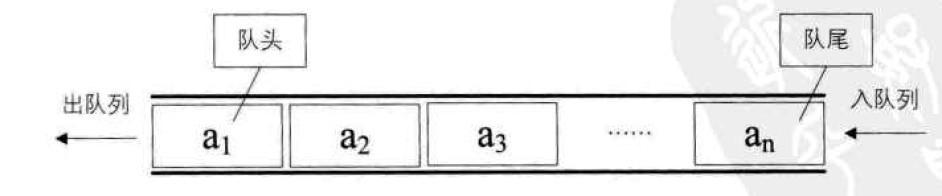
- 队列是一种容器适配器,专门用于在FIFO上下文(先进先出)中操作,其中从容器一端插入元素,另一端提取元素。
- 队列作为容器适配器实现,容器适配器即将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类,queue提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从队尾入队列,从队头出队列。
- 底层容器可以是标准容器类模板之一,也可以是其他专门设计的容器类。该底层容器应至少支持以下操作:
empty:检测队列是否为空
size:返回队列中有效元素的个数
front:返回队头元素的引用
back:返回队尾元素的引用
push_back:在队列尾部入队列
pop_front:在队列头部出队列
- 标准容器类deque和list满足了这些要求。默认情况下,如果没有为queue实例化指定容器类,则使用标准容器deque。
- 用代码来彻底理解容器适配器
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack> // 容器适配器 stack
#include <deque> // 底层默认容器 deque
int main() {
std::stack<int> my_stack;
// 栈的核心操作:入栈(只能从栈顶添加)
my_stack.push(10); // 栈:[10]
my_stack.push(20); // 栈:[10, 20](20 在栈顶)
my_stack.push(30); // 栈:[10, 20, 30](30 在栈顶)
// 栈的核心操作:取栈顶元素(只能看最上面的)
std::cout << "栈顶元素:" << my_stack.top() << std::endl; // 输出 30
// 栈的核心操作:出栈(只能从栈顶删除)
my_stack.pop(); // 移除 30,栈变为 [10, 20]
std::cout << "出栈后栈顶:" << my_stack.top() << std::endl; // 输出 20
// 查看栈的大小
std::cout << "栈的大小:" << my_stack.size() << std::endl; // 输出 2
return 0;
}上述代码是一个stack栈基本功能的实现,你可能会有疑问,这代码明明是stack功能实现。关deque什么事情?关容器适配器什么事情?
别急,这就是容器适配器的最核心的功能。
容器适配器它本身作为容器底层实现部分,它的代码实现你是看不到的。上述代码看似创建了stack,看似在stack中push、pop了,但是实际上只是在容器适配器------deque上进行的push、pop。只不过,容器适配器提供了几个接口来供我们使用,我们就觉得实际是在stack上操作的。
正式因为deque------容器适配器它太灵活,(功能太多)不符合栈的规则。因此我们创建了一个栈用来接受适配器为我们提供的部分接口,其余接口stack都用不到
2.2queue的函数使用
| 函数说明 | 接口说明 | 参数说明 | 返回类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
| queue() | 构造空队列 | 无参 | none |
| empty() | 检测队列是否为空,是则返回true,否则返回false | 无参 | bool |
| size() | 返回队列中有效元素的个数 | 无参 | size_type |
| front() | 返回队头元素的引用 | 无参 | 首元素 |
| back() | 返回队尾元素的引用 | 无参 | 末元素 |
| push() | 在队尾将元素val入队列 | const value_type& val或value_type&& val | none |
| pop() | 将队头元素出队列 | 无参 | none |
stack
最小栈
思路图解
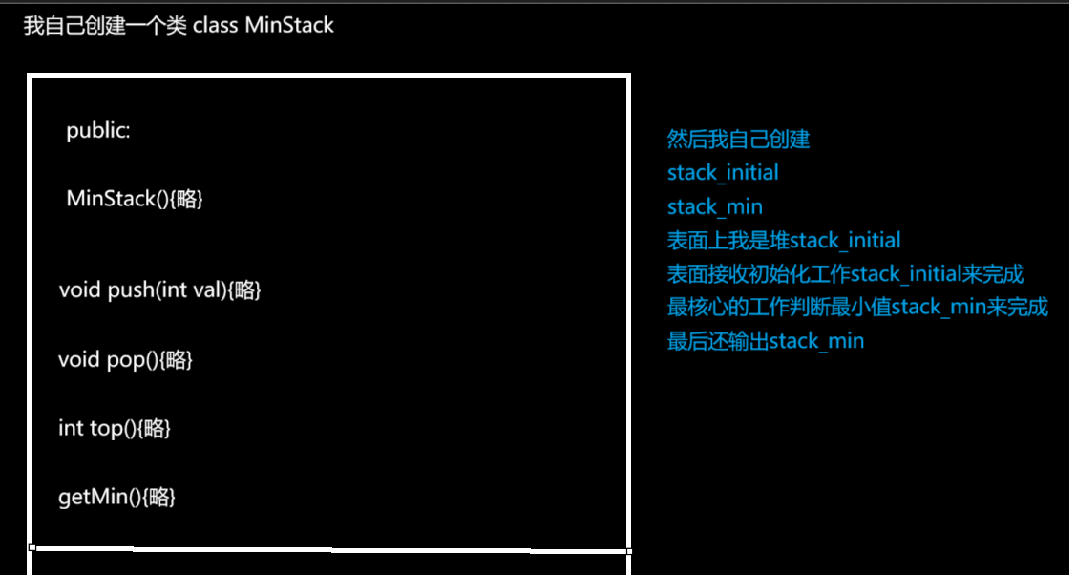
代码实现
cpp
#include<stack>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
class MinStack
{
stack<int>stack_initial;
stack<int>stack_min;
public:
MinStack()
{
stack_min.push(INT_MAX);//初始化技巧
}
void push(int val)
{
stack_initial.push(val);
stack_min.push(min(stack_min.top(),val));
}
void pop()
{
stack_initial.pop();
stack_min.pop();
}
int top()
{
return stack_initial.top();
}
int getMin()
{
return stack_min.top();
}
};
int main()
{
// 创建MinStack对象
MinStack minStack;
// 调用各种方法
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
cout << "当前最小值: " << minStack.getMin() << endl; // 输出 -3
minStack.pop(); // 弹出-3
cout << "栈顶元素: " << minStack.top() << endl; // 输出 0
cout << "当前最小值: " << minStack.getMin() << endl; // 输出 -2
}栈的弹出压入序列
栈的弹出压入序列链接
题目

思路图解
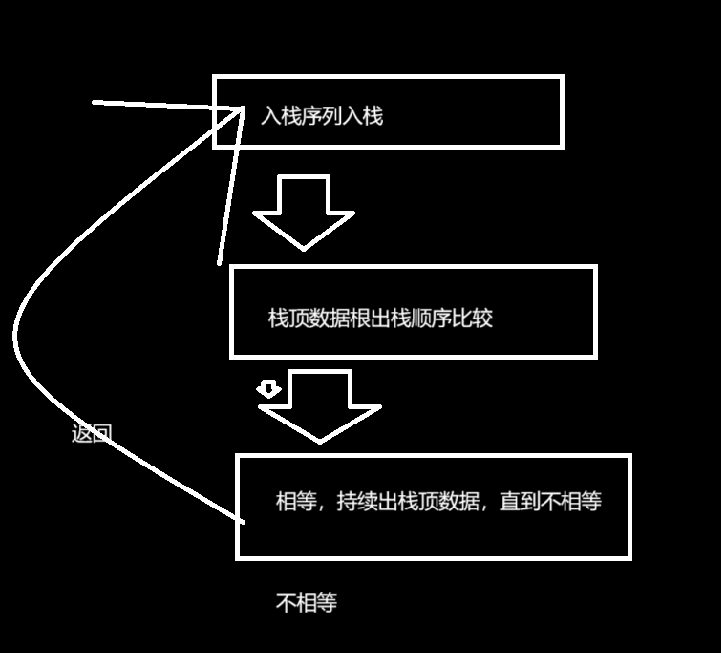
代码实现
cpp
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cout << "输入数据个数:";
cin >> n;
vector<int>initial_v(n);
vector<int>end_v(n);
auto it_ini = initial_v.begin();
auto it_end = end_v.begin();
while (it_ini != initial_v.end())
{
int i; cin >> i;
*it_ini = i;
it_ini++;
}
while (it_end != end_v.end())
{
int i; cin >> i;
*it_end = i;
it_end++;
}
stack<int>s1;
int id = 0;//id用来记录偏移量
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
s1.push(initial_v[i]);
while (s1.empty() == false&&s1.top() == end_v[id]) //为空时就会崩
{
s1.pop();
id++;
}
}
if (id == n)
{
cout << "相等" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "不等" << endl;
}
return 0;
}逆波兰表达式
逆波兰表达式链接
题目
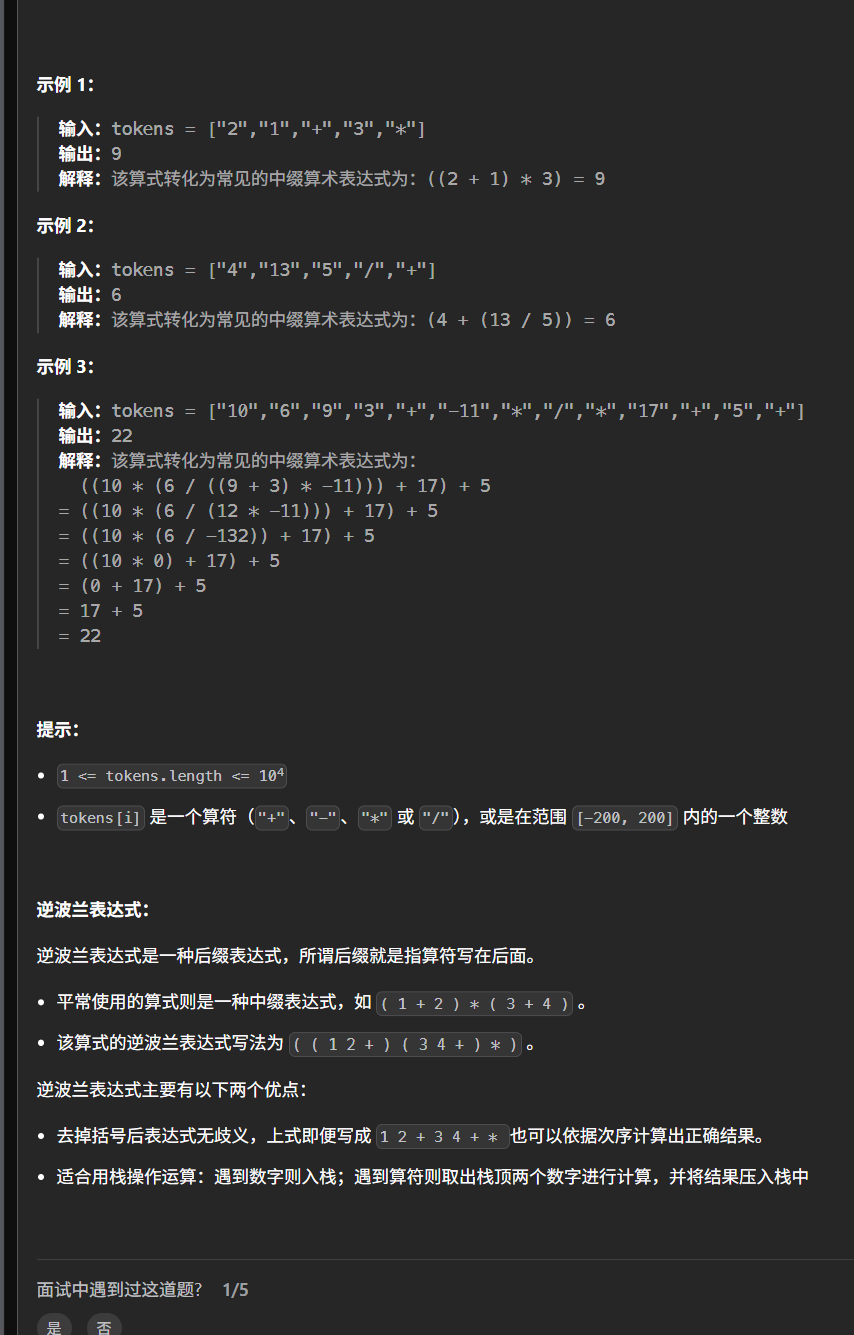
思路图解
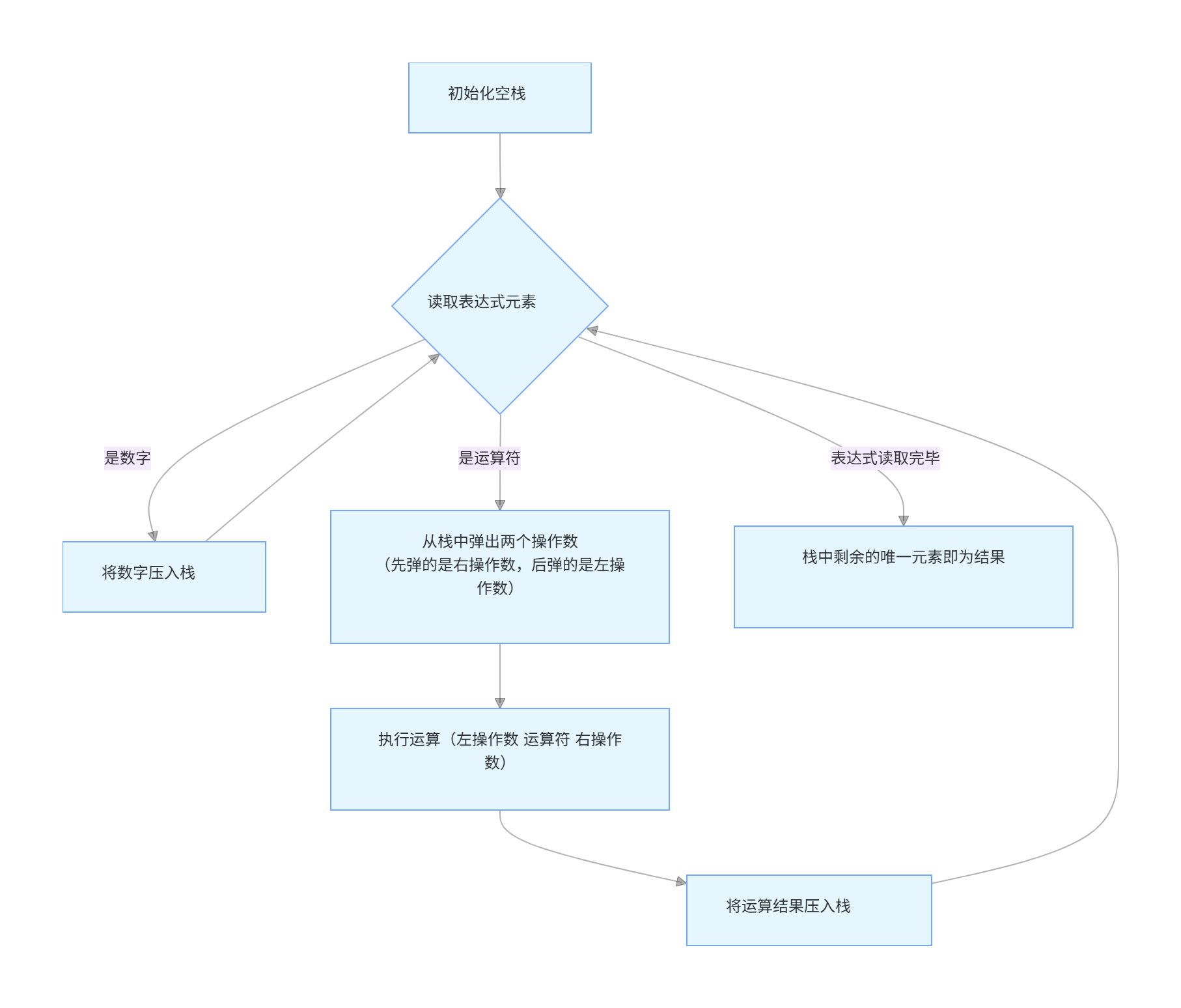
代码
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>//引入标准库,字符串整数函数atoi
using namespace std;
class Solution
{
public:
int evalRPN(vector<string>& tokens)//这里不是创建,创建需要花费更高代价
{
stack<int>st;
for (string&s:tokens)//范围for可以使用auto自动识别,也可以指名变量
{
if (s == "+" || s == "-" || s == "*" || s == "/")
{
int b = st.top();
st.pop();
int a = st.top();
st.pop();
if (s == "+")
{
st.push(a + b);
}
else if (s == "-")
{
st.push(a - b);
}
else if (s == "*")
{
st.push(a * b);
}
else if (s == "/")
{
st.push(a / b);
}
}
else
{
int num = atoi(s.c_str());
st.push(num);
}
}
return st.top();
}
};
// 主函数:演示如何调用evalRPN
int main() {
// 1. 构造逆波兰表达式的tokens向量
// 示例表达式:((10 * (6 / ((9 + 3) * -11))) + 17) + 5
vector<string> tokens = {
"10", "6", "9", "3", "+", "-11", "*", "/", "*", "17", "+", "5", "+"
};
// 2. 创建Solution对象
Solution solution;
// 3. 调用evalRPN函数计算结果
int result = solution.evalRPN(tokens);
// 4. 输出结果(预期输出:22)
cout << "表达式的计算结果为:" << result << endl;
return 0;
}队列
用队列实现栈
题目
题目就是用队列实现栈,没有找到相似的题目
代码实现
cpp
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
class MyStack {
private:
queue<int> q1; // 主队列(存储栈元素)
queue<int> q2; // 辅助队列(临时转移元素)
public:
MyStack() {} // 构造函数,默认初始化队列
// 入栈:直接加入主队列q1
void push(int x) {
q1.push(x);
}
// 出栈:弹出栈顶元素(q1的最后一个元素)
int pop() {
// 步骤1:将q1中除最后一个元素外,全部移到q2
while (q1.size() > 1) {
q2.push(q1.front()); // 取q1队头,加入q2
q1.pop(); // 移除q1队头
}
// 步骤2:此时q1只剩1个元素(栈顶),弹出并记录
int top_val = q1.front();
q1.pop();
// 步骤3:将q2的元素移回q1,恢复主队列
swap(q1, q2); // 交换两个队列,等价于q1 = q2,q2清空
return top_val;
}
// 获取栈顶元素(不弹出)
int top() {
// 复用pop的逻辑,但不移除最后一个元素
while (q1.size() > 1) {
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
}
int top_val = q1.front(); // 记录栈顶
// 把最后一个元素也移到q2,再整体移回q1(保持原状态)
q2.push(q1.front());
q1.pop();
swap(q1, q2);
return top_val;
}
// 判断栈是否为空
bool empty() {
return q1.empty(); // 主队列空则栈空
}
};