
🔥艾莉丝努力练剑:个人主页
❄专栏传送门:《C语言》、《数据结构与算法》、C/C++干货分享&学习过程记录、Linux操作系统编程详解、笔试/面试常见算法:从基础到进阶
⭐️为天地立心,为生民立命,为往圣继绝学,为万世开太平
🎬艾莉丝的简介:

🎬艾莉丝的C++专栏简介:
目录
[8 ~> 优先级队列:priority_queue的介绍和使用](#8 ~> 优先级队列:priority_queue的介绍和使用)
[8.1 priority_queue的介绍](#8.1 priority_queue的介绍)
[8.2 优先级队列的使用层](#8.2 优先级队列的使用层)
[8.3 算法题练习:在Top-K问题中的使用](#8.3 算法题练习:在Top-K问题中的使用)
[9 ~> 详解仿函数](#9 ~> 详解仿函数)
[9.1 传模板参数不能超远程传,若传三个,先传第二个再传第三个](#9.1 传模板参数不能超远程传,若传三个,先传第二个再传第三个)
[9.1.1 仿函数类似于回调函数,来回调](#9.1.1 仿函数类似于回调函数,来回调)
[9.1.2 运行](#9.1.2 运行)
[9.2 仿函数:逻辑的控制开关](#9.2 仿函数:逻辑的控制开关)
[9.3 举例:日期类------比较大小](#9.3 举例:日期类——比较大小)
[9.3.1 自己实现仿函数来控制比较](#9.3.1 自己实现仿函数来控制比较)
[9.3.2 继续拓展:sort && qsort](#9.3.2 继续拓展:sort && qsort)
[9.4 仿函数的多样性](#9.4 仿函数的多样性)
[9.4.1 remove && remove_if概念以及remove的应用](#9.4.1 remove && remove_if概念以及remove的应用)
[9.4.2 逻辑模拟:按某个条件去删除,条件用仿函数控制](#9.4.2 逻辑模拟:按某个条件去删除,条件用仿函数控制)
[9.4.3 remove_if的应用:以删除所有的偶数为例](#9.4.3 remove_if的应用:以删除所有的偶数为例)
[9.4.4 find_if](#9.4.4 find_if)
C++的两个参考文档
老朋友(非官方文档):cplusplus
官方文档(同步更新):cppreference
stack容器文档链接:stack****queue容器文档链接:queue****

8 ~> 优先级队列:priority_queue的介绍和使用
8.1 priority_queue的介绍
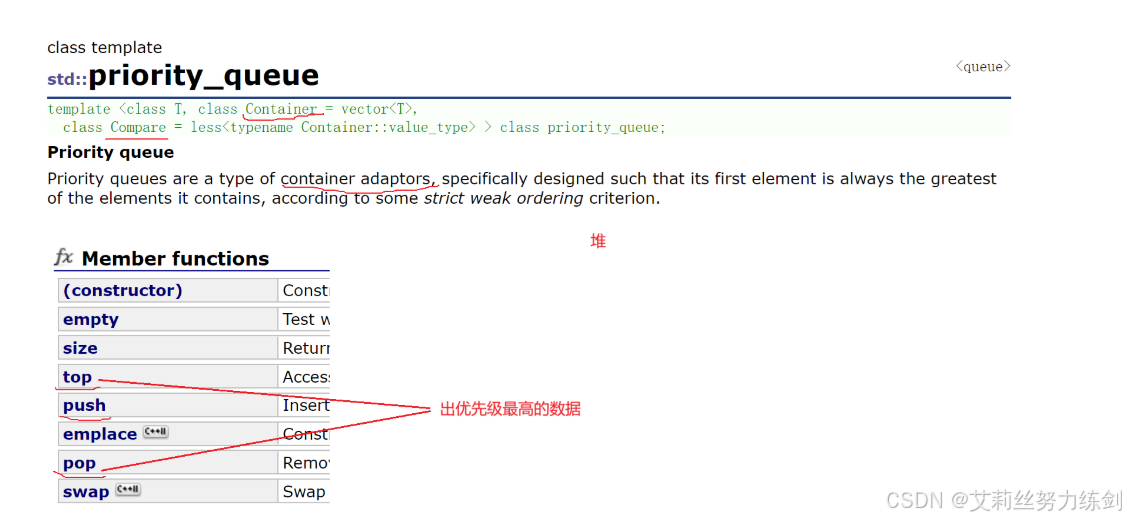
priority_queue的文档介绍:优先级队列文档
文档内容提炼
1、优先队列是一种容器适配器,根据严格的弱排序标准,它的第一个元素总是它所包含的元素中最大的。
2、此上下文类似于堆,在堆中可以随时插入元素,并且只能检索最大堆元素(优先队列中位于顶
部的元素)。
3、优先队列被实现为容器适配器,容器适配器即将特定容器类封装作为其底层容器类,queue
提供一组特定的成员函数来访问其元素。元素从特定容器的"尾部"弹出,其称为优先队列的顶部。
4、底层容器可以是任何标准容器类模板,也可以是其他特定设计的容器类。容器应该可以通过
随机访问迭代器访问,并支持以下操作:
(1)empty():检测容器是否为空
(2)size():返回容器中有效元素个数
(3)front():返回容器中第一个元素的引用
(4)push_back():在容器尾部插入元素
(5)pop_back():删除容器尾部元素
5、标准容器类vector和deque满足这些需求。默认情况下,如果没有为特定的priority_queue
类实例化指定容器类,则使用vector。
6、需要支持随机访问迭代器,以便始终在内部保持堆结构。容器适配器通过在需要时自动调用
算法函数make_heap、push_heap和pop_heap来自动完成此操作。
8.2 优先级队列的使用层
优先级队列默认使用vector作为其底层存储数据的容器,在vector上又使用了堆算法将vector中
元素构造成堆的结构,因此priority_queue就是堆,所有需要用到堆的位置,都可以考虑使用
priority_queue。
注意:默认情况下priority_queue是大堆。
| 函数声明 | 接口说明 |
|---|---|
priority_queue() |
构造一个空的优先级队列(最大堆) |
priority_queue(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) |
用迭代器范围[first, last)构造优先级队列 |
bool empty() const |
检测优先级队列是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
const value_type& top() const |
返回优先级队列中最大(或最小)元素,即堆顶元素 |
void push(const value_type& val) |
在优先级队列中插入元素val |
void pop() |
删除优先级队列中最大(或最小)元素,即堆顶元素 |
下面是带文档链接的接口说明------
|--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|-------------------------------|
| 函数说明 | 接口说明 |
| priority_queue / priority_queue(firest,last) | 构造一个空的优先级队列 |
| empty() | 检测优先级队列是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| top() | 返回优先级队列中最大(最小元素),即堆顶元素 |
| push(x) | 在优先级队列中插入元素x |
| pop() | 删除优先级队列中最大(最小)元素,即堆顶元素 |
1、默认情况下,priority_queue是大堆。
忘记了的uu可以去看博主之前在【数据结构与算法】专栏中更新的博客,链接------
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解二叉树(二)------堆
【数据结构与算法】数据结构初阶:详解二叉树(三)------堆(续):向上向下调整算法的证明及时间复杂度、TOP-K问题详解
cpp
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <functional> // greater算法的头文件
void TestPriorityQueue()
{
// 默认情况下,创建的是大堆,其底层按照小于号比较
vector<int> v{ 3,2,7,6,0,4,1,9,8,5 };
priority_queue<int> q1;
for (auto& e : v)
q1.push(e);
cout << q1.top() << endl;
// 如果要创建小堆,将第三个模板参数换成greater比较方式
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q2(v.begin(), v.end());
cout << q2.top() << endl;
}2、如果在priority_queue中放自定义类型的数据,用户需要在自定义类型中提供 > 或者 < 的重载------
cpp
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
bool operator<(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d)const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
void TestPriorityQueue()
{
// 大堆,需要用户在自定义类型中提供<的重载
priority_queue<Date> q1;
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 29));
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 28));
q1.push(Date(2018, 10, 30));
cout << q1.top() << endl;
// 如果要创建小堆,需要用户提供>的重载
priority_queue<Date, vector<Date>, greater<Date>> q2;
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 29));
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 28));
q2.push(Date(2018, 10, 30));
cout << q2.top() << endl;
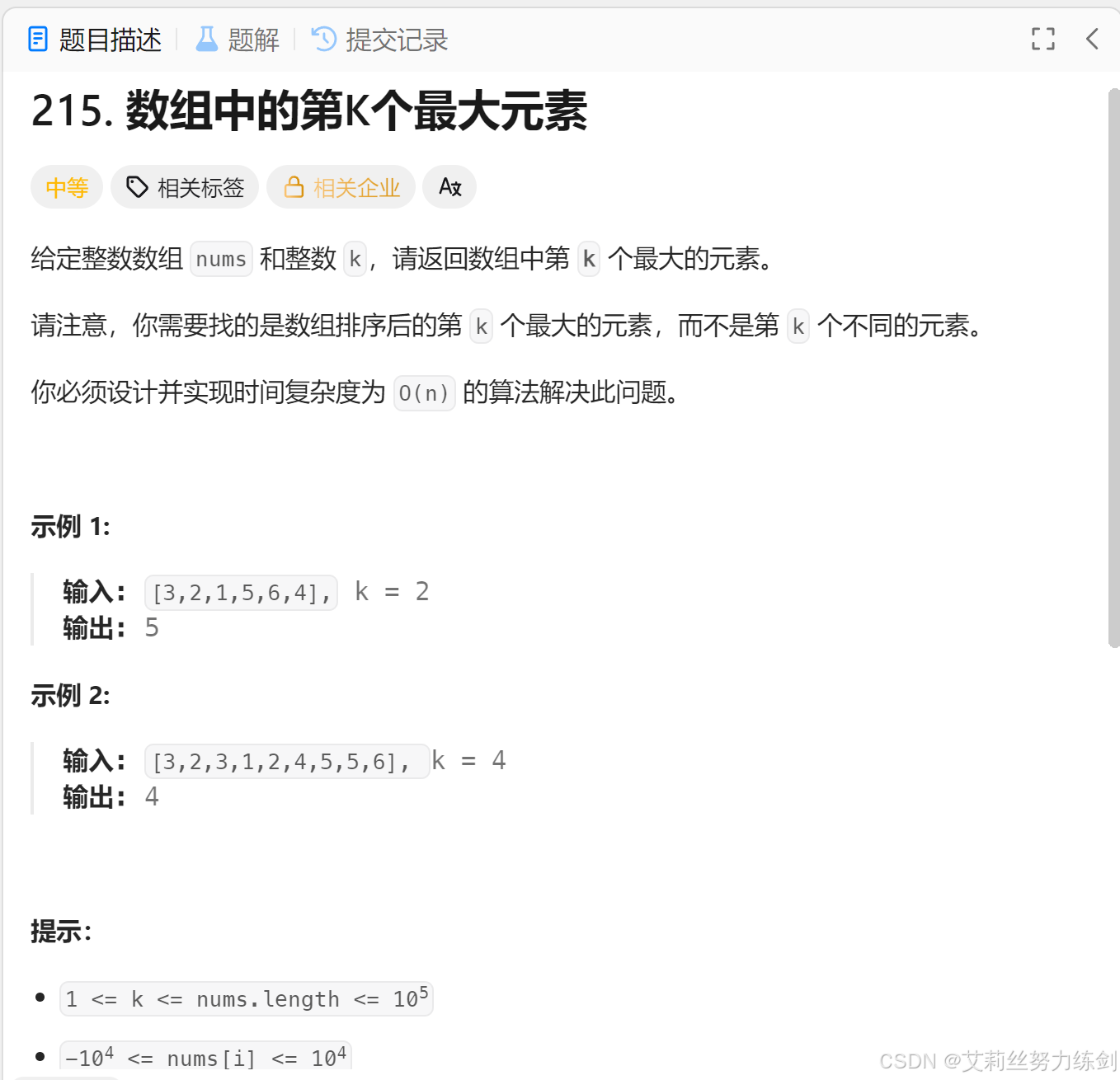
}8.3 算法题练习:在Top-K问题中的使用
力扣链接:****215. 数组中的第K个最大元素
力扣题解链接:优先级队列解决【数组中的第K个最大元素】问题
题目描述:
算法实现:
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
// 将数组中的元素先放入优先级队列中
priority_queue<int> p(nums.begin(), nums.end());
// 将优先级队列中前k-1个元素删除掉
for (int i = 0; i < k - 1; ++i)
{
p.pop();
}
return p.top();
}
};用优先级队列就不用再想堆的事了,几行代码搞定。
1、将数组中的元素先放入优先级队列中;
2、将优先级队列中前k-1个元素删除掉;
3、返回top位置的值,p.top()。
9 ~> 详解仿函数
仿函数:对象可以像函数一样被使用。
9.1 传模板参数不能超远程传,若传三个,先传第二个再传第三个
9.1.1 仿函数类似于回调函数,来回调
9.1.2 运行
9.2 仿函数:逻辑的控制开关
运行一下------
9.3 举例:日期类------比较大小
运行一下------
9.3.1 自己实现仿函数来控制比较
new出来的地址带有很强的随机性,这个比较大小没有意义------自己实现仿函数来控制。

现在就不再是按指针去比较的了,而是按指针变量指向的内容去比较的。
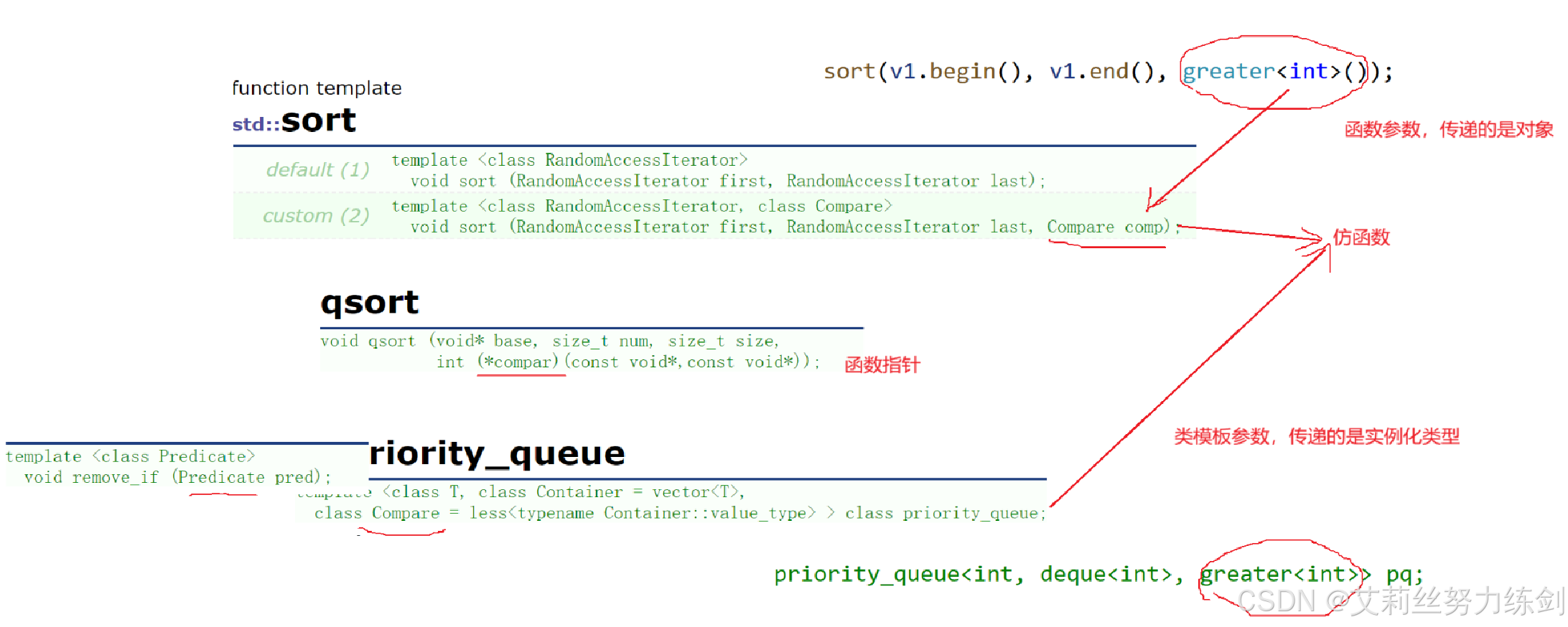
9.3.2 继续拓展:sort && qsort

1、底层不会用比较器比较(写死了),用仿函数比较更加灵活,逻辑翻转;
2、先级队列那里没加(),这里加了(),用的是对象(匿名对象),所以匿名对象的语法虽然很奇怪,在一些场景还是很有用的,sort这里函数参数,传递的是对象,优先级队列那里是类模板参数,传递的是实例化类型。
运行一下------
9.4 仿函数的多样性
9.4.1 remove && remove_if概念以及remove的应用

运行一下------
9.4.2 逻辑模拟:按某个条件去删除,条件用仿函数控制
这个代码算是个伪代码,大家主要对比感受一下------
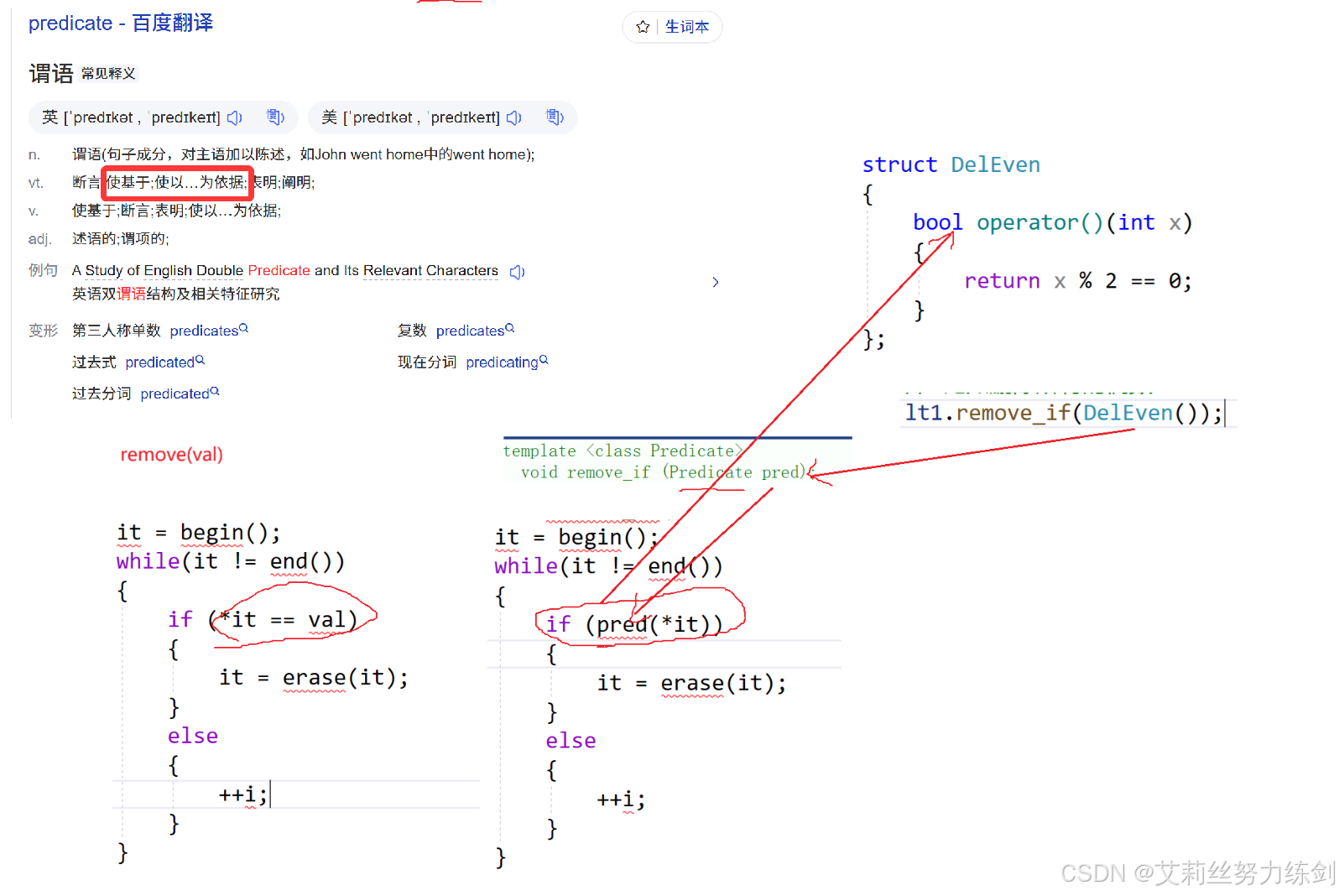
9.4.3 remove_if的应用:以删除所有的偶数为例
自定义一个删除偶数的函数------
运行一下------

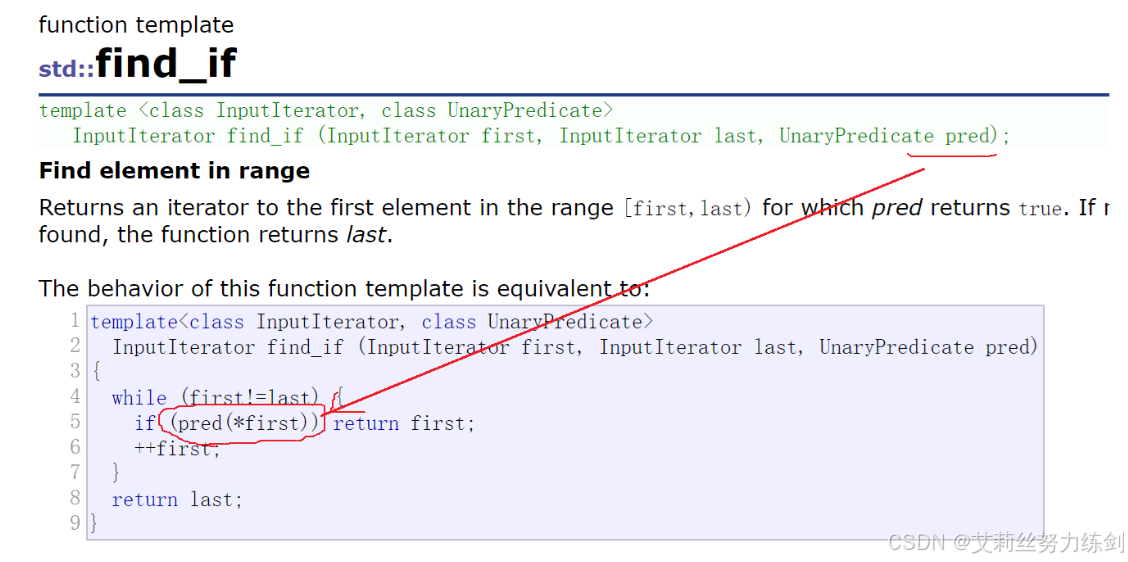
9.4.4 find_if
1、算法(algorithm)里面也有类似实现:find_if(跟remove_if一样),也是predicate,基于某个条件形成的回调。
2、凡是XXX_if这种形式的,基本上都是基于某个条件的仿函数。
3、仿函数当前我们接触到的就是这两种类型,但是仿函数的用途很广,现在知道:基于条件的仿函数和比较的仿函数就可以了。
4、仿函数有很多种玩法:比如说写一个函数去实现回调 ------ 是函数模版就传对象名,是类模板就传类型名,传了什么就用什么去调用就可以了。

本文代码完整展示
pirority_queue.h:
cpp
#pragma once
#include<vector>
namespace jqj
{
// -------------也可以用自己写的--------------
// 仿函数
template <class T>
struct less
{
bool operator() (const T& x, const T& y) const { return x < y; }
};
template <class T>
struct Greater
{
bool operator() (const T& x, const T& y) const { return x < y; }
};
// ---------------可以用库里面的------------------
// 默认大的优先级高
template<class T, class Container = std::vector<T>,class Compare = less<T>>
class priority_queue
{
public:
template<class InputInterator>
priority_queue(InputInterator first, InputInterator last)
:_con(first, last)
{
//建堆 ------ 向下调整算法建堆(效率比向上调整建堆高)
for (int i = (_con.size() - 1 - 1) / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
adjust_down(i);
}
}
// 强制编译器生成默认构造
priority_queue() = default;
void adjust_up(int child)
{
Compare com; // com是仿函数类型的对象,可以像函数一样去使用
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
//if (_con[parent] < _con[child]) // 交换一个位置,小于是大堆
if (com(_con[parent],_con[child])) // 和上面等价,转换成调operator()
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]); // 交换双亲和孩子节点的位置
child = parent; // 把父亲的值给儿子
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjust_down(int parent)
{
Compare com;
size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
while (child < _con.size())
{
/*if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] > _con[child])*/
//if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child] < _con[child + 1]) // 先交换位置,反过来
if (child + 1 < _con.size() && com(_con[child],_con[child + 1]))
{
++child;
}
/*if (_con[child] > _con[parent])*/
if (com(_con[parent],_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
//// 大堆换成小堆,以前的逻辑:符号换一下
//void adjust_up(int child)
//{
// int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// while (child > 0)
// {
// if (_con[child] < _con[parent])
// {
// swap(_con[child], _con[parent]); // 交换双亲和孩子节点的位置
// child = parent; // 把父亲的值给儿子
// parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// }
// else
// {
// break;
// }
// }
//}
//void adjust_down(int parent)
//{
// size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
// while (child < _con.size())
// {
// if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] < _con[child])
// {
// ++child;
// }
//
// if (_con[child] < _con[parent])
// {
// swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
// parent = child;
// child = parent * 2 + 1;
// }
// else
// {
// break;
// }
// }
//}
//// 不可能说要变成小堆了,就把代码给改一下,那肯定是不行的
// 怎么灵活地去控制大小堆?C语言是通过函数,但是C++是尽可能不去使用函数指针这种东西
// 因为函数指针、数组指针都是很恶心的东西------类型的定义很恶心
/*void (*p)() ------ 函数指针*/
//void adjust_up(int child)
//{
// int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// while (child > 0)
// {
// if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
// {
// swap(_con[child], _con[parent]); // 交换双亲和孩子节点的位置
// child = parent; // 把父亲的值给儿子
// parent = (child - 1) / 2;
// }
// else
// {
// break;
// }
// }
//}
//void adjust_down(int parent)
//{
// size_t child = parent * 2 + 1;
// while (child < _con.size())
// {
// if (child + 1 < _con.size() && _con[child + 1] > _con[child])
// {
// ++child;
// }
// if (_con[child] > _con[parent])
// {
// swap(_con[child], _con[parent]);
// parent = child;
// child = parent * 2 + 1;
// }
// else
// {
// break;
// }
// }
//}
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjust_up(_con.size() - 1);
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]); // 交换首尾位置
_con.pop_back();
adjust_down(0);
}
const T& top() const
{
return _con[0];
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}stack.h:
cpp
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
namespace jqj
{
//template<class T>
//class stack
//{
// // ...
//private:
// T* _a;
// size_t _top;
// size_t _capacity;
//};
// deque:双端队列
template<class T,class Container = deque<T>>
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_back();
}
const T& top()
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}queue.h:
cpp
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
namespace jqj
{
// 容器适配器
// deque:双端队列
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front(); // 队头,先进先出后进后出
}
const T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
const T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size() const
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty() const
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;
};
}Test.cpp:
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
// stack 和 queue的使用:构造、增删
//int main()
//{
// stack<int> st;
// st.push(1);
// st.push(2);
// st.push(3);
// st.emplace(4);
//
// while (!st.empty())
// {
// cout << st.top() << " ";
// st.pop();
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// queue<int> q;
// q.push(1);
// q.push(2);
// q.push(3);
// q.emplace(4);
//
// while (!q.empty())
// {
// cout << q.front() << " "; // 队头
// q.pop();
// }
//
// return 0;
//}
//// stack
#include"stack.h"
//int main()
//{
// //jqj::stack<int, vector<int>> st; // 数组栈
// //jqj::stack<int, list<int>> st; // 链式栈
// jqj::stack<int> st;
// st.push(1);
// st.push(2);
// st.push(3);
// st.push(4);
//
// while (!st.empty())
// {
// cout << st.top() << " ";
// st.pop();
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// return 0;
//}
// queue
#include"queue.h"
#include<deque>
//int main()
//{
////jqj::queue<int> q;
////jqj::queue<int, vector<int>> q; // 顺序数组------不支持
//jqj::queue<int, list<int>> q; // 链式数组
//q.push(1);
//q.push(2);
//q.push(3);
//q.push(4);
//while (!q.empty())
//{
// cout << q.front() << " "; // 队头
// q.pop();
//}
//cout << endl;
// deque<int> dp;
// dp.push_back(1);
// dp.push_back(1);
// dp.push_back(1);
// dp.push_front(2);
// dp.push_front(3);
// dp.push_front(4);
//
// dp[0] += 10;
// for (auto e : dp)
// {
// cout << e << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// int i = 0;
// ++i;
//
// return 0;
//}
void Test_op1()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 10000000;
deque<int> dq;
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
v.push_back(e);
dq.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
sort(dq.begin(), dq.end());
int end2 = clock();
printf("vector:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("deque:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
void Test_op2()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 10000000;
deque<int> dq1;
deque<int> dq2;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
dq1.push_back(e);
dq2.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
sort(dq1.begin(), dq1.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
// 拷贝到vector
vector<int> v(dq2.begin(), dq2.end());
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
dq2.assign(v.begin(), v.end());
int end2 = clock();
printf("vector:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("deque copy vector sort,sort back deque:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
//int main()
//{
// Test_op2();
//
// return 0;
//}
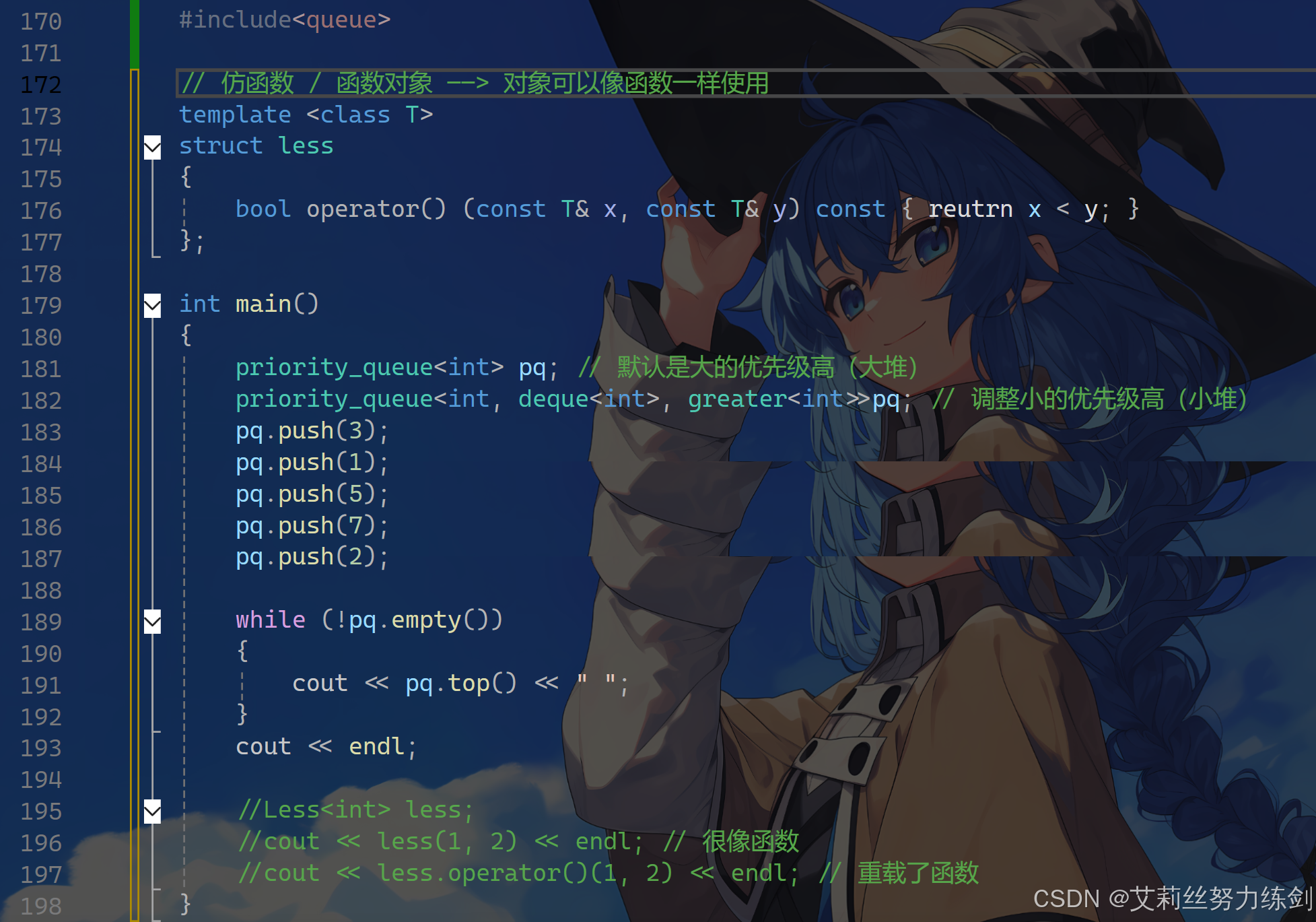
#include<queue>
//// 仿函数 / 函数对象 对象可以像函数一样使用
//template <class T>
//struct less
//{
// bool operator() (const T& x, const T& y) const { reutrn x < y; }
//};
//
//int main()
//{
// priority_queue<int> pq; // 默认是大的优先级高(大堆)
// priority_queue<int, deque<int>, greater<int>>pq; // 调整小的优先级高(小堆)
// pq.push(3);
// pq.push(1);
// pq.push(5);
// pq.push(7);
// pq.push(2);
//
// while (!pq.empty())
// {
// cout << pq.top() << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
//
// //Less<int> less;
// //cout << less(1, 2) << endl; // 很像函数
// //cout << less.operator()(1, 2) << endl;
//}
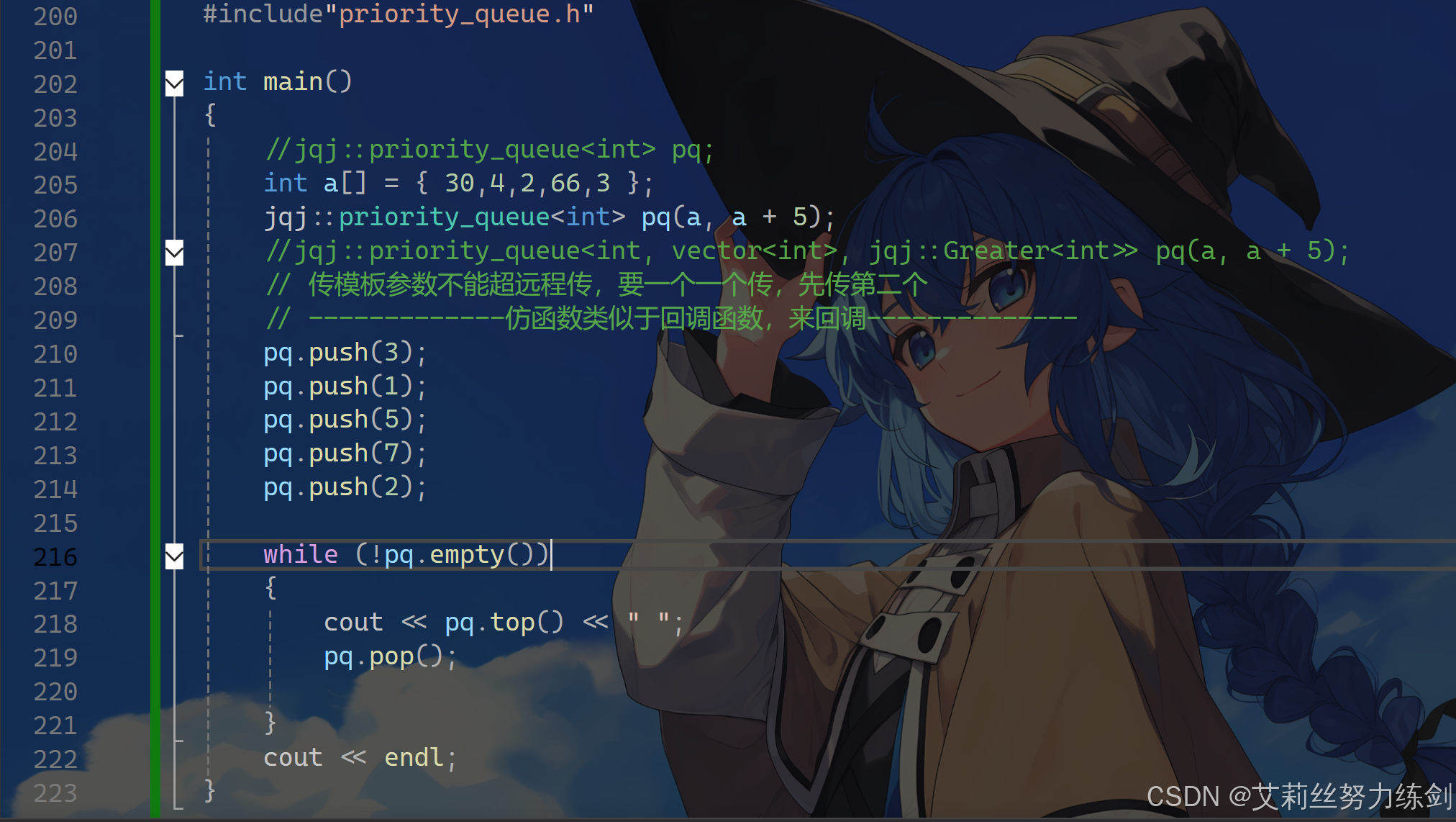
#include"priority_queue.h"
//int main()
//{
// //jqj::priority_queue<int> pq;
// int a[] = { 30,4,2,66,3 };
// jqj::priority_queue<int> pq(a, a + 5);
// //jqj::priority_queue<int, vector<int>, jqj::Greater<int>> pq(a, a + 5);
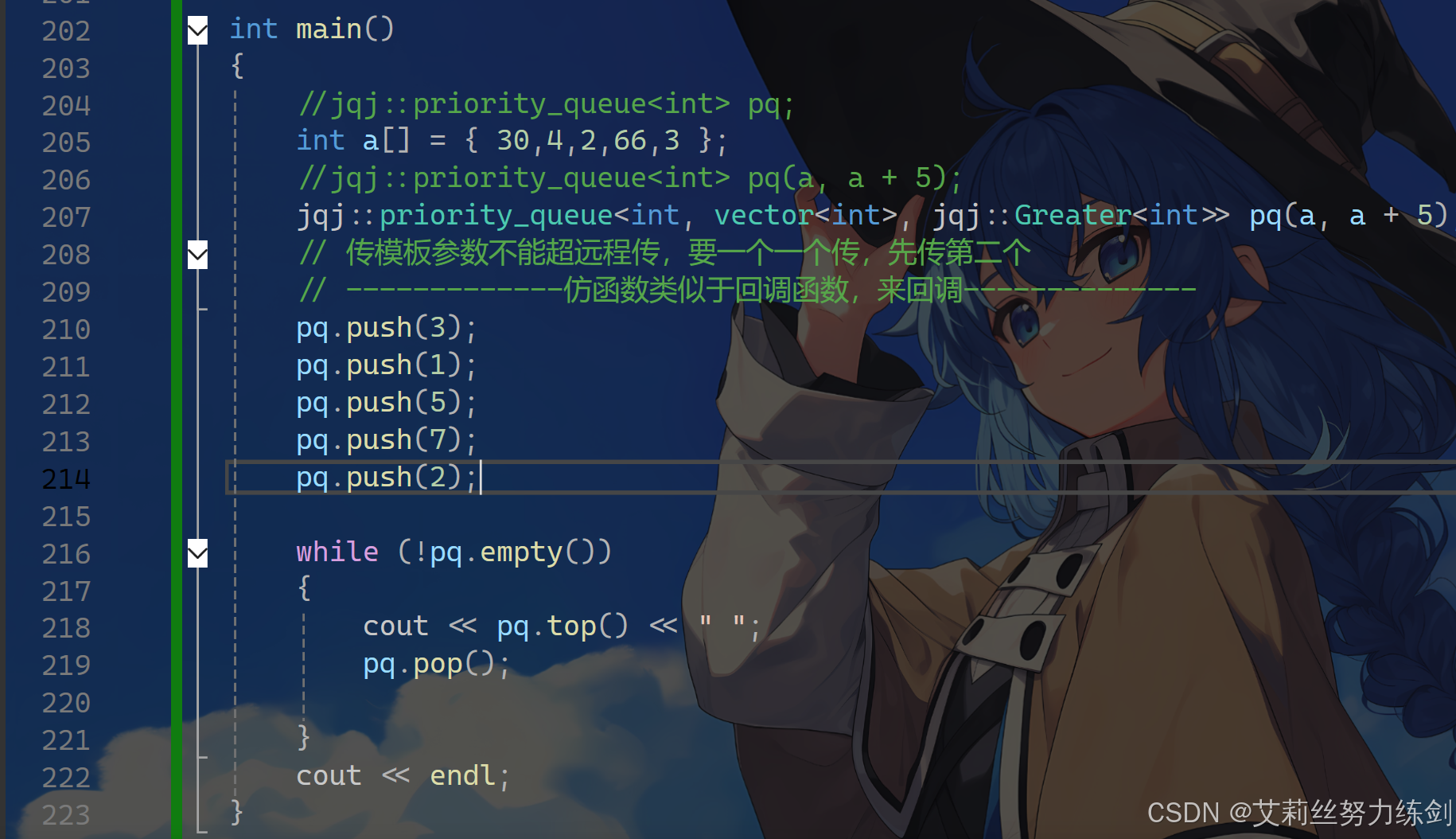
// // 传模板参数不能超远程传,要一个一个传,先传第二个
// // -------------仿函数类似于回调函数,来回调--------------
// pq.push(3);
// pq.push(1);
// pq.push(5);
// pq.push(7);
// pq.push(2);
//
// while (!pq.empty())
// {
// cout << pq.top() << " ";
// pq.pop();
//
// }
// cout << endl;
//}
// --------------------仿函数------------------------
// 日期类:比较大小
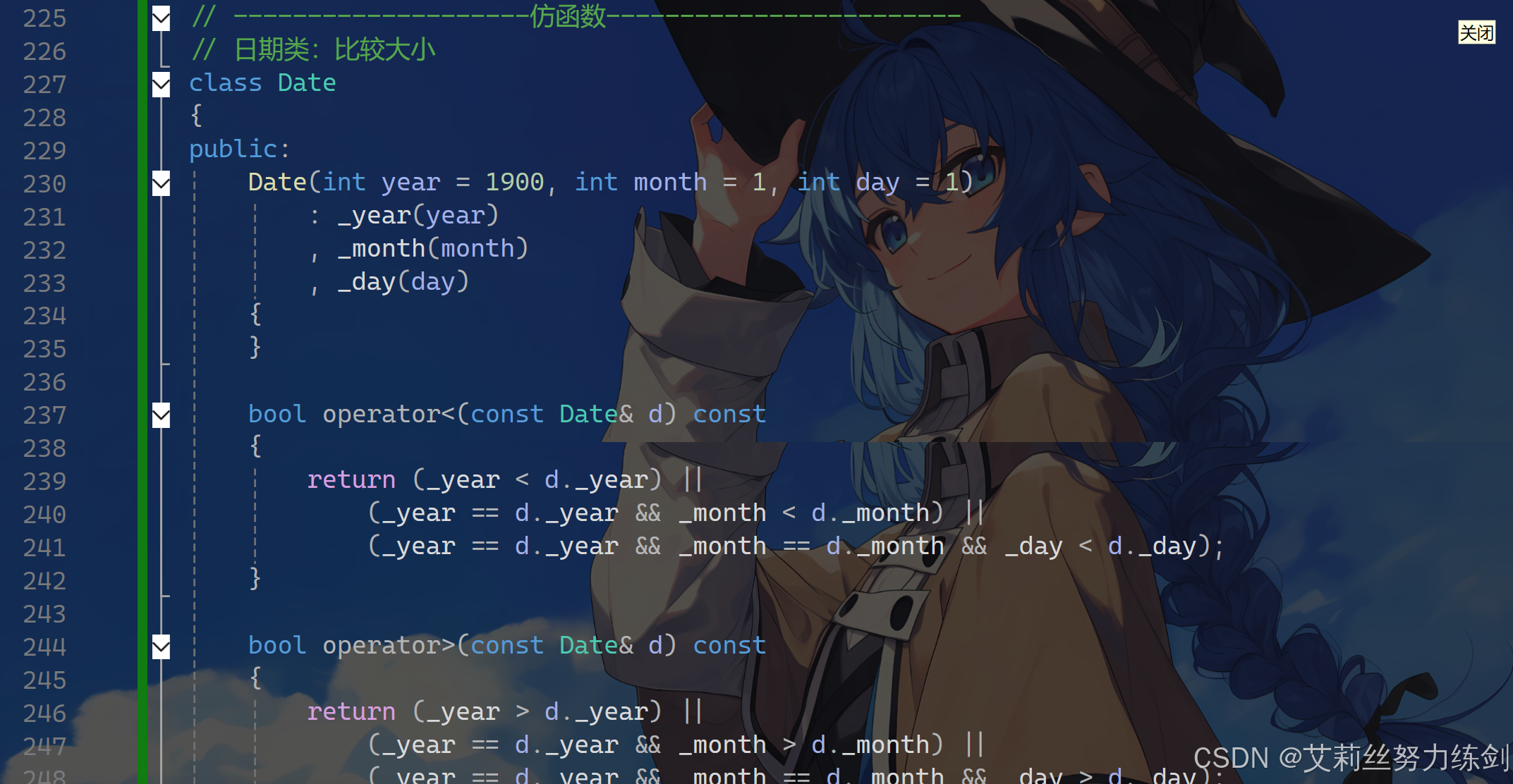
class Date
{
public:
Date(int year = 1900, int month = 1, int day = 1)
: _year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{
}
bool operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year < d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month < d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day < d._day);
}
bool operator>(const Date& d) const
{
return (_year > d._year) ||
(_year == d._year && _month > d._month) ||
(_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day > d._day);
}
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d); // 不是成员函数,而是友元函数
// 变成内联函数
// 内联函数不能声明和定义分离;显示加inline也可以
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
};
ostream& operator<<(ostream& _cout, const Date& d)
{
_cout << d._year << "-" << d._month << "-" << d._day;
return _cout;
}
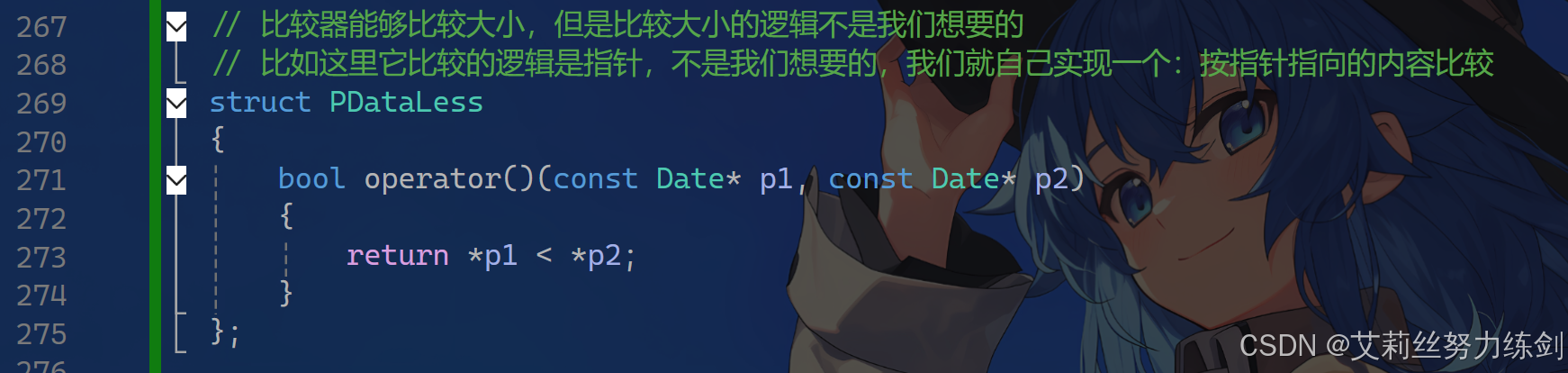
// 比较器能够比较大小,但是比较大小的逻辑不是我们想要的
// 比如这里它比较的逻辑是指针,不是我们想要的,我们就自己实现一个:按指针指向的内容比较
struct PDataLess
{
bool operator()(const Date* p1, const Date* p2)
{
return *p1 < *p2;
}
};
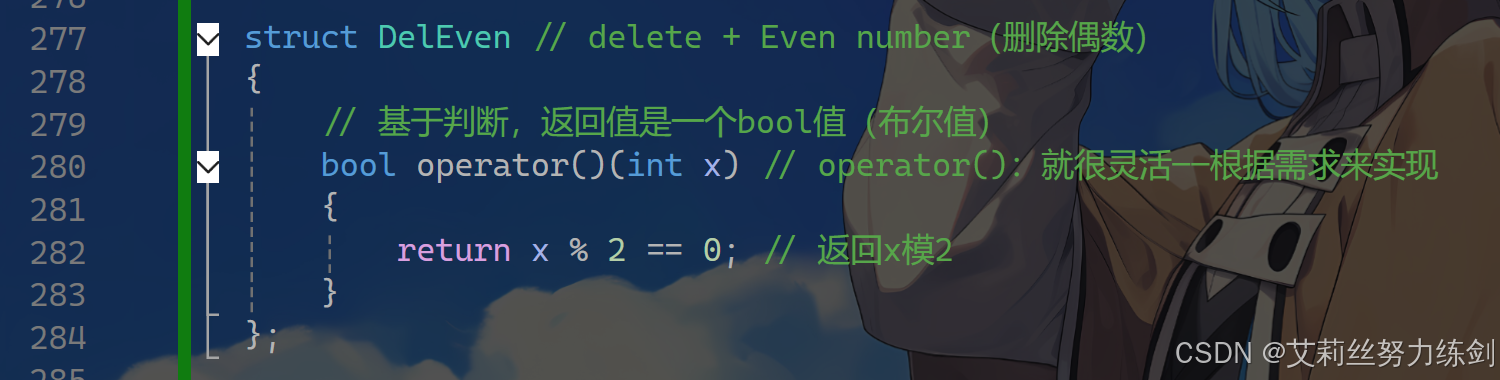
struct DelEven // delete + Even number(删除偶数)
{
// 基于判断,返回值是一个bool值(布尔值)
bool operator()(int x) // operator():就很灵活------根据需求来实现
{
return x % 2 == 0; // 返回x模2
}
};
int main()
{
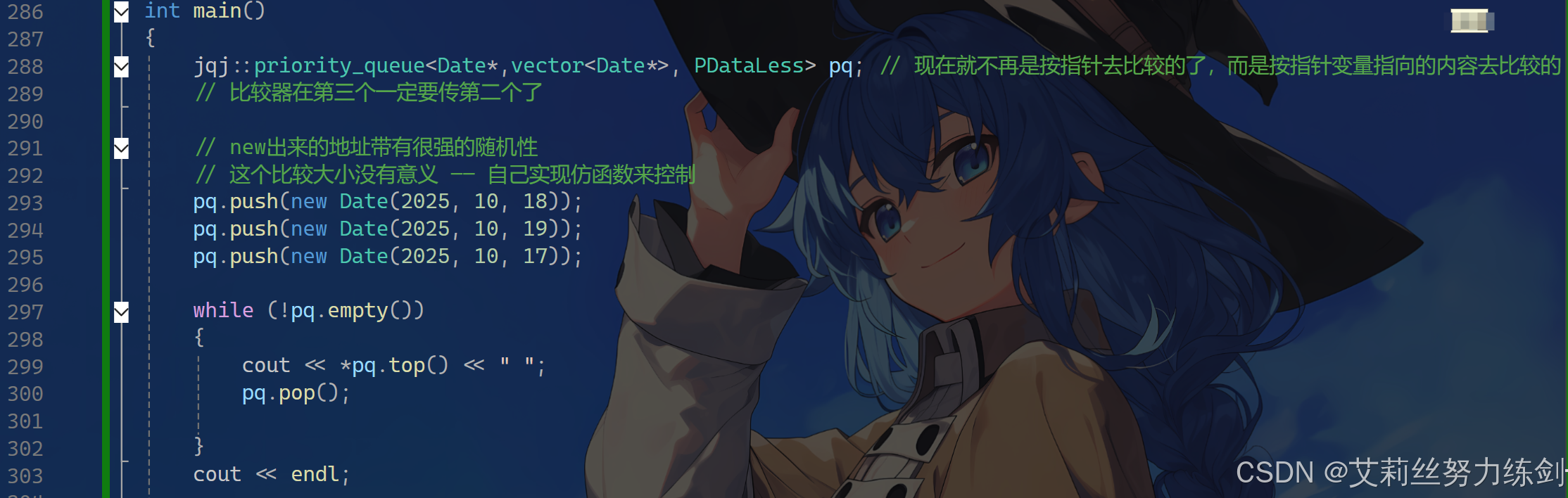
jqj::priority_queue<Date*,vector<Date*>, PDataLess> pq; // 现在就不再是按指针去比较的了,而是按指针变量指向的内容去比较的
// 比较器在第三个一定要传第二个了
// new出来的地址带有很强的随机性
// 这个比较大小没有意义 ------ 自己实现仿函数来控制
pq.push(new Date(2025, 10, 18));
pq.push(new Date(2025, 10, 19));
pq.push(new Date(2025, 10, 17));
while (!pq.empty())
{
cout << *pq.top() << " ";
pq.pop();
}
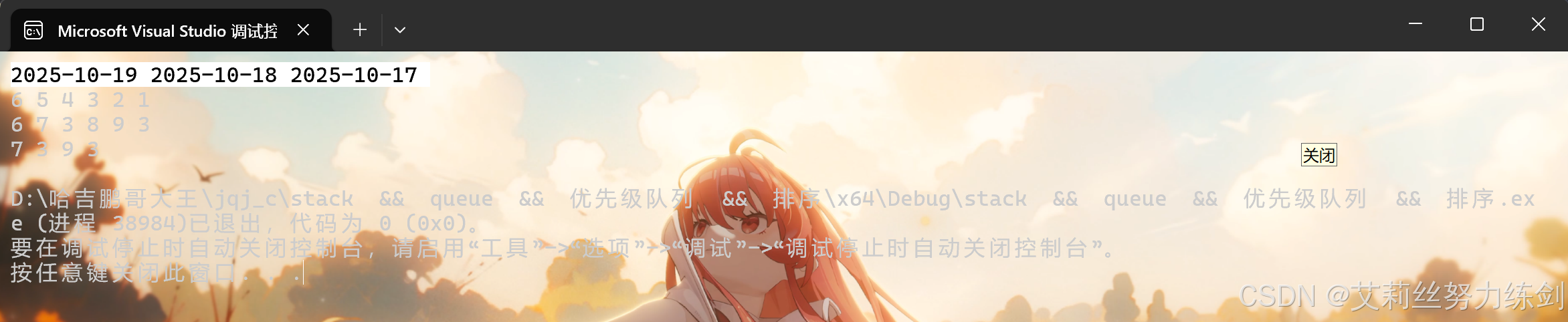
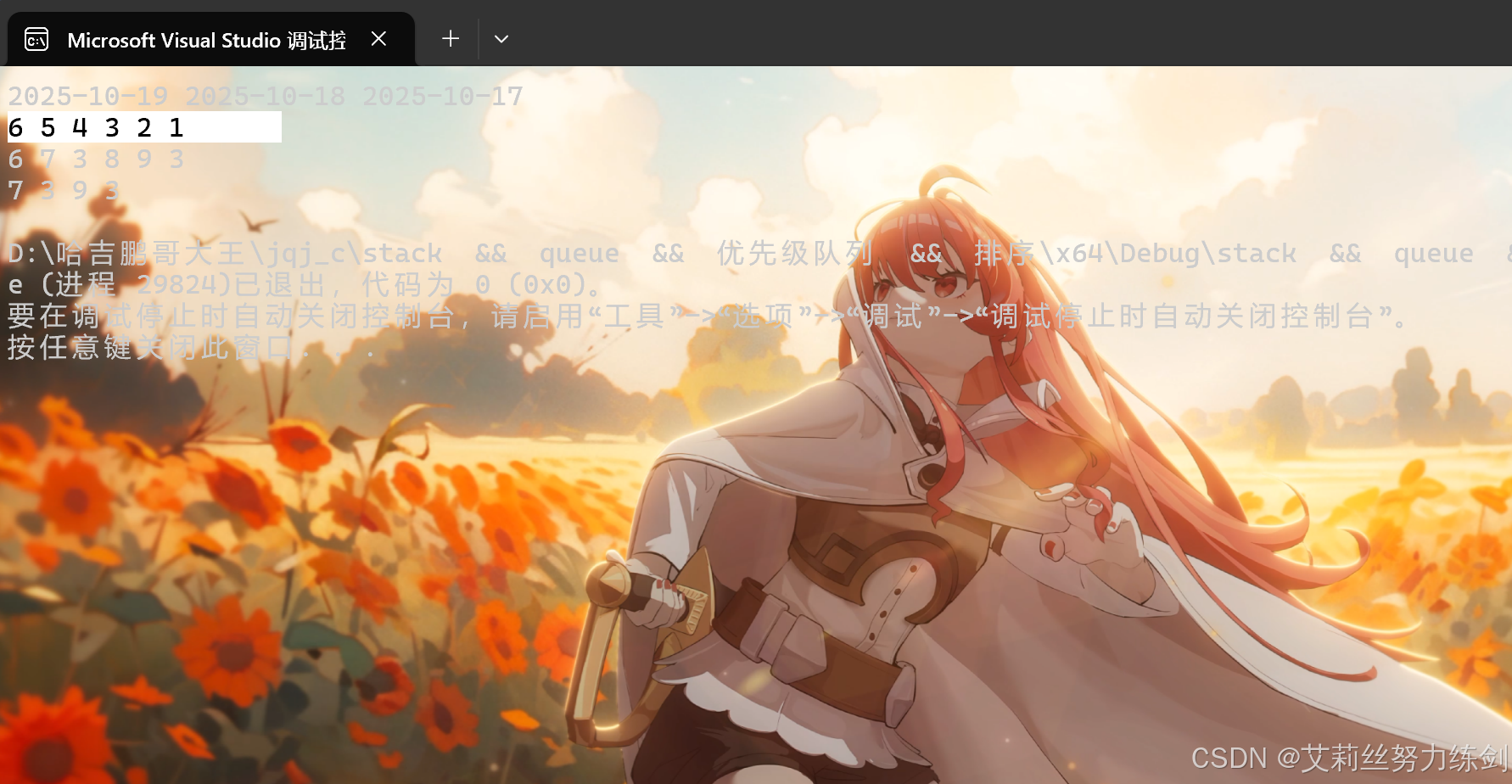
cout << endl;
// --------------------继续拓展----------------------
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,3,4,5,6 };
// C语言:qsort,函数指针
// <(看开口方向)升序
// >(看开口方向)降序
greater<int> gt; // 降序
//sort(v1.begin(), v1.end()); // 升序
//sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), gt); // 底层不会用比较器比较(写死了),用仿函数比较更加灵活,逻辑翻转
// 正常来说我们不会像上面这样写代码,而是这样写------
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<int>()); // 优先级大佬那里没加(),这里加了()
// 用的是对象(匿名对象),所以匿名对象的语法虽然很奇怪,在一些场景还是很有用的
// sort这里函数参数,传递的是对象
// 优先级队列那里是类模板参数,传递的是实例化类型
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 输出:6 5 4 3 2 1
// ---------------展示仿函数多样性--------------------
// remove:查找 + 删除(find + erase)
// remove_if(也是一个仿函数)
// Predicate:以......为依据,基于
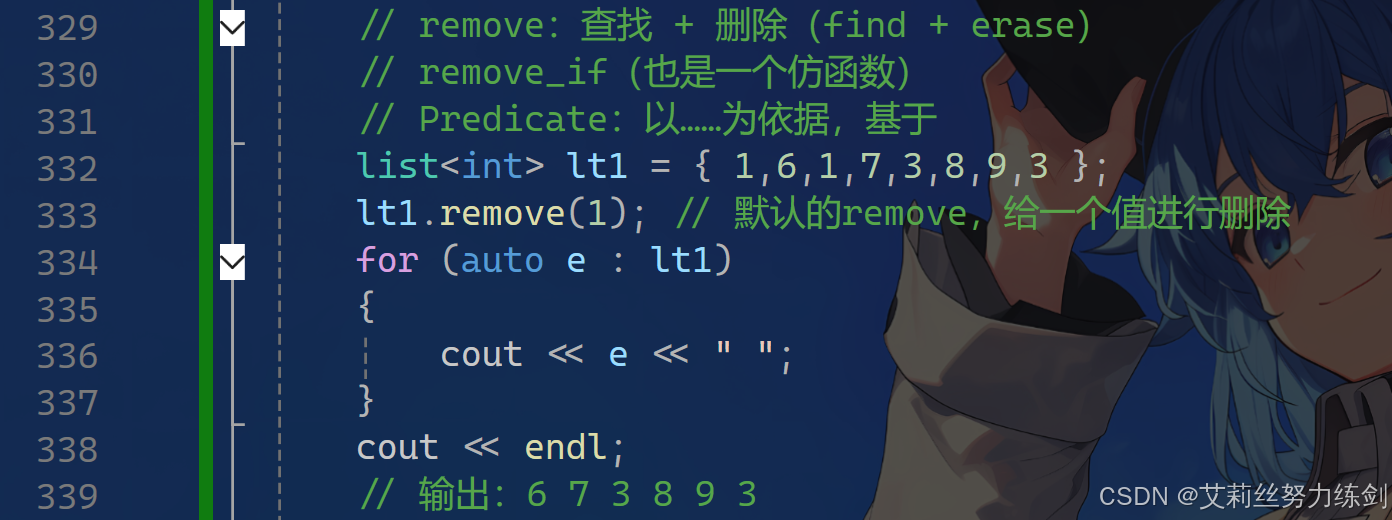
list<int> lt1 = { 1,6,1,7,3,8,9,3 };
lt1.remove(1); // 默认的remove,给一个值进行删除
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 输出:6 7 3 8 9 3
//// 按某个条件去删除,条件用仿函数控制
//// 比如删除所有的偶数
//// remove(val)的实现
//lt1.remove_if();
//it = begin();// 迭代器
//while(it != end())
//{
// if (*it == val)
// {
// it = erase(it);
// }
// else
// {
// ++i;
// }
//}
//// 这里本质还是仿函数去控制逻辑
//// 外部逻辑控制内部比较
//it = begin();// 迭代器
//while (it != end())
//{
// if (pred(*it)) // 相当于回调
// {
// it = erase(it);
// }
// else
// {
// ++i;
// }
//}
// 按某个条件去删除,条件用仿函数控制
// 比如删除所有的偶数
lt1.remove_if(DelEven()); // 传这样一个对象过去,按照某个条件去删
// 可以实现更复杂的删除,不再是写死的
// 参数没有规定,返回类型也没有规定,这里根据需求去传就可以了
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 输出:7 3 9 3
return 0;
}
// 算法(algorithm)里面也有类似实现:find_if(跟remove_if一样),也是predicate,基于某个条件形成的回调
// 凡是XXX_if,基本上都是基于某个条件的仿函数
// 仿函数当前我们接触到的就是这两种类型,但是仿函数的用途很广,现在知道:基于条件的仿函数和比较的仿函数就可以了
// 仿函数有很多种玩法:比如说写一个函数去实现回调 ------ 是函数模版就传对象名,是类模板就传类型名
// 传了就用这个去调用就可以了结尾
往期回顾:
【C++STL :stack && queue (二) 】stack 与 queue 的模拟实现与双端队列探秘
结语:都看到这里啦!那请大佬不要忘记给博主来个"一键四连"哦!
🗡博主在这里放了一只小狗,大家看完了摸摸小狗放松一下吧!🗡
૮₍ ˶ ˊ ᴥ ˋ˶₎ა
