锋哥原创的TensorFlow2 Python深度学习视频教程:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1X5xVz6E4w/
课程介绍
本课程主要讲解基于TensorFlow2的Python深度学习知识,包括深度学习概述,TensorFlow2框架入门知识,以及卷积神经网络(CNN),循环神经网络(RNN),生成对抗网络(GAN),模型保存与加载等。
TensorFlow2 Python深度学习 - 循环神经网络(LSTM)示例
LSTM(长短期记忆网络,Long Short-Term Memory)是一种特殊类型的循环神经网络(RNN),用于处理和预测序列数据。它能够有效地解决标准RNN在长期依赖问题中的缺点,如梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题。LSTM的关键在于其特殊的结构,其中包括了三个"门"机制:输入门、遗忘门和输出门,这些门控制信息流的进入、遗忘和输出,允许模型更好地捕捉和保持长期的依赖关系。
LSTM的基本结构
LSTM单元的结构包括以下几部分:
-
输入门(Input Gate):决定哪些新信息被写入到单元状态。
-
遗忘门(Forget Gate):决定哪些信息会从单元状态中丢弃或保留。
-
输出门(Output Gate):决定哪些信息将用于输出。
tf.keras.layers.LSTM(
units,
activation='tanh',
recurrent_activation='sigmoid',
use_bias=True,
kernel_initializer='glorot_uniform',
recurrent_initializer='orthogonal',
bias_initializer='zeros',
unit_forget_bias=True,
dropout=0.0,
recurrent_dropout=0.0,
return_sequences=False,
return_state=False,
go_backwards=False,
stateful=False,
time_major=False,
unroll=False,
**kwargs
)
核心参数:
units- 最重要的参数
-
作用:定义LSTM层中记忆单元的数量
-
通俗理解:LSTM的"脑容量"或"记忆力大小"
-
影响:值越大,模型表达能力越强,但计算复杂度越高
-
建议范围:32-1024,根据任务复杂度选择
return_sequences- 输出控制
-
作用:控制是否返回所有时间步的输出
-
默认值 :
False(只返回最后一个时间步的输出) -
使用场景:
-
False:用于分类、情感分析等只需要最终结果的场景 -
True:用于序列标注、机器翻译等需要每个时间步输出的场景
-
dropout和recurrent_dropout- 正则化参数
-
dropout:输入单元的丢弃率,防止过拟合 -
recurrent_dropout:循环连接的丢弃率,防止循环过拟合 -
建议值:0.2-0.5,根据数据量和模型复杂度调整
activation和recurrent_activation- 激活函数
-
activation:主要计算的激活函数,默认'tanh' -
recurrent_activation:门控单元的激活函数,默认'sigmoid'
return_state- 状态返回
-
作用:是否返回LSTM的隐藏状态和细胞状态
-
使用场景:编码器-解码器结构、状态传递等高级应用
stateful- 状态保持
-
作用:批次间是否保持LSTM状态
-
使用场景:处理超长序列需要分批时保持状态连续性
unroll- 展开计算
-
作用:是否将RNN展开为前馈网络
-
优点:加速训练(适合短序列)
-
缺点:内存消耗大(不适合长序列)
示例:
import tensorflow as tf
from keras import Input, layers
from keras.src.utils import pad_sequences
# 1. 加载 IMDB 数据集
max_features = 10000 # 使用词汇表中前 10000 个常见单词
maxlen = 100 # 每条评论的最大长度
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.imdb.load_data(num_words=max_features)
print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape)
print(x_train[0])
print(y_train)
# 2. 数据预处理:对每条评论进行填充,使其长度统一
x_train = pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen=maxlen)
x_test = pad_sequences(x_test, maxlen=maxlen)
# 3. 构建 RNN 模型
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
Input(shape=(maxlen,)),
layers.Embedding(input_dim=max_features, output_dim=128), # 嵌入层,将单词索引映射为向量 output_dim 嵌入向量的维度(即每个输入词的嵌入表示的长度)
layers.LSTM(units=64, dropout=0.2, recurrent_dropout=0.2),
# LSTM 层:包含 64 个神经元,激活函数默认使用 tanh dropout表示在每个时间步上丢弃20% recurrent_dropout 递归状态(即隐藏状态)的dropout比率为20%
layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid') # 输出层:用于二分类(正面或负面),激活函数为 sigmoid
])
# 4. 模型编译
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='binary_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
# 5. 模型训练
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=5, validation_data=(x_test, y_test), verbose=1)
# 6. 模型评估
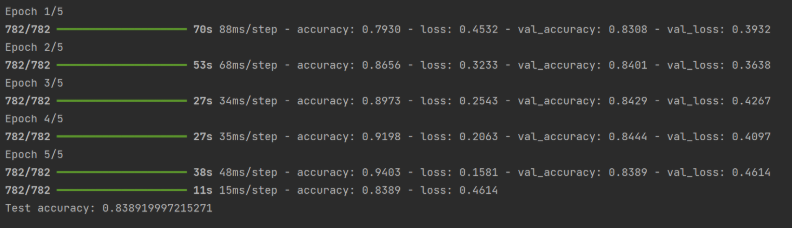
test_loss, test_acc = model.evaluate(x_test, y_test)
print(f"Test accuracy: {test_acc}")运行结果: