前言:在学习string之前,我们得先了解STL容器,什么是STL容器呢?
STL(standard template libaray-标准模板库):是C++标准库的重要组成部分,不仅是一个可复用的 组件库,而且是一个包罗数据结构与算法的软件框架。
下图是STL的六大组件,后面会一一的了解容器,算法,仿函数,迭代器等等
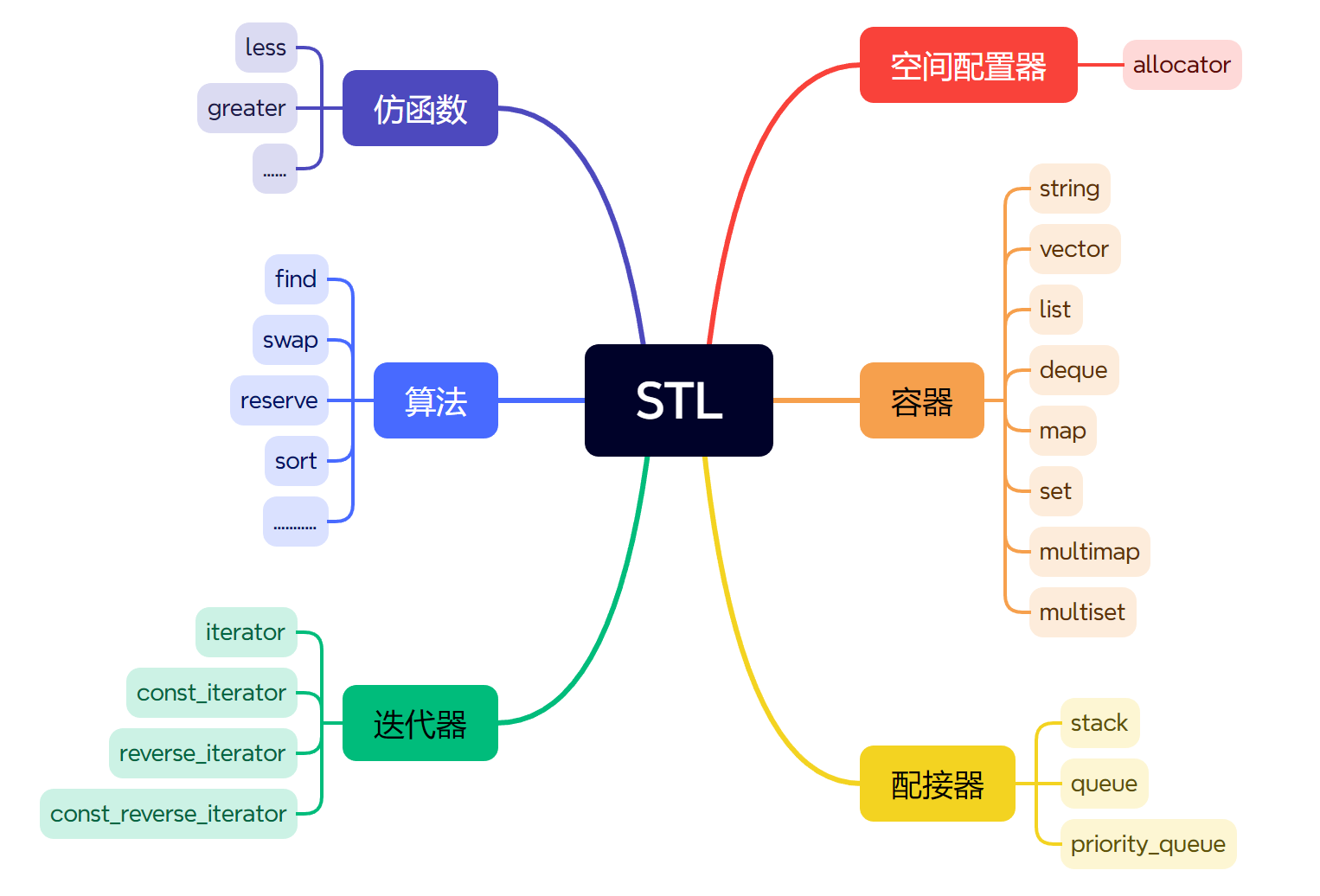
那么C++的STL库的作用是什么?这就不得不说没学C++之前都是使用的C语言刷题,写一道题需要大量的代码,而C++提供STL库,我们可以使用里面的算法,它都帮我实现好了,比如两个队列模拟实现栈,C语言需要手动创建队列的结构,而利用STL直接套用就行。
好了话不多说,我们直接开始学习第一个容器string!!!
1. 标准库中的string
1.1 auto和范围for
auto:
在早期C/C++中auto的含义是:使用auto修饰的变量,是具有自动存储器的局部变量,后来这个不重要了。C++11中,标准委员会变废为宝赋予了auto全新的含义即:auto不再是一个存储类型指示符,而是作为一个新的类型指示符来指示编译器,auto声明的变量必须由编译器在编译时期推导而得。
什么意思呢?就跟类模板推导参数类型类似。
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int func1()
{
return 10;
}
auto func2()
{
return 100;
}
void func3(auto x) //error: 不允许使用auto做参数
{
}
int main()
{
auto a = 10; //这里的auto=int
auto* ra = &a; //auto=int
auto rra = &a; //auto=int*
auto b=3.14; //auto=char
auto& rb=b;
int ma = 10, mb = 30, mc = 90;
auto md = 100, me = 200;
auto ch = 'a', z = 10;//error,auto只对ch推导
return 0;
}1. auto声明指针类型时:用auto和auto*没有区别;但是在声明引用类型时,必须加&(即auto&);
2. 当在同一行声明多个变量时,这些变量必须是相同的类型,否则编译器将会报错,因为编译器实际只对第一个类型进行推导,然后用推导出来的类型定义其他变量;
3. auto不能作为函数的参数,可以做返回值,但是建议谨慎使用;
4. auto不能直接用来声明数组。
这里可能觉得使用auto没什么用,但是到了后面的容器就会觉得太安逸了。
范围for:
for循环后的括号由冒号" :"分为两部分:第一部分是范围 内用于迭代的变量,第二部分则表示被迭代的范围,自动迭代(自动++),自动取数据,自动判断结束。(即arr数组中取得值赋值给ch,ch自动++,自动判断结束)
相对于for循环,三个自动胜过一切。常用于数组和对象的遍历。那范围for是如何实现的?这就得去理解它的底层迭代器,至于什么是迭代器,模拟实现得时候会初步讲解,现在只需要理解如何使用!
cpp
void test01()
{
int arr[10] = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
for (auto& e : arr)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
char s[] = { "hello,world" };
for (auto& ch : s)
{
cout << ch;
}
cout << endl;
string str("hello world");
for (auto ch : str)
{
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}这里建议使用引用,这里是普通数组还好,如果是对象呢?那每次取值得时候就得调用拷贝构造!
2. string常用接口说明
2.1 string类的常见构造
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string(官网关于string的介绍)
这里来说一些构造非常常用的接口:
|------------------------------|------------------------------------|
| 函数名 | 功能说明 |
| string() | 默认构造,构造空字符串 |
| string(const char* s) | 用字符串构造string类型字符串(string不含\0) |
| string(size_t n, char c) | 构造由n个字符c构成的字符串 |
| string(const string&s) | 拷贝构造,用string对象构造另一个string对象 |
|----------------|-----------------------------------|
| ~string() | 析构函数:浅拷贝(自动生成的足够)/深拷贝(需要手动实现) |
cpp
void test02()
{
string s1;
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2("A ship in harbor is safe, but that's not what ships are built for");
cout << s2 << endl;
string s3("hello world");
cout << s3 << endl;
string s4(10, 'x');
cout << s4 << endl;
string s5(s2);
cout << s5 << endl;
}2.2 string类的插入
(1)尾插:末尾插入数据
|-----------------------|
| void push_back(char); |
cpp
void test03()
{
string s1("hello world");
s1.push_back(' ');
s1.push_back('x');
s1.push_back('i');
s1.push_back('a');
s1.push_back('o');
s1.push_back('l');
s1.push_back('i');
cout << s1 << endl;
s1.pop_back();
cout << s1 << endl;
}(2)使用insert在指定位置插入数据
|------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c); //在pos位置插入n个字符c |
| string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s); //在pos位置插入字符串 |
| string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str); //在pos位置插入string |
cpp
void test05()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
//头插
s1.insert(0, 3, 'x');
s1.insert(0, "excuse");
//中间插入
string s2("hi");
s2.insert(1,3,'z');
s2.insert(2, "hello");
//尾插
string s3("today");
s3.insert(4, s2);
}2.3 string类的删除
(1)尾删:尾部删除数据
|------------------|
| void pop_back(); |
cpp
void test06()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
s1.pop_back();
s1.pop_back();
s1.pop_back();
cout << s1 << endl;
}(2)erase:任意位置的删除
|----------------------------------------------------------------------|
| string& erase (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos); |
| iterator erase (iterator first, iterator last); //迭代器版本的删除指定范围数据 |
cpp
void test07()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
s1.erase(0, 2);
s1.erase(5, 3);
string s2("hello,tomorror");
string::iterator it = s2.begin();//迭代器
s2.erase(it + 3, it + 5);
}2.4 string类的拼接
(1)append:在字符末尾拼接字符/字符串
|-------------------------------------------|
| string& append (const string& str); |
| string& append (const char* s); |
| string& append (size_t n, char c); |
cpp
void test08()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
s1.append(3, 'x');
string s2("hello,tomorror");
s2.append(" today");
s2.append(s1);
}2.5 string类的替换
(1)assign:为字符串分配一个新值,替换其当前内容。
|-------------------------------------------|
| string& assign (size_t n, char c); |
| string& assign (const char* s); |
| string& assign (const string& str); |
cpp
void test09()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
s1.assign("excuse me");
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2("hello,tomorror");
s2.assign(s1);
cout << s2 << endl;
}(2)replace:将字符串中以字符pos开头并跨len字符的部分(或字符串中介于[i1,i2) 之间的部分替换为新内容
|--------------------------------------------------------------------|
| string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const string& str); |
| string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, const char* s); |
| string& replace (size_t pos, size_t len, size_t n, char c); |
这里每一个都有对应的迭代器版本!
cpp
//replace
void test10()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
s1.replace(2, 3, 5,'x');//从下标为2的位置开始长度为3个字符替换成5个x
cout << s1 << endl; ////hexxxxx,xiaoli
string s2("hello,tomorror");
s2.replace(3, 5, "excuse"); //helexcusemorror
cout << s2 << endl;
}可能有点懵,就是我只是保证从pos开始跨len个字符的部分内容修改,其余内容不变。这len个字符替换成给的内容。就比如s1,我只保证llo内容改变,llo替换成xxxxx,其余不动。
2.6 string类的查找
(1)find:查找字符串中的内容(如果指定pos,就从pos位置开始查找,仅匹配其中一个字符是不够的,而是整个序列必须匹配;如果匹配返回匹配的第一个位置的下标,否则返回npos)
|-------------------------------------------------------------|
| size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const; |
| size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; |
| size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; |
cpp
//find
void test11()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
cout<<s1.find("llo")<<endl; //从下标为0开始找,返回2
cout << s1.find("he",6)<< endl; //从下标为6开始找,返回18446744073709551615
string s2("hello,tomorror");
cout << s2.find(s1, 3) << endl; //返回18446744073709551615
}(2)rfind:从后往前开始匹配
|--------------------------------------------------------------|
| size_t rfind (char c, size_t pos = 0) const; |
| size_t rfind (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const; |
| size_t rfind (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const; |
cpp
//rfind
void test12()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
cout << s1.rfind("llo") << endl; //从下标为0开始往前找
cout << s1.rfind("he", 6) << endl; //从下标为6开始往前找
string s2("hello,tomorror");
cout << s2.rfind(s1, 3) << endl;
string s3("hello,today,hello tomorror");
cout<<s3.rfind("hello")<<endl; //12,匹配第二个hello
cout<<s3.find("hello")<<endl; //0,匹配第一个hello
}注意:rfind是从尾往前(即从右往左)开始找,但是子字符串时从左往右开始匹配。
2.7 string类的容量
(1)size:字符串的有效字符的长度
|--------------------------|
| size_t size() const; |
cpp
void test13()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
cout << s1.size() << endl; //12
string s2("hello,tomorror");
cout << s2.size() << endl; //14
}(2)capacity:字符串的总空间大小
|------------------------------|
| size_t capacity() const; |
cpp
void test14()
{
string s1("A ship in harbor is safe, but that's not what ships are built for");
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //79
string s2("hello,tomorror");
cout << s2.capacity() << endl; //15
}(3)length:字符串的有效字符的长度
|----------------------------|
| size_t length() const; |
cpp
void test13()
{
string s1("hello,xiaoli");
cout << s1.length() << endl; //12
string s2("hello,tomorror");
cout << s2.length() << endl; //14
}(4)reserve:开辟指定大小的空间,当n<size()时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
|----------------------------------|
| void reserve (size_t n = 0); |
cpp
void test15()
{
string s1("A ship in harbor is safe, but that's not what ships are built for");
s1.reserve(120);
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;
string s2("hello,tomorror");
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
s2.reserve(10);
cout << s2.capacity() << endl;
}注意:这里reserve(120),编译器会多开几个空间,因为编译器的扩容是按1.5倍增长。
(5)empty:检查字符串是否是空串
|-------------------------|
| bool empty() const; |
(6)clear:清空有效字符
(7)resize:将有效字符的个数变成n个,多出的空间用字符c填充。
|-------------------------------------|
| void resize (size_t n); |
| void resize (size_t n, char c); |

cpp
void test16()
{
string s1("xiaoli");
cout << s1.size() << endl;//6
cout << s1.capacity() << endl;//15
//s1.resize(20);
//cout << s1.size() << endl; //20
//s1.resize(12);
//cout << s1.size() << endl; //12
s1.resize(3);
cout << s1.size() << endl; //3
cout << s1.capacity() << endl; //15
}2.8 string类的遍历和访问
(1)operator[ ]:访问指定下标的元素(string类里面已经实现operator[ ]的重载)
|---------------------------------------------------|
| char& operator[] (size_t pos); |
| const char& operator[] (size_t pos) const; |
cpp
void test17()
{
string s1("xiaoli");
cout << s1[2] << endl;
}at同operator[ ],就不再叙述了。
(2)front和back:取首元素和最后一个元素,一样的操作。
(3)begin:返回第一个字符迭代器(通俗一点:返回第一个字符的指针)
end:返回最后一个字符迭代器(通俗一点:返回最后一个字符的指针)
(4)rbegin:返回最后一个字符迭代器(通俗一点:返回第一个字符的指针)
rend:返回第一个字符迭代器(通俗一点:返回最后一个字符的指针)
注意:(3)和(4)与迭代器有着非常紧密的关系,会常常使用
这里一般用于数组或者对象的遍历。如下:有三种遍历方式
cpp
void test18()
{
string s1("hello xiaoli");
//遍历方式
// 下标 + []
for (size_t i = 0; i < s1.size(); i++)
{
cout << s1[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
// 迭代器
string::iterator it = s1.begin(); //在模拟实现的时候具体讲解
while (it != s1.end())
{
(*it)++;
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
// 范围for
for (auto ch : s1)
{
ch--;
cout << ch << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}2.9 string类的交换
(1)swap:交换两个string的内容
|-------------------------------|
| void swap (string& str); |
cpp
void test19()
{
string s1("hello xiaoli");
string s2("A ship in harbor is safe, but that's not what ships are built for");
swap(s1, s2);
cout << s1 << endl;
cout << s2 << endl;
}2.10 string类的运算符
(1)operator=:赋值运算符,在string中实现了函数重载(相当于修改字符串内容),其实功能和assign是类似的。
|----------------------------------------------|
| string& operator= (char c); |
| string& operator= (const char* s); |
| string& operator= (const string& str); |
cpp
void test20()
{
string s1("I Love you!");
s1 = "hello,world";
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 = 'x';
cout << s1 << endl;
}(2)operator+=:在string中实现了函数重载(相当于在末端追加字符串内容),相当于push_back的升级版,多了尾插字符串和string功能。
|-----------------------------------------------|
| string& operator+= (char c); |
| string& operator+= (const char* s); |
| string& operator+= (const string& str); |
cpp
void test21()
{
string s1("I Love you!");
s1 += "hello,world";
cout << s1 << endl;
s1 += ' x';
cout << s1 << endl;
}(3)上面两个都是成员函数,这里余下的大小关系的比较是不属于成员函数的,因为成员函数的第一个参数是隐藏的this指针,而比较可能是字符和字符比较,也可以是字符串和字符串比较。
并且字符和字符串比较都是先比较第一个字符,比较的是字符的ascll码值。
cpp
void test21()
{
string s1("I Love you!");
string s2("I love Code");
cout << (s1 < s2) << endl;//注意优先级关系
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;//注意优先级关系
}(4)operator>> 和 operator<< :输入流和输出流,也是非成员函数,理由和上面一样,第一个不一定是this指针。
2.11 string类中getline函数
在 C++ 中,使用 >> 运算符进行输入提取时,默认情况下确实会以空白字符(包括空格、制表符、换行符等)作为分隔符,并在遇到空白字符时停止当前的提取操作.
而使用getline,则分为两种情况,一种是遇到'\0'停止;另一种是遇到自己定义的终止符停止提取。
|----------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);(遇到'\0'停止) |
| istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);(遇到delim停止) |
cpp
void test22()
{
string str;
cin >> str; // 输入 "Hello World"
cout << str; // 输出 "Hello"(只提取到第一个空格前的内容)
}第一种:读取一整行,遇到'\0'停止
cpp
void test23()
{
string s;
getline(cin, s); // 输入 "Hello World"
cout << s; // 输出 "Hello World"(读取整行内容)
}第二种:读取一整行,遇到delim停止
cpp
void test24()
{
string s1;
getline(cin, s1, '#'); // 输入 "Hello World"
cout << s1; // 输出 "Hello World"(读取整行内容)
}2.11 string类中的substr函数
|--------------------------------------------------------------|
| string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const; |
substr:生成子字符串,返回一个新构造的对象,其值初始化为该对象的子字符串的副本。也就是选取该字符串的一部分构造一个新对象。
cpp
void test25()
{
string s1("A ship in harbor is safe, but that's not what ships are built for");
cout << s1.substr(3, 15) << endl;
string s2 = s1.substr(5, 10);
cout << s2 << endl;
}那么到这里,string一些常见的接口就了解的差不多了,下一期来模拟实现string。