什么是装饰器模式
装饰器模式是一种结构型设计模式,它允许在不改变对象原有结构的情况下,动态地给对象添加额外的功能。这种模式通过创建包装对象来实现功能的扩展,是继承的一个替代方案。
核心思想:在保持接口不变的前提下,对原有功能进行扩展和增强。
装饰器模式的结构
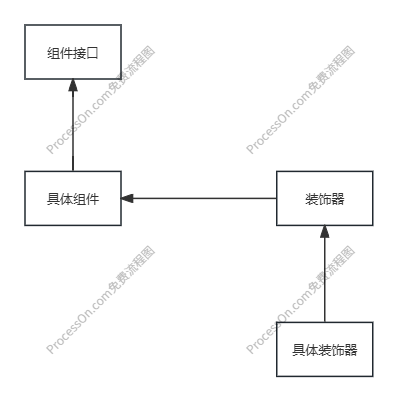
装饰器模式的优势
- 灵活性:比继承更灵活,可以在运行时动态添加功能
- 符合开闭原则:对扩展开放,对修改关闭
- 避免类爆炸:不需要为每个功能组合创建子类
- 职责分离:不同的装饰器负责不同的功能
缓冲输入流装饰器
java
package com.YA33.design.decorator;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/**
* 缓冲输入流装饰器 - 为文件输入流添加缓冲功能
* 作者:YA33
*/
public class BufferedInputStream extends InputStream {
private final FileInputStream fileInputStream;
// 缓冲区,存储从文件读取的数据
private final byte[] buffer = new byte[8192]; // 8KB缓冲区
// 当前读取位置指针
private int position = -1;
// 缓冲区中有效数据的容量
private int capacity = -1;
public BufferedInputStream(FileInputStream fileInputStream) {
this.fileInputStream = fileInputStream;
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
/**
* 读取逻辑:
* 1. 如果缓冲区有数据,直接从缓冲区读取
* 2. 如果缓冲区为空,先刷新缓冲区
* 3. 如果刷新后仍无数据,返回-1表示结束
*/
if (bufferCanRead()) {
return readFromBuffer();
}
refreshBuffer();
if (!bufferCanRead()) {
return -1;
}
return readFromBuffer();
}
/**
* 从缓冲区读取一个字节
*/
private int readFromBuffer() {
// 与上0xff去掉符号位,将byte转为无符号int
// 因为byte的范围是-128~127,而我们需要0~255的范围
return buffer[position++] & 0xff;
}
/**
* 刷新缓冲区,从文件流中读取新数据
*/
private void refreshBuffer() throws IOException {
capacity = this.fileInputStream.read(buffer);
position = 0;
}
/**
* 检查缓冲区是否可读
*/
private boolean bufferCanRead() {
// 容量为-1表示未初始化
if (-1 == capacity) return false;
// 位置等于容量表示已读完
if (capacity == position) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
fileInputStream.close();
super.close();
}
}历史记录集合装饰器
java
package com.YA33.design.decorator;
import java.util.*;
/**
* 历史记录集合装饰器 - 记录被删除的元素历史
* YA
*/
public class HistorySet<E> implements Set<E> {
// 记录被删除的元素
private final List<E> removeHistory = new ArrayList<>();
// 被装饰的原始集合
private final Set<E> delegate;
public HistorySet(Set<E> delegateSet) {
this.delegate = delegateSet;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
/**
* 增强的删除方法:
* - 执行原始删除操作
* - 如果删除成功,记录到删除历史中
*/
if (delegate.remove(o)) {
removeHistory.add((E) o);
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* 获取删除历史记录
*/
public List<E> getRemoveHistory() {
return new ArrayList<>(removeHistory);
}
/**
* 清空删除历史
*/
public void clearHistory() {
removeHistory.clear();
}
// 以下方法直接委托给原始集合
@Override
public int size() {
return delegate.size();
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return delegate.isEmpty();
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return delegate.contains(o);
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return delegate.iterator();
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
return delegate.toArray();
}
@Override
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
return delegate.toArray(a);
}
@Override
public boolean add(E e) {
return delegate.add(e);
}
@Override
public boolean containsAll(Collection<?> c) {
return delegate.containsAll(c);
}
@Override
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) {
return delegate.addAll(c);
}
@Override
public boolean retainAll(Collection<?> c) {
return delegate.retainAll(c);
}
@Override
public boolean removeAll(Collection<?> c) {
boolean modified = false;
for (Object item : c) {
modified |= remove(item);
}
return modified;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
// 清空时记录所有元素到删除历史
removeHistory.addAll(delegate);
delegate.clear();
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "当前集合: " + delegate.toString() +
"\n删除历史: " + removeHistory;
}
}日志输出流装饰器
java
package com.YA33.design.decorator;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 日志输出流装饰器 - 为输出流添加日志记录功能
* 作者:YA33
*/
public class LoggingOutputStream extends OutputStream {
private final OutputStream delegate;
private final SimpleDateFormat dateFormat =
new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public LoggingOutputStream(OutputStream delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
}
@Override
public void write(int b) throws IOException {
log("写入单个字节: " + b);
delegate.write(b);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] b) throws IOException {
log("写入字节数组,长度: " + b.length);
delegate.write(b);
}
@Override
public void write(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
log(String.format("写入字节数组,偏移量: %d, 长度: %d", off, len));
delegate.write(b, off, len);
}
@Override
public void flush() throws IOException {
log("刷新输出流");
delegate.flush();
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
log("关闭输出流");
delegate.close();
}
/**
* 记录日志信息
*/
private void log(String message) {
String timestamp = dateFormat.format(new Date());
System.out.println("[" + timestamp + "] " + message);
}
}测试代码
java
package com.YA33.design.decorator;
import java.io.*;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.*;
public class DecoratorPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 装饰器模式演示 ===\n");
// 测试历史记录集合
testHistorySet();
// 测试缓冲输入流
testBufferedInputStream();
// 测试日志输出流
testLoggingOutputStream();
}
/**
* 测试历史记录集合装饰器
*/
public static void testHistorySet() {
System.out.println("1. 历史记录集合测试:");
Set<String> historySet = new HistorySet<>(new HashSet<>());
// 添加元素
historySet.add("Apple");
historySet.add("Banana");
historySet.add("Orange");
historySet.add("Grape");
System.out.println("初始集合: " + historySet);
// 删除元素
historySet.remove("Banana");
historySet.remove("Grape");
System.out.println("删除后集合: " + historySet);
// 获取删除历史
HistorySet<String> typedSet = (HistorySet<String>) historySet;
System.out.println("删除历史: " + typedSet.getRemoveHistory());
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 测试缓冲输入流性能
*/
public static void testBufferedInputStream() {
System.out.println("2. 缓冲输入流性能测试:");
try {
// 创建一个测试文件
File testFile = createTestFile();
// 测试普通文件流
long startTime = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
readWithFileInputStream(testFile);
long endTime = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
System.out.println("普通文件流耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
// 测试缓冲文件流
startTime = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
readWithBufferedInputStream(testFile);
endTime = Instant.now().toEpochMilli();
System.out.println("缓冲文件流耗时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms");
// 清理测试文件
testFile.delete();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("文件操作错误: " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 测试日志输出流
*/
public static void testLoggingOutputStream() {
System.out.println("3. 日志输出流测试:");
try {
ByteArrayOutputStream byteArrayOutput = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
LoggingOutputStream loggingOutput = new LoggingOutputStream(byteArrayOutput);
loggingOutput.write("Hello, Decorator Pattern!".getBytes());
loggingOutput.write(65); // 写入字符'A'
loggingOutput.flush();
loggingOutput.close();
System.out.println("输出内容: " + byteArrayOutput.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("输出流错误: " + e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 创建测试文件
*/
private static File createTestFile() throws IOException {
File file = new File("test_data.txt");
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
// 写入1MB测试数据
byte[] data = new byte[1024]; // 1KB
Arrays.fill(data, (byte) 'A');
for (int i = 0; i < 1024; i++) { // 写入1024次,共1MB
fos.write(data);
}
}
return file;
}
private static void readWithFileInputStream(File file) throws IOException {
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file)) {
while (fis.read() != -1) {
// 逐个字节读取
}
}
}
private static void readWithBufferedInputStream(File file) throws IOException {
try (InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file))) {
while (bis.read() != -1) {
// 通过缓冲流读取
}
}
}
}装饰器模式的应用场景
- IO流处理:Java中的BufferedInputStream、DataInputStream等
- 集合框架:Collections.synchronizedCollection()等工具方法
- Web开发:HTTP请求/响应的过滤器链
- GUI开发:为可视化组件添加滚动、边框等功能
- 中间件:为服务调用添加日志、监控、重试等功能
总结
装饰器模式通过组合的方式,在不修改原有代码的基础上为对象动态添加功能,体现了"组合优于继承"的设计原则。在实际开发中,合理使用装饰器模式可以让代码更加灵活、可扩展,同时保持良好的结构清晰度。
通过本文的三个示例,我们可以看到装饰器模式在不同场景下的应用:缓冲功能、历史记录功能和日志功能。每种装饰器都专注于单一职责,通过组合可以创造出功能丰富的对象,这正是装饰器模式的魅力所在。