目录
[1. 参数与断言检查](#1. 参数与断言检查)
[2. 元素前移覆盖(核心逻辑)](#2. 元素前移覆盖(核心逻辑))
[3. 更新有效元素个数](#3. 更新有效元素个数)
[2. 删除有序数组中的重复项](#2. 删除有序数组中的重复项)
前言
数据结构:顺序表讲解 文章将讲解顺序表介绍,顺序表分类,顺序表动态顺序表的实现,顺序表算法题,顺序表问题与思考知识的相关内容,其中顺序表介绍、顺序表概念与结构、顺序表分类、动态顺序表的实现、尾插,头插,尾删,头删时间复杂度对比为上一章节知识的内容,本章节将讲解剩余的知识:
一、动态顺序表的实现(继续)
在上篇博客中我们已经完成了顺序表的头插,尾插,头删,尾删等操作( 数据结构:顺序表讲解(1)-CSDN博客),本篇博客将讲解剩余的操作:
1.顺序表的指定位置查找
int Find(SL* h, type x);
cpp
int Find(SL* h, type x)
{
assert(h);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size; i++)
{
if (h->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}解释:
- 该函数用于在顺序表(
SL)中查找指定元素x,返回其下标(找到时)或-1(未找到时),核心逻辑为遍历数组比较元素。
根据上篇文章:我们已经了解了尾插,头插,尾删,头删的内容,我们可以先实现一下代码操作:
但是我们在尾插,头插等操作时使用了malloc函数动态开辟内存,在结束程序时需要释放下开辟的空间,所以需要有销毁函数。
2.顺序表的销毁
void SLDestory(SL* h)
cpp
void SLDestory(SL* h)
{
if (h->arr)
free(h->arr);
h->arr = NULL;
h->size = 0;
h->capacity = 0;
}解释:
SLDestory是顺序表的销毁函数,用于释放动态分配的内存资源并重置结构状态,核心目标是避免内存泄漏。- 作用 :
h->arr是顺序表中存储元素的动态数组(通过malloc/calloc分配),free(h->arr)会将其占用的内存归还给系统。- 为什么加
if (h->arr)?
- 若
h->arr为NULL(空表或已释放),free(NULL)在 C 语言中是安全的(无操作),因此此判断非必需 ,可简化为直接free(h->arr)。
结合之前的代码举例:(我写了3个文件)
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//定义顺序表的结构
typedef int type;
typedef struct Seqlist
{
type* arr;//存储数据
int size;//有效数据个数
int capacity;//空间容量
}SL;
void SLinit(SL* h);
void kuo(SL* h);
void SLpushback(SL* h,type x);
void SLpushfront(SL* h, type x);
void popback(SL* h);
void popfront(SL* h);
int Find(SL* h, type x);
void SLDestory(SL* h);
void print(SL* h);
cpp
//定义顺序表的结构
#include"1.h"
void SLinit(SL* h)
{
h->arr = NULL;
h->capacity = h->size = 0;
}
void kuo(SL* h)
{
if (h->capacity == h->size)
{
int newcapacity = h->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * h->capacity;
type* tmp = (type*)realloc(h->arr, sizeof(type) * newcapacity);
if (tmp)
{
h->arr = tmp;
h->capacity = newcapacity;
}
else
{
exit(1);
}
}
}
void SLpushback(SL* h, type x)
{
kuo(h);
h->arr[h->size++] = x;
}
void SLpushfront(SL* h, type x)
{
kuo(h);
int i;
for (i = h->size; i > 0; i--)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i - 1];
}
h->arr[i] = x;
h->size++;
}
void popback(SL* h)
{
assert(h && h->size);
h->size--;
}
void popfront(SL* h)
{
assert(h && h->size);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size - 1; i++)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i + 1];
}
h->size--;
}
int Find(SL* h, type x)
{
assert(h);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size; i++)
{
if (h->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLDestory(SL* h)
{
if (h->arr)
free(h->arr);
h->arr = NULL;
h->size = 0;
h->capacity = 0;
}
void print(SL* h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", h->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
cpp
#include"1.h"
void test1()
{
SL h;
SLinit(&h);
SLpushback(&h, 1); //1
SLpushback(&h, 2); //12
SLpushback(&h, 3); //123
SLpushback(&h, 4); //1234
SLpushfront(&h, 1); //11234
SLpushfront(&h, 2); //211234
SLpushfront(&h, 3); //3211234
SLpushfront(&h, 4); //43211234
print(&h);
popback(&h); //4321123
print(&h);
popback(&h); //432112
print(&h);
popfront(&h); //32112
print(&h);
popfront(&h); //2112
print(&h);
SLDestory(&h);
}
int main()
{
test1();
}结果为:

3.顺序表的指定位置插入
实现指定位置插入,顺序表的指定位置插入是指在数组的第 pos 个下标处插入新元素,核心操作是移动元素 + 赋值,需处理扩容、边界检查等关键步骤,接下来,我将展示代码:
void SLinsert(SL* h, int pos, type x);
cpp
//在pos前插入
void SLinsert(SL* h, int pos, type x)
{
assert(h);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= h->size);
kuo(h);
for (int i = h->size; i > pos; i--)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i - 1];
}
h->arr[pos] = x;
h->size++;
}讲解:
插入位置
pos的合法范围应为[0, size](含size),即允许在表尾插入。因此断言应为:
cppassert(pos >= 0 && pos <= h->size); // 允许在表尾(pos=size)插入1. 元素移动逻辑
cppfor (int i = h->size; i > pos; i--) // 从后往前移动元素 { h->arr[i] = h->arr[i - 1]; // 将arr[i-1]的值赋给arr[i] }
- 移动方向 :从
size开始到pos+1,正确(避免数据覆盖)。- 示例 :若原表为
[1,2,3](size=3),pos=1时:
i=3:arr[3] = arr[2](3 → 4号位置)i=2:arr[2] = arr[1](2 → 3号位置)- 结果:
[1, _, 2, 3],pos=1处空出,可插入新元素。2. 插入元素与更新 size
cpph->arr[pos] = x; // 在pos位置插入新元素(正确) h->size++; // 有效元素个数+1(正确)
代码举例:
cpp
#include"1.h"
void test1()
{
SL h;
SLinit(&h);
SLpushback(&h, 1); //1
SLpushback(&h, 2); //12
SLpushback(&h, 3); //123
SLpushback(&h, 4); //1234
SLpushfront(&h, 1); //11234
SLpushfront(&h, 2); //211234
SLpushfront(&h, 3); //3211234
SLpushfront(&h, 4); //43211234
print(&h);
popback(&h); //4321123
print(&h);
popback(&h); //432112
print(&h);
popfront(&h); //32112
print(&h);
popfront(&h); //2112
print(&h);
SLinsert(&h, 2, 55); //2 1 55 1 2
print(&h);
SLinsert(&h, 3, 125); //2 1 55 125 1 2
print(&h);
SLDestory(&h);
}
int main()
{
test1();
}
4.顺序表的指定位置删除
顺序表的指定位置删除是指移除数组中第 pos 个下标处的元素,核心操作是移动元素覆盖待删除值。接下来,我将展示该部分的代码以及实现:
void SLerase(SL* h, int pos)
cpp
void SLerase(SL* h, int pos)
{
assert(h);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < h->size);
int i;
for (i = pos;i<h->size-1;i++)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i+1];
}
h->size--;
}解析:
代码逐行讲解
1. 参数与断言检查
cppassert(h); // 确保顺序表指针h非空(必须,避免空指针访问) assert(pos >= 0 && pos < h->size); // 检查删除位置pos的合法性
- pos 合法性 :
pos必须在[0, size-1]范围内(例如size=3时,可删除 0、1、2 位置,不能删除pos=3)。- 隐含检查 :
pos < h->size已隐含size > 0(若size=0,pos < 0会触发断言失败),无需额外检查h->size > 0。2. 元素前移覆盖(核心逻辑)
cppfor (i = pos; i < h->size - 1; i++) // 循环条件:i从pos到size-2 { h->arr[i] = h->arr[i + 1]; // 将后一个元素(i+1)覆盖当前元素(i) }
循环范围 :
i < h->size - 1等价于i <= h->size - 2,即从pos移动到倒数第二个元素 (size-2)。
- 示例 :若原表为
[1,2,3,4](size=4),删除pos=1(值为2):
i=1:arr[1] = arr[2](3 → 2号位置,表变为[1,3,3,4])i=2:arr[2] = arr[3](4 → 3号位置,表变为[1,3,4,4])- 循环结束(
i=3时3 < 4-1不成立)。为什么是
size-1?
- 若
i < h->size(错误条件),当i = size-1时,i+1 = size会访问越界内存 (数组最大下标为size-1)。- 原代码
size-1确保i+1最大为size-1(合法),避免越界。3. 更新有效元素个数
cpph->size--; // 有效元素个数-1(逻辑删除,无需释放内存)
- 效果 :删除后顺序表实际存储的有效元素为前
size-1个(覆盖后最后一个元素arr[size-1]变为无效数据,但不影响访问)。
例:
cpp
SLinsert(&h, 3, 125); //2 1 55 125 1 2
print(&h);
SLerase(&h, 3);
print(&h); //2 1 55 1 2 将下标为3的删去5.实现的总代码
本代码,我通过3个文件来实现的,分别为头文件(1.h)、实现文件(1.c)、测试文件(maic.c)
代码如下:
1.h
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
//定义顺序表的结构
typedef int type;
typedef struct Seqlist
{
type* arr;//存储数据
int size;//有效数据个数
int capacity;//空间容量
}SL;
void SLinit(SL* h);
void kuo(SL* h);
void SLpushback(SL* h,type x);
void SLpushfront(SL* h, type x);
void popback(SL* h);
void popfront(SL* h);
int Find(SL* h, type x);
void SLDestory(SL* h);
void print(SL* h);
void SLinsert(SL* h, int pos, type x);
void SLerase(SL* h, int pos);1.c
cpp
//定义顺序表的结构
#include"1.h"
void SLinit(SL* h)
{
h->arr = NULL;
h->capacity = h->size = 0;
}
void kuo(SL* h)
{
if (h->capacity == h->size)
{
int newcapacity = h->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * h->capacity;
type* tmp = (type*)realloc(h->arr, sizeof(type) * newcapacity);
if (tmp)
{
h->arr = tmp;
h->capacity = newcapacity;
}
else
{
exit(1);
}
}
}
void SLpushback(SL* h, type x)
{
kuo(h);
h->arr[h->size++] = x;
}
void SLpushfront(SL* h, type x)
{
kuo(h);
int i;
for (i = h->size; i > 0; i--)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i - 1];
}
h->arr[i] = x;
h->size++;
}
void popback(SL* h)
{
assert(h && h->size);
h->size--;
}
void popfront(SL* h)
{
assert(h && h->size);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size - 1; i++)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i + 1];
}
h->size--;
}
int Find(SL* h, type x)
{
assert(h);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size; i++)
{
if (h->arr[i] == x)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void SLDestory(SL* h)
{
if (h->arr)
free(h->arr);
h->arr = NULL;
h->size = 0;
h->capacity = 0;
}
void print(SL* h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", h->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//在pos前插入
void SLinsert(SL* h, int pos, type x)
{
assert(h);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= h->size);
kuo(h);
for (int i = h->size; i > pos; i--)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i - 1];
}
h->arr[pos] = x;
h->size++;
}
void SLerase(SL* h, int pos)
{
assert(h);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos < h->size);
int i;
for (i = pos;i<h->size-1;i++)
{
h->arr[i] = h->arr[i+1];
}
h->size--;
}main.c
cpp
#include"1.h"
void test1()
{
SL h;
SLinit(&h);
SLpushback(&h, 1); //1
SLpushback(&h, 2); //12
SLpushback(&h, 3); //123
SLpushback(&h, 4); //1234
SLpushfront(&h, 1); //11234
SLpushfront(&h, 2); //211234
SLpushfront(&h, 3); //3211234
SLpushfront(&h, 4); //43211234
print(&h);
popback(&h); //4321123
print(&h);
popback(&h); //432112
print(&h);
popfront(&h); //32112
print(&h);
popfront(&h); //2112
print(&h);
SLinsert(&h, 2, 55); //2 1 55 1 2
print(&h);
SLinsert(&h, 3, 125); //2 1 55 125 1 2
print(&h);
SLerase(&h, 3);
print(&h); //2 1 55 1 2 将下标为3的删去
SLDestory(&h);
}
int main()
{
test1();
}二、顺序表算法题
根据我们讲解的知识点,我们来看几道关于该知识的算法题:
1.移除元素

本题思路:我们可以选用双指针法来实现该题,具体操作为:我们在开始时创建两个int变量,src,dst,通过src(数组下标)遍历整个数组,如果发现数组值不为val,我们则将值传入到以dst为下标的数组中,如此情况: 这是简单的讲法,接下来,我将通过代码来讲解:
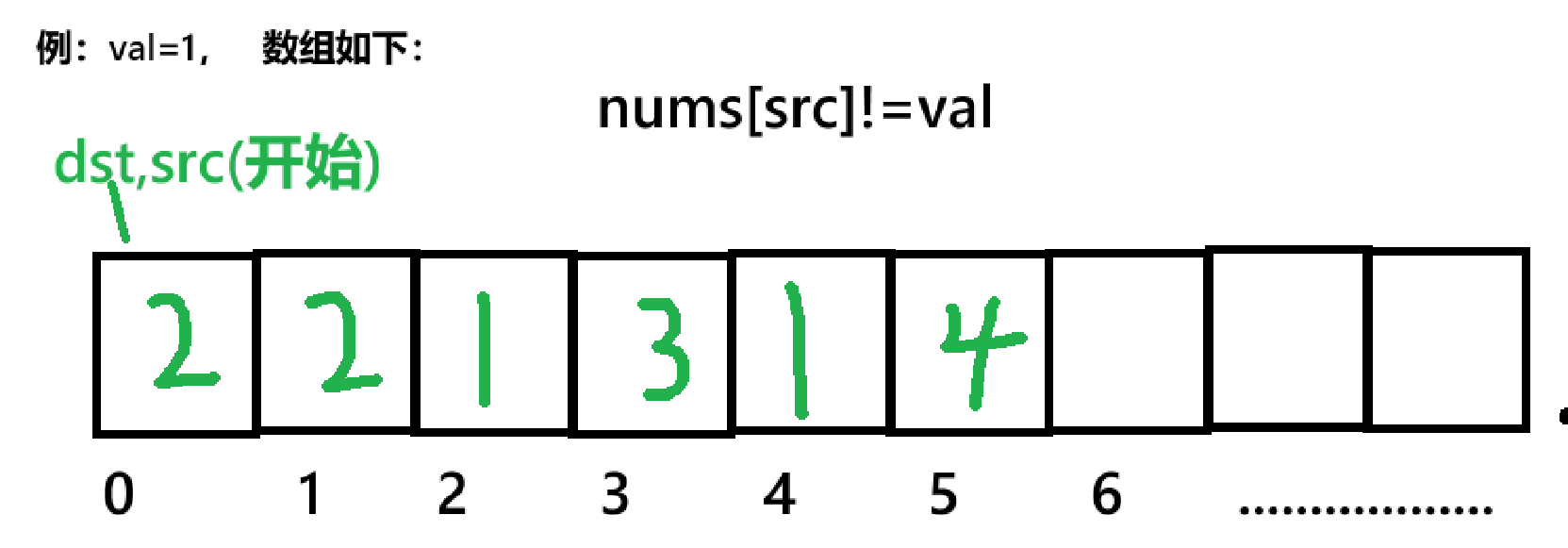
代码:
cpp
int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val) {
int src=0,dst=0;
while(src<numsSize)
{
if(nums[src]!=val)
{
nums[dst]=nums[src];
dst++;
}
src++;
}
return dst;
}
详细讲解:
该算法空间复杂度为 O(1),时间复杂度为O(n)。
核心逻辑:双指针法
通过两个指针
src(源指针)和dst(目标指针)遍历数组,将不等于val的元素"搬运"到数组前端,覆盖需要移除的元素。
src:遍历整个数组,寻找不等于val的元素。dst:指向当前需要填充的位置,仅在src找到有效元素时移动。步骤分解
- 初始化指针 :
src = 0,dst = 0(均从数组起始位置开始)。- 遍历数组 :
src从 0 到numsSize-1循环:
- 若
nums[src] != val:将nums[src]赋值给nums[dst],dst后移一位(指向下一个待填充位置)。- 若
nums[src] == val:dst不动(跳过该元素,后续被覆盖)。- 无论是否匹配,
src始终后移一位。- 返回新长度 :
dst的值即为移除后有效元素的个数(因为dst每填充一个有效元素就 +1)。
2.删除有序数组中的重复项
26. 删除有序数组中的重复项 - 力扣(LeetCode)

本题思路:我们可以选用双指针法来实现该题,具体操作为:我们在开始时创建两个int变量,src=0,dst=0,通过src(数组下标)遍历整个数组(这一部分与上一题基本相同,但后来操作上有较大不同),如果发现数组值不重复,我们则将值传入到以dst为下标的数组中,忽视掉重复的值,如此情况: 这是简单的讲法,接下来,我将通过代码来讲解:
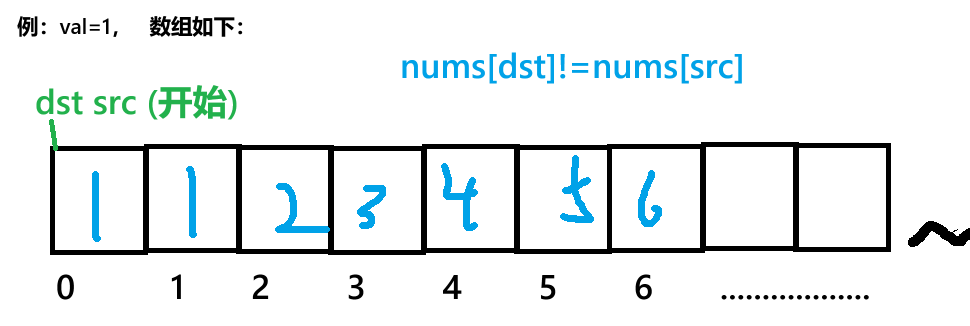
cpp
int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize) {
int src=0,dst=0;
while(src<numsSize)
{
if(nums[dst]!=nums[src])
{
nums[++dst]=nums[src];
}
src++;
}
return dst+1;
}
详细讲解:
该函数用于移除非严格递增排序数组中的重复元素(只保留一个),返回移除后数组的新长度,空间复杂度为 O(1)(原数组上修改)。
核心逻辑:双指针法(快慢指针)
利用数组已排序 的特性,通过两个指针
src(快指针)和dst(慢指针)遍历数组,仅保留不重复的元素。
src:遍历整个数组,寻找与dst指向元素不同的新元素。dst:指向当前已确认的不重复元素的最后一个位置,仅在src找到新元素时移动。步骤分解
- 初始化指针 :
src = 0,dst = 0(均从数组起始位置开始)。- 遍历数组 :
src从 0 到numsSize-1循环:
- 若
nums[dst] != nums[src]:说明src找到新的不重复元素,将dst先 +1(移动到下一个待填充位置),再将nums[src]赋值给nums[dst]。- 若
nums[dst] == nums[src]:dst不动(跳过重复元素)。- 无论是否重复,
src始终后移一位。- 返回新长度 :
dst + 1(因为dst指向最后一个有效元素的索引,长度需 +1)。
3.合并两个有序数组

本题思路:题目的要求挺多,注意:最终,合并后数组不应由函数返回,而是存储在数组
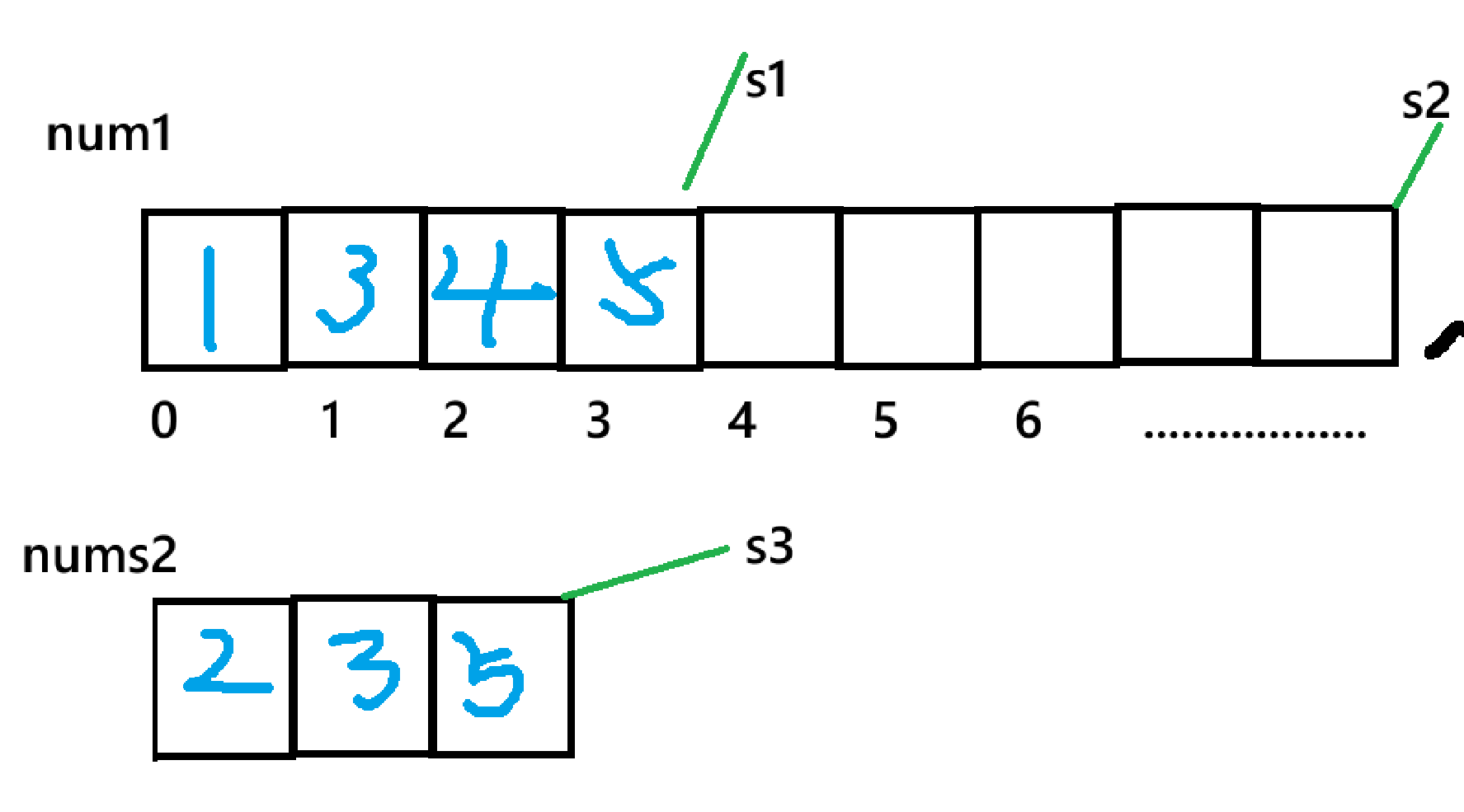
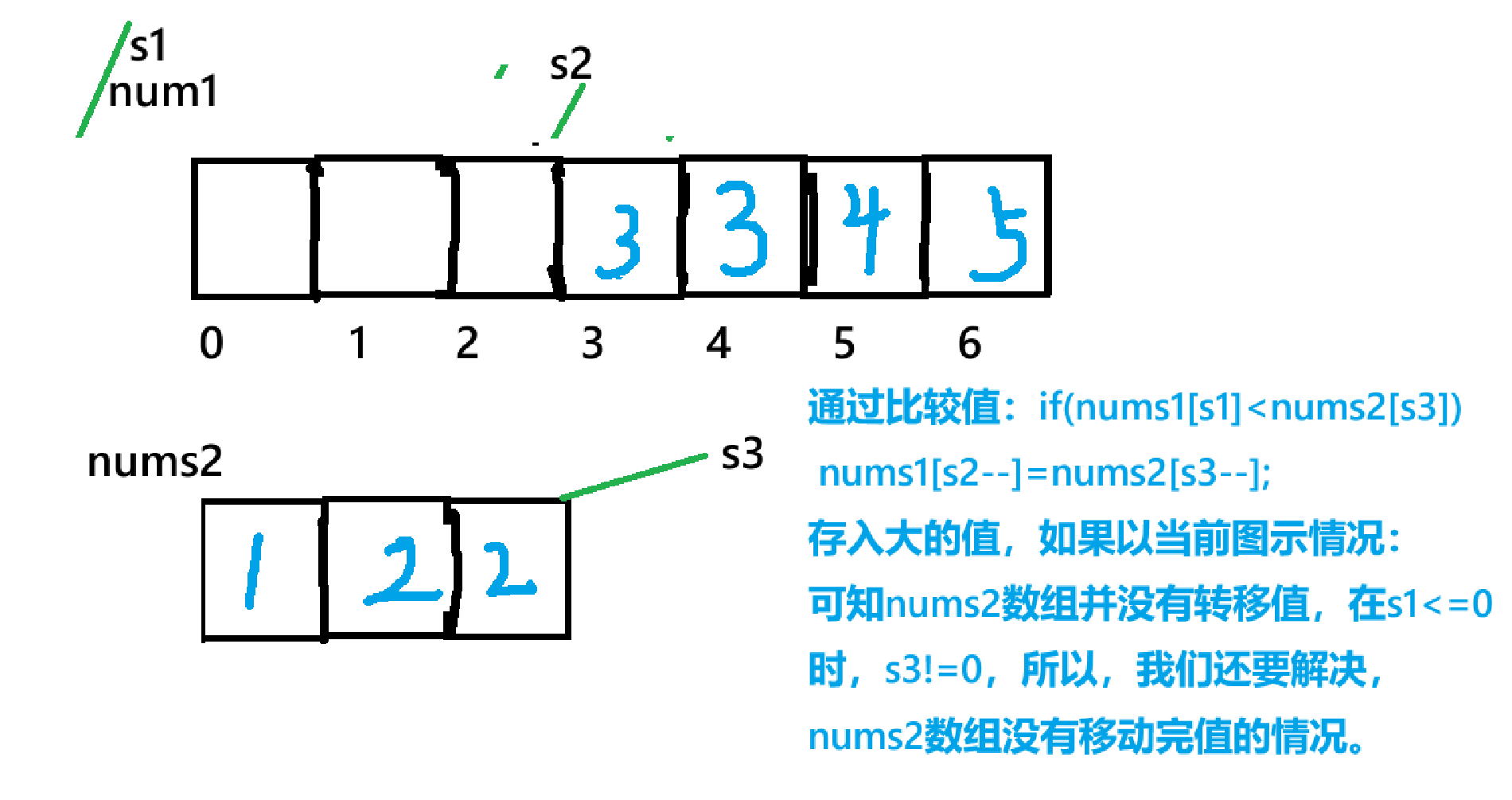
nums1中。 此处提示我们要利用好原数组的空间,所以,我们本题的解法围绕着**nums1**后解法:三指针法: 创建三个整形指针,例:s1,s2,s3 分别指向:1数组的头,尾部,2数组的尾部,之后再进行操作:
- 即比较两数组下标s1,s3值对应的大小,nums1[s1] < nums2[s3]:将 nums2[s3] 放入 nums1[s2],s3 和 s2 均左移一位(s3--,s2--)。
- 否则:将 nums1[s1] 放入 nums1[s2],s1 和 s2 均左移一位(s1--,s2--)。
- 处理剩余元素:若 nums2 仍有未合并的元素(s3 >= 0),直接将剩余元素依次放入 nums1 的头部(此时 nums1 的有效元素已全部合并,s1 已遍历完,s2 指向剩余空位的起始位置)。
具体操作通过代码讲解:
特殊例:
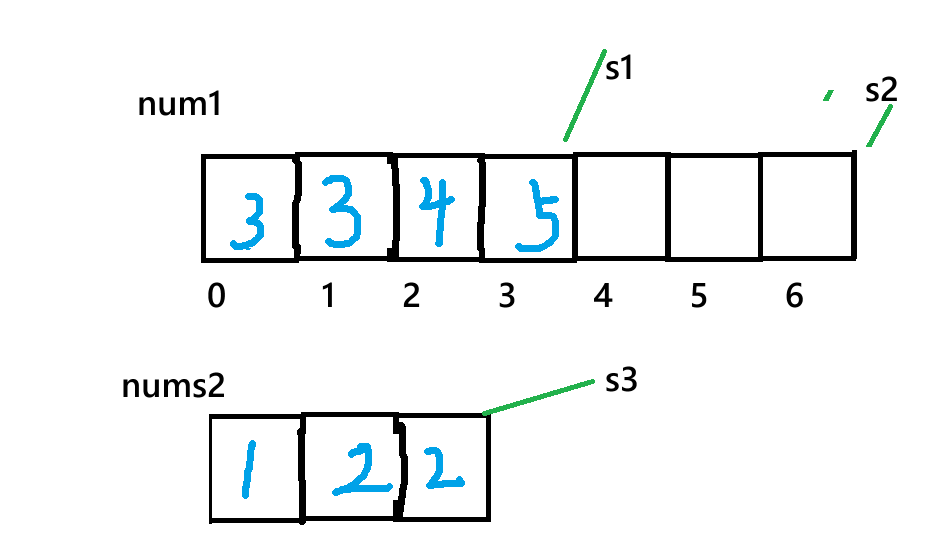
cpp
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n)
{ int s1=m-1;
int s2=n+m-1;
int s3=n-1;
while(s1>=0&&s3>=0)
{
if(nums1[s1]<nums2[s3])
nums1[s2--]=nums2[s3--];
else
nums1[s2--]=nums1[s1--];
}
if(s3>=0)
{ while(s3>=0)
{
nums1[s2--]=nums2[s3--];
}
}
}
总结
以上就是今天要讲的内容,本篇文章涉及的知识点为:顺序表动态顺序表的实现,顺序表算法题 等知识的相关内容,为本章节知识的内容,希望大家能喜欢我的文章,谢谢各位,接下来的内容我会很快更新有关链表的知识。
