一、HTTP协议
虽然我们说,应用层协议是我们程序猿自己定的,但实际上,已经有大佬们定义了一些现成的、有非常好用的应用层协议,供我们直接参考使用。HTTP(超文本传输协议)就是其中之一。
在互联网世界中,HTTP(H yperT ext T ransfer Protocol,超文本传输协议)是一个至关重要的协议。它定义了客户端(如浏览器)与服务器之间如何通信,以交换或传输超文本(如HTML文档)。
HTTP协议是客户端与服务器之间通信的基础。客户端通过HTTP协议向服务器发送请求,服务器收到请求后处理并返回响应。HTTP协议是一个无连接、无状态的协议,即每次请求都需要建立一个新的连接,且服务器不会保存客户端的状态信息。
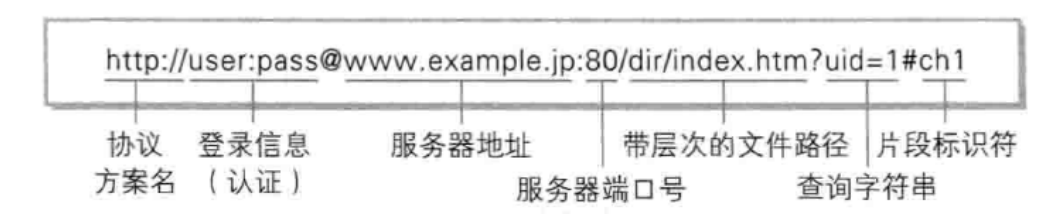
1.1 认识URL
平时我们常说的"网址"其实就是说URL。
1.2 urlencode 和 urldecode(了解)
像 **/ ? :**等这样的字符,已经被 url 当做特殊意义理解了。因此这些字符不能随意出现。
比如,某个参数中需要带有这些特殊字符,就必须先对特殊字符进行转义。
转义的规则如下:
将需要转码的字符转为16进制,然后从右到左取4位(不足4位直接处理),每2位作1位,前面加上%,编码成%XY格式。
例如:
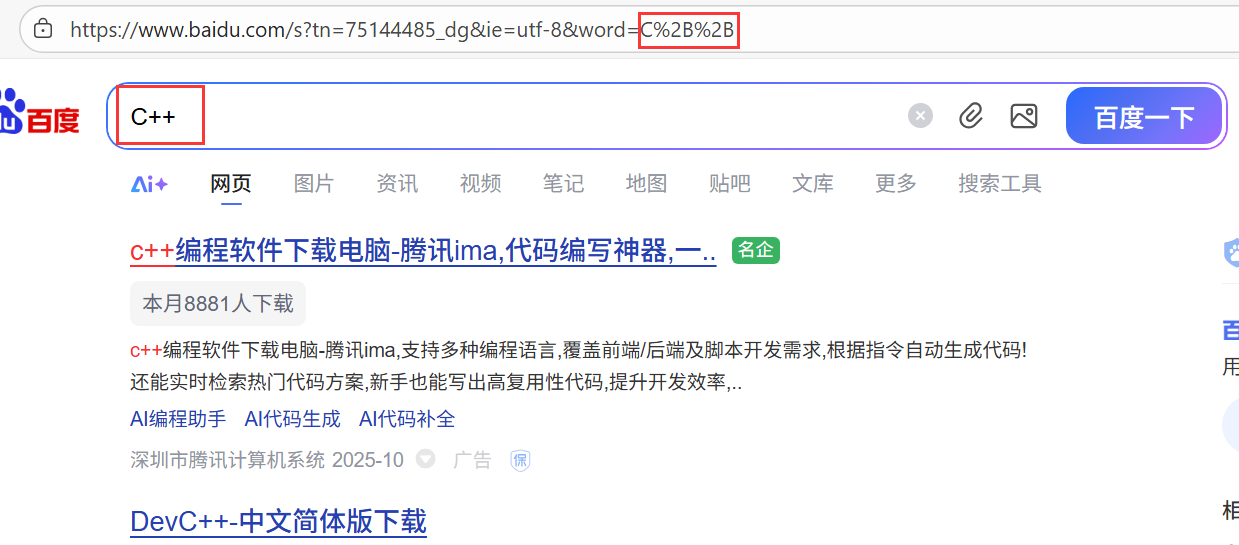
"+" 被转义成了 "%2B" +
urldecode 就是 urlencode 的逆过程。
二、HTTP协议请求与响应格式
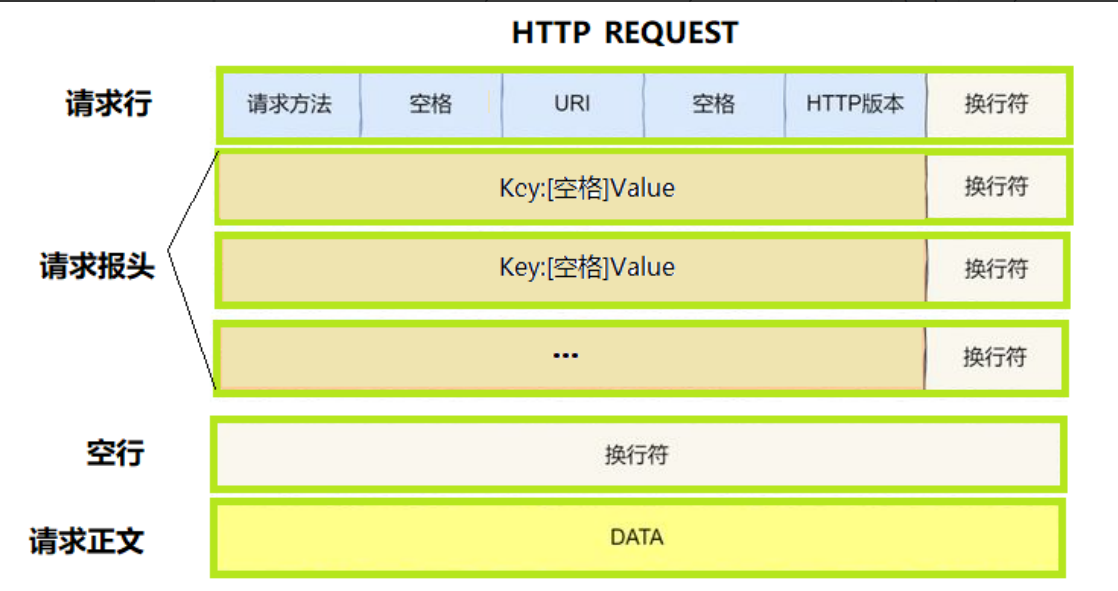
2.1 HTTP请求

- 首行:[方法] + [URL] + [版本]
- Header:请求的属性,冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用\r\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束。
- Body:空行后面的内容都是Body。Body允许为空字符串。如果Body存在,则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度。
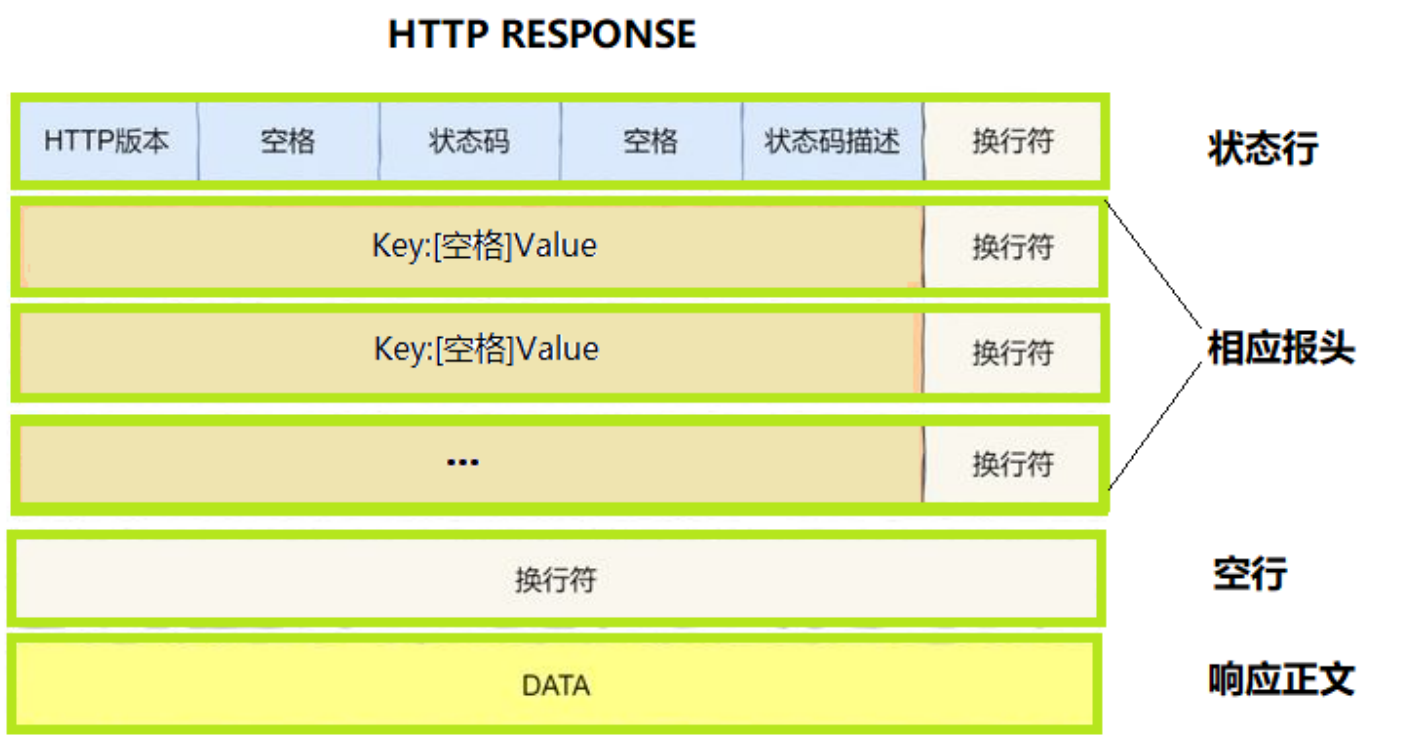
2.2 HTTP响应
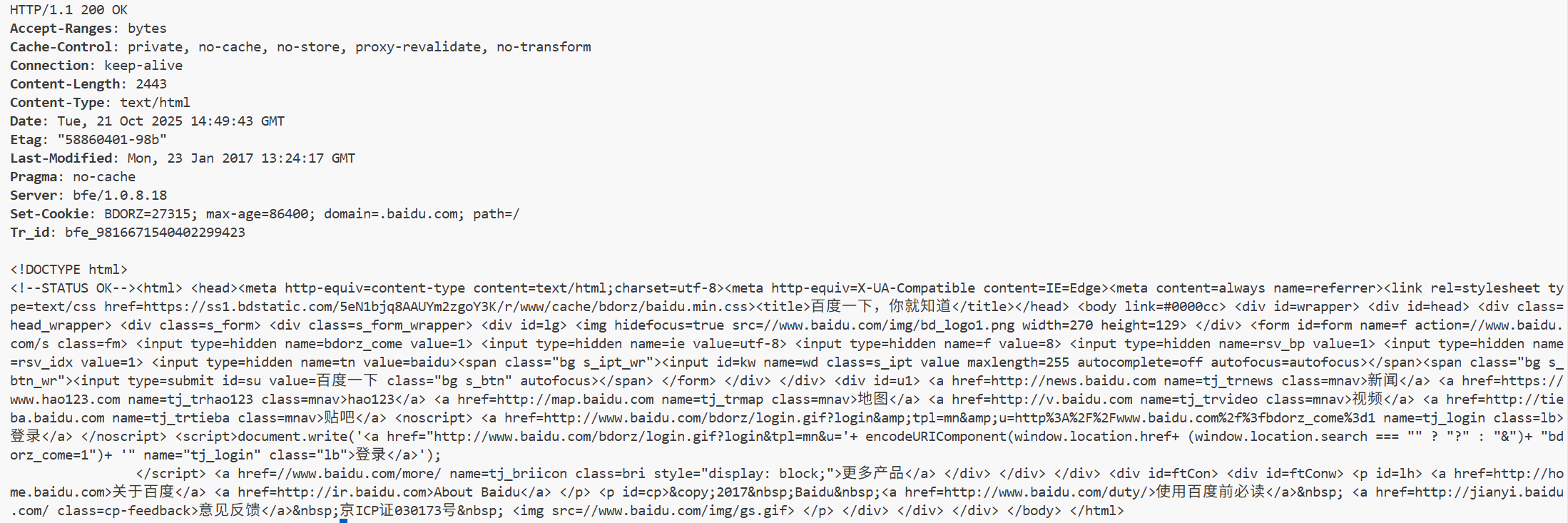
- 首行:[版本号] + [状态码] + [状态码解释]
- Header:响应的属性,冒号分割的键值对;每组属性之间使用\r\n分隔;遇到空行表示Header部分结束。
- Body:空行后面的内容都是Body。Body允许为空字符串。如果Body存在,则在Header中会有一个Content-Length属性来标识Body的长度。如果服务器返回了一个 html 页面,那么 html 页面的内容就是在 Body中。
三、HTTP的方法
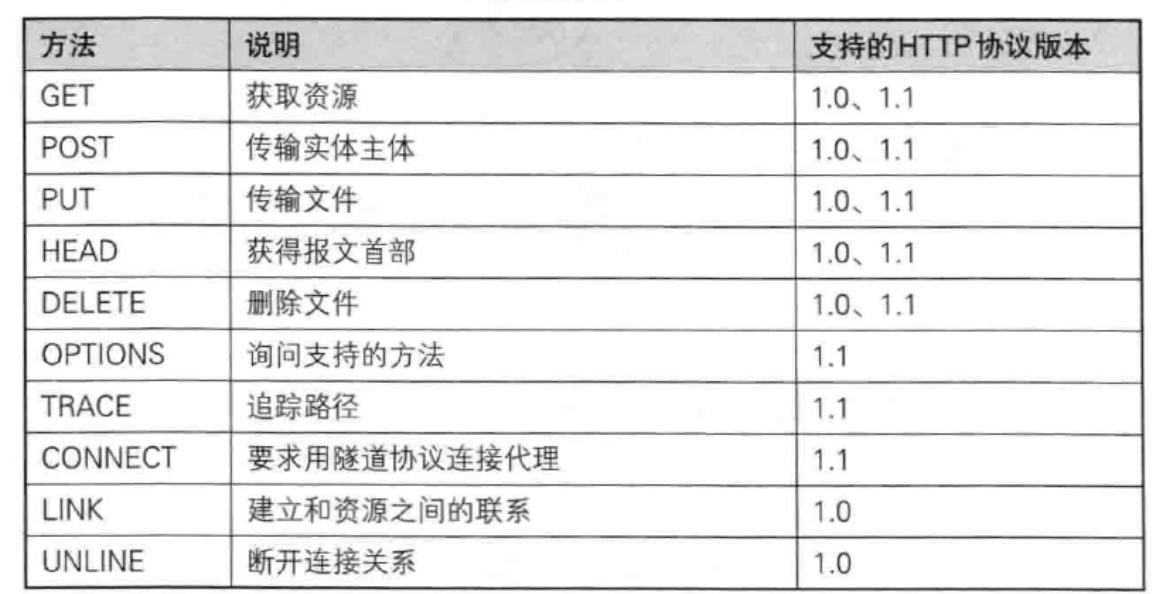
其中最常用的就是GET方法和POST方法。
3.1 GET方法(重点)
- 用途:用于请求URL指定的资源。
- 示例:GET /index.html HTTP/1.1
- 特性:指定资源经服务器端解析后返回响应内容。
cpp
std::string GetContent(const std::string &path) {
std::string content;
std::ifstream in(path, std::ios::binary);
if(!in.is_open()) return std::string();
in.seekg(0, in.end);
size_t filesize = in.tellg();
in.seekg(0, in.beg);
content.resize(filesize);
in.read((char*)content.c_str(), filesize);
in.close();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "content length: " << content.size();
return content;
}这里读取文件数据需要通过二进制方式读取,因为存在图片等数据。
3.2 POST方法(重点)
- 用途:用于传输实体的主体,通常用于提交表单的数据。
- 示例:POST /submit.cgi HTTP/1.1
- 特性:可以发送大量的数据给服务器,并且数据包含在请求体中。
cpp
// 解析客户端发送过来的信息
void Deserialize(std::string &req_header) {
if(ParseOneLine(req_header, &_req_line, Sep)) {
std::stringstream ss(_req_line);
ss >> _method >> _uri >> _version;
ParseHeader(req_header);
_body = req_header;
if(_method == "GET") {
auto pos = _uri.find("?");
if(pos != std::string::npos) {
_isexec = true;
// https://www.baidu.com/s?tn=75144485_dg&ie=utf-8&word=c%2B%2B
_path = _uri.substr(0, pos);
_args = _uri.substr(pos + 1);
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "path: " << _path;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "args: " << _args;
}
else _path = _uri;
}
else if(_method == "POST") {
_isexec = true; // 参数在正文
_path = _uri;
_args = _body;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "path: " << _path;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "args: " << _args;
}
}
}3.3 PUT方法(不常用)
- 用途:用于传输文件,将请求报文主体中的文件保存到请求URL指定的位置。
- 示例:PUT /example.html HTTP/1.1
- 特性:不太常用,但在某些情况下,如RESTful API中,用于更新资源。
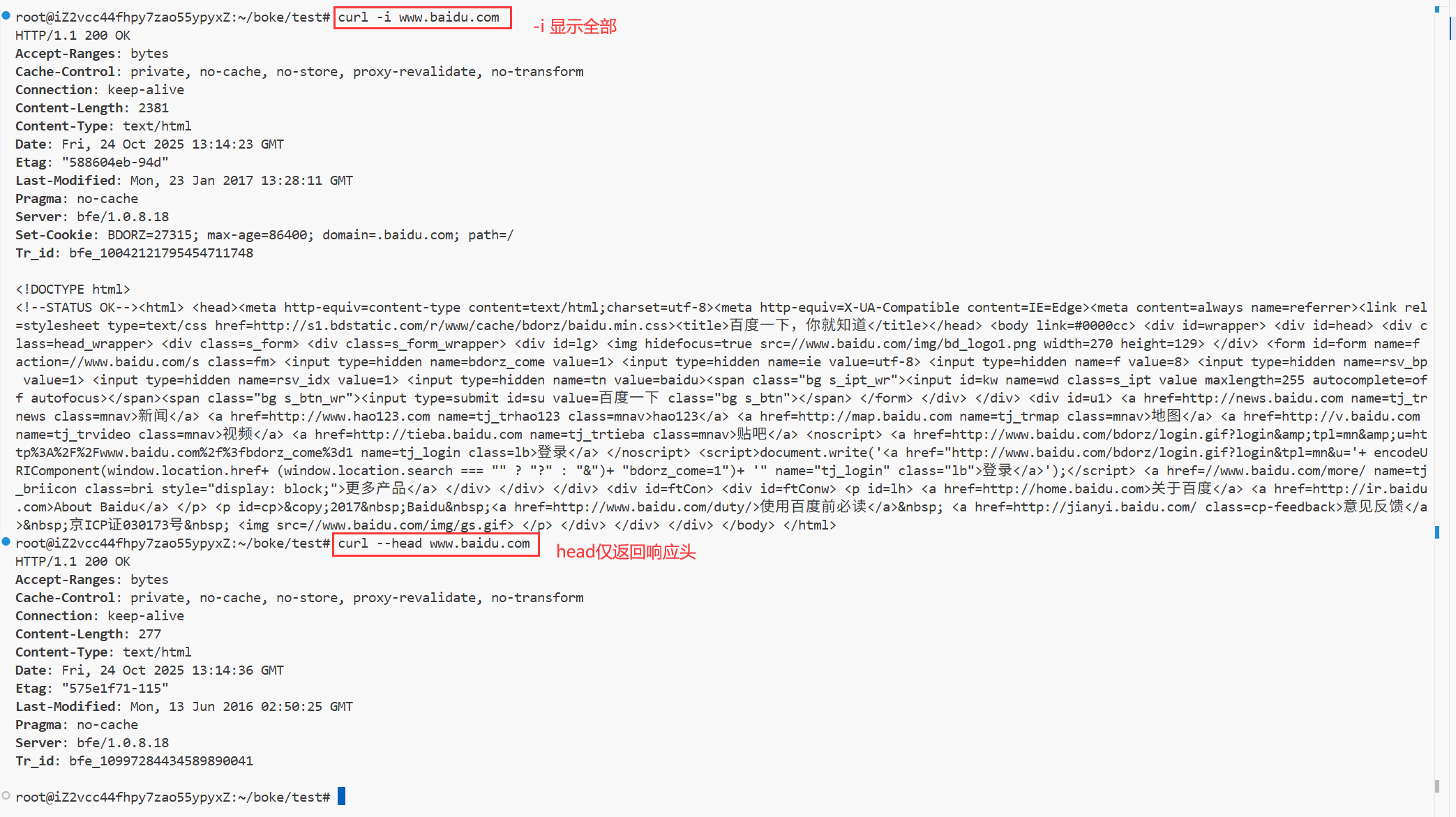
3.4 HEAD方法
- 用途:与GET方法类似,但不返回报文主体部分,仅返回响应头。
- 示例:HEAD /index.html HTTP/1.1
- 特性:用于确认URL的有效性,及资源更新的日期时间等。
3.5 DELETE方法(不常用)
- 用途:用于删除文件,是PUT的相反操作。
- 示例:DELETE /example.html HTTP/1.1
- 特性:按请求URL删除指定的资源。
3.6 OPTIONS方法
- 用途:用于查询针对请求URL指定的资源支持的方法。
- 示例:OPTIONS * HTTP/1.1
- 特性:返回允许的方法,如GET、POST等。
四、HTTP的状态码
最常见的状态码,比如:200(OK)、404(Not Found)、403(Forbidden)、302(Redirect,重定向)、504(Bad Gateway)。
|-----|-----------------------|-------------------------------|
| 状态码 | 含义 | 应用样例 |
| 100 | Continue | 上传大文件时,服务器告诉客⼾端可以继续上传 |
| 200 | OK | 访问⽹站⾸页,服务器返回⽹页内容 |
| 201 | Created | 发布新⽂章,服务器返回⽂章创建成功的信息 |
| 204 | No Content | 删除⽂章后,服务器返回"⽆内容"表⽰操作成功 |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | ⽹站换域名后,⾃动跳转到新域名;搜索引擎更新⽹站链接时使⽤ |
| 302 | Found 或 See Other | ⽤户登录成功后,重定向到⽤户⾸页 |
| 304 | Not Modified | 浏览器缓存机制,对未修改的资源返回304状态码 |
| 400 | Bad Request | 填写表单时,格式不正确导致提交失败 |
| 401 | Unauthorized | 访问需要登录的页⾯时,未登录或认证失败 |
| 403 | Forbidden | 尝试访问你没有权限查看的页⾯ |
| 404 | Not Found | 访问不存在的⽹页链接 |
| 500 | Internal Server Error | 服务器崩溃或数据库错误导致页⾯⽆法加载 |
| 502 | Bad Gateway | 使⽤代理服务器时,代理服务器⽆法从上游服务器获取有效响应 |
| 503 | Service Unavailable | 服务器维护或过载,暂时⽆法处理请求 |
以下是仅包含重定向相关的状态码表格:
|-----|--------------------|----------|-------------------------------|
| 状态码 | 含义 | 是否为临时重定向 | 使用样例 |
| 301 | Moved Permanently | 否(永久重定向) | ⽹站换域名后,⾃动跳转到新域名;搜索引擎更新⽹站链接时使⽤ |
| 302 | Found 或 See Other | 是(临时重定向) | ⽤户登录成功后,重定向到⽤户⾸页 |
| 307 | Temporary Redirect | 是(临时重定向) | 临时重定向资源到新的位置(较少使⽤) |
| 308 | Permanent Redirect | 否(永久重定向) | 永久重定向资源到新的位置(较少使⽤) |
关于重定向的验证,以301为代表:
**HTTP状态码301(永久重定向)和302(临时重定向)都依赖Location选项。**以下是两者依赖Location选项的详细说明:
HTTP状态码301(永久重定向)
- 当服务器返回 HTTP301 状态码时,表示请求的资源已被永久移到新的位置。
- 在这种情况下,服务器会在响应中添加一个Location头部,用于指定资源的新位置。这个Location头部包含了新的URL地址,浏览器会自动重定向到该地址。
- 例如,在HTTP响应中,可能会看到类似于以下的头部信息:
HTTP/ 1.1 301 Moved Permanently\r\n
Location: https: //www.new-url.com\r\n
HTTP状态码302(临时重定向)
- 当服务器返回 HTTP302 状态码时,表示请求的资源已被临时移到新的位置。
- 同样的,服务器会在响应中添加一个Location头部,用于指定资源的新位置。浏览器会暂时使用新的URL进行后续的请求,但不会缓存这个重定向。
- 例如,在HTTP响应中,可能会看到类似于以下的头部信息:
HTTP/ 1.1 302 Found\r\n
Location: https: //www.new-url.com\r\n
总结:无论是HTTP 301还是HTTP 302重定向,都需要依赖Location这个选项来指定资源新的位置。这个Location选项是一个标准的HTTP响应头部,用于告诉浏览器应该将请求重定向到哪个新的URL地址。
五、HTTP常见Header
- Content-Type:数据类型(text/html等)
- Content-Length:Body的长度
- Host:客户端告知服务器,所请求的资源在哪个主机的哪个端口
- User-Agent:声明用户的操作系统和浏览器版本信息
- Referer:当前页面是从哪个页面跳转过来的
- Location:搭配3xx状态码使用,告诉客户端接下来要去哪里访问
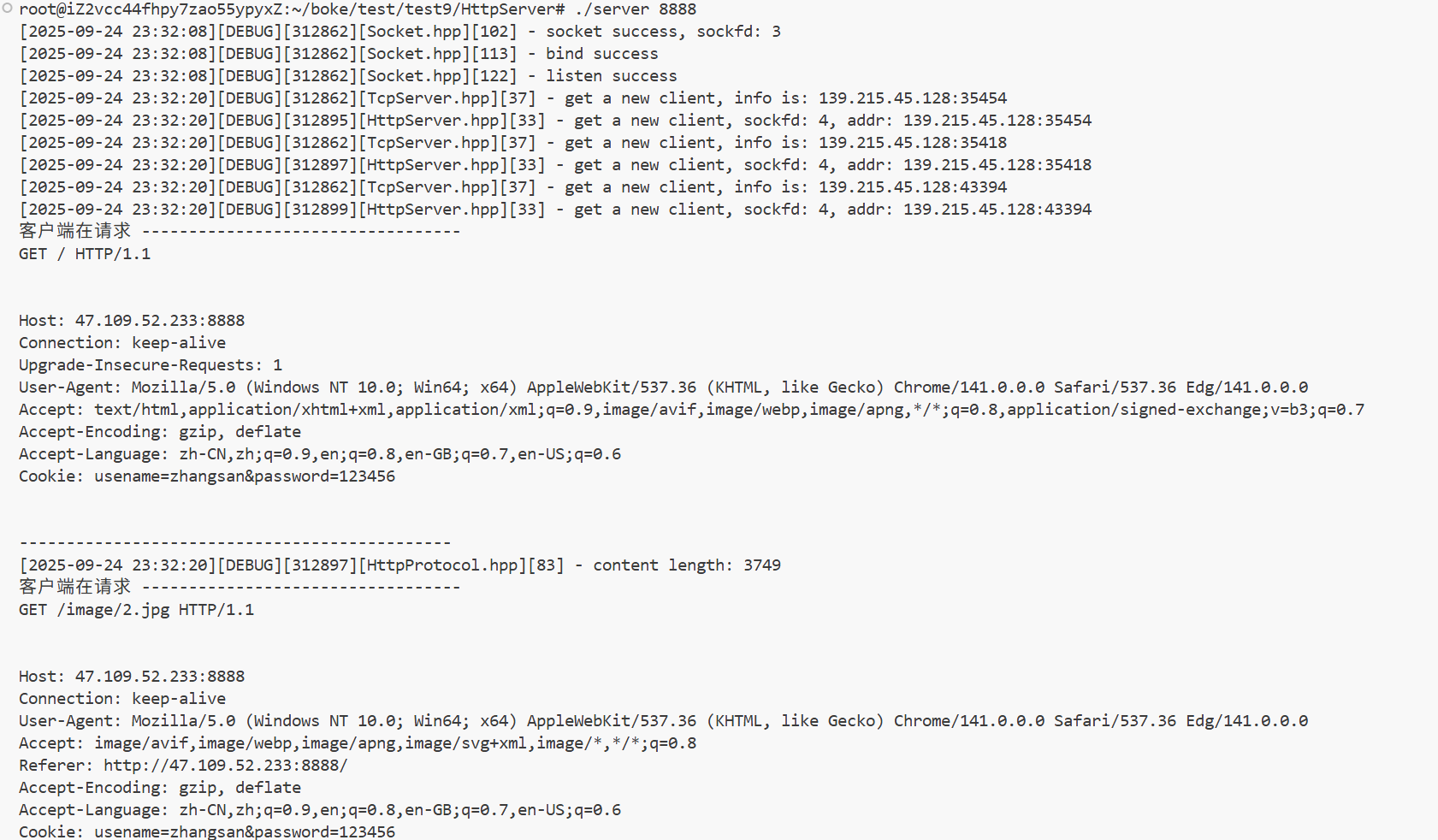
- Cookie:用于在客户端存储少量信息,通常用于实现会话(session)的功能。
关于 connection 报头
HTTP中的 Connection 字段是HTTP报文头的一部分,它主要用于控制和管理客户端与服务器之间的连接状态。
核心作用
- 管理持久连接:Connection 字段还用于管理持久连接(也称为长连接)。持久连接允许客户端和服务器在请求/响应完成之后不立即关闭TCP连接,以便在同一个连接上发送多个请求和接收多个响应。
持久连接(长连接)
- HTTP/1.1:在HTTP/1.1协议中,默认使用持久连接。当客户端和服务器都不明确指定关闭连接时,连接将保持打开状态,以便后续的请求和响应可以复用同一个连接。
- HTTP/1.0:在HTTP/1.1协议中,默认使用非持久的。如果希望在HTTP/1.0中使用持久连接,需要在请求头中显示设置 Connection: keep-alive。
语法格式
- Connection: keep-alive:表示希望保持连接以复用TCP连接。
- Connection: close:表示请求/响应完成后,应该关闭TCP连接。
下面附上一张关于HTTP常见的header的表格:
|-----------------|-------------------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| 字段名 | 含义 | 样例 |
| Accept | 客户端可接受的响应内容类型 | Accept: text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xm l;q=0.9,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8 |
| Accept-Encoding | 客户端⽀持的数据压缩格式 | Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate, br |
| Accept-Language | 客户端可接受的语⾔类型 | Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8 |
| Host | 请求的主机名和端⼝号 | Host: www.example.com:8080 |
| User-Agent | 客户端的软件环境信息 | User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36 |
| Cookie | 客户端发送给服务器的HTTP cookie信息 | Cookie: session_id=abcdefg12345; user_id=123 |
| Referer | 请求的来源URL | Referer: http://www.example.com/previous_page.html |
| Content-Type | 实体主体的媒体类型 | Content-Type: application/x-www-form urlencoded (对于表单提交) 或 Content-Type: application/json (对于JSON数据) |
| Content-Length | 实体主体的字节⼤⼩ | Content-Length: 150 |
| Authorization | 认证信息,如⽤户名和密码 | Authorization: Basic QWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuIHNlc2FtZQ== (Base64编码后的⽤户 名:密码) |
| Cache-Control | 缓存控制指令 | 请求时: Cache-Control: no-cache 或 Cache Control: max-age=3600 ;响应时: Cache Control: public, max-age=3600 |
| Connection | 请求完后是关闭还是保持连接 | Connection: keep-alive 或 Connection: close |
| Date | 请求或响应的⽇期和时间 | Date: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 07:28:00 GMT |
| Location | 重定向的⽬标URL(与3xx状态码配合使⽤) | Location: http://www.example.com/new_location.html (与 302状态码配合使⽤) |
| Server | 服务器类型 | Server: Apache/2.4.41 (Unix) |
| Last-Modified | 资源的最后修改时间 | Last-Modified: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 07:20:00 GMT |
| ETag | 资源的唯⼀标识符,⽤于缓存 | ETag: "3f80f-1b6-5f4e2512a4100" |
| Expires | 响应过期的⽇期和时间 | Expires: Wed, 21 Oct 2023 08:28:00 GMT |
六、一个简单的HTTP服务器
cpp
// Common.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define Die(code) \
do \
{ \
exit(code); \
}while(0) \
#define CONV(addr_ptr) ((struct sockaddr*)(addr_ptr))
enum {
Usage_Err = 1,
Socket_Err,
Bind_Err,
Listen_Err
};
const static int gsockfd = -1;
const static int gbacklog = 6;
bool ParseOneLine(std::string &str, std::string *out, const std::string &sep) {
auto pos = str.find(sep);
if(pos == std::string::npos) return false;
*out = str.substr(0, pos);
str.erase(0, pos);
return true;
}
// Connection: Keep-alive
bool SplitString(std::string &header, const std::string &sep, std::string *key, std::string *value) {
auto pos = header.find(sep);
if(pos == std::string::npos) return false;
*key = header.substr(0, pos);
*value = header.substr(pos + sep.size());
return true;
}
cpp
// InetAddr.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include "Common.hpp"
class InetAddr
{
public:
InetAddr(){}
InetAddr(uint16_t port):_port(port) {
_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
}
InetAddr(const struct sockaddr_in& addr):_addr(addr){
Portntoh();
Ipntoh();
}
bool operator==(const InetAddr& net) {
return _port == net._port && _ip == net._ip;
}
struct sockaddr_in* GetNetAddr() { return &_addr; }
socklen_t NetAddrLen() { return sizeof(_addr); }
uint16_t GetPort() { return _port; }
std::string GetIp() { return _ip; }
std::string Addr() { return _ip + ":" + std::to_string(_port); }
void SetAddr(struct sockaddr_in &client) {
_addr = client;
Portntoh();
Ipntoh();
}
~InetAddr(){}
private:
void Portntoh() {
_port = ntohs(_addr.sin_port);
}
void Ipntoh() {
char buffer[64];
inet_ntop(AF_INET, &_addr.sin_addr, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
_ip = buffer;
}
private:
struct sockaddr_in _addr;
uint16_t _port;
std::string _ip;
};
cpp
// Socket.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include "Log.hpp"
#include "Common.hpp"
#include "InetAddr.hpp"
namespace SocketModule
{
using namespace LogModule;
class Socket;
using SocketPtr = std::shared_ptr<Socket>;
// 封装一个基类:Socket接口类
class Socket
{
public:
virtual ~Socket(){};
virtual SocketPtr Accept(InetAddr *client) = 0;
virtual int GetSockfd() = 0;
virtual void Close() = 0;
virtual bool Recv(std::string *in) = 0;
virtual void Send(std::string &out) = 0;
void BuildListenMethod(uint16_t port, int backlog = gbacklog) {
CreateSocket();
Setsockopt();
Bind(port);
Listen(backlog);
}
virtual void Setsockopt() = 0;
virtual void CreateSocket() = 0;
virtual void Bind(uint16_t port) = 0;
virtual void Listen(int backlog) = 0;
};
class TcpSocket : public Socket
{
public:
TcpSocket(int sockfd = gsockfd):_sockfd(sockfd){}
virtual SocketPtr Accept(InetAddr *client) {
if(!client) return nullptr;
struct sockaddr_in peer;
socklen_t len = sizeof(peer);
int newsockfd = accept(_sockfd, CONV(&peer), &len);
if(newsockfd < 0) {
LOG(LogLevel::WARNING) << "accept err";
return nullptr;
}
client->SetAddr(peer);
return std::make_shared<TcpSocket>(newsockfd);
}
~TcpSocket(){}
virtual int GetSockfd() {
return _sockfd;
}
virtual void Close() {
if(_sockfd != gsockfd) close(_sockfd);
}
virtual bool Recv(std::string *in) {
char inbuffer[1024 * 8];
ssize_t n = recv(_sockfd, inbuffer, sizeof(inbuffer) - 1, 0);
if(n > 0) {
inbuffer[n] = 0;
*in += inbuffer;
return true;
}
else return false;
}
virtual void Send(std::string &out) {
send(_sockfd, out.c_str(), out.size(), 0);
}
virtual void Setsockopt() {
// 保障我们的服务器,异常断开之后,能够自动重连,不会有bind问题
int opt = 1;
int n = setsockopt(_sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &opt, sizeof(opt));
(void)n;
}
virtual void CreateSocket() {
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if(_sockfd < 0) {
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "socket err";
exit(Socket_Err);
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "socket success, sockfd: " << _sockfd;
}
virtual void Bind(uint16_t port) {
InetAddr local(port);
ssize_t n = bind(_sockfd, CONV(local.GetNetAddr()), local.NetAddrLen());
if(n < 0) {
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "bind err";
exit(Bind_Err);
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "bind success";
}
virtual void Listen(int backlog) {
ssize_t n = listen(_sockfd, backlog);
if(n < 0) {
LOG(LogLevel::ERROR) << "listen err";
exit(Listen_Err);
}
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "listen success";
}
private:
int _sockfd;
};
}
cpp
// TcpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include "Socket.hpp"
namespace TcpServerModule
{
using namespace SocketModule;
using namespace LogModule;
using tcphandler_t = std::function<void(SocketPtr, InetAddr)>;
// 只进行IO,不对协议做任何处理
class TcpServer
{
public:
TcpServer(uint16_t port)
:_listensocket(new TcpSocket())
,_port(port)
,_running(false){}
void InitServer(tcphandler_t handler) {
_handler = handler;
_listensocket->BuildListenMethod(_port);
}
void Loop() {
_running = true;
while(_running) {
InetAddr client;
auto sockptr = _listensocket->Accept(&client);
if(!sockptr) continue;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "get a new client, info is: " << client.Addr();
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0) {
_listensocket->Close();
if(fork() > 0) {
sockptr->Close();
exit(0);
}
_handler(sockptr, client);
sockptr->Close();
exit(0);
}
sockptr->Close();
waitpid(id, nullptr, 0);
}
_running = false;
}
~TcpServer() {
_listensocket->Close();
delete _listensocket;
}
private:
Socket* _listensocket;
uint16_t _port;
bool _running;
tcphandler_t _handler;
};
}
cpp
// HttpProtocol.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <fstream>
#include "Common.hpp"
#include "Log.hpp"
const std::string Sep = "\r\n";
const std::string LineSep = " ";
const std::string HeaderLineSep = ": ";
const std::string BlankSep = Sep;
const std::string default_homepage = "wwwroot";
const std::string http_version = "HTTP/1.0";
const std::string page_404 = "wwwroot/404.html";
const std::string first_page = "index.html";
using namespace LogModule;
class HttpRequest
{
public:
// GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1\r\n
// Host: 8.137.19.140:8080
// Connection: keep-alive
// User-Agent: Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/131.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/131.0.0.0
// Accept: image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,image/svg+xml,image/*,*/*;q=0.8
// Referer: http://8.137.19.140:8080/?msg=i_have_sent_a_message_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_he_
// Accept-Encoding: gzip, deflate
// Accept-Language: zh-CN,zh;q=0.9,en;q=0.8,en-GB;q=0.7,en-US;q=0.6
// dnt: 1
// sec-gpc: 1
//
HttpRequest(){}
~HttpRequest(){}
bool IsHashArgs() { return _isexec; }
void Deserialize(std::string &req_header) {
if(ParseOneLine(req_header, &_req_line, Sep)) {
std::stringstream ss(_req_line);
ss >> _method >> _uri >> _version;
ParseHeader(req_header);
_body = req_header;
if(_method == "GET") {
auto pos = _uri.find("?");
if(pos != std::string::npos) {
_isexec = true;
// https://www.baidu.com/s?tn=75144485_dg&ie=utf-8&word=c%2B%2B
_path = _uri.substr(0, pos);
_args = _uri.substr(pos + 1);
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "path: " << _path;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "args: " << _args;
}
else _path = _uri;
}
else if(_method == "POST") {
_isexec = true; // 参数在正文
_path = _uri;
_args = _body;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "path: " << _path;
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "args: " << _args;
}
}
}
std::string GetContent(const std::string &path) {
std::string content;
std::ifstream in(path, std::ios::binary);
if(!in.is_open()) return std::string();
in.seekg(0, in.end);
size_t filesize = in.tellg();
in.seekg(0, in.beg);
content.resize(filesize);
in.read((char*)content.c_str(), filesize);
in.close();
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "content length: " << content.size();
return content;
}
void Print() {
std::cout << _method << ' ' << _uri << ' ' << _version << std::endl;
for(auto& header: _req_header) std::cout << header << std::endl;
std::cout << _blank_line;
std::cout << _body << std::endl;
}
void SetUri(std::string &newuri) { _uri = newuri; }
std::string GetUri() { return _uri; }
std::string GetPath() { return _path; }
std::string GetArgs() { return _args; }
std::string Suffix() {
// 默认为 html 格式
auto pos = _uri.rfind(".");
if(pos == std::string::npos) return ".html";
else return _uri.substr(pos);
}
private:
bool ParseHeaderkv() {
std::string key, value;
for(auto& line: _req_header) {
if(SplitString(line, HeaderLineSep, &key, &value)) _header_kv[key] = value;
else return false;
}
return true;
}
bool ParseHeader(std::string &req_header) {
std::string line;
while(true) {
bool r = ParseOneLine(req_header, &line, Sep);
if(r && line.size()) _req_header.push_back(line);
else if(r && line.empty()) {
_blank_line = Sep;
break;
}
else return false;
}
return ParseHeaderkv();
}
private:
std::string _req_line;
std::vector<std::string> _req_header;
std::string _blank_line;
std::string _body; // body中可能会有数据
// 在序列化中,细化我们解析出来的字段
std::string _method;
std::string _uri;
std::string _path;
std::string _args;
std::string _version;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _header_kv;
bool _isexec = false;
};
// 对于http, 任何请求都要有应答
class HttpResponse
{
public:
HttpResponse()
:_version(http_version), _blank_line(Sep){}
~HttpResponse(){}
void Build(HttpRequest &req) {
std::string uri = default_homepage + req.GetPath();
if(uri.back() == '/') // wwwroot/
uri += first_page; // wwwroot/index.html
std::cout << "客户端在请求 ----------------------------------" << std::endl;
req.Print();
std::cout << "----------------------------------------------" << std::endl;
_content = req.GetContent(uri);
if(_content.empty()) {
_code = 404;
_content = CodeToDesc(_code);
}
else _code = 200;
_desc_code = CodeToDesc(_code); // 和状态码强相关
if(_content.size()) SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(_content.size()));
SetHeader("Content-Type", SuffixToDesc(req.Suffix()));
_body = _content;
}
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &value) {
_header_kv[key] = value;
}
void SetCode(int code) {
_code = code;
_desc_code = CodeToDesc(code);
}
void SetBody(const std::string &body) {
_body = body;
}
void Serialize(std::string *resp_ptr) {
for(auto& header : _header_kv) _resp_header.push_back(header.first + HeaderLineSep + header.second);
_resp_line = _version + " " + std::to_string(_code) + " " + _desc_code;
*resp_ptr = _resp_line + Sep;
for(auto& header : _resp_header) *resp_ptr += header + Sep;
*resp_ptr += _blank_line;
*resp_ptr += _body;
}
private:
std::string CodeToDesc(int code) {
switch(code) {
case 200: return "OK";
case 404: return "Not Found";
case 301: return "Moved Permanently";
case 302: return "Found";
default: return std::string();
}
}
std::string SuffixToDesc(const std::string &suffix) {
if(suffix == ".html")
return "text/html";
else if(suffix == ".jpg")
return "application/x-jpg";
else return "text/html";
}
private:
std::string _version;
int _code;
std::string _desc_code;
std::string _content;
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::string> _header_kv;
// 构建应答,最终需要的四部分
std::string _resp_line;
std::vector<std::string> _resp_header;
std::string _blank_line;
std::string _body;
};
cpp
// HttpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include <unordered_map>
#include "TcpServer.hpp"
#include "HttpProtocol.hpp"
using namespace TcpServerModule;
using http_handler_t = std::function<void(HttpRequest&, HttpResponse&)>;
class HttpServer
{
public:
HttpServer(uint16_t port):_tsptr(std::make_unique<TcpServer>(port)){}
void Register(std::string funcname, http_handler_t func) {
_route[funcname] = func;
}
bool SafeCheck(std::string funcname) {
auto it = _route.find(funcname);
return it != _route.end();
}
void Start() {
_tsptr->InitServer([this](SocketPtr sock, InetAddr client){
return this->HandlerHttpRequest(sock, client);
});
_tsptr->Loop();
}
bool HandlerHttpRequest(SocketPtr sock, InetAddr client) {
LOG(LogLevel::DEBUG) << "get a new client, sockfd: " << sock->GetSockfd() << ", addr: " << client.Addr();
std::string req_str;
sock->Recv(&req_str);
HttpRequest req;
req.Deserialize(req_str);
HttpResponse resp;
if(req.IsHashArgs()) {
std::string path = req.GetPath();
if(SafeCheck(path)) _route[path](req, resp);
else resp.Build(req);
}
else resp.Build(req);
std::string resp_str;
resp.Serialize(&resp_str);
sock->Send(resp_str);
return true;
}
~HttpServer(){}
private:
std::unique_ptr<TcpServer> _tsptr;
std::unordered_map<std::string, http_handler_t> _route; // 功能路由
};
cpp
// HttpServer.cc
#include "HttpServer.hpp"
// 这个登入功能只是简单实现,能够大致展示HTTP服务器的执行,大家可以详细实现以下
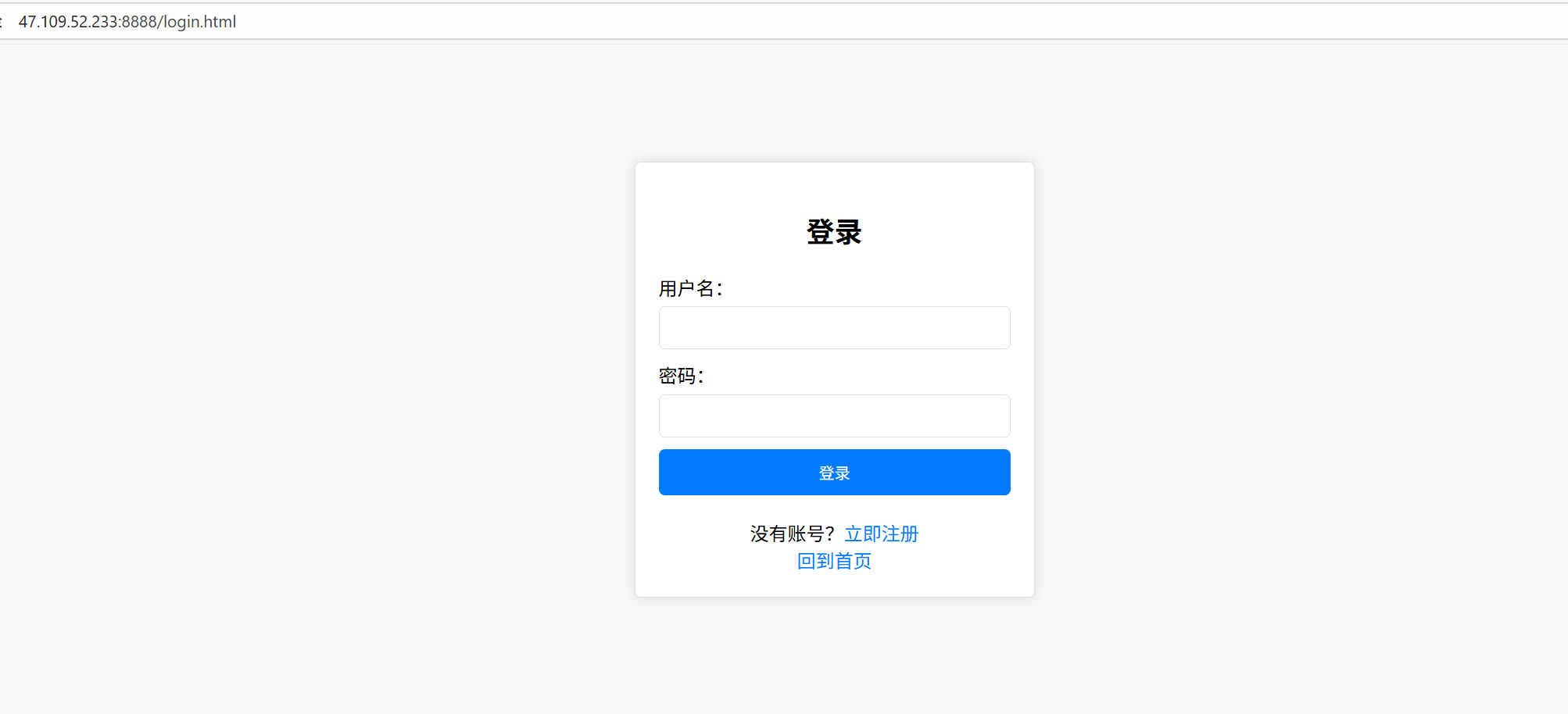
void Login(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &resp) {
std::string req_args = req.GetArgs();
// 1. 解析参数格式,获取想要的数据
// 2. 访问数据,验证用户是否合法,其他操作
// 3. 登入成功
std::string body = req.GetContent("wwwroot/success.html");
resp.SetCode(200);
resp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(body.size()));
resp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");
resp.SetHeader("Set-Cookie", "usename=zhangsan&password=123456");
resp.SetBody(body);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
if(argc != 2) {
std::cout << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " server_port" << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::unique_ptr<HttpServer> hs_ptr = std::make_unique<HttpServer>(std::stoi(argv[1]));
hs_ptr->Register("/login", Login);
hs_ptr->Start();
return 0;
}