本文是小编巩固自身而作,如有错误,欢迎指出!
目录
[一、unordered map and unordered set](#一、unordered map and unordered set)
一、unordered map and unordered set
在前文我们已经学过了map和set而unordered map 和 unordered set又是什么呢?首先,很明显unordered的意思是"无序的",和寻常的map和set在表达上最大的区别就map和set是有序的,而后者是无序的 ,在底层上最大的区别就是map和set是由红黑树组成,而后者是由哈希表组成。
二、哈希表
1.直接定址法
当关键字的范围⽐较集中时,直接定址法就是⾮常简单⾼效的⽅法,⽐如⼀组关键字都在[0,99]之间, 那么我们开⼀个100个数的数组,每个关键字的值直接就是存储位置的下标。
而我们今天学习的哈希表的实现就是类似这样的实现方法,采用一一映射的方法使数据被储存在不同的空间中。
2.哈希冲突
在上述的直接定址法,存在一个很大的缺陷:
当关键字的范围⽐较分散时,就很浪费内存甚⾄内存不够⽤。假设我 们只有数据范围是[0,9999]的N个值,我们要映射到⼀个M个空间的数组中(⼀般情况下M>=N),那么 就要借助哈希函数 (hashfunction)hf,关键字key被放到数组的h(key)位置,这⾥要注意的是h(key)计 算出的值必须在[0,M)之间。
而在这种情况下,就会出现一种情况是什么呢?就是两个不同的key会映射到相同的位置上去,那么此刻该怎么处理呢?就是我们今天要学习的哈希表的核心问题。
3.负载因子
假设哈希表中已经映射存储了N个值,哈希表的⼤⼩为M,那么负载因子=N/M,负载因⼦有些地⽅ 也翻译为载荷因⼦/装载因⼦等,他的英⽂为load factor。负载因⼦越⼤,哈希冲突的概率越⾼,空间 利⽤率越⾼;负载因⼦越⼩,哈希冲突的概率越低,空间利⽤率越低;
4.1除法散列法/除留余数法
除法散列法也叫做除留余数法,顾名思义,假设哈希表的⼤⼩为M,那么通过key除以M的余数作为 映射位置的下标,也就是哈希函数为:h(key)=key%M。
当使⽤除法散列法时,要尽量避免M为某些值,如2的幂,10的幂等。如果是2^x ,那么key %2^x本质相当于保留key的后X位,那么后x位相同的值,计算出的哈希值都是⼀样的,就冲突了。如:{63 , 31}看起来没有关联的值,如果M是16,也就是 ,那么计算出的哈希值都是15,因为63的⼆进制后8位是 00111111,31的⼆进制后8位是 00011111。如果是 10^x,就更明显了,保留的都是10进值的后x位,如:{112, 12312},如果M是100,也就是10^2 ,那么计算出的哈希值都是12。
三、哈希冲突的处理
实践中哈希表⼀般还是选择除法散列法作为哈希函数,当然哈希表⽆论选择什么哈希函数也避免不了 冲突,那么插⼊数据时,如何解决冲突呢?主要有两种两种⽅法,开放定址法和链地址法。
1.开放定址法
开放定址法其中一个主要的方法就是用我们上面所述的除法散列法。
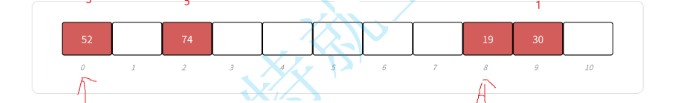
然后使用线性探测:从发⽣冲突的位置开始,依次线性向后探测,直到寻找到下⼀个没有存储数据的位置为⽌,如果⾛走到哈希表尾,则回绕到哈希表头的位置。

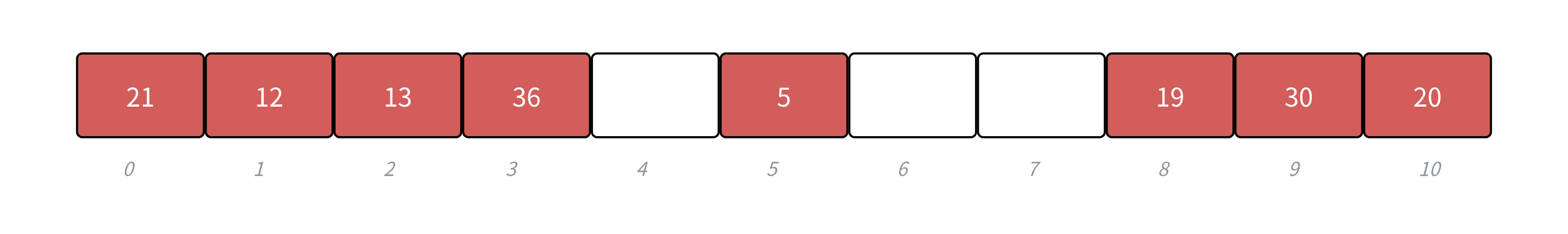
下⾯演⽰ {19,30,5,36,13,20,21,12} 等这⼀组值映射到M=11的表中
cpp
namespace open_way
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable()
:_tables(11)
, _n(0)
{
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if ((double)_n / (double)_tables.size() >= 0.7)//扩容
{
//std::vector<HashData<K, V>> newtables(_tables.size()*2);
////遍历旧表将其映射到新表
//for (auto& data : _tables)
//{
// if (data._status == EXIST)
// {
// //...
// }
//}
//_tables.swap(newtables);
HashTable<K, V, Hash> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(_tables.size() * 2); // 新表大小为原表2倍
//遍历旧表将其映射到新表
for (auto& data : _tables)
{
if (data._status == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(data._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
_n = newHT._n; // 同步新表的有效元素数
}
Hash hs;
size_t hash0 = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
size_t hashi = hash0;
size_t i = 1;
//线性探测
while (_tables[hashi]._status == EXIST)//当前位置已经存在时
{
hashi = (hash0 + i) % _tables.size();
++i;
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._status = EXIST;
++_n;
return true;
}
HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hash0 = hs(key) % _tables.size();
size_t hashi = hash0;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._status != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._status == EXIST && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi = (hash0 + i) % _tables.size();
++i;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
auto* ptr = Find(key);
if (ptr)
{
ptr->_status = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
private:
std::vector<HashData<K, V>> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;//有效数据的个数
};
void testhash1()
{
HashTable<int, int> ht;
int a[] = { 19,30,5,36,13,20,21,12,58 };
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert({ e, e });
}
cout << ht.Find(5) << endl;
cout << ht.Find(58) << endl;
ht.Erase(5);
cout << ht.Find(5) << endl;
cout << ht.Find(58) << endl;
for (size_t i = 100; i < 200; i++)
{
ht.Insert({ i, i });
}
}
struct StringHashFunc
{
// BKDR
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash += ch;
hash *= 131;
}
return hash;
}
};
void testhash2()
{
HashTable<string, string, StringHashFunc> dict;
dict.Insert({ "insert", "插入" });
auto ptr = dict.Find("insert");
if (ptr)
{
cout << ptr->_kv.second << endl;
}
StringHashFunc hf;
cout << hf("abcd") << endl;
cout << hf("bcad") << endl;
cout << hf("aadd") << endl;
}
}上述的代码就是我们通过除法散列法实现的哈希表,除了上面我们讲到的关于如何处理哈希冲突,我们这里还额外强调一点就是key不是整数而是string类的情况
cpp
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<> // 模板特化标记
struct HashFunc<string> // 特化string类型
{
size_t operator()(const string& str) // 复用你的BKDR算法
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash += ch;
hash *= 131;
}
return hash;
}
};这里我们专门实现了一个模版用来将我们的key转化为整数。
2.链地址法
所谓链地址法,很好理解,就是解决哈希冲突的方法是通过链表来实现的,在前面我们学习的线性探测法,是出现冲突就将其向后挪,而链地址法,就是出现了冲突,我们直接将其制作成一个链表,将其链接在下面
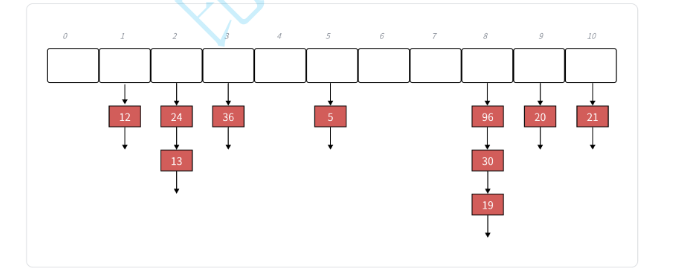
像这种这种方法解决哈希冲突我们一般将其称作哈希桶。
与上面的开放定址法的一个很大区别就在于链地址法的负载因子可以达到一再进行扩容。
四、完整代码实现及测试结果
.h文件
cpp
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<utility>
using namespace std;
enum Status
{
EXIST,
EMPTY,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
Status _status=EMPTY;
};
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<> // 模板特化标记
struct HashFunc<string> // 特化string类型
{
size_t operator()(const string& str) // 复用你的BKDR算法
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash += ch;
hash *= 131;
}
return hash;
}
};
namespace open_way
{
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable()
:_tables(11)
, _n(0)
{
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if ((double)_n / (double)_tables.size() >= 0.7)//扩容
{
//std::vector<HashData<K, V>> newtables(_tables.size()*2);
////遍历旧表将其映射到新表
//for (auto& data : _tables)
//{
// if (data._status == EXIST)
// {
// //...
// }
//}
//_tables.swap(newtables);
HashTable<K, V, Hash> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(_tables.size() * 2); // 新表大小为原表2倍
//遍历旧表将其映射到新表
for (auto& data : _tables)
{
if (data._status == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(data._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
_n = newHT._n; // 同步新表的有效元素数
}
Hash hs;
size_t hash0 = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();
size_t hashi = hash0;
size_t i = 1;
//线性探测
while (_tables[hashi]._status == EXIST)//当前位置已经存在时
{
hashi = (hash0 + i) % _tables.size();
++i;
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._status = EXIST;
++_n;
return true;
}
HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hs;
size_t hash0 = hs(key) % _tables.size();
size_t hashi = hash0;
size_t i = 1;
while (_tables[hashi]._status != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._status == EXIST && _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi = (hash0 + i) % _tables.size();
++i;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
auto* ptr = Find(key);
if (ptr)
{
ptr->_status = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
private:
std::vector<HashData<K, V>> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;//有效数据的个数
};
void testhash1()
{
HashTable<int, int> ht;
int a[] = { 19,30,5,36,13,20,21,12,58 };
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert({ e, e });
}
cout << ht.Find(5) << endl;
cout << ht.Find(58) << endl;
ht.Erase(5);
cout << ht.Find(5) << endl;
cout << ht.Find(58) << endl;
for (size_t i = 100; i < 200; i++)
{
ht.Insert({ i, i });
}
}
struct StringHashFunc
{
// BKDR
size_t operator()(const string& str)
{
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto ch : str)
{
hash += ch;
hash *= 131;
}
return hash;
}
};
void testhash2()
{
HashTable<string, string, StringHashFunc> dict;
dict.Insert({ "insert", "插入" });
auto ptr = dict.Find("insert");
if (ptr)
{
cout << ptr->_kv.second << endl;
}
StringHashFunc hf;
cout << hf("abcd") << endl;
cout << hf("bcad") << endl;
cout << hf("aadd") << endl;
}
}
namespace Hash_bucket
{
template<class K,class V>
struct HashNode
{
pair<K, V> _KV;
HashNode<K, V>* _next;
HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv)
:_KV(kv)
, _next(nullptr)
{
}
};
template<class K, class V>
class HashTable
{
typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;
public:
HashTable()
:_tables(11)
,_n(0)
{
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
//扩容
if (_n == _tables.size())
{
//HashTable<K, V> newHT;
//newHT._tables.resize(_tables.size() * 2);
//for (auto cur : _tables)
//{
// newHT.Insert(cur->_kv);
// cur = cur->_next;
//}
//_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
vector<Node*> newtables(_tables.size() * 2);
for (size_t i = 0;i < _tables.size();i++)
{
Node* cur = _tables[i];
while (cur)
{
Node* next = cur->_next;
size_t hashi = cur->_KV.first % newtables.size();
cur->_next = newtables[hashi];
newtables[hashi] = cur;
cur = next;
}
_tables[i] = nullptr;
}
_tables.swap(newtables);
}
size_t hashi = kv.first % _tables.size();
//头插
Node* newNode = new Node(kv);
newNode->_next = _tables[hashi];
_tables[hashi] = newNode;
++_n;
return true;
}
Node* Find(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
whiel(cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return nullptr;
}
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
size_t hashi = key % _tables.size();
Node* prev=nullptr;
Node* cur = _tables[hashi];
while(cur)
{
if (cur->_kv.first == key)
{
if (prev == nullptr)//第一个节点
{
_tables[hashi] = cur->next;
}
else
{
prev->_next = cur->_next;
}
delete cur;
return true;
}
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
private:
vector<Node*> _tables;
size_t _n = 0;
};
void testhash1()
{
HashTable<int, int> ht;
int a[] = { 19,30,5,36,13,20,21,12,58 };
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert({ e, e });
}
//cout << ht.Find(5) << endl;
//cout << ht.Find(58) << endl;
//ht.Erase(5);
//cout << ht.Find(5) << endl;
//cout << ht.Find(58) << endl;
// for (size_t i = 100; i < 200; i++)
// {
// ht.Insert({ i, i });
// }
}
}.cpp文件
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<set>
#include"HashTable.h"
using namespace std;
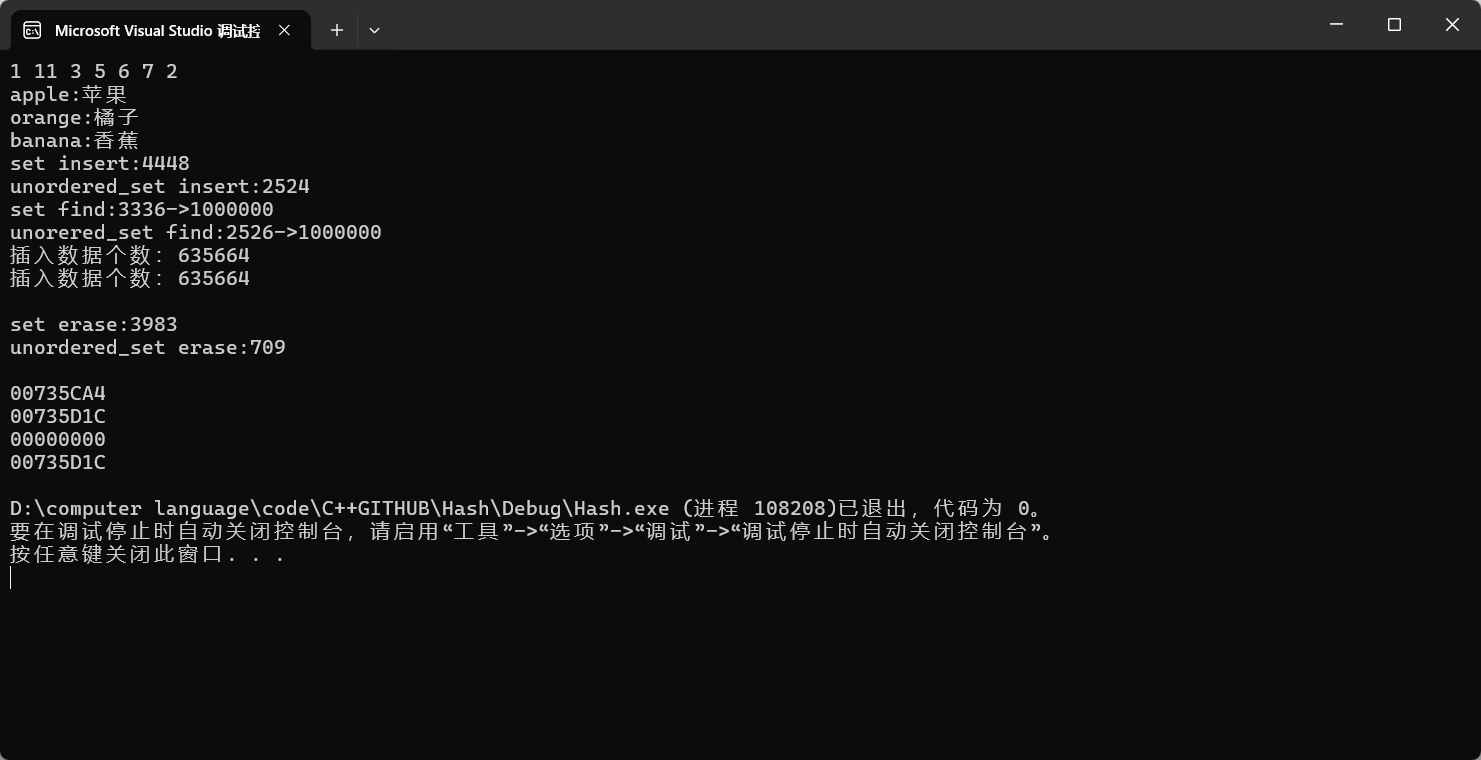
void test01()
{
unordered_set<int> s1 = { 1,3,5,6,7,2 };
s1.insert(11);
auto it = s1.begin();
while (it != s1.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
it++;
}
cout << endl;
unordered_map<string, string> dict;
dict.insert({ "apple","苹果" });
dict.insert({ "orange","橘子" });
dict.insert({ "banana","香蕉" });
for (auto& [k, v] : dict)
{
cout << k << ":" << v << endl;
}
}
int test02()
{
const size_t N = 1000000;
unordered_set<int> us;
set<int> s;
vector<int> v;
v.reserve(N);
srand(time(0));
for (size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
//v.push_back(rand()); // N比较大时,重复值比较多
v.push_back(rand() + i); // 重复值相对少
//v.push_back(i); // 没有重复,有序
}
size_t begin1 = clock();
for (auto e : v)
{
s.insert(e);
}
size_t end1 = clock();
cout << "set insert:" << end1 - begin1 << endl;
size_t begin2 = clock();
us.reserve(N);
for (auto e : v)
{
us.insert(e);
}
size_t end2 = clock();
cout << "unordered_set insert:" << end2 - begin2 << endl;
int m1 = 0;
size_t begin3 = clock();
for (auto e : v)
{
auto ret = s.find(e);
if (ret != s.end())
{
++m1;
}
}
size_t end3 = clock();
cout << "set find:" << end3 - begin3 << "->" << m1 << endl;
int m2 = 0;
size_t begin4 = clock();
for (auto e : v)
{
auto ret = us.find(e);
if (ret != us.end())
{
++m2;
}
}
size_t end4 = clock();
cout << "unorered_set find:" << end4 - begin4 << "->" << m2 << endl;
cout << "插入数据个数:" << s.size() << endl;
cout << "插入数据个数:" << us.size() << endl << endl;
size_t begin5 = clock();
for (auto e : v)
{
s.erase(e);
}
size_t end5 = clock();
cout << "set erase:" << end5 - begin5 << endl;
size_t begin6 = clock();
for (auto e : v)
{
us.erase(e);
}
size_t end6 = clock();
cout << "unordered_set erase:" << end6 - begin6 << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
int main()
{
//test01();
//test02();
//testhash1();
//testhash2();
Hash_bucket::testhash1();
return 0;
}
本次分享就到这里结束了,后续会继续更新,感谢阅读!