一、 主机
| ip | 主机名 |
|---|---|
| 192.168.25.250 | ES01 |
| 192.168.25.130 | ES02 |
| 192.168.25.131 | ES03 |
二、系统初始化
所有主机执行:
systemctl disable firewalld --now
sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/g' /etc/selinux/config
setenforce 0
swapoff -a && sed -i "s/^[^#]*swap*/#&/g" /etc/fstab
groupadd elasticsearch
useradd elasticsearch
useradd -g elasticsearch elasticsearch
echo "elasticsearch" | passwd --stdin elasticsearch
echo "elasticsearch ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: ALL" >> /etc/sudoers.d/elasticsearch
echo "
# 设置elasticsearch用户进程能打开的最大文件句柄
elasticsearch - nofile 65535
# 设置elasticsearch用户进程锁定使用物理内存
elasticsearch soft memlock unlimited
elasticsearch hard memlock unlimited
# 设置elasticsearch 用户进程创建的最大线程数
elasticsearch soft nproc 4096
elasticsearch hard nproc 4096
# 不限制elasticsearch用户创建文件的大小
elasticsearch soft fsize unlimited
elasticsearch hard fsize unlimited
" >> /etc/security/limits.conf
# 重新登录shell终端生效
echo "
# 设置个进程可创建的最大内存映射区域数量
vm.max_map_count=262144
# 设置tcp重传个数
net.ipv4.tcp_retries2=5
" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
# 立即生效
sysctl -phosts配置:
echo "192.168.25.250 ES01
192.168.25.130 ES02
192.168.25.131 ES03 " >> /etc/hosts三、部署Elasticsearch
1. 下载Elasticsearch
所有主机执行:
mkdir /opt/es && cd /opt/es
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-9.1.5-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-9.1.5-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch * -R
su elasticsearch
cd elasticsearch-9.1.52. 配置修改
2.1. JVM参数修改
所有主机执行:
config/jvm.options.d/custom_jvm.options:
clike
# 统一内存堆栈大小,不可超过物理内存50%
-Xms2g
-Xmx2g
# 使用G1 垃圾回收
-XX:+UseG1GC
# es 运行时产生的临时可执行文件
-Djava.io.tmpdir=/home/elasticsearch/es/tmp
# 指定gc参数及日志文件存放地址
-Xlog:gc*,gc+age=trace,safepoint:file=/home/elasticsearch/es/logs/gc.log:utctime,level,pid,tags:filecount=32,filesize=64m
# JVM 内存溢出时,将日志文件写入指的目录下
-XX:HeapDumpPath=/home/elasticsearch/es/HeapDump目录文件提前下载:
mkdir -pv /home/elasticsearch/es/tmp
mkdir -pv /home/elasticsearch/es/HeapDump
mkdir -pv /home/elasticsearch/es/data
mkdir -pv /home/elasticsearch/es/logs2.2. elasticsearch配置修改
ES01 :
config/elasticsearch.yml:
clike
# 集群名称
cluster.name: elasticsearch-cluster
# 节点角色
node.roles: [master, data]
# 节点名称
node.name: ES01
# 设置日志和数据存储目录,建议是设置到es目录外,应为es升级会删除数据
path.data: /home/elasticsearch/es/data
path.logs: /home/elasticsearch/es/logs
# 锁定es必须使用物理内存
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
# 设置网络接口和端口绑定
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
# 设置选举使用的9300端口绑定到本地所有接口上
transport.host: 0.0.0.0
# 设置是否允许使用通配符删除索引
action.destructive_requires_name: false
# 客户端通过http接口发送给 Elasticsearch 的请求体最大值
http.max_content_length: 100mb
# 参与主节点选举的节点,所有节点加入后注释掉此项
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["ES01","ES02","ES03"]
# 节点发现
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.25.250:9300", "192.168.25.130:9300", "192.168.25.131:9300"]
# 关闭安全特性
xpack.security.enabled: falseES02 :
config/elasticsearch.yml:
clike
# 集群名称
cluster.name: elasticsearch-cluster
# 节点角色
node.roles: [master, data]
# 节点名称
node.name: ES02
# 设置日志和数据存储目录,建议是设置到es目录外,应为es升级会删除数据
path.data: /home/elasticsearch/es/data
path.logs: /home/elasticsearch/es/logs
# 锁定es必须使用物理内存
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
# 设置网络接口和端口绑定
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
# 设置选举使用的9300端口绑定到本地所有接口上
transport.host: 0.0.0.0
# 设置是否允许使用通配符删除索引
action.destructive_requires_name: false
# 客户端通过http接口发送给 Elasticsearch 的请求体最大值
http.max_content_length: 100mb
# 节点发现
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.25.250:9300", "192.168.25.130:9300", "192.168.25.131:9300"]
# 关闭安全特性
xpack.security.enabled: falseES03:
config/elasticsearch.yml
clike
# 集群名称
cluster.name: elasticsearch-cluster
# 节点角色
node.roles: [master, data]
# 节点名称
node.name: ES03
# 设置日志和数据存储目录,建议是设置到es目录外,应为es升级会删除数据
path.data: /home/elasticsearch/es/data
path.logs: /home/elasticsearch/es/logs
# 锁定es必须使用物理内存
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
# 设置网络接口和端口绑定
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
# 设置选举使用的9300端口绑定到本地所有接口上
transport.host: 0.0.0.0
# 设置是否允许使用通配符删除索引
action.destructive_requires_name: false
# 客户端通过http接口发送给 Elasticsearch 的请求体最大值
http.max_content_length: 100mb
# 节点发现
discovery.seed_hosts: ["192.168.25.250:9300", "192.168.25.130:9300", "192.168.25.131:9300"]
# 关闭安全特性
xpack.security.enabled: false启动:
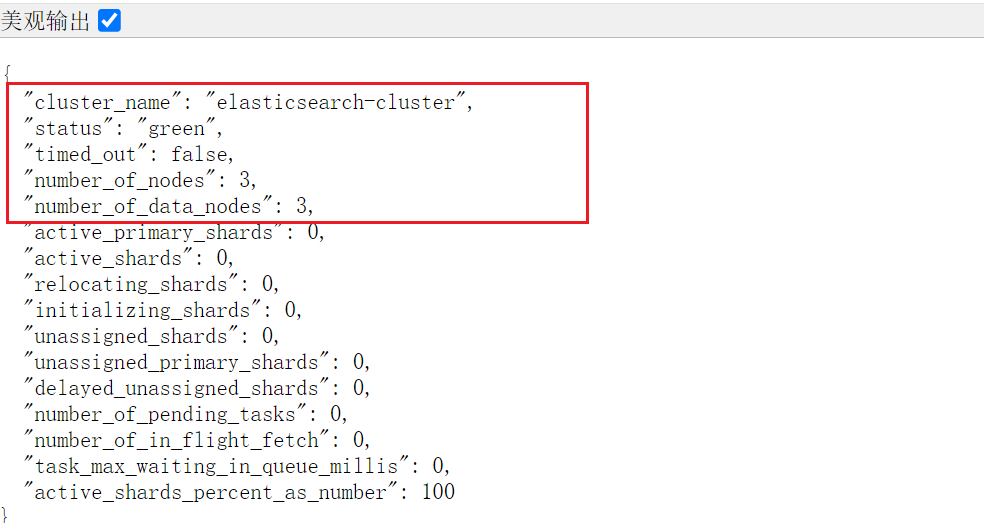
./bin/elasticsearch查看集群状态
http://ip:9200/_cluster/health
查看主节点:
curl http://localhost:9200/_cat/master?v
clike
id host ip node
5X28PDTrSXiaikpy89RVrg 192.168.25.250 192.168.25.250 ES01四、部署kibana
1. 下载kibana
cd /opt/es
sudo wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-9.1.5-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
sudo tar -zxvf kibana-9.1.5-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
sudo chown elasticsearch.elasticsearch kibana-9.1.5 -R
cd kibana-9.1.52.配置文件修改
config/kibana.yml:
clike
# 接口地址和端口号
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0" # 允许所有IP访问
# 公网域名(若通过域名访问,建议配置,如 "https://kibana.example.com")
# server.publicBaseUrl: ""
# 限制客户端请求体大小(5MB,合理,避免大请求攻击)
server.maxPayload: 5242880
# Kibana服务名(自定义,便于识别)
server.name: "kibana-server"
# =================== System: Logging ===================
# 日志级别(info 适合生产,平衡信息量和性能)
logging.root.level: info
# 日志输出器(仅保留滚动文件配置,支持按大小轮转)
logging.appenders.default:
type: rolling-file
fileName: logs/kibana.log # 日志路径,当前路径下
policy:
type: size-limit
size: 100mb # 单文件100MB
strategy:
type: numeric
max: 10 # 保留10个历史文件(总约1GB)
layout:
type: json # JSON格式,便于日志分析
# =================== System: Other ===================
# 自定义数据目录
path.data: data # 数据路径(当前目录下的data)
# 性能指标采样间隔/ms
ops.interval: 5000
# 界面语言
i18n.locale: "zh-CN"
# PID文件路径(系统标准目录,更规范)
# pid.file: kibana.pid # pid文件路径
# =================== Saved Objects: Migrations ===================
# 迁移配置(生产环境优化)
migrations.batchSize: 500 # 单批迁移500个对象,降低内存压力
migrations.maxBatchSizeBytes: 90mb # 小于ES的http.max_content_length(默认100mb)
migrations.retryAttempts: 15 # 重试次数./bin/kibana由于关闭了安全特性,所以不需要密码就可以直接登录
访问kibana
五、部署filebeat
1. 下载filebeat
su - root
cd /opt/es
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-9.1.5-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxvf filebeat-9.1.5-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
cd filebeat-9.1.5-linux-x86_642. 配置修改
filebeat.yml:
clike
filebeat.config.inputs:
enabled: true # 启用外部配置文件
paths:
- ./conf.d/*.yml
reload.enabled: true
reload.period: 10s # 每隔10s检查配置有没有被修改
#自动添加IP(host.ip)
processors:
- add_host_metadata:
matchers:
- ip:
private: true
public: false
# 索引模板配置
setup.template.enabled: true
setup.template.name: "filebeat"
setup.template.fields: "fields.yml"
setup.template.overwrite: true
setup.template.pattern: "%{[fields.log_type]}-%{[agent.version]}-*"
setup.template.settings:
index.number_of_shards: 3 # 主分片数(建议与节点数匹配)
index.number_of_replicas: 1 # 副本分片数(高可用)
# 输出配置
output.elasticsearch:
hosts: ["192.168.25.250:9200", "192.168.25.130:9200","192.168.25.131:9200"]
protocol: http
path: /
# 自定义索引
index: "%{[fields.log_type]}-%{[agent.version]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"
max_retries: 3 # 日志发送失败后的最大重试次数(-1 表示无限重试)
retry_backoff: 1s # 重试间隔时间
bulk_max_size: 2048 # 批量发送的最大日志条数
worker: 2 # 并发发送日志的工作线程数(默认 1)
# 定义采集到的日志发送到哪里,这里配置发送到 elasticsearch进行后续处理
logging.level: info # 日志级别(可选:trace > debug > info > warn > error > fatal)
logging.to_files: true # 是否将自身日志写入文件
logging.files:
path: /opt/es/filebeat-9.1.5-linux-x86_64/logs # 日志的存储路径
name: filebeat # 日志文件名前缀
keepfiles: 7 # 日志文件的保留天数
permissions: 0600 # 日志文件的权限通过外部配置文件获取日志:
mkdir conf.dconf.d/message.yml:
clike
# 系统日志采集:/var/log/messages
- type: filestream
id: system-messages
enabled: true
paths:
- /var/log/messages # 读取的日志路径
fields:
log_type: system-log # 标记日志类型(用于索引名)
service: os
encoding: utf-8
ignore_older: 24h # 忽略24小时前的日志
start_position: end # 从文件末尾开始读取
tags: ["system", "os","linux"]启动filebeat:
./filebeat查看ES中是否已经有了索引
curl 'http://192.168.25.250:9200/_cat/indices?v'
clike
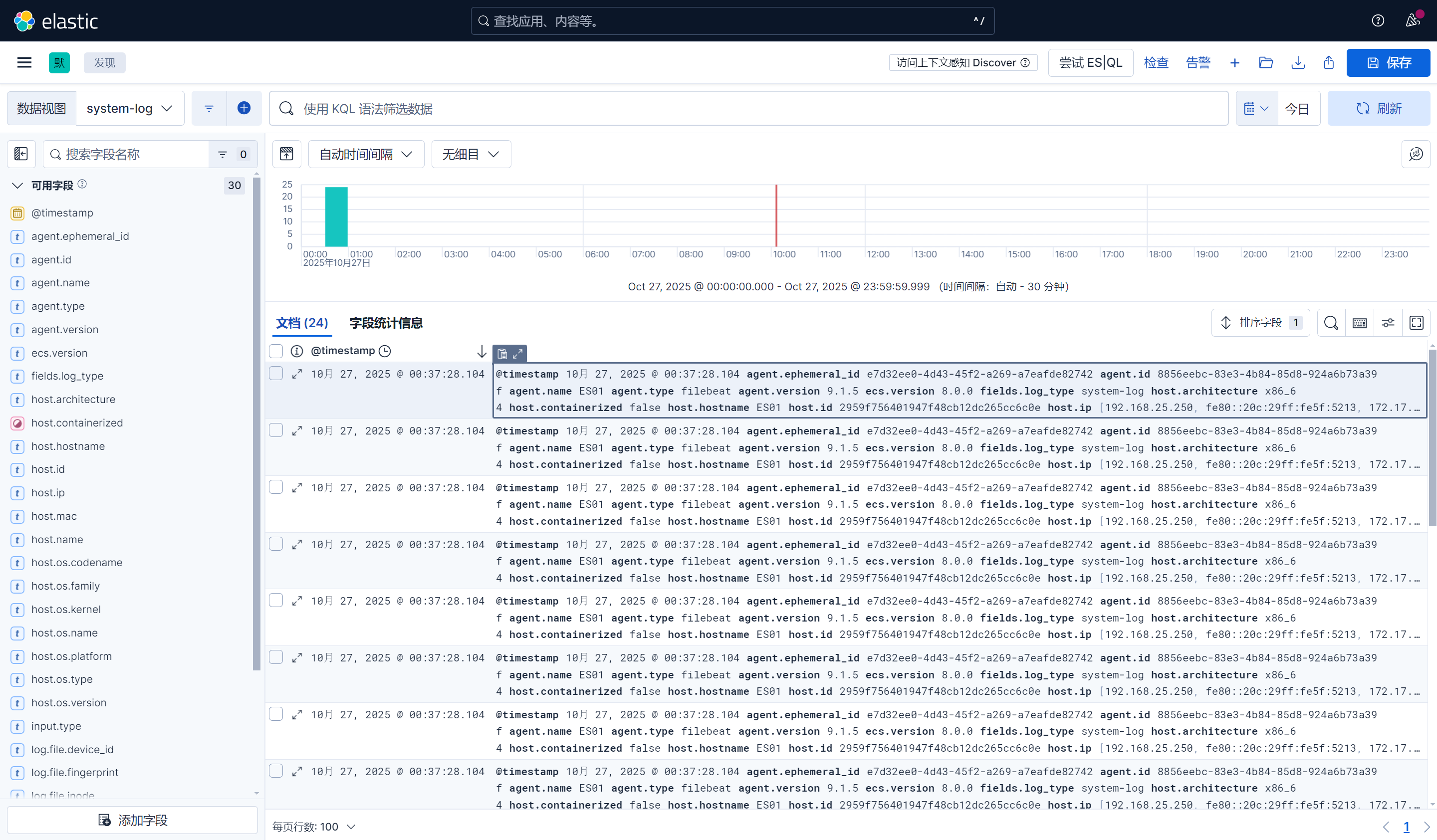
green open system-log-9.1.5-2025.10.27 AJ5dZj8uRVGQvjtVymjPIw 1 1 24 0 75.1kb 37.5kb 37.5kb六、在kibana上查看日志
1. 创建视图
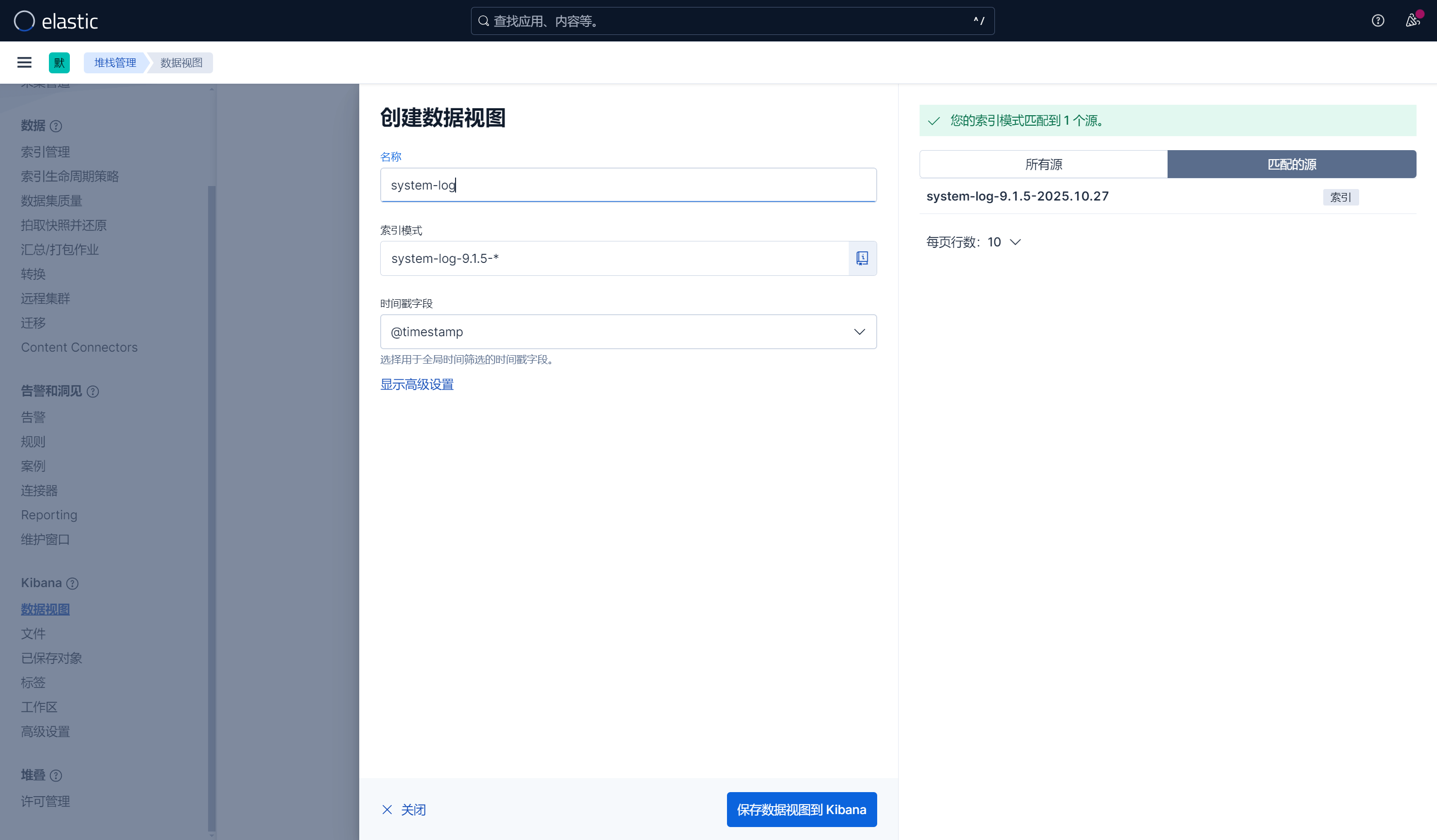
查看日志: