系列
前言
最近在做 2D 图形渲染相关的项目。由于真实数据还不完善,我一直使用手写 mock 数据进行测试,但这样很难覆盖所有业务场景。于是我开始思考------是否可以借助 AI 自动生成测试数据?更进一步,如果让 AI 直接生成设计稿,再交给渲染系统呈现,不就能同时提升开发效率和产品质量吗?如今不少产品已经开始接入 AI 提效,这件事值得折腾一下。
效果图:
左侧为设计,右侧为html
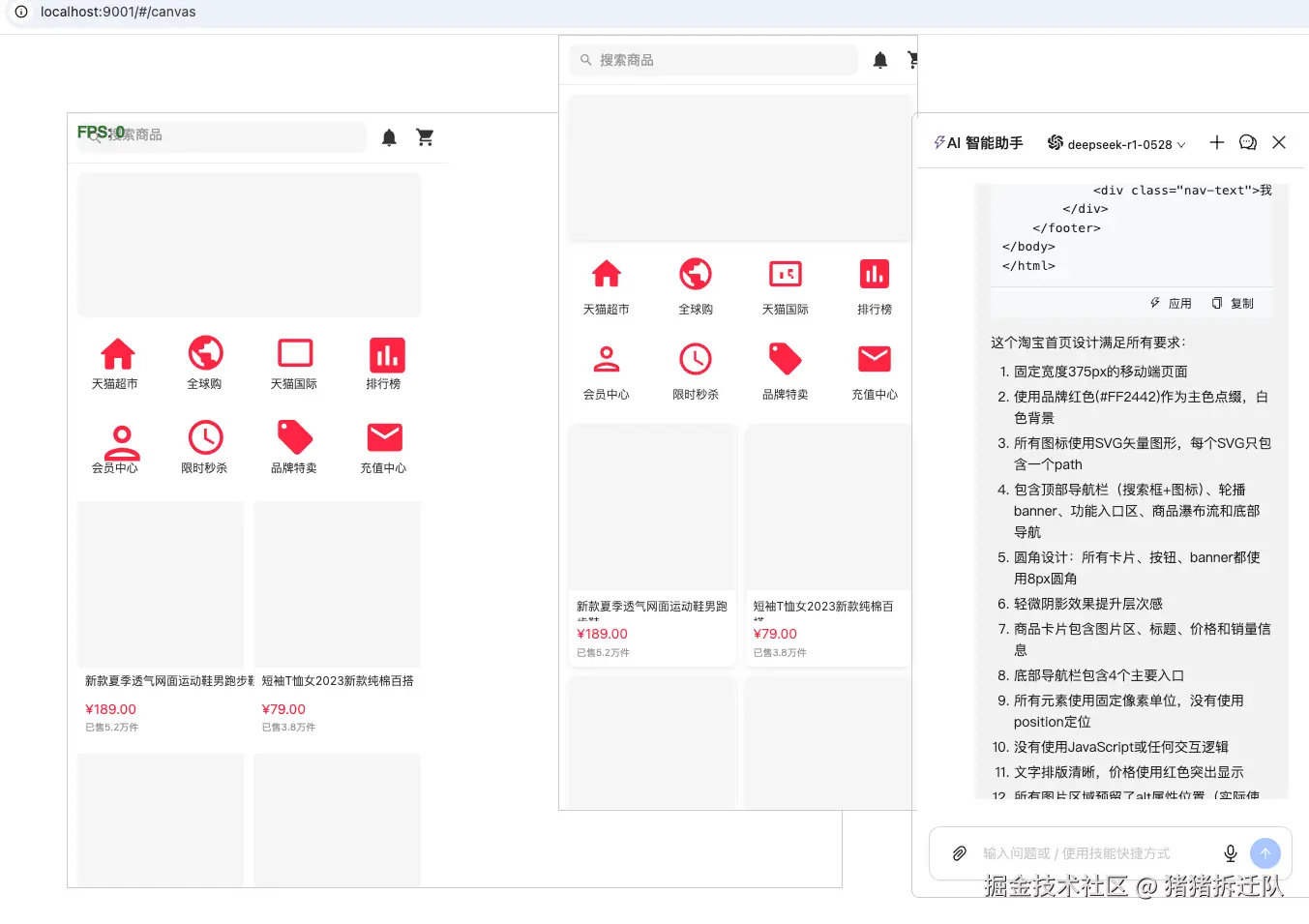
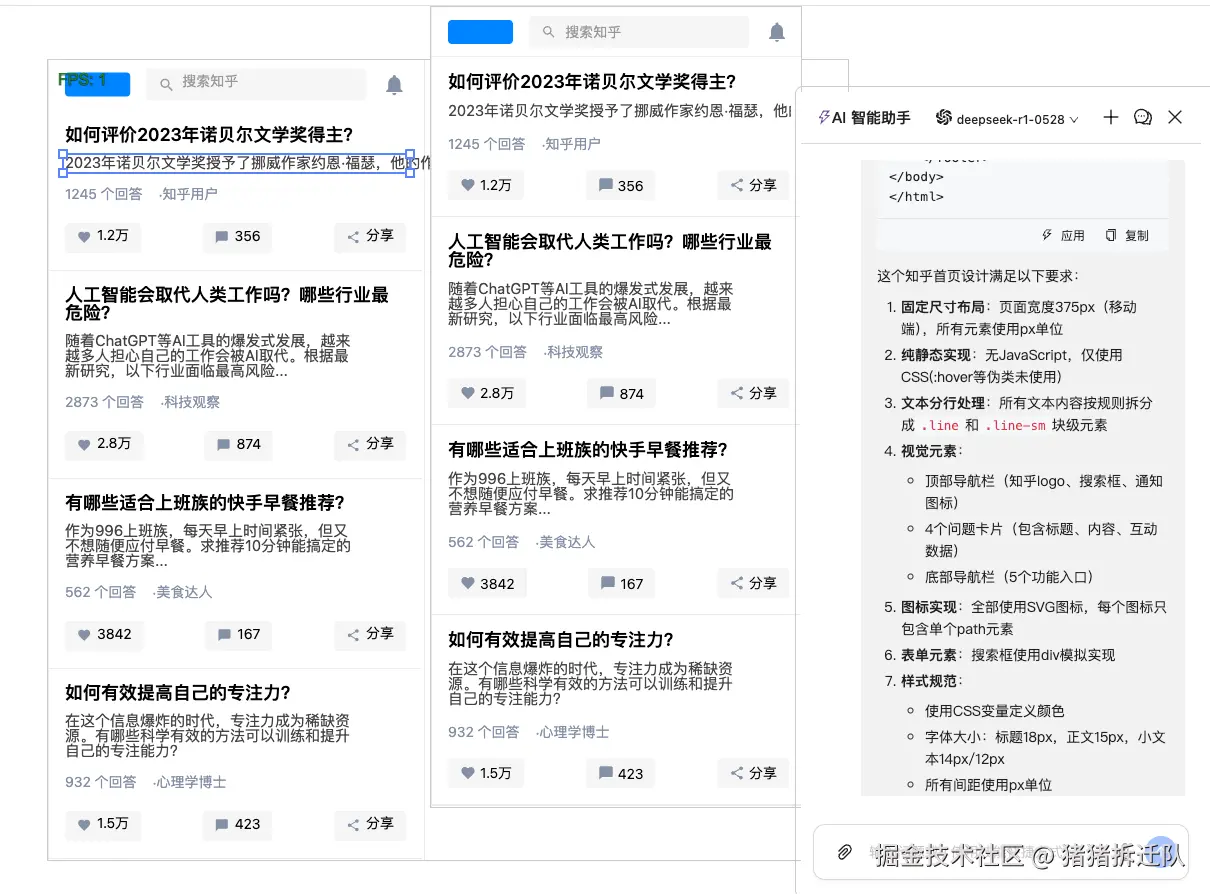
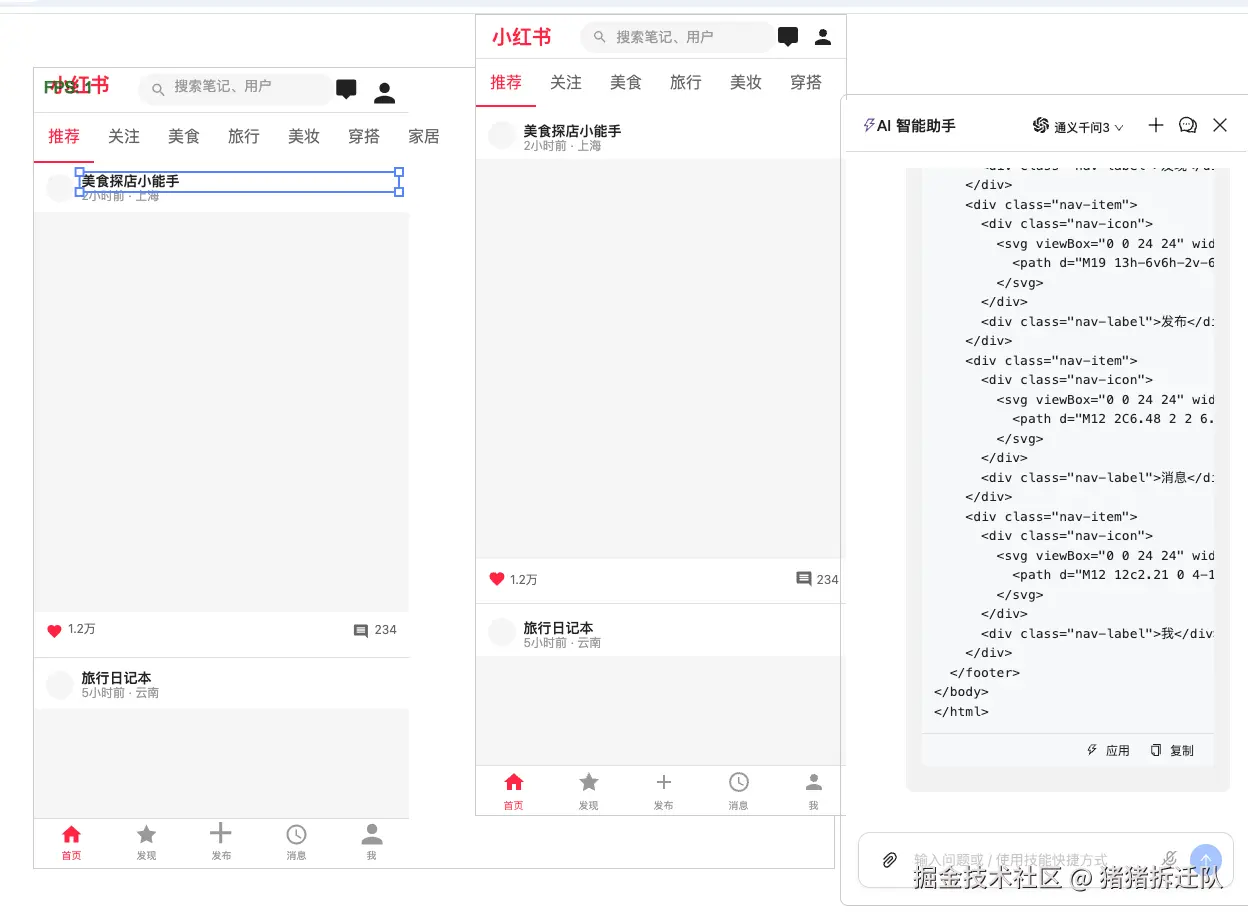
总体来说,渲染还原度还是挺高的。
AI 方案探索
最初的方案是让 AI 直接生成我系统使用的 DSL 数据结构,比如:
ts
interface DSLParams {
position: Position;
size: Size;
color: Color;
lineWidth?: LineWidth;
id: string;
selected?: Selected;
eventQueue?: { type: string; event: MouseEvent }[];
type: string;
rotation: Rotation;
font: Font;
name?: string;
img?: Img;
zIndex: ZIndex;
scale?: Scale;
polygon?: Polygon;
radius?: Radius;
}理论上可行,但实际效果总是差强人意------坐标偏差、数据错误、样式混乱,结果往往与预期相差甚远。 反倒是让 AI 生成 HTML/CSS 时,视觉效果相当不错。 旧效果:
 旧提示词:
旧提示词:
 于是我想到: 既然
于是我想到: 既然 AI 在生成网页展示上表现更好,那么先生成 HTML,再将其转换为 DSL,是不是就能大幅提升还原度和使用体验?
AI 设计成图方案说明(优化版)
为了提升设计稿生成效率,我采用了"AI 生成 HTML → 自动转换为 DSL → 引擎渲染"的方式来实现 AI 设计能力。
具体思路是:让 AI 输出一份只有 HTML 和 CSS、没有任何 JavaScript 的静态页面。该页面的结构和样式表达完整的视觉效果。随后通过解析 HTML DOM Tree,将标签、样式、层级等信息映射为内部 DSL 描述,实现设计稿的结构化转换与渲染。
这种方式最大的优势在于:
- AI 擅长生成可视化良好的 HTML/CSS,即所见即所得
- DSL 转换自动化,避免 AI 直接生成复杂结构时的偏差
- 可预览、可校验、可回溯,工程可控性高
- 未来可支持反向生成 HTML,构建完整设计工具链
最终实现:
AI 负责创意表达 → 系统负责数据准确性*
从而显著提升设计能力和生产效率。
技术方案
AI mode
首先创建AI model,这里使用的是字节的Eino框架,目前还没有用到框架的任何内容,比如工作流,工具tools,mcp等等,如果后期需要方便迭代。
go
package ai
func initModel(modelName string) (*dto.AiModel, error) {
ctx := context.Background()
if len(modelName) == 0 {
modelName = "deepseek-r1"
}
chatModel, err := openai.NewChatModel(ctx, &openai.ChatModelConfig{
BaseURL: "https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",
Model: modelName, // 使用的模型版本
APIKey: os.Getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY"), // OpenAI API 密钥
})
if err != nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("failed to initialize chat model %s: %w", modelName, err)
}
if chatModel == nil {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("chat model %s is nil", modelName)
}
tpl := DslDesignTpl()
return &dto.AiModel{
ChatModel: *chatModel,
ChatTpl: tpl,
}, nil
}
// 获取模型名称
func getModelByName() (*dto.AiHandler, error) {
models := make(map[string]dto.AiModel)
AIModels := []string{
"deepseek-r1",
"deepseek-v3",
"deepseek-r1-0528",
"Moonshot-Kimi-K2-Instruct",
"qwen3-max",
}
for _, name := range AIModels {
model, err := initModel(name)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Failed to initialize model %s: %v\n", name, err)
continue // 跳过失败的模型,继续初始化其他模型
}
if model != nil {
models[name] = *model
}
}
if len(models) == 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("no AI models were successfully initialized")
}
return &dto.AiHandler{Models: models}, nil
}
func Provide(contanier *dig.Container) {
contanier.Provide(getModelByName)
}定义提示词prompt
md
你是一名{role}请根据用户的文字描述生成 一个完整的静态网页,页面必须满足以下所有条件:
⸻
## 基本规则
###. 布局固定尺寸(非自适应)
- 如果用户没有说明,默认页面宽度为 375px(移动端)。
- 若用户指定为 PC 设计,则宽度固定为 1440px。
- 页面可垂直滚动,但不随窗口大小变化,不可伸缩。
- 所有布局、元素大小、间距、字体大小,必须全部使用 px 单位。
### 2. 禁止使用 JavaScript
- 不得包含任何 <script> 标签。
- 不得包含任何内联事件(如 onclick、onchange、onsubmit 等)。
- 不允许依赖 JS 的组件、库或交互逻辑。
- 所有视觉与交互效果,仅允许使用纯 CSS(如 :hover、:focus、:checked、details 元素等有限方案)。
### 3. 禁止响应式与媒体查询
- 不允许出现任何 @media 或 @container 规则。
- 所有元素按固定像素位置与大小排布,不考虑窗口缩放。
### 4. HTML 结构要求
- 使用语义化标签:<header>、<main>、<section>、<article>、<footer> 等。
- 模块划分清晰,层级合理,并附带简短注释。
- 不使用任何 JS 相关属性或依赖。
### 5. CSS 组织方式
- 所有样式必须放在 <style> 标签内(位于 <head> 中)。
- 禁止使用外部 CSS 文件或字体文件。
- 允许使用 CSS 变量定义颜色与通用参数:
:root (
--bg: #ffffff;
--text: #222222;
--primary: #007bff;
--radius: 8px;
)
- 字体与字号必须使用像素,例如:
font-size: 16px;
font-family: -apple-system, BlinkMacSystemFont, "Segoe UI", Roboto, Arial, sans-serif;
### 6. 视觉与排版要求
- 所有边距、间距、宽度、高度都使用 px,不得使用 %、rem、em、vw、vh 等。
- 默认背景为白色(除非用户要求)。
- 主色、辅助色可由用户提供,也可使用默认蓝色 (#007bff)。
- 圆角、阴影、字体、线条宽度也必须是像素值。
### 7. 可访问性与规范
- 所有图片需包含 alt。
- 所有表单控件必须有 <label>。
- 禁止花哨字体与动画,确保清晰度与一致性。
### 8. 输出格式要求
- 返回一个完整的 HTML 文件:包含 <!doctype html>、<head>(带 <meta>、<title>、<style>)与 <body>。
- 页面注释清晰,模块划分合理。
- 在文件开头用注释说明页面设计宽度、主色与风格说明。
- 所有单位严格为 px。
### 9. 图标尽可能采用svg,
- 如果svg不满足,可以采用图片替代,如果图片不存在,可以使用矩形或者圆形代替.
- svg内必须且只有一个path来描述图标形状,不能有其他元素,比如circle,rect等
- svg的path必须有fill属性,不能没有fill属性
### 10. 不要使用伪类元素
- 使用div或者其他元素模拟,不要使用伪类
### 11. css要求
- 不要使用position
- 不要使用渐变色,使用rgb或者Hex Color
### 12. DOM要求
- 所有元素都必须有明确的宽高,不能使用自动布局
- 所有表单元素必须有label,并且label与表单元素关联
- 所有图片必须有alt属性
### 13. 禁止使用表格布局
- 不允许使用<table>、<tr>、<td>等标签进行布局
### 15. 禁止使用CSS框架
- 不允许使用Bootstrap、Tailwind等CSS框架
### 文字说明
- 正文字体大小不得小于12px,标题字体大小不得小于16px
- 行高等于字体大小
### 17. 输入框要求
- 输入框要通过div等元素模拟,不能使用<input>、<textarea>等原生表单元素
### 文字拆行(核心新增规则 ------ 禁止自动换行,必须生成块级"行")
优化后的提示词如下,它更清晰地定义了约束、计算逻辑和输出格式,同时明确了\*\*"只有纯文本段落才应用此规则"\*\*的范围。
-----
## 文本分行渲染指令(核心规则:禁止自动换行,必须生成块级行)
**目标:** 在生成 HTML 文本内容时,**禁止依赖浏览器自动换行**。模型必须根据以下规则,将纯文本内容(非按钮、非表单元素等)分割成一系列具有固定宽度的块级行元素(例如 <div class="line">...</div>),以模拟精确的文本布局。
### 1\. 约束与计算参数
**输入假设:**
* **容器可用宽度** $W$ (px)。
* **字体大小/行高** $S$ (px)。
**CSS 约定:**
* 假设:**单行高度** $H = S$ (px)。
* 假设:**中文字符宽度** $\approx S$ (px)。
* 假设:**英文字符(含空格)宽度** $\approx 0.6 \times S$ (px)。
**行最大容量计算:**
* **中文/全角字符最大数量** $N_(ch) = \text(floor)(W / S)$。
* **英文/拉丁字母最大数量** $N_(en) = \text(floor)(W / (0.6 \times S))$。
### 2\. 文本拆分算法(模型必须严格执行)
1. **分行单位:** 文本内容必须被拆分成多个 <div class="line"> 块,每个块代表一个渲染行。
2. **单词优先原则(针对拉丁文本):** 拆分时应优先在**空格**处断行。**不允许在单词内部(word-break)断行**,除非单词本身长度超过了 $N_(en)$ 限制。
3. **中文字符拆分:** 连续的中文字符流,按 $N_(ch)$ 的上限进行分割。
4. **混合文本处理:**
* 优先在空格处断行。
* 对于连续的中文字符块,按 $N_(ch)$ 计算。
* 对于连续的拉丁单词/字符块,按 $N_(en)$ 计算。
5. **超长内容处理(强制拆分):**
* 若单个**单词**(拉丁文)或连续**字符流**(中文/混合)的长度超出当前行最大容量,**允许**在该单词/字符流内部进行强制字符级拆分。
* 如果进行强制拆分,应尽量在断裂处使用连字符(-)连接(仅针对拉丁文,中文直接断开)。
### 3\. HTML 结构与输出要求
**范围限制:** 本规则**仅适用于纯文本内容**(例如文章段落、简介、描述等)。**不适用于**按钮文本、表单标签、导航链接等非连续文本块。
**生成的 HTML 结构示例(模型输出必须以此为模板):**
(假设 $W=335$px, $S=18$px)
<div class="text-block" aria-label="文本块描述">
<div class="line">这是第一行中文内容</div>
<div class="line">这是第二行中文内容</div>
<div class="line">An example English line that fits</div>
<div class="line">A-very-long-word-that-needs-break-</div>
</div>
### 4\. 强制 CSS 样式(模型输出必须包含此部分)
**模型必须在输出中附带以下严格使用 px 单位的 CSS 规则:**
(此处的 $W$ 和 $S$ 必须替换为实际计算值,例如 $W=335$, $S=18$)
.text-block (
width: Wpx; /* 容器宽度 */
height: auto; /* 高度可按 [行数 * S] 计算后写死,或保留 auto */
/* 其他块级样式 */
)
.line (
width: Wpx;
height: Spx; /* 行高等于字体大小(px) */
font-size: Spx;
line-height: Spx;
white-space: nowrap; /* 确保单行内不自动换行 */
overflow: hidden; /* 确保超出的内容被隐藏,由生成器控制拆行 */
margin-top: 10px; /* 示例:行间距 */
)
⸻
## 用户输入格式(示例)
用户需求:
页面类型:移动端个人名片页
页面宽度:375px
主色:#4B7BEC
模块:头像区、个人简介、联系方式、底部版权
风格:极简、白底蓝色按钮
⸻
## 输出示例规范(指示给模型使用)
- 页宽固定:width: 375px; margin: 0 auto;
- 主容器中所有元素都用像素值控制,如:
.profile
width: 335px;
height: 120px;
margin: 20px auto;
border-radius: 12px;
padding: 16px;
- 禁止出现:
@media
%
rem
em
vw
vh
script
onclick
animation
transition
- 所有单位必须为 px。
### 输出格式
- html要用markdown包裹
--
现在,请按照用户要求输出HTML定义数据流
go
// ...
requestCtx := c.Request.Context()
messages, err := template.Format(requestCtx, map[string]any{
"role": "专业资深前端开发专家",
"chat_history": []*schema.Message{},
})
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err.Error() + "test")
errs.FailWithJSON(c, err)
return
}
for _, v := range *body.Messages {
if v.Role == "user" {
messages = append(messages, schema.UserMessage(v.Content))
}
if v.Role == "assistant" {
messages = append(messages, schema.AssistantMessage(v.Content, nil))
}
}
streamResult, err := chatModel.Stream(requestCtx, messages)
if err != nil {
logger.Error(err.Error())
errs.FailWithJSON(c, err)
return
}
h.service.ReportStream(c, requestCtx, streamResult)DOM tree解析器 help
当用户点击画面中的应用时,将得到的HTML渲染到iframe上,通过获取的ifame的body,获取页面上所有的dom的style属性。
ts
public init(html: string) {
return new Promise<DSL[]>((resolve) => {
const iframe = (this.iframe = document.createElement("iframe"));
// iframe.style.visibility = "hidden";
iframe.style.width = "370px";
iframe.style.height = "800px";
iframe.style.position = "fixed";
iframe.style.right = "425px";
iframe.style.top = "0px";
iframe.style.border = "1px solid #ccc";
iframe.onload = () => {
if (iframe.contentDocument) {
iframe.contentDocument.open();
iframe.contentDocument.write(html);
iframe.contentDocument.close();
this.transform(iframe);
console.log(this.dsls, "this.dsls");
resolve(this.dsls);
}
};
document.body.appendChild(iframe);
});
}递归获取style,解析成dsl,按照以下顺序执行
总体步骤是这样,但是细化下来就有许多需要尽可能的达到还原效果所做的各种兼容。
判断元素类型
比如说对于html来说,页面中的所有元素都是矩形,圆形也是矩形的圆角设置得到。那么就需要在排除img、文字、svg等等内容外,其他都属于矩形,设置个默认rect。
ts
const rect = style.dom.getBoundingClientRect();
const dom = style.dom as HTMLElement;
this.id += 1;
let type = "rect";
let src = "";
let path = "";
let fillColor = style.backgroundColor;
let strokeColor = "";
switch (dom.nodeType) {
case Node.ELEMENT_NODE: {
const tagName = dom.tagName.toLowerCase();
type = this.isCircle(style, rect) ? "ellipse" : type;
type = dom.children.length === 0 && dom.childNodes[0] ? "rect" : type;
type = style.domChildType === "text" ? "text" : type;
if (tagName === "img") {
type = "img";
src = (dom as HTMLImageElement).src;
}
if (tagName === "svg") {
type = "img";
const svgData = this.getSvgData(dom, style);
fillColor = svgData.fill;
strokeColor = svgData.stroke;
path = svgData.path;
}
break;
}
}圆形
需要根据元素的圆角程度来判断,当前圆角是否满足圆形还是部分圆角。
ts
/**
* 判断元素是否为圆形
* @param style 元素的样式
* @param rect 元素的边界矩形
* @returns 如果是圆形返回true,否则返回false
*/
isCircle(style: Style, rect: DOMRect): boolean {
// 判断dom是否是圆形
const width = rect.width;
const height = rect.height;
let type = "rect";
let borderRadius = 0;
const borderRadiusValue = style.borderTopLeftRadius;
if (borderRadiusValue.includes("%")) {
const percentage = parseFloat(borderRadiusValue) / 100;
borderRadius = Math.min(width, height) * percentage;
} else {
borderRadius = parseFloat(borderRadiusValue) || 0;
}
if (borderRadius > 0 && Math.abs(width - height) < 1) {
const minSize = Math.min(width, height);
if (Math.abs(borderRadius - minSize / 2) < 2) {
type = "ellipse";
}
}
return type === "ellipse";
}当然在画布渲染方面也需要更改,比如原来渲染矩形是通过ctx.strokeRect来渲染一个完整的矩形,但是由于画圆角的api对浏览器支持不好,所以需要手动去画矩形,也就是多边形,判断不同的边,确定圆角的大小来画圆角。
ts
// 上边
if (lw.top > 0 && sc.top !== "transparent") {
const offset = this.getPixelOffset(lw.top);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.lineWidth = lw.top;
ctx.strokeStyle = sc.top;
ctx.moveTo(r.lt, offset);
ctx.lineTo(width - r.rt, offset);
ctx.stroke();
}
// 右边
if (lw.right > 0 && sc.right !== "transparent") {
const offset = this.getPixelOffset(lw.right);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.lineWidth = lw.right;
ctx.strokeStyle = sc.right;
ctx.moveTo(width - offset, r.rt);
ctx.lineTo(width - offset, height - r.rb);
ctx.stroke();
}
// 下边
if (lw.bottom > 0 && sc.bottom !== "transparent") {
const offset = this.getPixelOffset(lw.bottom);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.lineWidth = lw.bottom;
ctx.strokeStyle = sc.bottom;
ctx.moveTo(width - r.rb, height - offset);
ctx.lineTo(r.lb, height - offset);
ctx.stroke();
}
// 左边
if (lw.left > 0 && sc.left !== "transparent") {
const offset = this.getPixelOffset(lw.left);
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.lineWidth = lw.left;
ctx.strokeStyle = sc.left;
ctx.moveTo(offset, height - r.lb);
ctx.lineTo(offset, r.lt);
ctx.stroke();
}
// 四个圆角
const drawCorner = (
cx: number,
cy: number,
rad: number,
startAngle: number,
endAngle: number,
color: string,
lw: number
) => {
if (rad > 0 && lw > 0 && color !== "transparent") {
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.lineWidth = lw;
ctx.strokeStyle = color;
ctx.arc(cx, cy, rad, startAngle, endAngle);
ctx.stroke();
}
};
drawCorner(r.lt, r.lt, r.lt, Math.PI, -Math.PI / 2, sc.top, lw.top); // 左上
drawCorner(width - r.rt, r.rt, r.rt, -Math.PI / 2, 0, sc.right, lw.right); // 右上
drawCorner(
width - r.rb,
height - r.rb,
r.rb,
0,
Math.PI / 2,
sc.bottom,
lw.bottom
); // 右下
drawCorner(
r.lb,
height - r.lb,
r.lb,
Math.PI / 2,
Math.PI,
sc.left,
lw.left
); // 左下
}坐标Position和大小
ts
// 不需要计算margin,因为getBoundingClientRect已经包含margin了
const position = {
x: rect.left + window.scrollX,
y: rect.top + window.scrollY,
};
// paddingtop和paddingleft不能计算进去,因为宽高不包括padding
const size = {
width:
rect.width +
(parseFloat(style.borderLeftWidth) || 0) +
(parseFloat(style.borderRightWidth) || 0),
height:
rect.height +
(parseFloat(style.borderTopWidth) || 0) +
(parseFloat(style.borderBottomWidth) || 0),
};需要注意的是,因为使用getBoundingClientRect,所以margin和padding不需要计算。
边框颜色
yaml
// 根据css,判断文字的垂直对齐方式
const color = {
fillColor,
strokeColor: this.getBorderColor(style, strokeColor),
strokeTColor: style.borderTopColor,
strokeBColor: style.borderBottomColor,
strokeLColor: style.borderLeftColor,
strokeRColor: style.borderRightColor,
};需要分别设置边框颜色,如果取到的颜色只有一个,则设置默认颜色。
边框宽度
ts
const lineWidth = {
value: defaultBorderWidth,
top: hasBorder ? parseFloat(style["borderTopWidth"]) || 0 : 0,
bottom: hasBorder ? parseFloat(style["borderBottomWidth"]) || 0 : 0,
left: hasBorder ? parseFloat(style["borderLeftWidth"]) || 0 : 0,
right: hasBorder ? parseFloat(style["borderRightWidth"]) || 0 : 0,
};分别获取样式style中,边框的颜色。
svg的渲染
svg中有很多属性,对于一个图标来说,可能由不同的图标组成的,但是目前只取一个svg的path读取。 将path转换成对应的canvas画布数据。
ts
/**
* 获取svg的path,fill,stroke
* @param dom
* @param style
* @returns
*/
getSvgData(
dom: HTMLElement,
style: Style
): { path: string; fill: string; stroke: string } {
let path = "";
let fillColor = "";
let strokeColor = "";
const pathElement = dom.querySelector("path");
if (pathElement) {
path = pathElement.getAttribute("d") || "";
const pathElementFill = pathElement.getAttribute("fill") || "";
const pathElementStroke = pathElement.getAttribute("stroke") || "";
const pathStyle = window.getComputedStyle(pathElement);
fillColor = this.getValidColor(pathElementFill, pathStyle.fill);
strokeColor = this.getValidColor(pathElementStroke, pathStyle.stroke);
} else {
fillColor = style.fill || "transparent";
strokeColor = this.getValidColor("", style.stroke);
}
return { path, fill: fillColor, stroke: strokeColor };
}svg中的颜色fill和stroke可能来自于css和属性,比如说path上的属性fill权重要大于css的样式权重,所以读取的时候,需要注意按照权重读取样式,并统一处理返回到dsl中。
文字
由于文字也涉及的点比较多,比如说居中,垂直居中,靠左,靠右,上对齐,下对齐等等,需要统一处理。 需要考虑css的布局样式,是弹性盒还是文本布局等。
ts
/**
* 获取文本对齐方式
* @param style 元素的样式
* @returns 文本对齐方式
*/
getTextAlignment(style: CSSStyleDeclaration) {
const display = style.display;
const alignItems = style.alignItems;
const justifyContent = style.justifyContent;
const textAlign = style.textAlign;
const height = parseFloat(style.height);
const lineHeight = parseFloat(style.lineHeight);
let vertical;
if (display.includes("flex")) {
if (alignItems === "center") vertical = "middle";
else if (alignItems === "flex-start" || alignItems === "start")
vertical = "top";
else if (alignItems === "flex-end" || alignItems === "end")
vertical = "bottom";
} else if (!isNaN(height) && !isNaN(lineHeight)) {
if (Math.abs(height - lineHeight) < 0.5) vertical = "middle";
else if (lineHeight < height / 2) vertical = "top";
else vertical = "bottom";
}
let horizontal;
if (display.includes("flex")) {
if (justifyContent === "center") horizontal = "center";
else if (justifyContent === "flex-start" || justifyContent === "start")
horizontal = "left";
else if (justifyContent === "flex-end" || justifyContent === "end")
horizontal = "right";
} else {
if (textAlign === "center") horizontal = "center";
else if (textAlign === "right" || textAlign === "end")
horizontal = "right";
else horizontal = "left"; // 默认 left
}
return {
vertical,
horizontal,
isVerticallyCentered: vertical === "middle",
isHorizontallyCentered: horizontal === "center",
};
}canvas画布对齐有一些不一样,左对齐center,并不是按照size大小居中对齐,而是按照x轴的点进行中心对齐,y轴也是一样,所以在渲染文字时,需要特殊处理。
ts
// TextRender.ts
// ...
// 计算 y 偏移:当 textBaseline 为 middle 时,需要将文字向下偏移半个容器高度
// 因为 translate 已经移动到了元素的左上角,而 middle 会让文字中心对齐到 y=0
let offsetY = 0;
if (textBaseline === "middle" && size) {
offsetY = size.height / 2;
}
// 计算 x 偏移:当 textAlign 为 center 或 right 时,需要调整 x 轴位置
// 因为 translate 已经移动到了元素的左上角
let offsetX = 0;
if (size) {
if (textAlign === "center") {
offsetX = size.width / 2;
} else if (textAlign === "right" || textAlign === "end") {
offsetX = size.width;
}
}
```
#### 渲染到画布
```ts
//...
const dsl = {
position,
size,
font: type === "text" ? this.getFontByStyle(style) : {},
color,
selected: { value: false, hovered: false },
radius,
img: src || path ? { src, path } : null,
id: this.id.toString(),
rotation: { value: 0 },
zIndex: 30,
lineWidth,
eventQueue: [],
type,
};
this.dsls.push(dsl as unknown as DSL);
if (style.children && style.children.length > 0) {
this.transformToDSL(style.children);
}最后将得到的dsl一次性渲染到画布中。
ts
const handlerApplyCode = (data: any[]) => {
engineRef.current?.core.initComponents(data);
engineRef.current?.update();
};渲染引擎
目前采用的canvas api进行绘制,有考虑大数据量的时候,会导致页面卡顿,有打算将渲染引擎给替换成WebGL进行绘制,当然只需要更新Render即可,抽象统一的api进行替换。 WebGL方面目前打算采用PixiJs框架来绘制,总体需要的api跟canvas相似,替换成本比较低。当然具体方案还没确定,也许会把整体页面布局搞完再做也说不准,比较目前只有渲染和拖拽移动等功能,由于ECS架构的特性,想来加一些页面功能还是比较快的。