目录
Git初识
问题 :随着文件修改的版本增多,你对最新的修改文件不满意,想回退到之前的版本,想要知道每次版本修改的内容是什么?但是之前的版本已经被修改,如何回退到之前想要的版本呢?
解决方法 :使用版本控制器,用于记录每次的修改内容以及版本迭代 的管理系统。
Git :可以控制电脑上所有格式的文档,对于程序员来说,上传和维护的是项目中的源代码文档。
细节:如果是文本文件,git可以记录你每次修改的内容,不用记录整个文本文件的内容,但是对于二进制文件不行,Git 对二进制文件无法记录修改细节,只能完整存储每个版本,这会反映在仓库大小的变化上。
Git安装
Git 是开放源代码的代码托管⼯具,最早是在Linux下开发的。开始也只能应⽤于Linux平台,后面慢慢的被移植到windows下,现在,Git可以在Linux、Unix、Mac和Windows这几大平台上正常运行了。
Linux-centos
git --version --查看你的git是否安装
sudo yum install git -y --安装git查看 Git 安装的版本:
git --version删除Git
sudo yum remove git -yGit基本操作
创建git本地仓库
要提前说的是,仓库是进行版本控制的⼀个文件目录。我们要想对文件进行版本控制,就必须先创建 ⼀个仓库 出来。
创建⼀个 Git 本地仓库对应的命令为 git init ,注意命令要在文件目录下执行,例如:
[zx@aliyun ~]$ mkdir gitcode --创建一个目录
[zx@aliyun ~]$ cd gitcode/
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git init --创建本地仓库
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/zx/gitcode/.git/
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ ll -a
total 0
drwxrwxr-x 3 zx zx 18 Oct 26 09:53 .
drwx------ 3 zx zx 21 Oct 26 09:52 ..
drwxrwxr-x 7 zx zx 119 Oct 26 09:53 .git初始化一个空的本地仓库,会出现.git目录,帮助和分析git追踪。不要手动修改这个目录里面的文件,不然改乱了,就把 Git 仓库给破坏了。
其中包含 Git 仓库的诸多细节,有兴趣的同学可以进入看看。
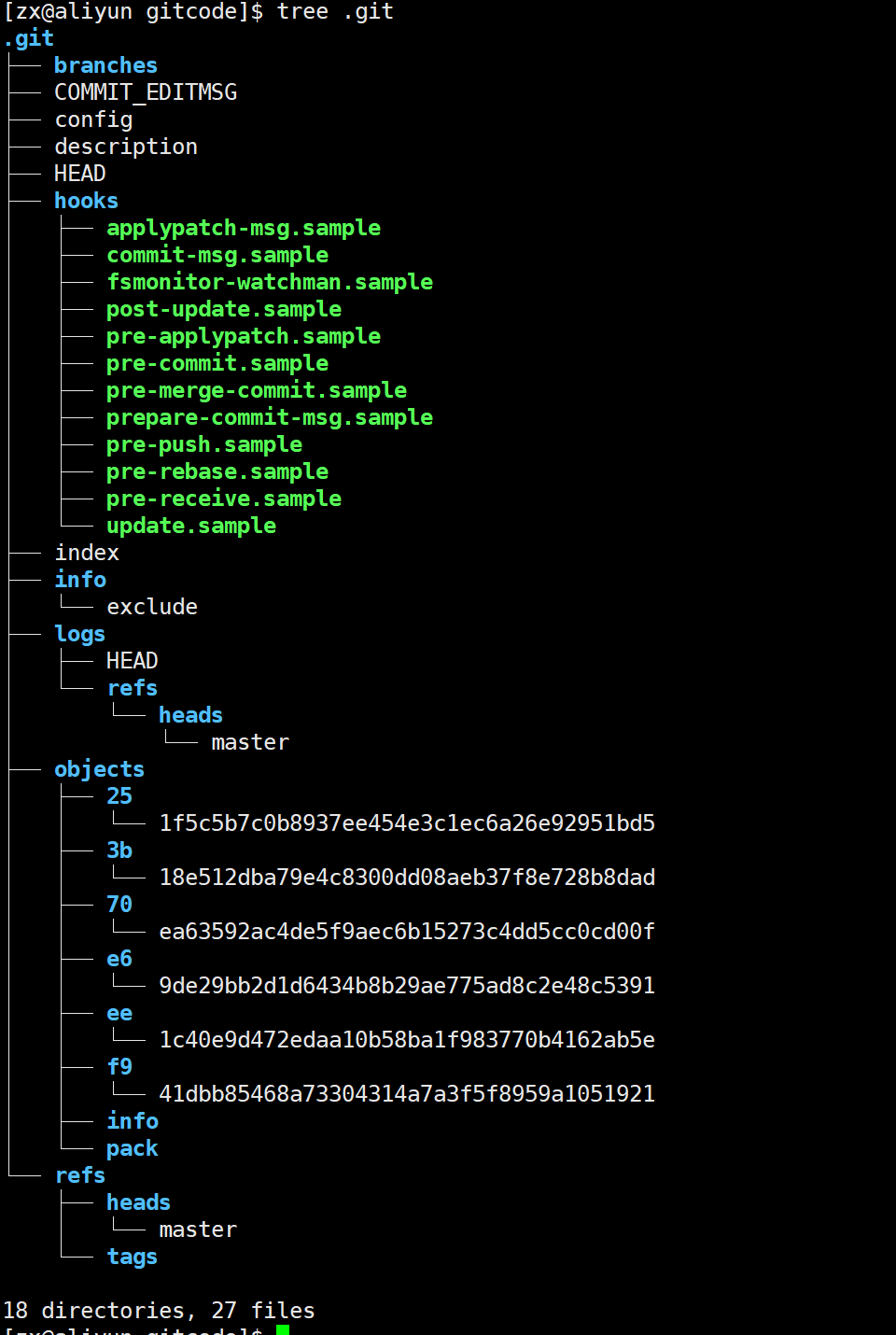
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ tree .git
.git
├── branches
├── config
├── description
├── HEAD
├── hooks
│ ├── applypatch-msg.sample
│ ├── commit-msg.sample
│ ├── fsmonitor-watchman.sample
│ ├── post-update.sample
│ ├── pre-applypatch.sample
│ ├── pre-commit.sample
│ ├── pre-merge-commit.sample
│ ├── prepare-commit-msg.sample
│ ├── pre-push.sample
│ ├── pre-rebase.sample
│ ├── pre-receive.sample
│ └── update.sample
├── info
│ └── exclude
├── objects
│ ├── info
│ └── pack
└── refs
├── heads
└── tags配置本地仓库
当安装 Git 后首先要做的事情是设置你的 用户名称 和 e-mail 地址,这是非常重要的。配置命令为:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config user.name 'zx' --为仓库设置用户名称
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config user.email '123456@qq.com' --为仓库设置e-mail 地址
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config -l --查看配置信息
core.repositoryformatversion=0
core.filemode=true
core.bare=false
core.logallrefupdates=true
user.name=zx
user.email=123456@qq.com删除配置
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --unset user.name --删除用户名称
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --unset user.email --删除e-mail 地址
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config -l
core.repositoryformatversion=0
core.filemode=true
core.bare=false
core.logallrefupdates=true全局配置,所有的本地仓库都会是这个配置
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --global user.name 'zx' --为仓库设置用户名称
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --global user.email '123456@qq.com' --为仓库设置e-mail 地址
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config -l
user.name=zx
user.email=123456@qq.com
core.repositoryformatversion=0
core.filemode=true
core.bare=false
core.logallrefupdates=true
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --unset user.name --本都仓库无法删除全局的配置
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --unset user.email
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config -l
user.name=zx
user.email=123456@qq.com
core.repositoryformatversion=0
core.filemode=true
core.bare=false
core.logallrefupdates=true删除全局的配置
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --global --unset user.name
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config --global --unset user.email
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git config -l
core.repositoryformatversion=0
core.filemode=true
core.bare=false
core.logallrefupdates=true认识工作区-暂存区-版本区
在gitcode目录中创建了ReadMe文件,git现在能管理吗?不能,因为只有在版本库中的文件才会被git管理。
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ touch ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ ll
total 0
-rw-rw-r-- 1 zx zx 0 Oct 26 10:11 ReadMe- 工作区:是在电脑上你要写代码或文件的目录。
- 暂存区:英文叫 stage 或 index。⼀般存放在 .git 目录下的 index 文件(.git/index)中,我们把暂存区有时也叫作索引(index)。
- 版本库 :又名仓库,英文名 repository 。工作区有⼀个隐藏目录 .git ,它不算工作区,而是 Git 的版本库。这个版本库里面的所有⽂件都可以被 Git 管理起来,每个文件的修改、除,Git都能跟踪,以便任何时刻都可以追踪历史,或者在将来某个时刻可以"还原"。
下面这个图展示了工作区、暂存区和版本库之间的关系:
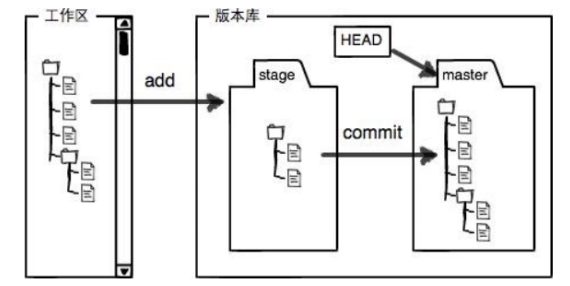
- 图中左侧为工作区 ,右侧为版本库。Git 的版本库里存了很多东西,其中最重要的就是暂存区。
- 在gitcode本地仓库新建的文件不能直接被git管理,在gitcode目录下的.git(版本库)才能管理,此时gitcode被称为工作区。
- stage 叫做暂存区,工作区中的文件需要通过add 操作才能提交到暂存区,在暂存区是git还不能管理文件,master版本库中git才能管理文件。
- commit 操作将暂存区中的内容提交到master版本库中,此时git可以进行管理了。
由上述描述我们便能得知:通过新建或粘贴进目录的文件,并不能称之为向仓库中新增文件,而只是在工作区新增了文件。必须要通过使用 git add 和 git commit 命令才能将文件添加到仓库中进行管理!!!
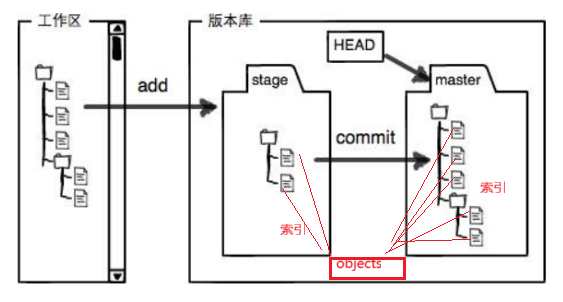
注意:在add时,还会将工作区文件修改(删除,修改,添加)的内容添加到objects对象库的一个git对象中,来进行版本控制,所以暂存区和master(HEAD是指针,指向master第一个所索引)版本库不需要保存一整个文件,只需要存储索引就够了,通过索引找到git对象,就能知道文件的修改内容。
添加文件
在包含 .git 的目录下新建⼀个 ReadMe 文件,我们可以使用git add 命令可以将文件添加到暂存区:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ ll
total 0
-rw-rw-r-- 1 zx zx 0 Oct 26 10:11 ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ ll
total 0
-rw-rw-r-- 1 zx zx 0 Oct 26 10:11 ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git add ReadMe --添加指定文件到暂存区
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git add . --添加所有被修改过的文件到暂存区使用git commit 将暂存区中内容提交到master版本库中
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit ReadMe -m'motify ReadMe' --将指定文件提交到master版本库中
[master (root-commit) f941dbb] motify ReadMe
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-) --一个文件被改动,0条插入和删除记录
create mode 100644 ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit -m'motify ReadMe' --将暂存区中的所有内容提交到master版本库中
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean注意 git commit 后面的 -m 选项,要跟上描述本次提交的message,由用户自己完成,这部分内容绝对不能省略,并要好好描述,是用来记录你的提交细节,是给我们人看的。
我们可以使用 git log 命令,来查看下历史提交记录:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git log
commit f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 (HEAD -> master)
Author: zx <123456qq.com>
Date: Sun Oct 26 10:51:38 2025 +0800
motify ReadMe该命令显示从最近到最远的提交日志,并且可以看到我们 commit 时的日志消息。
commit后面跟的是commit id,每次文件修改后提交到暂存区都会有一个commit id,可以帮助定位到每次的提交。
如果嫌输出信息太多,看得眼花缭乱的,可以试试加上 --pretty=oneline(漂亮的打印一行) 参数:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git log --pretty=oneline
f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 (HEAD -> master) motify ReadMe查看.git文件
-
index 就是我们的暂存区,add 后的内容都是添加到这里的
-
HEAD 就是我们的默认指向 master 分支的指针
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat .git/HEAD
ref: refs/heads/master
而默认的 master 分支,其实就是:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat .git/refs/heads/master
ee1c40e9d472edaa10b58ba1f983770b4162ab5e打印的 f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 是什么东西呢?保存的就是当前最新的 commit id,在objects对象库中可以看。
objects为 Git 的对象库,里面包含了创建的各种版本库对象及内容。当执行 git add 命令时,暂存区的目录树被更新,同时工作区修改(或新增)的文件内容被写入到对象库中的⼀个新的对象中,就位于 ".git/objects" 目录下,让我们来看看这些对象有何用处:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ ls .git/objects/
70 e6 f9 info pack查找 object 时要将 commit id 分成2部分 ,其前2位是文件夹名称,后38位是文件名称。
找到这个文件之后,⼀般不能直接看到里⾯是什么,该类文件是经过 sha (安全哈希算法)加密过的文件,好在我们可以使用
git cat-file命令来查看版本库对象的内容:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git cat-file -p ee1c40e9d472edaa10b58ba1f983770b4162ab5e
tree 251f5c5b7c0b8937ee454e3c1ec6a26e92951bd5 --tree相当于一个目录索引,记录了当前项目里有哪些文件和文件夹。
parent f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 --上次提交的commit id
author zx <123456qq.com> 1761449328 +0800
committer zx <123456qq.com> 1761449328 +0800
motify ReadMe:hello world
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git cat-file -p 251f5c5b7c0b8937ee454e3c1ec6a26e92951bd5
100644 blob 3b18e512dba79e4c8300dd08aeb37f8e728b8dad ReadMe在看 ReadMe 对应的 3b18e512dba79e4c8300dd08aeb37f8e728b8dad :
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git cat-file -p 3b18e512dba79e4c8300dd08aeb37f8e728b8dad
hello world
# 这是我们对ReadMe做的修改!!被git记录了下来!!git cat-file -p 查看某个 Git 对象里面到底存储了什么内容。
总结一下,在本地的 git 仓库中,有几个文件或者目录很特殊
• index: 暂存区, git add 后会更新该内容。
• HEAD: 默认指向 master 分⽀的⼀个指针。
• refs/heads/master: 文件里保存当前 master 分⽀的最新 commit id 。
• objects: 包含了创建的各种版本库对象及内容,可以简单理解为放了 git 维护的所有修改。
修改文件
Git 比其他版本控制系统 设计得优秀,因为 Git 跟踪并管理的是修改,而非文件。
修改指的是增加文件,修改文件,删除文件都可以算作修改。
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git status - - 查看当前仓库的状态
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean先对ReadMe文件做修改
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ vim ReadMe
hello world --原有内容
xxx code --添加内容
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git status
On branch master
Changes not staged for commit: --修改的内容还没有提交到暂存区中,还在工作区
(use "git add <file>..." to update what will be committed)
(use "git restore <file>..." to discard changes in working directory)
modified: ReadMe
no changes added to commit (use "git add" and/or "git commit -a")上面的结果告诉我们,ReadMe 被修改过了,但还没有完成添加与提交。
git diff 可以查看该文件工作区和暂存区的不同
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git diff ReadMe
diff --git a/ReadMe b/ReadMe --a代表ReadMe修改前 --b代表ReadMe修改后
index 3b18e51..5210b26 100644
--- a/ReadMe
+++ b/ReadMe
@@ -1 +1,2 @@ -- -1表示ReadMe修改前内容是第一行,+1,2表示ReadMe修改后内容是第一行到第二行,这样我们就能知道ReadMe修改了哪些内容。
hello world
+xxx code
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git add ReadMe --提交到暂存区
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git status
On branch master
Changes to be committed: --暂存区有内容,需要去提交到master版本库
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit -m'modify ReadMe:xxx code' --提交到master版本库
[master 334695a] modify ReadMe:xxx code
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+)
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean --没有可以提交的,工作区和版本库,暂存区是一致的版本回退
之前我们也提到过,Git 能够管理文件的历史版本,这也是版本控制器重要的能力。如果有一天你发现之前前的工作做的出现了很大的问题,需要在某个特定的历史版本重新开始,这个时候,就需要版本回退的功能了。
执行git reset 命令用于回退版本,可以指定退回某⼀次提交的版本。要解释⼀下"回退"本质是要将版本库中的内容进行回退 ,工作区 或暂存区是否回退由命令参数决定。
git reset 命令语法格式为: git reset [--soft | --mixed | --hard] [HEAD]-
-soft:该参数将版本库的内容退回为指定提交版本内容,工作区和暂存区文件保持不变。
--mixed:默认选项,此时可以不带参数,该参数将暂存区的内容退回为指定提交版本内容,工作区文件保持不变。
--hard:该参数将版本库,暂存区,工作区的内容退回为指定提交版本内容,切记工作区有未提交的代码时不要用这个命令 ,因为⼯作区会回滚,你没有提交的代码就再也找不回了,以使用该参数前⼀定要慎重。
HEAD说明:• 可直接写成 commit id,表示指定退回的版本
◦ HEAD 表示当前版本
◦ HEAD^ 上⼀个版本
◦ HEAD^^ 上上⼀个版本
◦ 以此类推...
• 可以使⽤ 〜数字表示 :
◦ HEAD~0 表示当前版本
◦ HEAD~1 上⼀个版本
◦ HEAD^2 上上⼀个版本
◦ 以此类推
git reflog会记录每次的提交记录
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reflog
334695a (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{0}: commit: modify ReadMe:xxx code
ee1c40e HEAD@{1}: reset: moving to HEAD
ee1c40e HEAD@{2}: commit: motify ReadMe:hello world
f941dbb HEAD@{3}: commit (initial): motify ReadMe为了方便测试,预设置了ReadMe三个版本,并将这三个版本都提交到版本库中,由git进行管理。
version 1:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
version 2:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
version 3:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc此时版本库中最新版本是version 3,如果我们想回退到version 2,但只回退版本库中的版本
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git log --pretty=oneline
ad631ba324c8f45cf89ed22ea89f7188dbaf114c (HEAD -> master) my ReadMe:ccc --版本库最新版本
cae2cc0f72868ae1b155911cbf3a5a5b881bf13f my ReadMe:bbb
e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069 my ReadMe:aaa
334695a3aa5fc1ed3bbdcae825d4ee17f3e0dd54 modify ReadMe:xxx code
ee1c40e9d472edaa10b58ba1f983770b4162ab5e motify ReadMe:hello world
f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 motify ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --soft cae2cc0f72868ae1b155911cbf3a5a5b881bf13f
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git log --pretty=oneline
cae2cc0f72868ae1b155911cbf3a5a5b881bf13f (HEAD -> master) my ReadMe:bbb --回退到version 2了
e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069 my ReadMe:aaa
334695a3aa5fc1ed3bbdcae825d4ee17f3e0dd54 modify ReadMe:xxx code
ee1c40e9d472edaa10b58ba1f983770b4162ab5e motify ReadMe:hello world
f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 motify ReadMe如果想再回退到version 3怎么办?可以再次使用git reset命令
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --soft ad631ba324c8f45cf89ed22ea89f7188dbaf114c
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git log --pretty=oneline
ad631ba324c8f45cf89ed22ea89f7188dbaf114c (HEAD -> master) my ReadMe:ccc
cae2cc0f72868ae1b155911cbf3a5a5b881bf13f my ReadMe:bbb
e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069 my ReadMe:aaa
334695a3aa5fc1ed3bbdcae825d4ee17f3e0dd54 modify ReadMe:xxx code
ee1c40e9d472edaa10b58ba1f983770b4162ab5e motify ReadMe:hello world
f941dbb85468a73304314a7a3f5f8959a1051921 motify ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc此时版本库中最新版本是version 3,如果我们想回退到version 1,并且工作区的内容也要修改,此时可以使用--mixed选项。
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --hard e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069
HEAD is now at e9949cb my ReadMe:aaa
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa回退到version 3,我们能回退的原因是因为我们知道version 3的commit id,如果找不到commit id,就不能回退了。查看commit id的方法有两种,git log可以查看提交记录,git reflog记录了你在本地仓库中的所有操作历史。
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --hard ad631ba324c8f45cf89ed22ea89f7188dbaf114c
HEAD is now at ad631ba my ReadMe:ccc
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reflog
ad631ba (HEAD -> master) HEAD@{0}: reset: moving to ad631ba324c8f45cf89ed22ea89f7188dbaf114c
e9949cb HEAD@{1}: reset: moving to e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069
e9949cb HEAD@{2}: reset: moving to e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069
e9949cb HEAD@{3}: reset: moving to e9949cbe2151eb2374a3c2fa2b03e2ce57eb5069这样,你就可以很⽅便的找到你的所有操作记录了,但 ad631ba 这个是啥东西?这个是 version 3 的 commit id 的部分。没错,Git 版本回退的时候,也可以使用部分 commit id 来代表目标版本。
可往往是理想很丰满,现实很⻣感。在实际开发中,由于⻓时间的开发了,导致 commit id 早就找不到了,可突然某⼀天,我⼜想回退到 version3,那该如何操作呢?貌似现在不可能了。
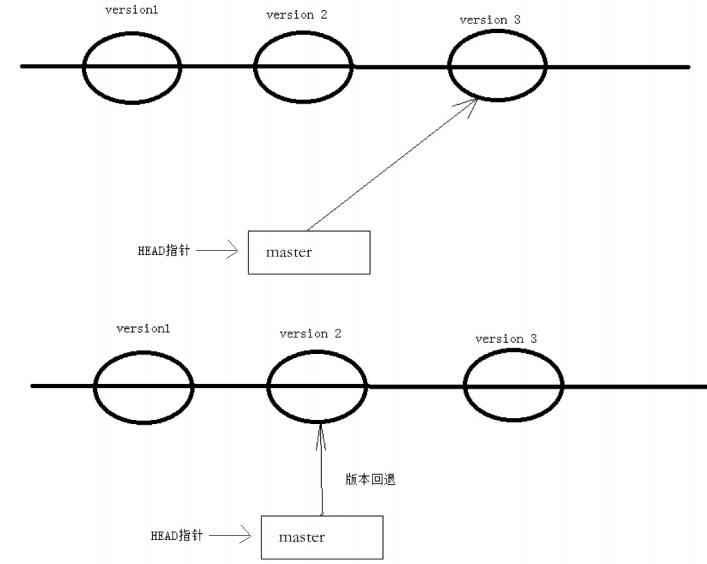
值得说的是,Git 的版本回退速度⾮常快,因为 Git 在内部有个指向当前分支(此处是master)的
HEAD指针, refs/heads/master 文件里保存当前 master 分支的最新commit id。当我们在回退版本的时候,Git 仅仅是给 refs/heads/master 中存储⼀个特定的version,可以简单理解成如下示意图:
撤销情况
情况一:如果我想撤销工作区刚修改的内容,此时还并没有提交到暂存区中,可以使用:
git checkout -- [filename] --注意:--不能省略,省略了就是其他的意思了。
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc
xxx code --新增内容
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git checkout -- ReadMe --撤销操作
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc情况二:如果我想撤销工作区和暂存区刚修改的内容,此时已经提交到暂存区中,但还没提交到master版本库中,有两种方法:
方法一:先通过版本回退,将暂存区中的内容回退到版本库中的版本,再撤销工作区中的内容
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ vim ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
xxx code --修改内容
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --mixed HEAD --先让暂存区回退
Unstaged changes after reset:
M ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git checkout -- ReadMe 再让工作区撤销
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc
方法二:直接通过版本回退,将工作区和暂存区中的内容回退到版本库中的版本
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ vim ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
xxx code --修改内容
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --hard HEAD
HEAD is now at ad631ba my ReadMe:ccc
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git status --此时暂存区是干净的
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean情况三 :已经add,并且也commit了,直接使用--hard版本回退操作
c
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ vim ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
xxx code --修改内容
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git add .
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit -m'my ReadMe:xxx code'
[master 1c745de] my ReadMe:xxx code
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 3 deletions(-)
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git reset --hard HEAD^ --表示回退到上一个版本
HEAD is now at ad631ba my ReadMe:ccc
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ cat ReadMe
hello world
aaa
bbb
ccc
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git status
On branch master
nothing to commit, working tree clean删除文件
实要从版本库中删除该文件,需要使用git rm fiilename和git commit -m' '两个操作。
方法一:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ touch file1
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git add .
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit -m'add file1'
[master f242c1a] add file1
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
create mode 100644 file1
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ rm file1 --也是一种修改
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git add .
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit -m'rm file1'
[master 87e0759] rm file1
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
delete mode 100644 file1
方法二:
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git rm file1
rm 'file1'
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ ll
total 4
-rw-rw-r-- 1 zx zx 24 Oct 26 18:06 ReadMe
[zx@aliyun gitcode]$ git commit -m'rm file1'
[master ca140b5] rm file1
1 file changed, 0 insertions(+), 0 deletions(-)
delete mode 100644 file1git rm filename就相当于add和rm的结合。