这个条款揭示了C++多态体系中最重要的规则之一:通过基类指针删除派生类对象时,如果基类没有虚析构函数,将导致资源泄漏和未定义行为。这是理解C++对象生命周期和多态设计的核心。
思维导图:虚析构函数的完整体系
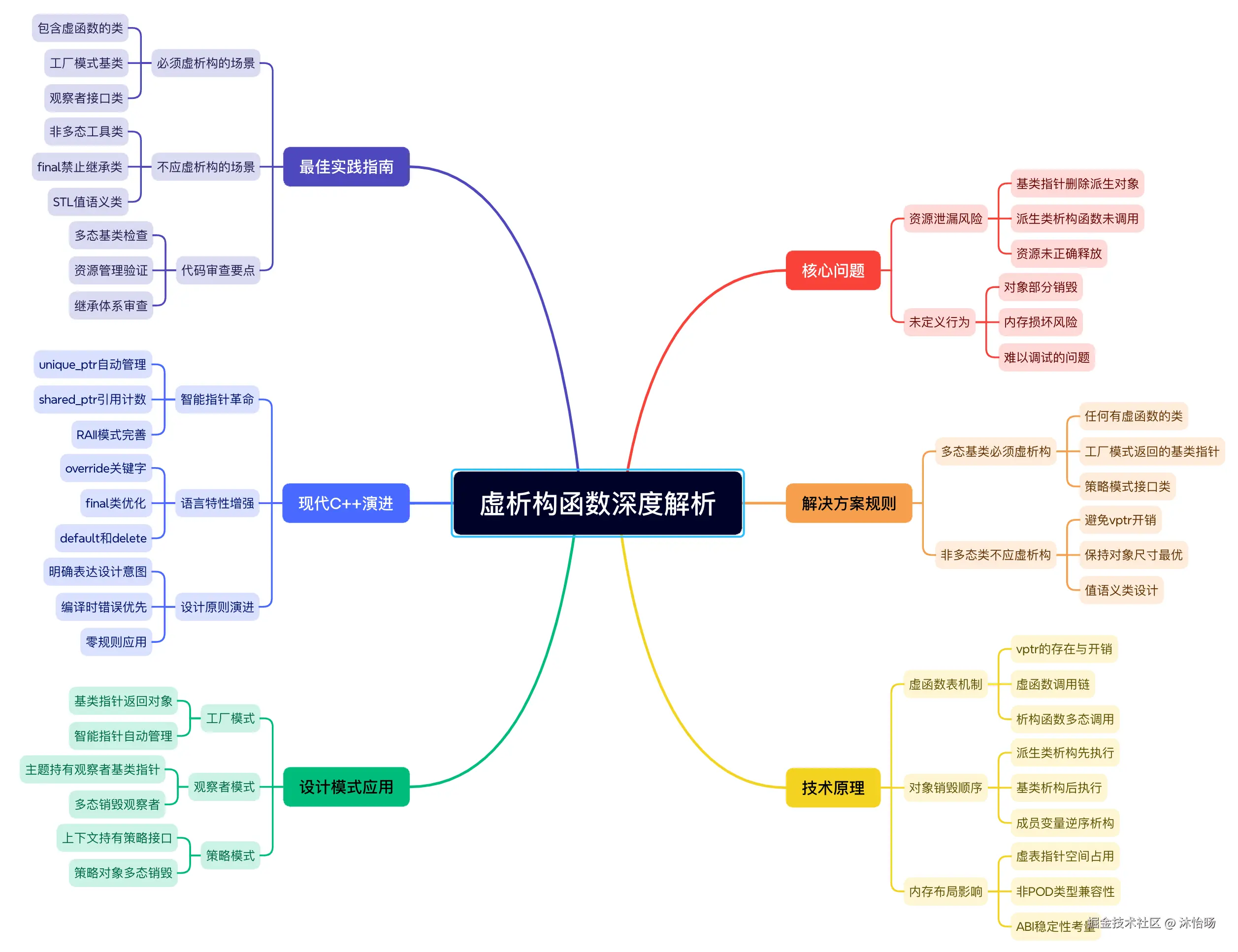
深入解析:虚析构函数的核心价值
1. 问题根源:多态删除的资源泄漏
危险的基类设计:
cpp
// 错误示例:多态基类没有虚析构函数
class TimeKeeper {
public:
TimeKeeper() = default;
~TimeKeeper() { std::cout << "TimeKeeper析构" << std::endl; } // 非虚析构!
virtual void getTime() { /* 获取时间 */ }
};
class AtomicClock : public TimeKeeper {
private:
int* heap_resource; // 派生类独有的堆资源
std::vector<double> data_cache; // 更多派生类资源
public:
AtomicClock() : heap_resource(new int(42)) {
data_cache.resize(1000); // 分配额外资源
}
~AtomicClock() {
delete heap_resource; // 释放派生类资源
std::cout << "AtomicClock析构" << std::endl;
}
};
void demonstrate_catastrophic_leak() {
TimeKeeper* ptk = new AtomicClock(); // 基类指针指向派生类对象
ptk->getTime(); // 多态调用,正常工作
delete ptk; // 灾难!只调用TimeKeeper::~TimeKeeper()
// AtomicClock::~AtomicClock()永远不会调用
// heap_resource和data_cache内存泄漏!
}运行结果分析:
TimeKeeper析构注意:AtomicClock析构永远不会输出,派生类的资源永远泄漏!
2. 解决方案:简单的虚析构声明
正确的基类设计:
cpp
// 正确示例:多态基类有虚析构函数
class TimeKeeper {
public:
TimeKeeper() = default;
virtual ~TimeKeeper() { std::cout << "TimeKeeper析构" << std::endl; } // 虚析构!
virtual void getTime() { /* 获取时间 */ }
};
class AtomicClock : public TimeKeeper {
private:
int* heap_resource;
std::vector<double> data_cache;
public:
AtomicClock() : heap_resource(new int(42)) {
data_cache.resize(1000);
}
~AtomicClock() override {
delete heap_resource; // 正确释放!
std::cout << "AtomicClock析构" << std::endl;
}
};
void demonstrate_correct_behavior() {
TimeKeeper* ptk = new AtomicClock();
ptk->getTime();
delete ptk; // 正确!调用AtomicClock::~AtomicClock(),然后TimeKeeper::~TimeKeeper()
}运行结果分析:
AtomicClock析构
TimeKeeper析构派生类和基类的析构函数都被正确调用,资源完全释放。
技术原理深度解析
1. 虚函数表机制与析构链
对象销毁的多态调用过程:
cpp
class Base {
public:
virtual ~Base() {
std::cout << "Base析构: " << this << std::endl;
}
virtual void operation() {
std::cout << "Base操作" << std::endl;
}
};
class Derived : public Base {
private:
std::string resource;
public:
Derived(const std::string& res) : resource(res) {}
~Derived() override {
std::cout << "Derived析构,释放资源: " << resource << std::endl;
}
void operation() override {
std::cout << "Derived操作,使用资源: " << resource << std::endl;
}
};
// 编译器生成的伪代码大致如下:
void polymorphic_destruction(Base* obj) {
// 1. 通过虚表找到正确的析构函数
auto vtable = *(void***)obj; // 获取虚表指针
auto destructor = (void(*)(void*))vtable[0]; // 析构函数在虚表第一个位置
// 2. 调用派生类析构函数
destructor(obj);
// 3. 最终释放内存
operator delete(obj);
}2. 纯虚析构函数的特殊用法
抽象基类的设计模式:
cpp
// 抽象基类:包含纯虚析构函数
class AbstractDatabase {
public:
virtual ~AbstractDatabase() = 0; // 纯虚析构函数
virtual void connect() = 0;
virtual void disconnect() = 0;
virtual void execute(const std::string& query) = 0;
// 非虚接口模式
void runTransaction(const std::string& query) {
connect();
execute(query);
disconnect();
}
};
// 关键:纯虚析构函数必须提供定义!
AbstractDatabase::~AbstractDatabase() {
std::cout << "AbstractDatabase基础清理完成" << std::endl;
}
class MySQLDatabase : public AbstractDatabase {
private:
MYSQL* connection_;
std::string connection_string_;
public:
explicit MySQLDatabase(const std::string& conn_str)
: connection_string_(conn_str), connection_(nullptr) {}
void connect() override {
std::cout << "连接MySQL: " << connection_string_ << std::endl;
// 实际连接逻辑
}
void disconnect() override {
std::cout << "断开MySQL连接" << std::endl;
// 实际断开逻辑
}
void execute(const std::string& query) override {
std::cout << "执行MySQL查询: " << query << std::endl;
// 实际执行逻辑
}
~MySQLDatabase() override {
if (connection_) {
disconnect();
}
std::cout << "MySQLDatabase资源完全释放" << std::endl;
}
};实战案例:现代C++设计模式
案例1:图形系统的多态体系
cpp
// 现代图形绘制系统的多态体系
class Drawable {
public:
virtual ~Drawable() = default; // 关键:虚析构函数
virtual void draw() const = 0;
virtual double area() const = 0;
virtual std::string name() const = 0;
// C++11现代特性:明确禁止拷贝
Drawable(const Drawable&) = delete;
Drawable& operator=(const Drawable&) = delete;
// 允许移动语义
Drawable(Drawable&&) = default;
Drawable& operator=(Drawable&&) = default;
protected:
Drawable() = default;
};
class Circle : public Drawable {
private:
double radius_;
std::vector<double> rendering_cache_; // 渲染缓存资源
mutable std::mutex cache_mutex_; // 线程安全保护
public:
explicit Circle(double radius) : radius_(radius) {
rendering_cache_.resize(1000); // 模拟大量渲染资源
std::cout << "Circle分配渲染缓存" << std::endl;
}
void draw() const override {
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lock(cache_mutex_);
std::cout << "绘制圆形,半径: " << radius_ << std::endl;
}
double area() const override {
return 3.14159 * radius_ * radius_;
}
std::string name() const override {
return "Circle";
}
~Circle() override {
std::cout << "Circle释放渲染缓存,半径=" << radius_ << std::endl;
}
};
class Rectangle : public Drawable {
private:
double width_, height_;
std::unique_ptr<double[]> vertex_data_; // 顶点数据智能指针管理
public:
Rectangle(double w, double h) : width_(w), height_(h),
vertex_data_(std::make_unique<double[]>(8)) {
std::cout << "Rectangle分配顶点数据" << std::endl;
}
void draw() const override {
std::cout << "绘制矩形 " << width_ << "x" << height_ << std::endl;
}
double area() const override {
return width_ * height_;
}
std::string name() const override {
return "Rectangle";
}
// 不需要显式析构函数 - unique_ptr自动管理
};
// 现代工厂模式
class ShapeFactory {
public:
static std::unique_ptr<Drawable> createShape(const std::string& type,
double param1, double param2 = 0) {
if (type == "circle")
return std::make_unique<Circle>(param1);
if (type == "rectangle")
return std::make_unique<Rectangle>(param1, param2);
return nullptr;
}
};
void demonstrate_modern_graphics() {
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Drawable>> scene;
// 创建各种图形对象
scene.push_back(ShapeFactory::createShape("circle", 10.0));
scene.push_back(ShapeFactory::createShape("rectangle", 5.0, 8.0));
scene.push_back(ShapeFactory::createShape("circle", 15.0));
// 渲染场景
for (const auto& shape : scene) {
std::cout << "渲染: " << shape->name()
<< ", 面积: " << shape->area() << std::endl;
shape->draw();
}
std::cout << "场景结束,开始清理..." << std::endl;
// scene离开作用域时,所有资源自动正确释放
// 因为Drawable有虚析构函数,unique_ptr能正确调用各派生类析构函数
}案例2:游戏引擎的组件系统
cpp
// 游戏引擎实体组件系统
class Component {
public:
virtual ~Component() = default; // 多态基类必须虚析构
virtual void update(float deltaTime) = 0;
virtual void render() = 0;
virtual std::string getType() const = 0;
// 现代C++特性
Component(const Component&) = delete;
Component& operator=(const Component&) = delete;
protected:
Component() = default;
};
class PhysicsComponent : public Component {
private:
std::vector<float> collision_data_;
std::unique_ptr<class PhysicsBody> physics_body_;
public:
PhysicsComponent() {
collision_data_.resize(256); // 碰撞数据缓存
physics_body_ = std::make_unique<PhysicsBody>();
std::cout << "PhysicsComponent初始化物理系统" << std::endl;
}
void update(float deltaTime) override {
std::cout << "物理更新: " << deltaTime << "秒" << std::endl;
// 物理模拟逻辑
}
void render() override {
std::cout << "渲染物理调试信息" << std::endl;
}
std::string getType() const override {
return "PhysicsComponent";
}
~PhysicsComponent() override {
std::cout << "PhysicsComponent清理物理资源" << std::endl;
}
};
class RenderComponent : public Component {
private:
std::shared_ptr<class Texture> texture_;
std::vector<float> vertex_buffer_;
std::vector<uint32_t> index_buffer_;
public:
RenderComponent() {
vertex_buffer_.resize(1024); // 顶点缓冲区
index_buffer_.resize(2048); // 索引缓冲区
std::cout << "RenderComponent分配图形资源" << std::endl;
}
void update(float deltaTime) override {
// 动画更新等
std::cout << "渲染组件更新" << std::endl;
}
void render() override {
std::cout << "执行渲染命令" << std::endl;
// 实际渲染逻辑
}
std::string getType() const override {
return "RenderComponent";
}
~RenderComponent() override {
std::cout << "RenderComponent释放图形资源" << std::endl;
}
};
// 游戏实体管理组件
class GameEntity {
private:
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Component>> components_;
public:
template<typename T, typename... Args>
void addComponent(Args&&... args) {
components_.push_back(std::make_unique<T>(std::forward<Args>(args)...));
}
void updateAll(float deltaTime) {
for (const auto& component : components_) {
component->update(deltaTime);
}
}
void renderAll() {
for (const auto& component : components_) {
component->render();
}
}
// 自动管理所有组件的生命周期
// 因为Component有虚析构函数,所有派生组件都能正确清理
};不应使用虚析构函数的场景
1. 非多态工具类优化
cpp
// 不应使用虚析构函数的场景 - 值语义类
class Vector3D { // 数学向量类,非多态,值语义
public:
Vector3D(double x, double y, double z) : x_(x), y_(y), z_(z) {}
// 不需要虚析构函数!避免不必要的虚表指针开销
~Vector3D() = default;
// 值语义操作
Vector3D operator+(const Vector3D& other) const {
return Vector3D(x_ + other.x_, y_ + other.y_, z_ + other.z_);
}
double dot(const Vector3D& other) const {
return x_ * other.x_ + y_ * other.y_ + z_ * other.z_;
}
double length() const {
return std::sqrt(x_ * x_ + y_ * y_ + z_ * z_);
}
private:
double x_, y_, z_;
};
// 性能敏感的数据结构
class FixedSizeArray {
public:
static constexpr size_t SIZE = 1000;
FixedSizeArray() {
std::fill(data_, data_ + SIZE, 0);
}
// 明确禁止继承 - 不需要虚析构函数
~FixedSizeArray() = default;
double& operator[](size_t index) {
return data_[index];
}
private:
double data_[SIZE];
};
void demonstrate_performance_impact() {
std::cout << "Vector3D大小: " << sizeof(Vector3D) << " 字节" << std::endl; // 24字节 (3*8)
class Vector3DWithVirtual {
double x, y, z;
public:
virtual ~Vector3DWithVirtual() = default; // 不必要的虚析构
};
std::cout << "Vector3DWithVirtual大小: " << sizeof(Vector3DWithVirtual)
<< " 字节" << std::endl; // 32字节 (3*8 + 8虚表指针)
// 在大量使用时,24字节 vs 32字节有显著的内存和缓存影响
}2. STL兼容性和final类优化
cpp
// STL风格容器 - 不应使用虚析构函数
template<typename T>
class SimpleVector {
private:
T* data_;
size_t size_;
size_t capacity_;
public:
SimpleVector() : data_(nullptr), size_(0), capacity_(0) {}
~SimpleVector() { // 非虚析构函数
delete[] data_;
}
// 值语义 - 需要拷贝控制
SimpleVector(const SimpleVector& other);
SimpleVector& operator=(const SimpleVector& other);
// 不应该从这个类继承!
};
// C++11 final类优化
class MathUtilities final { // final类:明确禁止继承
public:
static double pi() { return 3.141592653589793; }
static double degreesToRadians(double degrees) {
return degrees * pi() / 180.0;
}
// 不需要虚析构函数!
~MathUtilities() = default;
// 明确禁止构造
MathUtilities() = delete;
private:
// 所有功能通过静态方法提供
};
// 错误尝试继承final类
// class ExtendedMath : public MathUtilities { }; // 编译错误现代C++最佳实践
1. 明确的设计意图表达
cpp
// 现代C++多态基类设计模板
class PolymorphicBase {
public:
// 明确表达多态意图
virtual ~PolymorphicBase() = default;
// 明确禁止拷贝(多态对象通常不应拷贝)
PolymorphicBase(const PolymorphicBase&) = delete;
PolymorphicBase& operator=(const PolymorphicBase&) = delete;
// 允许移动(如果合理)
PolymorphicBase(PolymorphicBase&&) = default;
PolymorphicBase& operator=(PolymorphicBase&&) = default;
// 纯虚函数定义接口
virtual void perform() = 0;
protected:
PolymorphicBase() = default; // 保护构造,只能通过派生类创建
};
// 具体实现类使用override明确意图
class ConcreteImplementation : public PolymorphicBase {
public:
void perform() override {
std::cout << "具体实现工作" << std::endl;
}
// C++11 override关键字明确析构函数意图
~ConcreteImplementation() override = default;
};2. 智能指针与RAII自动管理
cpp
class NetworkConnection {
public:
virtual ~NetworkConnection() = default;
virtual void send(const std::string& data) = 0;
virtual std::string receive() = 0;
virtual bool isConnected() const = 0;
// 工厂方法返回智能指针
static std::unique_ptr<NetworkConnection> createTcp(const std::string& host, int port);
static std::unique_ptr<NetworkConnection> createUdp(const std::string& host, int port);
};
// 使用现代RAII模式
void modern_network_management() {
// 自动生命周期管理
auto connection = NetworkConnection::createTcp("example.com", 8080);
if (connection->isConnected()) {
connection->send("Hello Server");
auto response = connection->receive();
std::cout << "收到响应: " << response << std::endl;
}
// 不需要手动delete - 离开作用域时自动调用正确析构函数
// 即使NetworkConnection有多个派生类也能正确处理
}关键洞见与行动指南
必须使用虚析构函数的场景:
- 任何包含虚函数的类:虚函数的存在暗示了多态用途
- 工厂模式返回的基类指针:调用者可能通过基类指针删除对象
- 观察者模式中的观察者基类:主题持有基类指针列表
- 策略模式中的策略接口:上下文持有策略基类指针
- 任何可能被多态使用的基类:防御性编程原则
不应使用虚析构函数的场景:
- 非多态工具类:没有虚函数,不打算作为基类
- final类:明确禁止继承的类
- 性能关键的简单类:避免虚表指针的开销
- STL风格的值类型:基于值的语义,不是多态
现代C++开发建议:
- 默认使用=default:让编译器生成正确的析构函数
- 明确override意图:使用override关键字
- 智能指针管理:优先使用unique_ptr和shared_ptr
- 防御性设计:当不确定时,为基类提供虚析构函数
需要警惕的陷阱:
- 标准库继承:不要从STL容器公开继承
- 多重继承:确保所有相关基类都有适当的析构函数
- 菱形继承:虚基类的特殊析构要求
- 异常安全:析构函数不应抛出异常
最终建议: 将虚析构函数视为多态体系中的"保险机制"。培养"多态思维"------在设计每个继承体系时都问自己:"这个基类的析构函数是否需要是virtual的?" 这种严谨的态度是构建健壮C++系统的关键。
记住:在C++多态世界中,虚析构函数不是可选项,而是基类设计的基本契约。 条款7教会我们的不仅是一个语法规则,更是面向对象设计的基本原则。