前序遍历(递归实现)
java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
return prio(root,list);
}
public List<Integer> prio(TreeNode a,List<Integer>list)
{
if(a==null)
return list;
list.add(a.val);
prio(a.left,list);
prio(a.right,list);
return list;
}
}中序遍历(递归实现)
java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
return zhong(root,list);
}
public List<Integer> zhong(TreeNode a,List<Integer>list)
{
if(a==null)
return list;
zhong(a.left,list);
list.add(a.val);
zhong(a.right,list);
return list;
}}
后序遍历(递归实现)
java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
return hou(root,list);
}
public List<Integer> hou(TreeNode node,List<Integer>list)
{
if(node==null)
return list;
hou(node.left,list);
hou(node.right,list);
list.add(node.val);
return list;
}
}非递归实现中序遍历
java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();//栈记录走过的路程
//非递归实现
while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
{
if(root!=null)
{
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}else
{
TreeNode pop=stack.pop();
list.add(pop.val);
root=pop.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}非递归实现前序遍历
java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();
while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
{
if(root!=null)
{
list.add(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}else{
TreeNode pop=stack.pop();
root=pop.right;
}
}
return list;
}
}后序遍历(非递归实现)
java
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
LinkedList<TreeNode> stack=new LinkedList<>();
TreeNode pop=null;
while(root!=null||!stack.isEmpty())
{
if(root!=null)
{
stack.push(root);
root=root.left;
}else{
TreeNode peek=stack.peek();
if(peek.right==null||peek.right==pop)
{
pop=stack.pop();
list.add(pop.val);
}
else{
root=peek.right;
}
}
}
return list;
}
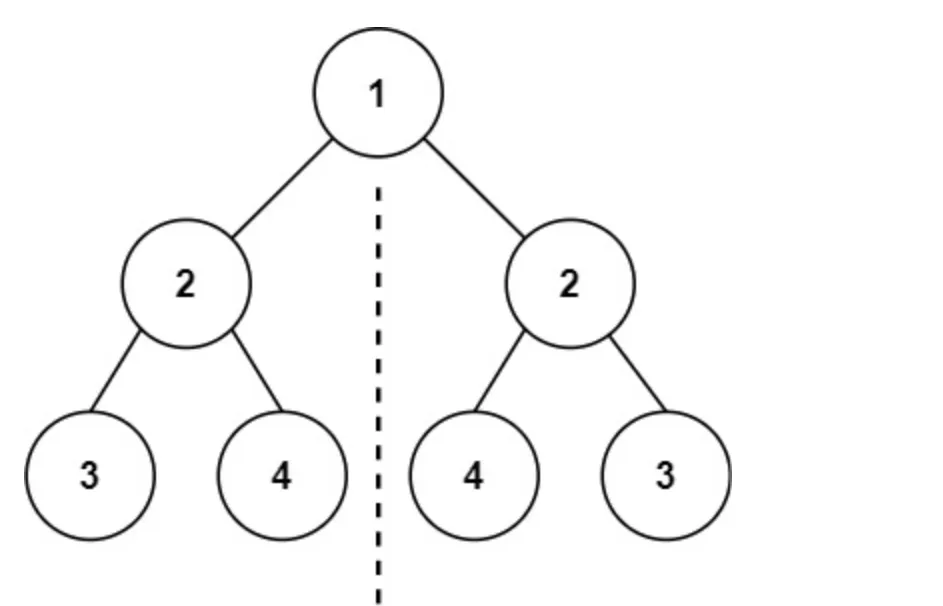
}判断二叉树是不是对称二叉树
java
代码实现(递归解法)
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return duichen(root.left,root.right);
}
public boolean duichen(TreeNode left,TreeNode right)
{
if(right==null&&left==null)
{
return true;
}
if(right==null||left==null)
{
return false;
}
if(left.val!=right.val)
{
return false;
}
return duichen(left.left,right.right)&&duichen(left.right,right.left);
}
}迭代解法
java
class Solution {
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
if(root.left==null&&root.right==null)
{
return 1;
}
int a=maxDepth(root.left);
int b=maxDepth(root.right);
int i=Math.max(a,b);
return i+1;
}
}
java
import java.util.*;
class Solution {
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if(root==null)
return 0;
int a=minDepth(root.left);
int b=minDepth(root.right);
int i=Math.min(a,b);
//要多做一个判断,如果左子树/右子树为0,那么就以不为0的那个为准
if(a==0)
return b+1;
if(b==0)
return a+1;
return i+1;
}
}
java
class Solution {
public TreeNode flipTree(TreeNode root) {
fn(root);
return root;
}
public void fn(TreeNode node)
{
if(node==null)
{
return;
}
TreeNode temp=node.left;
node.left=node.right;
node.right=temp;
fn(node.left);
fn(node.right);
}
}二叉搜索树