Lossless Semantic Trees (LST) 是 openrewrite的 代码解析和修改的核心理论,取代了传统的abstract syntax tree。
支持对java 和yaml文件进行LST解析
1 vs ast
1.1Lossless Semantic Tree (LST) is a tree representation of code
1.2比AST(abstract syntax tree) 可以提供精准搜索和转换,特性
- Type-attributed提供类型信息
Format-preserving格式保持
2 lifecycle
2.1OpenRewrite 进程创建一个存储在内存中的 LST。这反映了磁盘上存储库的当前状态。
2.2该过程通过对 LST 进行转换来继续。在过程中可以仅仅增加 search marker (search 类recipe) ,也可以修改代码
2.3配方运行完成后,LST 将转换回文本,然后用于覆盖任何已更改的现有文件(注意:如果是dryRun,不修改文件,仅输出diff)。
2.4覆盖所有文件后,该过程结束。recipe运行之间不存储任何内容。
2.5如果您在第一个recipe完成后运行另一个recipe,则届时将生成一个新的 LST。
2.6如果之前的recipe进行了更改,并且这些更改存在于本地,则新生成的 LST 将具有所有这些更改。如果之前的recipe没有进行任何更改,那么 LST 实际上将与之前相同。
3 Java LST
3.1CompilationUnit
3.1.1root of the Java LST,一个java 文件就是一个CompilationUnit
3.1.2Package
3.1.3Import
fieldAccess:这里的fieldAccess 其实import的类名称
3.1.4ClassDeclaration
- block
- Identifier 注意identifier 是任意名称(类,变量,方法 。。),即实际很多地方都有
- VariableDeclaration
- Expression anything that returns a value,MethodInvocation, Identifier, and Binary are all examples of expressions
- MethodDeclaration 包括了方案body
- MethodInvocation 包括了参数
- NewClass new 新实例/对象 Statement if, while, try, Block, return, and
MethodInvocation are all examples of statements. - VariableDeclarations
3.2注意其实type非常多,可以通过debug或者TreeVisitingPrinter来查看明细
3.2.1debug
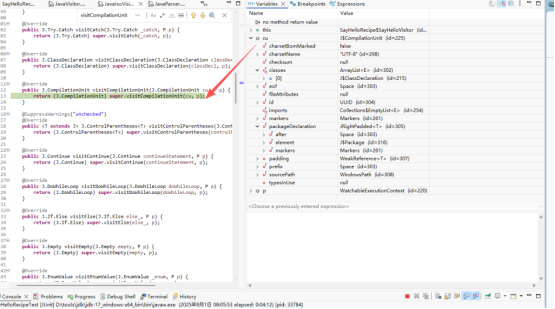
在JavaIsoVisitor类的visitCompilationUnit 增加断点
@Override
public J.CompilationUnit visitCompilationUnit(J.CompilationUnit cu, P p) {
return (J.CompilationUnit) super.visitCompilationUnit(cu, p);
}
查看CU对象
3.3使用TreeVisitingPrinter输出
java
public class TreeVisitingPrinterRecipe extends Recipe {
@Override
public String getDisplayName() {
return "JavaIsoVisitor"
}
@Override
public JavaIsoVisitor<ExecutionContext> getVisitor() {
return new JavaIsoVisitor<ExecutionContext>() {
@Override
public J.CompilationUnit visitCompilationUnit(J.CompilationUnit compUnit, ExecutionContext executionContext) {
// This next line could be omitted in favor of a breakpoint
// if you'd prefer to use the debugger instead.
System.out.println(TreeVisitingPrinter.printTree(getCursor()));
return super.visitCompilationUnit(compUnit, executionContext);
}
};
}
@Override
public @Description String getDescription() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return "JavaIsoVisitor."
}
}3.3.2output example
java
----J.CompilationUnit
\---J.ClassDeclaration
|---J.Identifier | "A"
\---J.Block
\-------J.MethodDeclaration | "MethodDeclaration{A{name=test,return=void,parameters=[]}}"
|---J.Primitive | "void"
|---J.Identifier | "test"
|-----------J.Empty
\---J.Block
|-------J.VariableDeclarations | "int a"
| |---J.Primitive | "int"
| \-------J.VariableDeclarations.NamedVariable | "a"
| \---J.Identifier | "a"
\-------J.Assignment | "a = 0"
|---J.Identifier | "a"
\-------J.Literal | "0"3.3.3comment 读取有一定问题,不会输出
3.4问题
3.4.1读取comment有一些问题
java
public static String readFile(String filePath) throws IOException {
byte[] bytes = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filePath)); // new file comment-----
return new String(bytes, "UTF-8"); // chatset ----->StandardCharsets.UTF_8
} 输出如下
java
visitReturn->TextComment(multiline=false, text= new file comment-----, suffix=
, markers=Markers(id=48453257-5524-4864-a28f-0a18937fcd4f, markers=[]))即最后一个comment没有读取到,而且把上一行的comment 挂到return上
另外方法前的comment也会挂到方法上而不是class内
测试所用方法
java
@Override
public Statement visitStatement(Statement statement, ExecutionContext executionContext) {
if (statement.getComments().size()>0) {
statement.getComments().forEach(
comment->{
TextComment text=(TextComment) comment
System.out.println("visitStatement->"+statement.print()+"->->"+ text.getText()+" -->end<--");
}
);
}
return (Statement) super.visitStatement(statement, executionContext);
}