一、需求分析
现有需求,一些数据暂时不方便直接读取或通过csv等文件导入数据库。只能以截图-图片/jpg形式发给业务,业务老师想直接上传图片后解析数据存到对应表中。
经查询OCR技术符合,现以Tess4J 演示
1.1 选择Tess4J 的原因
允许 Java 程序直接使用 Tesseract OCR 引擎进行光学字符识别(OCR),并且省去了额外安装 Tesseract 环境的麻烦。使用 Tess4J 时,Tesseract 的核心库已经被封装进了该库中,因此无需单独安装 Tesseract 引擎。
优势:
1.Tess4J 能够在 Windows、Linux 和 macOS 上运行,无需为不同操作系统安装不同版本的 Tesseract。
2.通过简单的 API 调用即可完成 OCR
1.2 使用步骤
老规矩, 1.2.1 加 maven 依赖
XML<!-- Tesseract-OCR 依赖 --> <dependency> <groupId>net.sourceforge.tess4j</groupId> <artifactId>tess4j</artifactId> <version>5.8.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
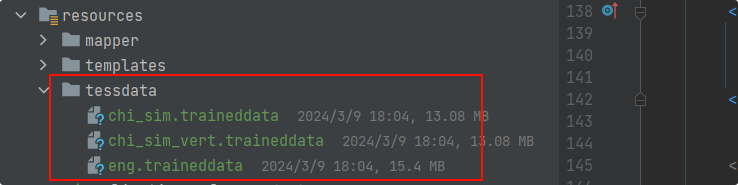
1.2.2 虽然 Tess4J 不需要单独安装 Tesseract 引擎,但你仍然需要下载 Tesseract 语言数据文件 (例如,chi_sim.traineddata 用于简体中文),并将其放在指定的路径中。Tesseract 官方 GitHub
下图展示
1.2.3 代码演示
java
// 临时文件存储路径(实际项目建议用分布式存储,如 MinIO)
private static final String TEMP_DIR = "temp/images";
@ApiOperation("上传图片解析内容")
@PostMapping("/upload-ocr")
@SneakyThrows
public String uploadAndOcr(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
// 1. 保存上传的图片到临时目录
File tempDir = new File(TEMP_DIR);
if (!tempDir.exists()) tempDir.mkdirs();
File tempFile = new File(TEMP_DIR +File.separator+ file.getOriginalFilename());
// 2. 强制转为绝对路径文件(关键!避免 Tomcat 重写路径)
File absoluteTempFile = tempFile.getAbsoluteFile();
file.transferTo(absoluteTempFile);
String tempPath = tempFile.getAbsolutePath();
String newPath = generateNewFileName(tempPath);
ImagePreprocessUtil.preprocessWithImageIO(tempPath,newPath);
// 再进行膨胀处理(1次即可,强化 -- 特征)
// ImagePreprocessUtil.dilateImage(newPath, newPath, 1);
service.uploadAndOcr(newPath);
// 4. 数据入库(调用 Service 层)
// service.saveBatch(cleanData);
// 5. 删除临时文件(可选)
// tempFile.delete();
return "解析成功!";
}
/**
* 生成新文件名(如 "23.jpg" → "23bak.jpg")
* @param originalFileName 原始文件名
* @return 新文件名
*/
public static String generateNewFileName(String originalFileName) {
if (originalFileName == null || originalFileName.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
int dotIndex = originalFileName.lastIndexOf(".");
if (dotIndex == -1) {
// 无扩展名:"23" → "23bak"
return originalFileName + "bak";
} else {
// 有扩展名:"23.jpg" → "23bak.jpg"
String prefix = originalFileName.substring(0, dotIndex);
String suffix = originalFileName.substring(dotIndex);
return prefix + "bak" + suffix;
}
}1.3 处理解析图片
java
@Override
@SneakyThrows
public String uploadAndOcr(String tempPath) {
// 2. 调用 OCR 解析图片文字
List<List<String>> tableData = OcrUtils.parseImageTable(tempPath);
// 3. 数据清洗过滤(移除"不佳、一般") 这个针对自身业务的,可不看
List<FundRiseVO> cleanData = OcrUtils.filterInvalidData(tableData);
System.out.println(cleanData);
return null;
}
java
package com.test.dawu.util;
import com.test.dawu.vo.FundRiseVO;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.ITesseract;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.Tesseract;
import net.sourceforge.tess4j.TesseractException;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* OCR 解析图片
*/
@Slf4j
public class OcrUtils {
// 初始化 Tesseract(需下载中文训练集 eng.traineddata 和 chi_sim.traineddata,放入 tessdata 目录)
private static final ITesseract TESSERACT = new Tesseract();
static {
// 设置训练集路径(本地 tessdata 目录)
TESSERACT.setDatapath("src/main/resources/tessdata");
// 设置语言(中文+英文)
TESSERACT.setLanguage("chi_sim+eng");
// 多次调用 setVariable 设置多个参数(替代批量设置)
TESSERACT.setVariable("load_system_dawg", "false"); // 关闭系统字典
TESSERACT.setVariable("load_freq_dawg", "false"); // 关闭频率字典
// 例如:只识别 数字、字母、中文、--、/ 等(根据你的场景调整)
// TESSERACT.setVariable("tessedit_char_whitelist", "\u4e00-\u9fa50123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ--/=");
TESSERACT.setVariable("preserve_interword_spaces", "1"); // 保留空格
// 设置页面分割模式
TESSERACT.setPageSegMode(6);
}
/**
* 解析图片中的表格文字,返回二维列表(行→列)
*/
public static List<List<String>> parseImageTable(String imagePath) throws TesseractException {
File imageFile = new File(imagePath);
// 1. OCR 识别图片文字(返回按行分割的字符串)
String ocrText = TESSERACT.doOCR(imageFile);
log.info("直接即系数据为{}",ocrText);
String[] lines = ocrText.split("\\n"); // 按换行符分割行
List<List<String>> tableData = new ArrayList<>();
// 2. 按制表符分割每行数据(假设图片表格用制表符分隔列,可根据实际调整分割符)
for (String line : lines) {
String[] columns = line.trim().split("\\t+"); // 多个制表符合并为一个
List<String> rowData = new ArrayList<>();
for (String col : columns) {
if (!col.isEmpty()) {
rowData.add(col); // 过滤空字符串
}
}
if (!rowData.isEmpty()) {
tableData.add(rowData);
}
}
return tableData;
}
// 无效内容列表(可配置到配置文件中)
private static final List<String> INVALID_CONTENTS = List.of("不佳", "一般", "良好", "优秀");
/**
* 过滤无效数据,将表格转为 FundRiseVO 列表
*/
public static List<FundRiseVO> filterInvalidData(List<List<String>> tableData) {
List<FundRiseVO> cleanData = new ArrayList<>();
// 假设表格第 3 行开始是数据行(索引 2,需根据实际 OCR 结果调整)
for (int i = 2; i < tableData.size(); i++) {
List<String> row = tableData.get(i);
if (row.size() < 4) continue; // 过滤列数不足的无效行
// 1. 提取原始数据(周期、涨跌幅、同类平均、同类排行)
String period = row.get(0); // 近1周、近1月
String riseRate = row.get(1); // -0.93%、5.69%
String peerAvg = row.get(2); // 2.16%、10.58%
String peerRank = row.get(3); // 4175/4394、3079/4249
// 2. 检查后续列是否包含无效内容(如"不佳""一般"),并剔除
for (int j = 4; j < row.size(); j++) {
String col = row.get(j);
if (INVALID_CONTENTS.contains(col)) {
// 无效内容已找到,直接跳出(避免影响其他数据)
break;
}
}
// 3. 封装为 VO(过滤空值)
if (!period.isEmpty() && !riseRate.isEmpty()) {
FundRiseVO vo = new FundRiseVO();
vo.setPeriod(period);
vo.setRiseRate(riseRate);
vo.setPeerAvg(peerAvg);
vo.setPeerRank(peerRank);
cleanData.add(vo);
}
}
return cleanData;
}
}二、工具类
为啥写这个工具类,前面的解析图片后发现以下情况
- 500/1050 【/1050】这个是灰色的,直接解析发现输出的数据中 只有500。此时需要将图片
java
package com.swsmu.esp.espbackend.util;
import javax.imageio.ImageIO;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.image.BufferedImage;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
/**
*
*@author dawu_jinsan
*@date 2025/10/27 16:17
*@version V1.0
* @desc 对图片进行简单预处理
*
*/
public class ImagePreprocessUtil {
/**
* 简单预处理:灰度化 + 对比度增强(基于亮度调整)
*/
public static void preprocessWithImageIO(String inputPath, String outputPath) throws IOException {
// 1. 读取图片
BufferedImage src = ImageIO.read(new File(inputPath));
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
// 2. 转为灰度图(同之前)
BufferedImage gray = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
Graphics2D g = gray.createGraphics();
g.drawImage(src, 0, 0, null);
g.dispose();
// 3. 增强对比度(核心优化:文字变暗,背景保持白色)
BufferedImage enhanced = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int grayValue = gray.getRGB(x, y) & 0xFF; // 0-255(0=黑,255=白)
// 关键逻辑:
// - 背景(接近白色,灰度值高):保持白色(255)
// - 文字(浅灰色,灰度值中等):按比例加深(降低灰度值)
int threshold = 230; // 背景阈值(高于此值视为背景,保持白色)
int enhancedValue;
if (grayValue > threshold) {
// 背景:强制为白色(255)
enhancedValue = 255;
} else {
// 文字:按比例加深(灰度值越低,文字越黑)
// 例如:将 150-230 的浅灰范围映射到 0-150 的深灰范围
enhancedValue = (int) (grayValue * (150.0 / threshold));
}
// 确保值在 0-255 范围内
enhancedValue = Math.max(0, Math.min(255, enhancedValue));
// 设置像素(灰度图:R=G=B=enhancedValue)
enhanced.setRGB(x, y, enhancedValue << 16 | enhancedValue << 8 | enhancedValue);
}
}
/* // 3. 二值化处理(替代对比度增强,适合背景干净的图片)
BufferedImage enhanced = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
int binaryThreshold = 200; // 二值化阈值(高于此值为白,低于为黑)
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int grayValue = gray.getRGB(x, y) & 0xFF;
// 非黑即白:文字(<200)→ 黑(0),背景(≥200)→ 白(255)
int binaryValue = grayValue < binaryThreshold ? 0 : 255;
enhanced.setRGB(x, y, binaryValue << 16 | binaryValue << 8 | binaryValue);
}
}*/
// 4. 保存图片
ImageIO.write(enhanced, "jpg", new File(outputPath));
}
/**
* 自适应阈值二值化:兼顾浅灰色文字和特殊符号
* @param inputPath 原始图片路径
* @param outputPath 处理后图片路径
* @param blockSize 局部区域大小(奇数,如 15,越大越平滑)
* @param c 阈值偏移量(负数可保留更多浅灰,如 -10)
*/
public static void adaptiveThreshold(String inputPath, String outputPath, int blockSize, int c) throws IOException {
// 1. 读取图片并转为灰度图
BufferedImage src = ImageIO.read(new File(inputPath));
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
BufferedImage gray = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
Graphics2D g = gray.createGraphics();
g.drawImage(src, 0, 0, null);
g.dispose();
// 2. 自适应阈值二值化(核心)
BufferedImage binary = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
// 计算当前像素周围 blockSize×blockSize 区域的平均灰度
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
int halfBlock = blockSize / 2;
// 遍历局部区域(避免越界)
for (int dy = -halfBlock; dy <= halfBlock; dy++) {
for (int dx = -halfBlock; dx <= halfBlock; dx++) {
int nx = x + dx;
int ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < width && ny >= 0 && ny < height) {
sum += gray.getRGB(nx, ny) & 0xFF;
count++;
}
}
}
// 局部区域平均灰度作为基准阈值
int localThreshold = sum / count + c;
// 当前像素灰度值
int pixel = gray.getRGB(x, y) & 0xFF;
// 二值化:低于局部阈值为黑(文字),高于为白(背景)
int binaryPixel = pixel < localThreshold ? 0 : 255;
binary.setRGB(x, y, binaryPixel << 16 | binaryPixel << 8 | binaryPixel);
}
}
// 3. 保存处理后的图片
ImageIO.write(binary, "jpg", new File(outputPath));
}
/**
* 低阈值二值化:保留浅灰色文字(如/1050),同时尽量减少背景噪声
* @param inputPath 原始图片路径
* @param outputPath 处理后图片路径
* @param threshold 二值化阈值(建议220-230,值越高保留的浅灰色越多)
*/
public static void lowThresholdBinarization(String inputPath, String outputPath, int threshold) throws IOException {
// 1. 读取图片并转为灰度图
BufferedImage src = ImageIO.read(new File(inputPath));
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
BufferedImage gray = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
Graphics2D g = gray.createGraphics();
g.drawImage(src, 0, 0, null);
g.dispose();
// 2. 低阈值二值化(核心:保留浅灰色)
BufferedImage binary = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int grayValue = gray.getRGB(x, y) & 0xFF; // 0-255(0=黑,255=白)
// 阈值判断:低于阈值→文字(黑),高于→背景(白)
// 阈值设为220-230,确保浅灰色(如200-220)被保留为文字
int binaryValue = grayValue < threshold ? 0 : 255;
binary.setRGB(x, y, binaryValue << 16 | binaryValue << 8 | binaryValue);
}
}
// 3. 保存处理后的图片
ImageIO.write(binary, "jpg", new File(outputPath));
}
/**
* 膨胀处理:加粗线条(让 -- 的两条横线更清晰,避免粘连或误判)
* @param inputPath 二值化后的图片路径(非黑即白,效果更佳)
* @param outputPath 处理后图片路径
* @param iterations 膨胀次数(1-2次即可,过多会导致线条粘连)
*/
public static void dilateImage(String inputPath, String outputPath, int iterations) throws IOException {
// 1. 读取二值化图片(非黑即白,确保膨胀效果)
BufferedImage binary = ImageIO.read(new File(inputPath));
int width = binary.getWidth();
int height = binary.getHeight();
BufferedImage dilated = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_BYTE_GRAY);
// 2. 膨胀逻辑:将黑色像素(文字)的周围像素也设为黑色,加粗线条
for (int i = 0; i < iterations; i++) {
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
int pixel = binary.getRGB(x, y) & 0xFF;
if (pixel == 0) { // 当前像素是黑色(文字)
// 将周围 3x3 区域的像素设为黑色(膨胀)
for (int dy = -1; dy <= 1; dy++) {
for (int dx = -1; dx <= 1; dx++) {
int nx = x + dx;
int ny = y + dy;
if (nx >= 0 && nx < width && ny >= 0 && ny < height) {
dilated.setRGB(nx, ny, 0 << 16 | 0 << 8 | 0); // 设为黑色
}
}
}
} else {
// 背景保持白色
dilated.setRGB(x, y, 255 << 16 | 255 << 8 | 255);
}
}
}
// 迭代时,将处理后的图片作为下一次的输入
binary = dilated;
}
// 3. 保存膨胀后的图片
ImageIO.write(dilated, "jpg", new File(outputPath));
}
}2.1 二值化 与 增强对比度 转为灰度图各自作用
-
二值化:
- 作用:将图像转为只有两种颜色(黑白),突出主要信息,简化图像。
- 应用:OCR,边缘检测,图像分割。
-
增强对比度:
- 作用:增强图像中不同亮度区域之间的对比度,使细节更加突出,改善图像的清晰度。
- 应用:OCR,图像优化,细节增强。
-
转为灰度图:
- 作用:去除颜色信息,只保留亮度信息,简化图像,减少复杂度。
- 应用:图像预处理,图像分析,OCR。
2.2 结果
因文中是某个产品的测试原图
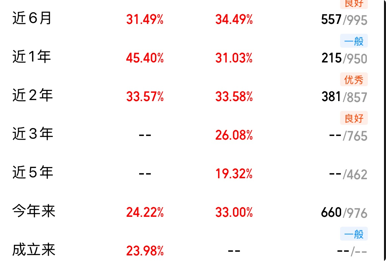
1.转为灰度图
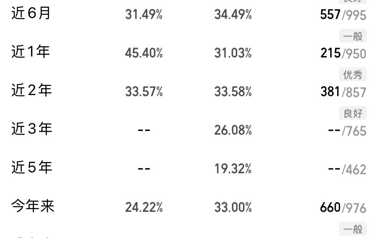
2.直接增强对比度
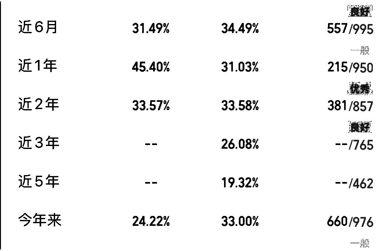
- 灰度图+增强对比度
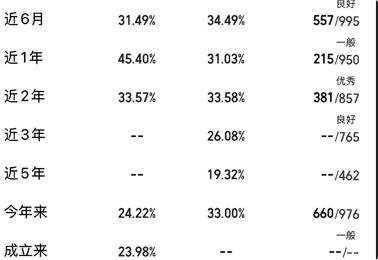
- 二值化处理
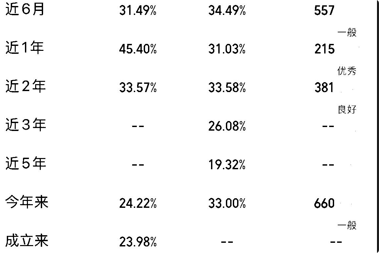
读取还是会有问题,比如--/-- 识别为 -~-/-- 或者 = 或者 ww
解决办法:
https://blog.csdn.net/daiyi666/article/details/131021701
里面的自定义字库
// 设置字符白名单,确保识别 "0-9", "-", "." 等 tesseract.setTessVariable("tessedit_char_whitelist", "0123456789-.")
注意:白名单设置会限制在这些范围内识别!仅仅适用于范围狭窄的 文字内容
三、spire_ocr_java
原因换种方式 试一试
1.导包 + Maven 在构建过程中查找依赖的仓库来源
XML<dependency> <groupId>e-iceblue</groupId> <artifactId>spire.ocr</artifactId> <version>2.1.1</version> </dependency> <repository> <id>com.e-iceblue</id> <name>e-iceblue</name> <url>https://repo.e-iceblue.cn/repository/maven-public/</url> </repository>
2.代码
代码中dependencis 文件地址 【我是直接解压放到E盘测试,看你自己放置位置】也可以在1中点击进入官方下载
https://www.e-iceblue.com/downloads/plugins/java/ocr/windows/dependencies.zip
java
@ApiOperation("上传图片解析内容")
@PostMapping("/upload-ocr/spire")
@SneakyThrows
public String uploadAndOcr2(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) {
// 1. 保存上传的图片到临时目录
File tempDir = new File(TEMP_DIR);
if (!tempDir.exists()) tempDir.mkdirs();
File tempFile = new File(TEMP_DIR + File.separator + file.getOriginalFilename());
// 2. 强制转为绝对路径文件(关键!避免 Tomcat 重写路径)
File absoluteTempFile = tempFile.getAbsoluteFile();
file.transferTo(absoluteTempFile);
// 2. 关键:旋转 180° 矫正上下颠倒
String rotatedImagePath = TEMP_DIR + File.separator + "rotated_" + file.getOriginalFilename();
rotate180(absoluteTempFile.getAbsolutePath(), rotatedImagePath);
// 指定依赖文件的路径
String dependencies = "E:\\dependencies";
// 指定输出文件的路径
String outputFile = TEMP_DIR+"/test_out.txt";
// 创建一个 OcrScanner 对象
OcrScanner scanner = new OcrScanner();
// 设置 OcrScanner 对象的依赖文件路径
scanner.setDependencies(dependencies);
// 使用 OcrScanner 对象扫描指定的图像文件
scanner.scan(rotatedImagePath);
// 获取 IOCRText 对象(而非直接字符串)
IOCRText ocrText = scanner.getText();
System.out.println(ocrText);
// 从 IOCRText 中提取完整文本(包含换行等格式)
String text = ocrText.toString();
// 创建一个输出文件对象
File output = new File(outputFile);
// 如果输出文件已经存在,则删除它
if (output.exists()) {
output.delete();
}
// 创建一个 BufferedWriter 对象用于向输出文件写入内容
BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(outputFile));
// 将扫描的文本内容写入输出文件中
writer.write(text);
// 关闭 BufferedWriter 对象以释放资源
writer.close();
return "解析成功";
}
/**
* 将图片旋转 180°(矫正上下颠倒)
* @param inputPath 原始图片路径
* @param outputPath 旋转后图片路径
*/
public static void rotate180(String inputPath, String outputPath) throws IOException {
// 读取原始图片
BufferedImage src = ImageIO.read(new File(inputPath));
int width = src.getWidth();
int height = src.getHeight();
// 创建旋转后的图片缓冲区
BufferedImage rotated = new BufferedImage(width, height, src.getType());
Graphics2D g = rotated.createGraphics();
// 旋转 180°:先平移到中心,旋转,再平移回来
g.translate(width / 2, height / 2);
g.rotate(Math.PI); // 旋转 180°(π 弧度)
g.translate(-width / 2, -height / 2);
// 绘制旋转后的图片
g.drawImage(src, 0, 0, null);
g.dispose();
// 保存旋转后的图片
ImageIO.write(rotated, "jpg", new File(outputPath));
}3.测试结果
我测试出来结果是倒着来的 ,【一般是从上到下,从左到右 的正常顺序】。
实际结果是 从下到上,从左到右。搜索得知
文字倒序的常见原因
- 图片被旋转:若图片因拍摄或处理失误被旋转了 180°(上下颠倒),OCR 会按 "倒着的文字" 顺序识别,导致结果倒序。
- 图片镜像翻转:图片左右翻转(如镜像效果),文字会从右到左排列,OCR 识别结果也会随之反转。
- 特殊排版:极少数情况下,图片文字本身是倒序排版(如设计需求),OCR 会忠实按排版顺序识别。
四、百度云中 通用文字识别
具体过程简单如下操作即可
大概参考https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37493556/article/details/109299207
因时间变动,会变得不同,最好根据下述官方来操作。上述可作为java代码参考
五、参考文档
https://blog.csdn.net/running17/article/details/127240736
六、Tess4J推荐------作者已做好工具类【灰度、对比、二值化分开的】
https://blog.csdn.net/gitblog_00167/article/details/153869561