什么是记忆化搜索,就是在规律中找出完全一模一样的进行存储,当搜索到这种情况时候,之间从存储的情况中返回
斐波那契数

解法一:递归
java
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
return dfs(n);
}
public int dfs(int n){
if(n==0 || n==1){
return n;
}
return dfs(n-1)+dfs(n-2);
}
}解法二:记忆化搜索
java
class Solution {
int[] memo;
public int fib(int n) {
memo=new int[32];
Arrays.fill(memo,-1);
return dfs(n);
}
public int dfs(int n){
if(memo[n]!=-1){
return memo[n];
}
if(n==0 || n==1){
return n;
}
memo[n]=dfs(n-1)+dfs(n-2);
return memo[n];
}
}解法三:动态规划
java
class Solution {
int[] dp;
public int fib(int n) {
dp=new int[31];
dp[0]=0;
dp[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i]=dp[i-1]+dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}不同路径
直接递归的话,会超出时间的限制
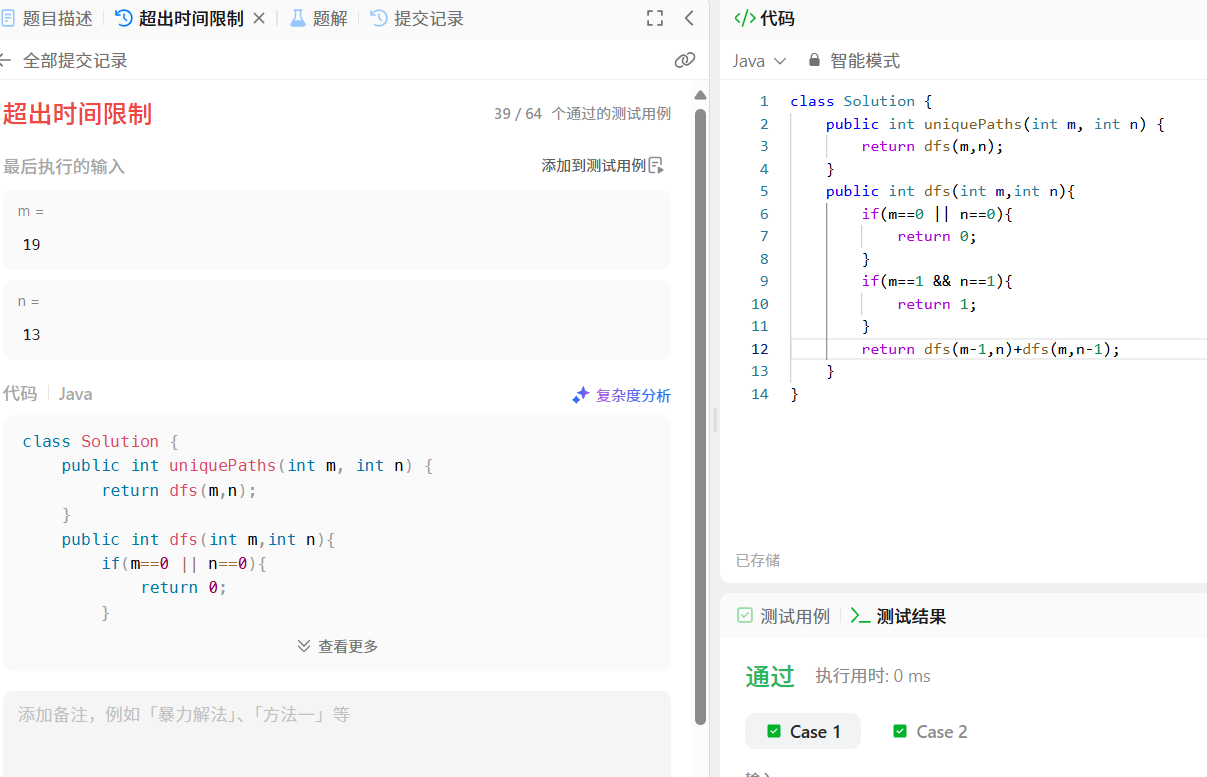
使用记忆化搜索的方式
java
class Solution {
int[][] memo;
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
memo=new int[m+1][n+1];
return dfs(m,n);
}
public int dfs(int m,int n){
if(memo[m][n]!=0){
return memo[m][n];
}
if(m==0 || n==0){
return 0;
}
if(m==1 && n==1){
memo[m][n]=1;
return 1;
}
memo[m][n]=dfs(m-1,n)+dfs(m,n-1);
return memo[m][n];
}
}使用动态规划
java
class Solution {
int[][] dp;
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
dp=new int[m+1][n+1];
dp[1][1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(i==1 && j==1){
continue;
}
dp[i][j]=dp[i][j-1]+dp[i-1][j];
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}最长递增子序列
直接使用递归会超时
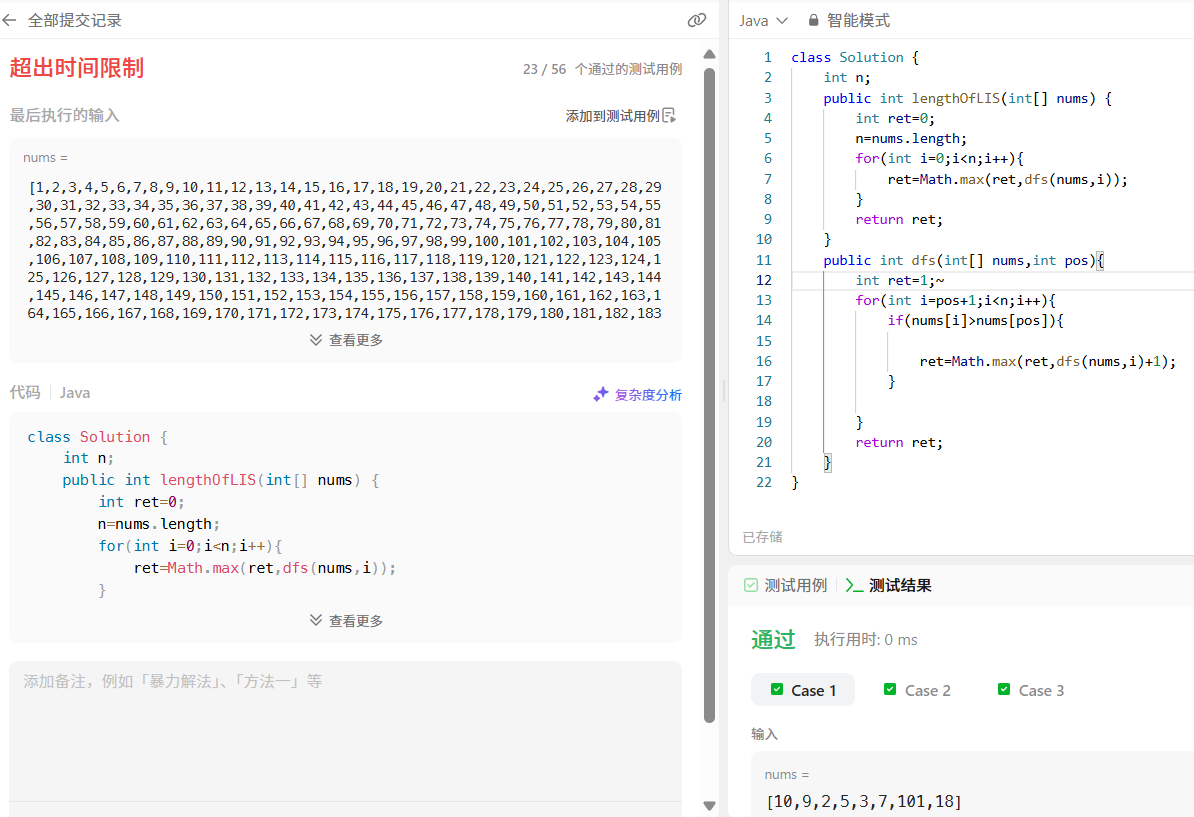
使用记忆化搜索
java
class Solution {
int n;
int[] memo;
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int ret=0;
n=nums.length;
memo=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
ret=Math.max(ret,dfs(nums,i,memo));
}
return ret;
}
public int dfs(int[] nums,int pos,int[] memo){
if(memo[pos]!=0){
return memo[pos];
}
int ret=1;
for(int i=pos+1;i<n;i++){
if(nums[i]>nums[pos]){
ret=Math.max(ret,dfs(nums,i,memo)+1);
}
}
memo[pos]=ret;
return ret;
}
}使用动态规划
java
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
int[] dp=new int[n];
int ret=0;
Arrays.fill(dp,1);
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=i+1;j<n;j++){
if(nums[i]<nums[j]){
dp[i]=Math.max(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
ret=Math.max(ret,dp[i]);
}
return ret;
}
}猜数字的大小Ⅱ
暴搜会超出时间的限制
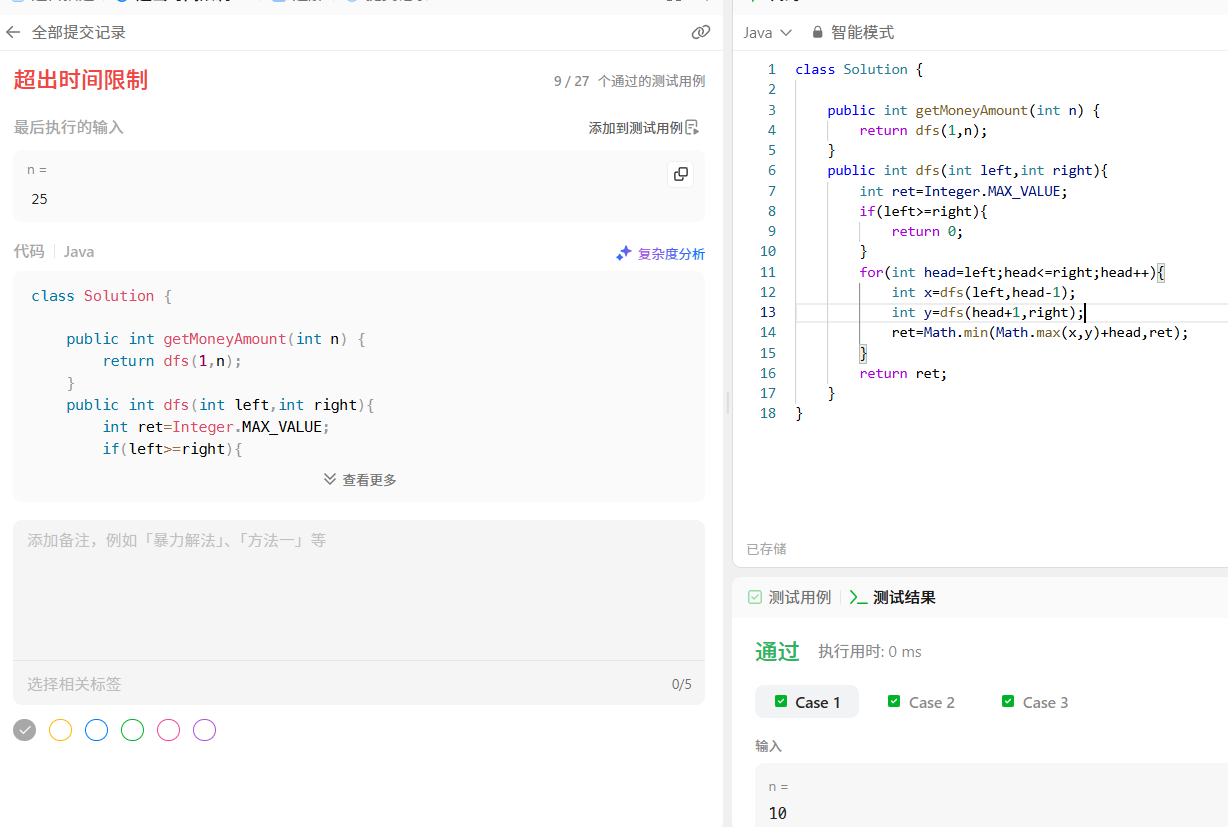
利用记忆化搜索
取最大值的意思就是 最坏情况(保证所有情况都能猜到10的前提下),然后在所有能猜中10的情况下找出最小值
java
class Solution {
int[][] memo;
public int getMoneyAmount(int n) {
memo=new int[n+1][n+1];
return dfs(1,n);
}
public int dfs(int left,int right){
int ret=Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if(left>=right){
return 0;
}
if(memo[left][right]!=0){
return memo[left][right];
}
for(int head=left;head<=right;head++){
int x=dfs(left,head-1);
int y=dfs(head+1,right);
ret=Math.min(Math.max(x,y)+head,ret);
}
memo[left][right]=ret;
return ret;
}
}矩阵中的最长递增路径
329. 矩阵中的最长递增路径 - 力扣(LeetCode)

直接暴搜会超时
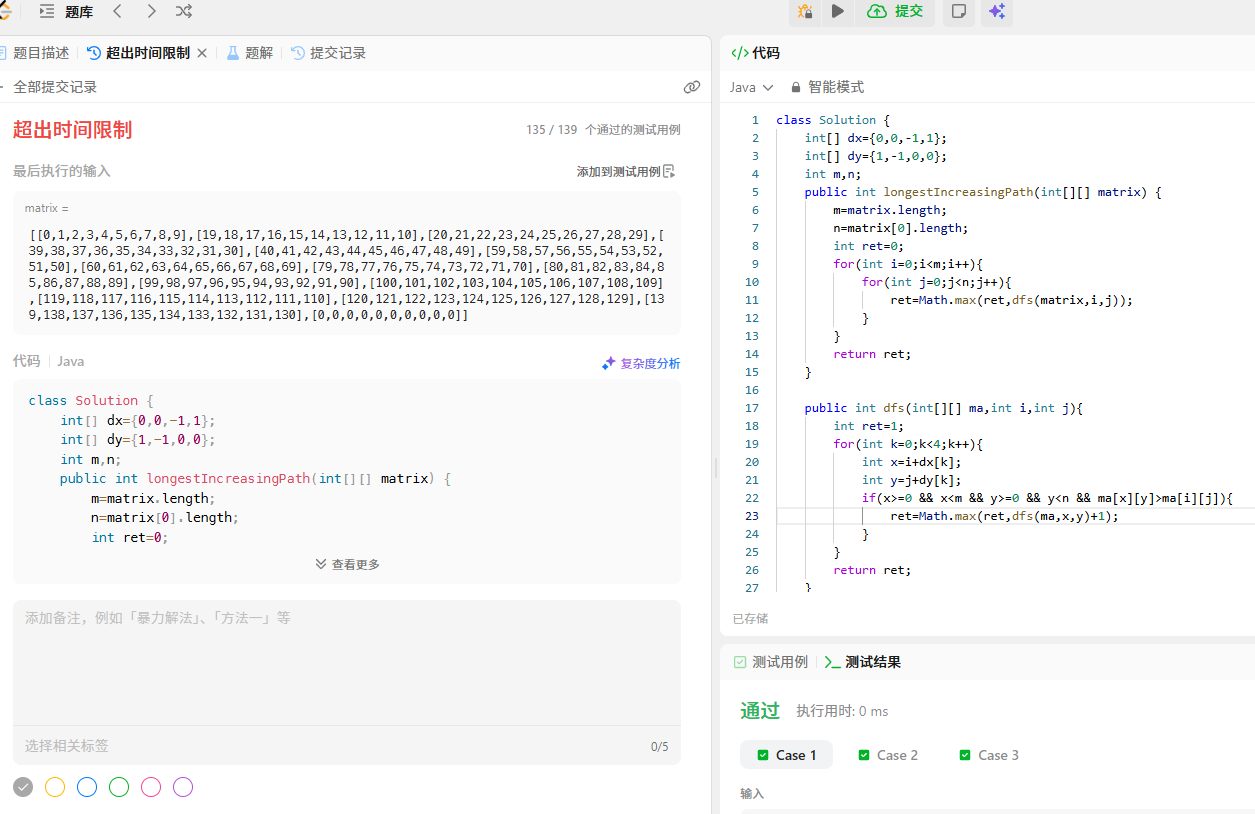
使用记忆化搜索
java
class Solution {
int[] dx={0,0,-1,1};
int[] dy={1,-1,0,0};
int[][] memo;
int m,n;
public int longestIncreasingPath(int[][] matrix) {
m=matrix.length;
n=matrix[0].length;
memo=new int[m][n];
int ret=0;
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
ret=Math.max(ret,dfs(matrix,i,j,memo));
}
}
return ret;
}
public int dfs(int[][] ma,int i,int j,int[][] memo){
if(memo[i][j]!=0){
return memo[i][j];
}
int ret=1;
for(int k=0;k<4;k++){
int x=i+dx[k];
int y=j+dy[k];
if(x>=0 && x<m && y>=0 && y<n && ma[x][y]>ma[i][j]){
ret=Math.max(ret,dfs(ma,x,y,memo)+1);
}
}
memo[i][j]=ret;
return ret;
}
}