三维重建【4-A】3D Gaussian Splatting:代码解读
- 一、高斯模型(gaussian_model.py)
-
- [1.1 build_scaling_rotation(s, r)](#1.1 build_scaling_rotation(s, r))
- [1.2 build_rotation(r)](#1.2 build_rotation(r))
- [1.3 RGB2SH(rgb)](#1.3 RGB2SH(rgb))
- 二、相机模型(cameras.py)
-
- [2.1 getWorld2View2(...)](#2.1 getWorld2View2(...))
- [2.2 getProjectionMatrix(...)](#2.2 getProjectionMatrix(...))
一、高斯模型(gaussian_model.py)
gaussian_model.py文件中主要写高斯模型的参数是如何构建的,如协方差矩阵、球谐函数、点云数据读取后的初始化、激活函数、学习率的设计、致密化所用的方法等。
首先是初始函数的设置:
python
def setup_functions(self):
# 定义一个函数(从缩放旋转矩阵中创建协方差矩阵)
def build_covariance_from_scaling_rotation(scaling, scaling_modifier, rotation):
# 定义一个L矩阵,关于函数build_scaling_rotation见1.1
L = build_scaling_rotation(scaling_modifier * scaling, rotation)
# 真实的协方差矩阵:L乘以L的转置(这里的转置只有第1维和第2维)
# 跳过第0维,因为第0维是高斯椭球的总数,即N
actual_covariance = L @ L.transpose(1, 2)
# 由于协方差矩阵是对称矩阵,为节省内存、方便存储
# 仅保留协方差矩阵的上三角部分
# 完成协方差矩阵的构建
symm = strip_symmetric(actual_covariance)
return symm
# 缩放因子的激活函数是指数函数
self.scaling_activation = torch.exp
# 缩放因子的反激活函数是对数函数
self.scaling_inverse_activation = torch.log
# 协方差矩阵没有用到激活函数,而是直接用上面定义的函数去构建
# 因为缩放因子和旋转因子均已激活过
self.covariance_activation = build_covariance_from_scaling_rotation
# 不透明度的激活函数采用sigmoid,为了保证不透明度的值在0~1之间
self.opacity_activation = torch.sigmoid
# 不透明度的反激活函数采用反sigmoid函数
self.inverse_opacity_activation = inverse_sigmoid
# 旋转矩阵的激活函数即归一化函数(求模值,再依次除以模值)
self.rotation_activation = torch.nn.functional.normalize接着是变量的初始化,即将其均设置为0或者NULL:
python
def __init__(self, sh_degree, optimizer_type="default"):
# 球谐函数的阶数,初始设置为0
self.active_sh_degree = 0
self.optimizer_type = optimizer_type
# 球谐函数的最高阶数依赖于传入的参数sh_degree
self.max_sh_degree = sh_degree
# 高斯椭球的位置xyz,设置为0
self._xyz = torch.empty(0)
# 球谐函数的直流分量
self._features_dc = torch.empty(0)
# 球谐函数的高阶分量
self._features_rest = torch.empty(0)
# 缩放因子
self._scaling = torch.empty(0)
# 旋转因子
self._rotation = torch.empty(0)
# 不透明度
self._opacity = torch.empty(0)
# 投影到平面后的,二维高斯分布的最大半径
self.max_radii2D = torch.empty(0)
# 点云位置的梯度的累积值
self.xyz_gradient_accum = torch.empty(0)
# 累积的梯度的总数
self.denom = torch.empty(0)
# 优化器
self.optimizer = None
# 百分比密度
self.percent_dense = 0
# 学习率
self.spatial_lr_scale = 0
self.setup_functions()然后是一些变量的实例化以及获取变量的方法:
python
# 可以看到这里在获取变量时,是激活后的变量
# 因此如果你需要使用变量时,要记得采用反激活函数进行处理
@property
def get_scaling(self):
return self.scaling_activation(self._scaling)
@property
def get_rotation(self):
return self.rotation_activation(self._rotation)
@property
def get_xyz(self):
return self._xyz
@property
def get_features(self):
features_dc = self._features_dc
features_rest = self._features_rest
return torch.cat((features_dc, features_rest), dim=1)
@property
def get_features_dc(self):
return self._features_dc
@property
def get_features_rest(self):
return self._features_rest
@property
def get_opacity(self):
return self.opacity_activation(self._opacity)
@property
def get_exposure(self):
return self._exposure
# 迭代球谐函数的阶数
# 当前球谐函数的阶数小于你所规定的最大阶数,球谐函数会增加
def oneupSHdegree(self):
if self.active_sh_degree < self.max_sh_degree:
self.active_sh_degree += 1然后是从点云文件中创建数据:
python
def create_from_pcd(self, pcd : BasicPointCloud, cam_infos : int, spatial_lr_scale : float):
self.spatial_lr_scale = spatial_lr_scale
# 创建一个张量保存点云数据:数组类型的点云数据存储到张量中
fused_point_cloud = torch.tensor(np.asarray(pcd.points)).float().cuda()
# 数组类型的颜色数据存储到张量中
# 应用RGB2SH函数,将RGB表示的颜色转换为球谐函数表示的颜色,该函数见1.3
# 首先只是直流分量,后期再叠加
fused_color = RGB2SH(torch.tensor(np.asarray(pcd.colors)).float().cuda())
# 存储球谐函数的系数
features = torch.zeros((fused_color.shape[0], 3, (self.max_sh_degree + 1) ** 2)).float().cuda()
# 首先只存直流分量,其余赋值为0
features[:, :3, 0 ] = fused_color
features[:, 3:, 1:] = 0.0
# 打印初始化点的数量
print("Number of points at initialisation : ", fused_point_cloud.shape[0])
# 检索当前高斯点附近最近的三个高斯点,计算其距离的平均值
# 以当前高斯点位中心,利用该平均值,构建高斯球,从而得到通过点云构建的初始高斯球
# 初始高斯椭球的最小半径是0.0000001,也就是说不会有两个重合的椭球,因为会有一个距离
dist2 = torch.clamp_min(distCUDA2(torch.from_numpy(np.asarray(pcd.points)).float().cuda()), 0.0000001)
scales = torch.log(torch.sqrt(dist2))[...,None].repeat(1, 3)
# 旋转因子,维度N×4,将旋转四元数初始化为0
rots = torch.zeros((fused_point_cloud.shape[0], 4), device="cuda")
rots[:, 0] = 1
# 不透明度
opacities = self.inverse_opacity_activation(0.1 * torch.ones((fused_point_cloud.shape[0], 1), dtype=torch.float, device="cuda"))
# 高斯椭球的位置,需要梯度进行优化
self._xyz = nn.Parameter(fused_point_cloud.requires_grad_(True))
# 球谐函数的直流分量和高阶分量,需要梯度进行优化
self._features_dc = nn.Parameter(features[:,:,0:1].transpose(1, 2).contiguous().requires_grad_(True))
self._features_rest = nn.Parameter(features[:,:,1:].transpose(1, 2).contiguous().requires_grad_(True))
# 缩放因子、旋转因子,需要梯度进行优化
self._scaling = nn.Parameter(scales.requires_grad_(True))
self._rotation = nn.Parameter(rots.requires_grad_(True))
# 不透明度,需要梯度进行优化
self._opacity = nn.Parameter(opacities.requires_grad_(True))
# 二维投影后的高斯分布的最大半径
self.max_radii2D = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0]), device="cuda")
self.exposure_mapping = {cam_info.image_name: idx for idx, cam_info in enumerate(cam_infos)}
self.pretrained_exposures = None
exposure = torch.eye(3, 4, device="cuda")[None].repeat(len(cam_infos), 1, 1)
self._exposure = nn.Parameter(exposure.requires_grad_(True))接着就是训练的一些初始值的设置、学习率的更新:
python
def training_setup(self, training_args):
self.percent_dense = training_args.percent_dense
self.xyz_gradient_accum = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda")
self.denom = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda")
# 训练过程中的学习率
# 每个参数都有不同的学习率控制其优化
l = [
{'params': [self._xyz], 'lr': training_args.position_lr_init * self.spatial_lr_scale, "name": "xyz"},
{'params': [self._features_dc], 'lr': training_args.feature_lr, "name": "f_dc"},
{'params': [self._features_rest], 'lr': training_args.feature_lr / 20.0, "name": "f_rest"},
{'params': [self._opacity], 'lr': training_args.opacity_lr, "name": "opacity"},
{'params': [self._scaling], 'lr': training_args.scaling_lr, "name": "scaling"},
{'params': [self._rotation], 'lr': training_args.rotation_lr, "name": "rotation"}
]
if self.optimizer_type == "default":
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(l, lr=0.0, eps=1e-15)
elif self.optimizer_type == "sparse_adam":
try:
self.optimizer = SparseGaussianAdam(l, lr=0.0, eps=1e-15)
except:
# A special version of the rasterizer is required to enable sparse adam
self.optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(l, lr=0.0, eps=1e-15)
self.exposure_optimizer = torch.optim.Adam([self._exposure])
self.xyz_scheduler_args = get_expon_lr_func(lr_init=training_args.position_lr_init*self.spatial_lr_scale,
lr_final=training_args.position_lr_final*self.spatial_lr_scale,
lr_delay_mult=training_args.position_lr_delay_mult,
max_steps=training_args.position_lr_max_steps)
self.exposure_scheduler_args = get_expon_lr_func(training_args.exposure_lr_init, training_args.exposure_lr_final,
lr_delay_steps=training_args.exposure_lr_delay_steps,
lr_delay_mult=training_args.exposure_lr_delay_mult,
max_steps=training_args.iterations)
def update_learning_rate(self, iteration):
''' Learning rate scheduling per step '''
if self.pretrained_exposures is None:
for param_group in self.exposure_optimizer.param_groups:
param_group['lr'] = self.exposure_scheduler_args(iteration)
for param_group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
if param_group["name"] == "xyz":
lr = self.xyz_scheduler_args(iteration)
param_group['lr'] = lr
return lr
# 创建一个属性列表
# 除了最初的点云的x、y、z和法向量,还需要增加球谐函数、不透明度、缩放因子、旋转因子
# 得到的ply文件的格式如下图所示
# 根据原文的描述,法向量其实是没有用到的,全是0值
def construct_list_of_attributes(self):
l = ['x', 'y', 'z', 'nx', 'ny', 'nz']
# All channels except the 3 DC
for i in range(self._features_dc.shape[1]*self._features_dc.shape[2]):
l.append('f_dc_{}'.format(i))
for i in range(self._features_rest.shape[1]*self._features_rest.shape[2]):
l.append('f_rest_{}'.format(i))
l.append('opacity')
for i in range(self._scaling.shape[1]):
l.append('scale_{}'.format(i))
for i in range(self._rotation.shape[1]):
l.append('rot_{}'.format(i))
return l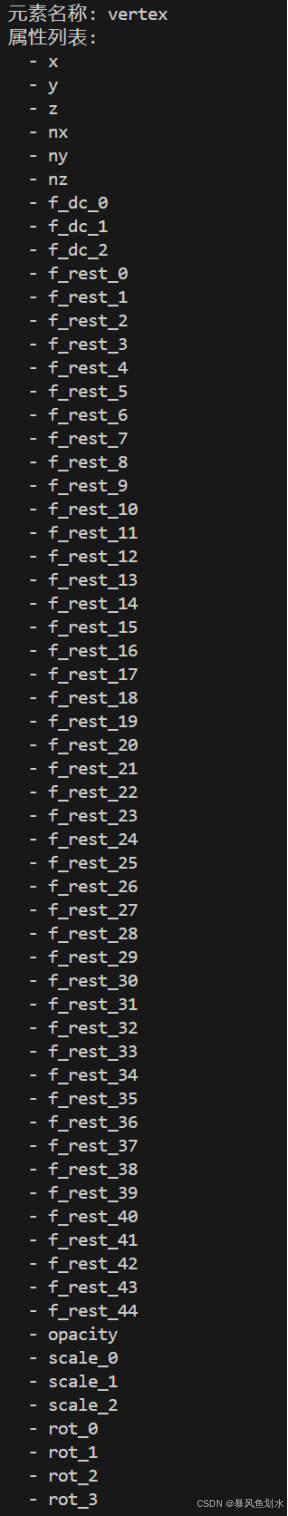
紧接着是一个重置不透明度的函数:
python
# 将不透明度设定在0.01以内
def reset_opacity(self):
opacities_new = self.inverse_opacity_activation(torch.min(self.get_opacity, torch.ones_like(self.get_opacity)*0.01))
optimizable_tensors = self.replace_tensor_to_optimizer(opacities_new, "opacity")
self._opacity = optimizable_tensors["opacity"]最后主要是3DGS的密度控制方法:
python
# 创建新的高斯点
def densification_postfix(self, new_xyz, new_features_dc, new_features_rest, new_opacities, new_scaling, new_rotation, new_tmp_radii):
# 首先创建一个列表,存储高斯椭球的属性,将你要添加的属性附到这些属性里面
d = {"xyz": new_xyz,
"f_dc": new_features_dc,
"f_rest": new_features_rest,
"opacity": new_opacities,
"scaling" : new_scaling,
"rotation" : new_rotation}
# 采用上面定义的创建变量到优化器的方法,将你的属性全部添加到优化器中
# 将新的值赋值到对象中,从而达到创建一个新的高斯点的目的
optimizable_tensors = self.cat_tensors_to_optimizer(d)
self._xyz = optimizable_tensors["xyz"]
self._features_dc = optimizable_tensors["f_dc"]
self._features_rest = optimizable_tensors["f_rest"]
self._opacity = optimizable_tensors["opacity"]
self._scaling = optimizable_tensors["scaling"]
self._rotation = optimizable_tensors["rotation"]
self.tmp_radii = torch.cat((self.tmp_radii, new_tmp_radii))
self.xyz_gradient_accum = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda")
self.denom = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0], 1), device="cuda")
self.max_radii2D = torch.zeros((self.get_xyz.shape[0]), device="cuda")
# 致密化操作
# 分裂
# 参数:梯度、梯度阈值、场景范围、常数N
def densify_and_split(self, grads, grad_threshold, scene_extent, N=2):
# 首先获取所有高斯分布的总数
n_init_points = self.get_xyz.shape[0]
# Extract points that satisfy the gradient condition
# 创建一个全零的张量,大小就是高斯分布的总数
# 该张量用于存储当前每个高斯分布的梯度
padded_grad = torch.zeros((n_init_points), device="cuda")
# 根据梯度先扩展一个维度
padded_grad[:grads.shape[0]] = grads.squeeze()
# 首先:如果梯度大于梯度阈值,将其下标标记出来,即生成一个掩码标记
selected_pts_mask = torch.where(padded_grad >= grad_threshold, True, False)
# 其次:当前高斯分布的缩放因子中最大一个维度的值大于这个场景范围乘以一个对应的比例因子
# 也就是说当前高斯分布的大小大于当前场景的最大范围,需要将当前高斯分布进行分裂
selected_pts_mask = torch.logical_and(selected_pts_mask,
torch.max(self.get_scaling, dim=1).values > self.percent_dense*scene_extent)
# 创建新的高斯分布
# 新的高斯分布的标准差取自于需要分裂的高斯分布的标准差,将其扩展为2个
stds = self.get_scaling[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1)
# 新的高斯分布的位置规定在全零的位置,即坐标系的原点
means =torch.zeros((stds.size(0), 3),device="cuda")
# 依据上面设置的标准差和均值定义采样点
samples = torch.normal(mean=means, std=stds)
# 旋转矩阵依旧依据待分裂的高斯分布的旋转矩阵来创建
rots = build_rotation(self._rotation[selected_pts_mask]).repeat(N,1,1)
# 首先用创建好的高斯分布增加一个维度,与旋转因子相乘,即得到协方差矩阵
# 然后将新增的维度删掉,得到新的协方差矩阵
# 再加上原本高斯分布的位置,从而得到新高斯分布的位置
new_xyz = torch.bmm(rots, samples.unsqueeze(-1)).squeeze(-1) + self.get_xyz[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N, 1)
# 得到两个新的高斯分布,但是此时的高斯分布并不能直接使用,需要同时除以1.6,得到两个小的高斯分布,即新的高斯分布
new_scaling = self.scaling_inverse_activation(self.get_scaling[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1) / (0.8*N))
# 其他属性:旋转矩阵、球谐函数、不透明度均与原高斯分布保持一致
new_rotation = self._rotation[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1)
new_features_dc = self._features_dc[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1,1)
new_features_rest = self._features_rest[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1,1)
new_opacity = self._opacity[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N,1)
new_tmp_radii = self.tmp_radii[selected_pts_mask].repeat(N)
# 将新的变量添加至高斯里面,从而实现新对象的创建
# 即:由一个高斯得到两个高斯
self.densification_postfix(new_xyz, new_features_dc, new_features_rest, new_opacity, new_scaling, new_rotation, new_tmp_radii)
# 创建一个过滤器,将原来标记过的高斯分布过滤掉
prune_filter = torch.cat((selected_pts_mask, torch.zeros(N * selected_pts_mask.sum(), device="cuda", dtype=bool)))
self.prune_points(prune_filter)
# 克隆
# 参数:梯度、梯度阈值、场景范围
def densify_and_clone(self, grads, grad_threshold, scene_extent):
# Extract points that satisfy the gradient condition
# 设置掩码,判断哪些高斯分布需要处理
# 首先梯度大于设定梯度阈值
selected_pts_mask = torch.where(torch.norm(grads, dim=-1) >= grad_threshold, True, False)
# 然后高斯分布的形状是否小于场景的范围
# 满足上述两个条件,将高斯分布进行标记
selected_pts_mask = torch.logical_and(selected_pts_mask,
torch.max(self.get_scaling, dim=1).values <= self.percent_dense*scene_extent)
# 克隆当前高斯分布
# 将原本高斯分布的所有参数添加到新变量中
new_xyz = self._xyz[selected_pts_mask]
new_features_dc = self._features_dc[selected_pts_mask]
new_features_rest = self._features_rest[selected_pts_mask]
new_opacities = self._opacity[selected_pts_mask]
new_scaling = self._scaling[selected_pts_mask]
new_rotation = self._rotation[selected_pts_mask]
new_tmp_radii = self.tmp_radii[selected_pts_mask]
# 直接创建一个新高斯
self.densification_postfix(new_xyz, new_features_dc, new_features_rest, new_opacities, new_scaling, new_rotation, new_tmp_radii)
# 高斯椭球的剔除
def densify_and_prune(self, max_grad, min_opacity, extent, max_screen_size, radii):
# 梯度的累加值除以分母,得到平均梯度
# 例如:累加n个梯度,则除以分母n
grads = self.xyz_gradient_accum / self.denom
# 归零操作
grads[grads.isnan()] = 0.0
# 在剔除的过程中进行分裂和克隆的操作
self.tmp_radii = radii
self.densify_and_clone(grads, max_grad, extent)
self.densify_and_split(grads, max_grad, extent)
# 如果高斯椭球的不透明度小于设定的最小不透明度,则将其标记出来
prune_mask = (self.get_opacity < min_opacity).squeeze()
if max_screen_size:
# 最大二维高斯分布大于屏幕尺寸
big_points_vs = self.max_radii2D > max_screen_size
# 高斯分布的尺寸大于场景乘以比例
big_points_ws = self.get_scaling.max(dim=1).values > 0.1 * extent
# 满足上面两个条件,也需要将高斯分布进行标记
prune_mask = torch.logical_or(torch.logical_or(prune_mask, big_points_vs), big_points_ws)
# 统一进行剔除操作
self.prune_points(prune_mask)
tmp_radii = self.tmp_radii
self.tmp_radii = None
# 清理缓存
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# 添加自适应密度控制过程中的状态
def add_densification_stats(self, viewspace_point_tensor, update_filter):
# 每累加一个梯度,对应的分母加一
self.xyz_gradient_accum[update_filter] += torch.norm(viewspace_point_tensor.grad[update_filter,:2], dim=-1, keepdim=True)
self.denom[update_filter] += 11.1 build_scaling_rotation(s, r)
python
# 参数:缩放因子、旋转因子
def build_scaling_rotation(s, r):
# 定义一个L矩阵,是一个维度是N×3×3的张量,N是指高斯数量的总数
# s.shape[0]:高斯数量的总数
L = torch.zeros((s.shape[0], 3, 3), dtype=torch.float, device="cuda")
# 创建一个旋转矩阵,关于函数build_rotation见1.2
R = build_rotation(r)
# 将缩放因子传入L矩阵
L[:,0,0] = s[:,0]
L[:,1,1] = s[:,1]
L[:,2,2] = s[:,2]
# 旋转矩阵与高斯矩阵相乘
# 高斯椭球的变化是通过旋转与缩放实现的
L = R @ L
return L1.2 build_rotation®
关于旋转四元数与旋转矩阵的关系,旋转四元数和旋转矩阵都是描述三维空间中旋转的数学工具。旋转四元数提供了一种有效的方式来表示和计算三维旋转,而旋转矩阵则是一种更直观的旋转表示方法。
- 旋转矩阵
旋转矩阵是一个3×3的正交矩阵(满足 R T R = I R^TR=I RTR=I,且行列式 d e t ( R ) = 1 det(R)=1 det(R)=1),每一列(或行)都是单位向量且互相垂直。 - 旋转四元数
旋转四元数是一个4维向量 q = [ r , x , y , z ] q=[r, x, y, z] q=[r,x,y,z],满足 r 2 + x 2 + y 2 + z 2 = 1 r^2+x^2+y^2+z^2=1 r2+x2+y2+z2=1(单位四元数),其中 r r r是实部, [ x , y , z ] [x,y,z] [x,y,z]是虚部(对应旋转轴的方向向量)。
python
# 创建旋转矩阵,参数:旋转四元数
def build_rotation(r):
# 求模值
norm = torch.sqrt(r[:,0]*r[:,0] + r[:,1]*r[:,1] + r[:,2]*r[:,2] + r[:,3]*r[:,3])
# 旋转四元数归一化,变为单位四元数
# 保证旋转的时候不改变幅值,只改变高斯分布的形状
q = r / norm[:, None]
# 构建旋转矩阵,是一个维度是N×3×3的张量
R = torch.zeros((q.size(0), 3, 3), device='cuda')
r = q[:, 0] # 旋转四元数的第一个维度
x = q[:, 1] # 旋转四元数的第二个维度
y = q[:, 2] # 旋转四元数的第三个维度
z = q[:, 3] # 旋转四元数的第四个维度
R[:, 0, 0] = 1 - 2 * (y*y + z*z)
R[:, 0, 1] = 2 * (x*y - r*z)
R[:, 0, 2] = 2 * (x*z + r*y)
R[:, 1, 0] = 2 * (x*y + r*z)
R[:, 1, 1] = 1 - 2 * (x*x + z*z)
R[:, 1, 2] = 2 * (y*z - r*x)
R[:, 2, 0] = 2 * (x*z - r*y)
R[:, 2, 1] = 2 * (y*z + r*x)
R[:, 2, 2] = 1 - 2 * (x*x + y*y)
return R1.3 RGB2SH(rgb)
python
C1 = 0.4886025119029199
C2 = [
1.0925484305920792,
-1.0925484305920792,
0.31539156525252005,
-1.0925484305920792,
0.5462742152960396
]
C3 = [
-0.5900435899266435,
2.890611442640554,
-0.4570457994644658,
0.3731763325901154,
-0.4570457994644658,
1.445305721320277,
-0.5900435899266435
]
C4 = [
2.5033429417967046,
-1.7701307697799304,
0.9461746957575601,
-0.6690465435572892,
0.10578554691520431,
-0.6690465435572892,
0.47308734787878004,
-1.7701307697799304,
0.6258357354491761,
]
# 球谐函数的计算
# 参数:球谐函数的阶数、球谐函数的系数、方向值
def eval_sh(deg, sh, dirs):
# 规定球谐函数的阶数在0~4
assert deg <= 4 and deg >= 0
# 球谐函数的系数数量是2^{deg+1}
coeff = (deg + 1) ** 2
# 所传的球谐函数的系数数量是否满足规定的数量
# 如果不满足,则说明球谐函数的系数数量与球谐函数的阶数是不匹配的
assert sh.shape[-1] >= coeff
# 零阶:C0×SH的第0项
result = C0 * sh[..., 0]
if deg > 0:
# 1阶的方向向量
x, y, z = dirs[..., 0:1], dirs[..., 1:2], dirs[..., 2:3]
result = (result -
C1 * y * sh[..., 1] +
C1 * z * sh[..., 2] -
C1 * x * sh[..., 3])
if deg > 1:
xx, yy, zz = x * x, y * y, z * z
xy, yz, xz = x * y, y * z, x * z
result = (result +
C2[0] * xy * sh[..., 4] +
C2[1] * yz * sh[..., 5] +
C2[2] * (2.0 * zz - xx - yy) * sh[..., 6] +
C2[3] * xz * sh[..., 7] +
C2[4] * (xx - yy) * sh[..., 8])
if deg > 2:
result = (result +
C3[0] * y * (3 * xx - yy) * sh[..., 9] +
C3[1] * xy * z * sh[..., 10] +
C3[2] * y * (4 * zz - xx - yy)* sh[..., 11] +
C3[3] * z * (2 * zz - 3 * xx - 3 * yy) * sh[..., 12] +
C3[4] * x * (4 * zz - xx - yy) * sh[..., 13] +
C3[5] * z * (xx - yy) * sh[..., 14] +
C3[6] * x * (xx - 3 * yy) * sh[..., 15])
if deg > 3:
result = (result + C4[0] * xy * (xx - yy) * sh[..., 16] +
C4[1] * yz * (3 * xx - yy) * sh[..., 17] +
C4[2] * xy * (7 * zz - 1) * sh[..., 18] +
C4[3] * yz * (7 * zz - 3) * sh[..., 19] +
C4[4] * (zz * (35 * zz - 30) + 3) * sh[..., 20] +
C4[5] * xz * (7 * zz - 3) * sh[..., 21] +
C4[6] * (xx - yy) * (7 * zz - 1) * sh[..., 22] +
C4[7] * xz * (xx - 3 * yy) * sh[..., 23] +
C4[8] * (xx * (xx - 3 * yy) - yy * (3 * xx - yy)) * sh[..., 24])
return result
# rgb颜色值范围0~1
def RGB2SH(rgb):
# 将颜色值统一到-0.5~0.5区间,再除以直流分量C0(该值是提前定义好的),
return (rgb - 0.5) / C0二、相机模型(cameras.py)
相机模型表达的是高斯分布在三维空间投影到二维空间(像素平面)的一个转换过程。
python
# 定义一个Camera大类
class Camera(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, resolution, colmap_id, R, T, FoVx, FoVy, depth_params, image, invdepthmap,
image_name, uid,
trans=np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]), scale=1.0, data_device = "cuda",
train_test_exp = False, is_test_dataset = False, is_test_view = False
):
super(Camera, self).__init__()
# uid:相机的唯一标识符
self.uid = uid
# colmap_id:colmap时相机位姿的id
self.colmap_id = colmap_id
# 旋转矩阵
self.R = R
# 平移矩阵
self.T = T
# 相机在水平方向和垂直方向的视野范围(角度)
self.FoVx = FoVx
self.FoVy = FoVy
# 图像名称
self.image_name = image_name
# 指定硬件设备
try:
self.data_device = torch.device(data_device)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
print(f"[Warning] Custom device {data_device} failed, fallback to default cuda device" )
self.data_device = torch.device("cuda")
# 将图像的范围指定到0~1之间
self.original_image = gt_image.clamp(0.0, 1.0).to(self.data_device)
# 将图像的宽、高设定在一个新的变量中
self.image_width = self.original_image.shape[2]
self.image_height = self.original_image.shape[1]
# 相机视角的近点和远点
self.zfar = 100.0
self.znear = 0.01
self.trans = trans
self.scale = scale
# 世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换
# getWorld2View2()函数见2.1
self.world_view_transform = torch.tensor(getWorld2View2(R, T, trans, scale)).transpose(0, 1).cuda()
# 将相机坐标系上的高斯分布投影到二维平面上
self.projection_matrix = getProjectionMatrix(znear=self.znear, zfar=self.zfar, fovX=self.FoVx, fovY=self.FoVy).transpose(0,1).cuda()
# 矩阵依次相乘 得到 世界坐标系到图像坐标系的转换
self.full_proj_transform = (self.world_view_transform.unsqueeze(0).bmm(self.projection_matrix.unsqueeze(0))).squeeze(0)
self.camera_center = self.world_view_transform.inverse()[3, :3]2.1 getWorld2View2(...)
python
# 参数:旋转矩阵、平移矩阵、转换数组、缩放因子
def getWorld2View2(R, t, translate=np.array([.0, .0, .0]), scale=1.0):
# 构建Rt矩阵,即世界坐标系到相机坐标系的转换矩阵
Rt = np.zeros((4, 4))
Rt[:3, :3] = R.transpose()
Rt[:3, 3] = t
Rt[3, 3] = 1.0
C2W = np.linalg.inv(Rt)
cam_center = C2W[:3, 3]
cam_center = (cam_center + translate) * scale
C2W[:3, 3] = cam_center
Rt = np.linalg.inv(C2W)
return np.float32(Rt)2.2 getProjectionMatrix(...)
python
# 参数:相机视野内的最近、最远点,水平方向和垂直方向的视野范围
def getProjectionMatrix(znear, zfar, fovX, fovY):
tanHalfFovY = math.tan((fovY / 2))
tanHalfFovX = math.tan((fovX / 2))
# 最近平面到相机光心的距离
top = tanHalfFovY * znear
bottom = -top
# 近平面最左边、最右边的位置
right = tanHalfFovX * znear
left = -right
# 创建新的转换矩阵
P = torch.zeros(4, 4)
z_sign = 1.0
P[0, 0] = 2.0 * znear / (right - left)
P[1, 1] = 2.0 * znear / (top - bottom)
P[0, 2] = (right + left) / (right - left)
P[1, 2] = (top + bottom) / (top - bottom)
P[3, 2] = z_sign
P[2, 2] = z_sign * zfar / (zfar - znear)
P[2, 3] = -(zfar * znear) / (zfar - znear)
return P