软件说明:
所有软件包下载地址:https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases
打开页面后选择对应的组件及版本即可!
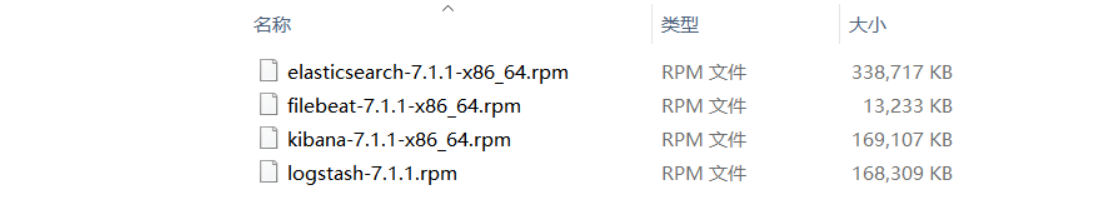
所有软件包名称如下:
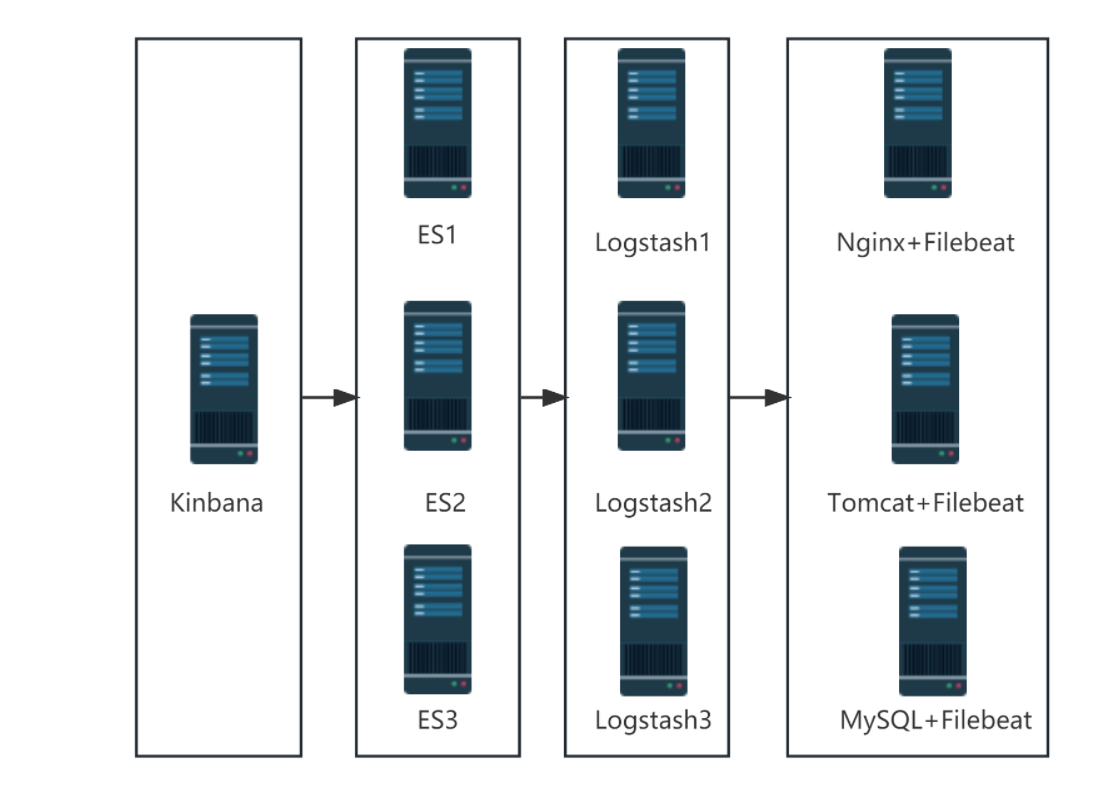
架构拓扑:
- 集群模式:
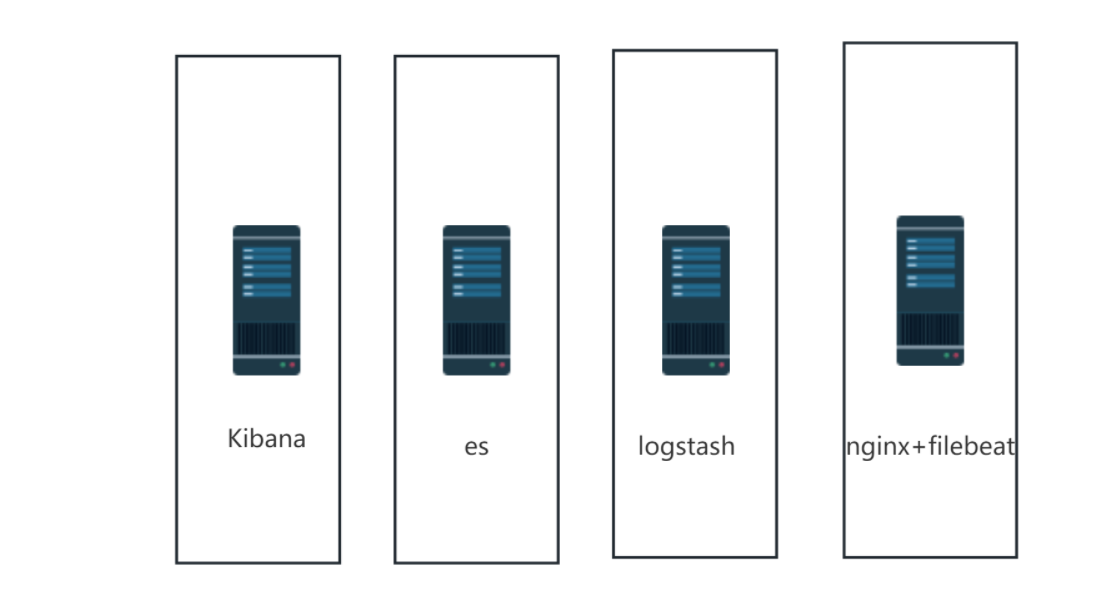
单机模式
架构规划:
- 集群模式
| 角色 | 主机名 | IP地址 |
|---|---|---|
| 图形展示 | kibana | 192.168.166.111 |
| 日志存储 | es1 | 192.168.158.6 |
| es2 | 192.168.166.113 | |
| es3 | 192.168.166.114 | |
| 日志收集分析 | lostash1 | 192.168.166.166 |
| lostash2 | 192.168.166.116 | |
| lostash3 | 192.168.166.117 | |
| 日志采集 | access、error | 192.168.166.118 |
-
单机模式
角色 主机名 IP地址 图形展示 kibana 192.168.166.111 日志存储 es 192.168.158.6 日志收集分析 lostash 192.168.166.113 日志采集 access、error 192.168.166.114 说明:以下部署过程为单机模式部署,集群模式请自行修改部署!!!
一、 Elasticsearch安装与配置
修改主机名
root@localhost \~\]# hostnamecl set-hostname es \[root@localhost \~\]# bash \[root@es \~\]#
配置主机名解析
root@es \~\]# cat /etc/hosts 192.168.166.111 kibana 192.168.158.6 es 192.168.166.113 logstash 192.168.166.114 nginx
安装JAVA8
root@es \~\]# yum install -y java
将elasticsearch软件包拷贝至elk主机执行安装
root@es \~\]# yum localinstall -y elasticsearch-7.1.1-x86_64.rpm
配置elasticsearch
bash
[root@es ~]# cd /etc/elasticsearch/
[root@es elasticsearch]# cat elasticsearch.yml | grep -Ev "^#"
cluster.name: my-application #集群名称
node.name: es #节点主机名
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch #数据存放目录
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch #日志存放目录
network.host: 192.168.158.6 #监听IP地址
http.port: 9200 #监听端口号
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["es"] #主节点
http.cors.enabled: true
http.cors.allow-origin: "*"
#####集群模式下修改为如下配置:
cluster.name: my-application #集群名称
node.name: es #节点主机名
path.data: /var/lib/elasticsearch #数据存放目录
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch #日志存放目录
network.host: 192.168.158.6 #监听IP地址
http.port: 9200 #监听端口号
http.cors.enabled: true #跨域访问
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" #跨域访问
cluster.initial_master_nodes: ["192.168.158.6","192.168.166.113","192.168.166.114"] #主节点
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["192.168.158.6", "192.168.166.113", "192.168.166.114"] # 配置自动发现
discovery.zen.minimum_master_nodes: 2 #防止集群"脑裂",需要配置集群最少主节点数目,通常为 (主节点数目/2) + 1启动elasticsearch服务并设置开机自启动
root@es \~\]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service \[root@es \~\]# systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
验证启动结果
root@es \~\]# systemctl status elasticsearch.service \[root@es \~\]# ss -antl\|grep 9200
es续期
curl -XPOST 'http://192.168.158.31:9200/_license/start_trial?acknowledge=true'
二、 logstash安装与配置
修改主机名
root@localhost \~\]# hostnamecl set-hostname logstash \[root@localhost \~\]# bash \[root@logstash \~\]#
配置主机名解析
root@logstash \~\]# cat /etc/hosts 192.168.166.111 kibana 192.168.158.6 es 192.168.166.113 logstash 192.168.166.114 nginx
安装JAVA8(系统自带)
root@logstash \~\]# yum install -y java
将logstash软件包拷贝至elk主机执行安装
root@logstash \~\]# yum localinstall -y logstash-7.1.1.rpm
优化logstash命令
root@logstash \~\]# ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/ **配置logstash** > \[root@logstash \~\]# cd /etc/logstash/ > > \[root@logstash logstash\]# cat logstash.yml > > path.data: /var/lib/logstash #数据存储路径 > > http.host: "192.168.166.113" #监听地址 > > http.port: 9600-9700 #监听端口范围 > > path.logs: /var/log/logstash #日志存储路径 **测试logstash服务的数据传输** > ##标准输入与输出 > > \[root@logstash \~\]# logstash -e 'input{ stdin{} }output { stdout{} }' > > ##使用rubydebug解码 > > \[root@logstash \~\]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=\>rubydebug }}' > > ##输出到elasticsearch > > \[root@logstash \~\]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch{ hosts=\>\["192.168.158.6:9200"\]} }' **创建配置文件** **1、使用tags标签** ```bash [root@logstash ~]# cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash/conf.d [root@logstash ~]# cat pipline.conf input { beats { port => 5044 } } output { if "access" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.6:9200"] index => "access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } if "error" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.6:9200"] index => "error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } ###日志进行标准输出,观察日志获取的过程### stdout { codec => rubydebug } } #####集群模式下修改问如下配置: input { beats { port => 5044 } } output { if "access" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.6:9200"] index => "access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } if "error" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.6:9200"] index => "error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } ###日志进行标准输出,观察日志获取的过程### stdout { codec => rubydebug } } ``` **2、使用filter过滤器** ```bash input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" start_position => "beginning" } beats { port => 5044 } } filter { if [host][name] { mutate { add_field => { "hostname" => "%{[host][name]}" } } } else if [agent][hostname] { mutate { add_field => { "hostname" => "%{[agent][hostname]}" } } } else { mutate { add_field => { "hostname" => "%{host}" } } } } output { if [hostname] == "logstash" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.79:9200"] index => "system-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } else if [hostname] == "web1" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.79:9200"] index => "web1-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } stdout { codec => rubydebug } } ``` **收集不同主机及对应应用的不同日志** ```bash input { file { path => "/var/log/messages" start_position => "beginning" } beats { port => 5044 } } filter { if [host][name] { mutate { add_field => { "hostname" => "%{[host][name]}" } } } else if [agent][hostname] { mutate { add_field => { "hostname" => "%{[agent][hostname]}" } } } else { mutate { add_field => { "hostname" => "%{host}" } } } } output { if [hostname] == "logstash" { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.79:9200"] index => "system-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } else if [hostname] == "web1" { if "system" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.79:9200"] index => "web1-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } if "nginx-access" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.79:9200"] index => "web1-nginx-access-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } if "nginx-error" in [tags] { elasticsearch { hosts => ["192.168.158.79:9200"] index => "web1-nginx-error-log-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}" } } } stdout { codec => rubydebug } } ``` **启动logstash服务** > \[root@logstash \~\]# logstash -f /etc/logstash/conf.d/pipline.conf \& ### 三、 nginx、filebeat安装与配置 #### 修改主机名 > \[root@localhost \~\]# hostnamecl set-hostname nginx > > \[root@localhost \~\]# bash > > \[root@nginx \~\]# #### 配置主机名解析 > \[root@logstash \~\]# cat /etc/hosts > > 192.168.166.111 kibana > > 192.168.158.6 es > > 192.168.166.113 logstash > > 192.168.166.114 nginx #### nginx安装与启动 > \[root@nginx \~\]# yum install -y epel-release > > \[root@nginx \~\]# yum install -y nginx > > \[root@nginx \~\]# systemctl start nginx #### filebeat安装 > \[root@nginx \~\]# yum localinstall -y filebeat-7.1.1-x86_64.rpm #### filebeat配置项 > \[root@nginx \~\]# cd /etc/filebeat > > \[root@nginx \~\]# cat filebeat.yml | 配置项 | 作用 | |----------------------|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------| | filebeat.inputs | 输入配置块,用于指定 Filebeat 应该监听哪些文件并将其作为输入。你可以指定文件路径、文件类型、文件格式等。 | | filebeat.prospectors | 这是一种更灵活的输入方式,它允许你同时监听多个目录或文件系统中的多个文件。它结合了输入和输出配置项,使得配置更加灵活。 | | filebeat.config | 用于加载和执行自定义的配置文件。你可以使用此选项加载其他 YAML 文件,以便在 Filebeat 中使用自定义规则和插件。 | | output.elasticsearch | 输出配置块,用于将日志数据发送到 Elasticsearch。你可以指定 Elasticsearch 的地址、端口、索引名称等。 | | output.logstash | 输出配置块,用于将日志数据发送到 Logstash。你可以指定 Logstash 的地址、端口、输入格式等。 | | filebeat.harvester | Harvester 是 Filebeat 的核心组件之一,负责监听文件并将其拆分为事件。你可以通过配置项来调整 Harvester 的行为,例如事件级别、分隔符等。 | | filebeat.scanner | Scanner 负责定期扫描指定路径中的新文件并触发事件收集。你可以通过配置项来调整 Scanner 的行为,例如扫描频率、延迟等。 | | filebeat.processor | 处理器用于对收集到的日志事件进行处理和解析。你可以使用内置的处理器类型(如过滤器、映射器等)来对事件进行过滤、转换和编码。 | | filebeat.registry | 注册表用于存储 Filebeat 的配置信息、事件数据和资源状态。你可以通过配置项来调整注册表的行为和存储方式。 | #### 日志收集 **filebeat 7.1以上支持模版收集日志和传统方式收集日志,具体每个方式的配置如下:** **1、 采用filebeat的nginx模块收集nginx日志** ```bash ##filebeat模块操作命令: #查看支持的模块 [root@nginx ~]# filebeat modules list #启用nginx模块 [root@nginx ~]# filebeat modules enable nginx #配置nginx模块 [root@nginx ~]# cd /etc/filebeat/modules.d [root@nginx ~]# cat nginx.yml - module: nginx # Access logs access: enabled: true var.paths: ["/var/log/nginx/access.log"] # Error logs error: enabled: true var.paths: ["/var/log/nginx/error.log"] #################测试配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# filebeat test config -e ``` **2、传统方式收集** 【**输出给logstash**】 ```bash [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml filebeat.inputs: - type: log enabled: true paths: - /var/log/access/*.log tags: "nignx1" - type: log enabled: true paths: - /var/log/error/*.log tags: "nignx2" output.logstash: hosts: ["192.168.166.113:5044"] #################测试配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# filebeat test config -e ``` 【**输出给elasticsearch**】 ```bash [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml filebeat.inputs: - type: log enabled: true paths: - /var/log/nginx/access.log - /var/log/nginx/error.log output.elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. hosts: ["192.168.166.129:9200"] index: "nginx-access-%{[host.name]}-%{+yyyy.MM.dd}"# 自定义索引名称 setup.ilm.enabled: false # 索引生命周期 ilm 功能默认开启,开启情况下索引名称只能为 filebeat-* setup.template.name: "nginx1" # 定义模板名称 setup.template.pattern: "nginx1-*" # 定义模板的匹配索引名称 #####产生不同索引的方法##### output.elasticsearch: # Array of hosts to connect to. hosts: ["192.168.166.22:9200"] indices: - index: "nginx1-access-logs" when: contains: { "message": "GET"} - index: "nginx1-error-logs" when: contains: { "message": "error" } setup.ilm.enabled: false setup.template.name: "nginx1" setup.template.pattern: "nginx1-*" #################测试配置文件 [root@localhost ~]# filebeat test config -e ``` **启动filebeat** > \[root@nginx \~\]# systemctl start filebeat > > \[root@nginx \~\]# systemctl enabled filebeat ### 四、 Kibana安装与配置 **修改主机名** > \[root@localhost \~\]# hostnamecl set-hostname logstash > > \[root@localhost \~\]# bash > > \[root@logstash \~\]# **配置主机名解析** > \[root@logstash \~\]# cat /etc/hosts > > 192.168.166.111 kibana > > 192.168.158.6 elk > > 192.168.166.113 logstash > > 192.168.166.114 nginx > > 192.168.166.166 tomcat > > 192.168.166.116 mysql **安装JAVA8** > \[root@logstash \~\]# yum install -y java **将logstash软件包拷贝至elk主机执行安装** > \[root@logstash \~\]# yum localinstall -y kibana-7.1.1-x86_64.rpm **配置kibana** ```bash [root@kibana]# cd /etc/kibana/ [root@kibana kibana]# cat kibana.yml server.port: 5601 #监听端口 server.host: "192.168.166.111" #监听地址 server.name: "kibana" #主机名 elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.158.6:9200"] #连接的elasticsearch服务器 kibana.index: ".kibana" #kibana的索引 i18n.locale: "zh-CN" #汉化 ##集群模式下配置: server.port: 5601 #监听端口 server.host: "192.168.166.111" #监听地址 server.name: "kibana" #主机名 elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.158.6:9200","http://192.168.166.113:9200","http://192.168.166.114:9200"] #连接的elasticsearch服务器 kibana.index: ".kibana" #kibana的索引 i18n.locale: "zh-CN" #汉化 ``` **访问kibana** > #在浏览器中输入: > > http://192.168.166.111:5601 **创建索引** 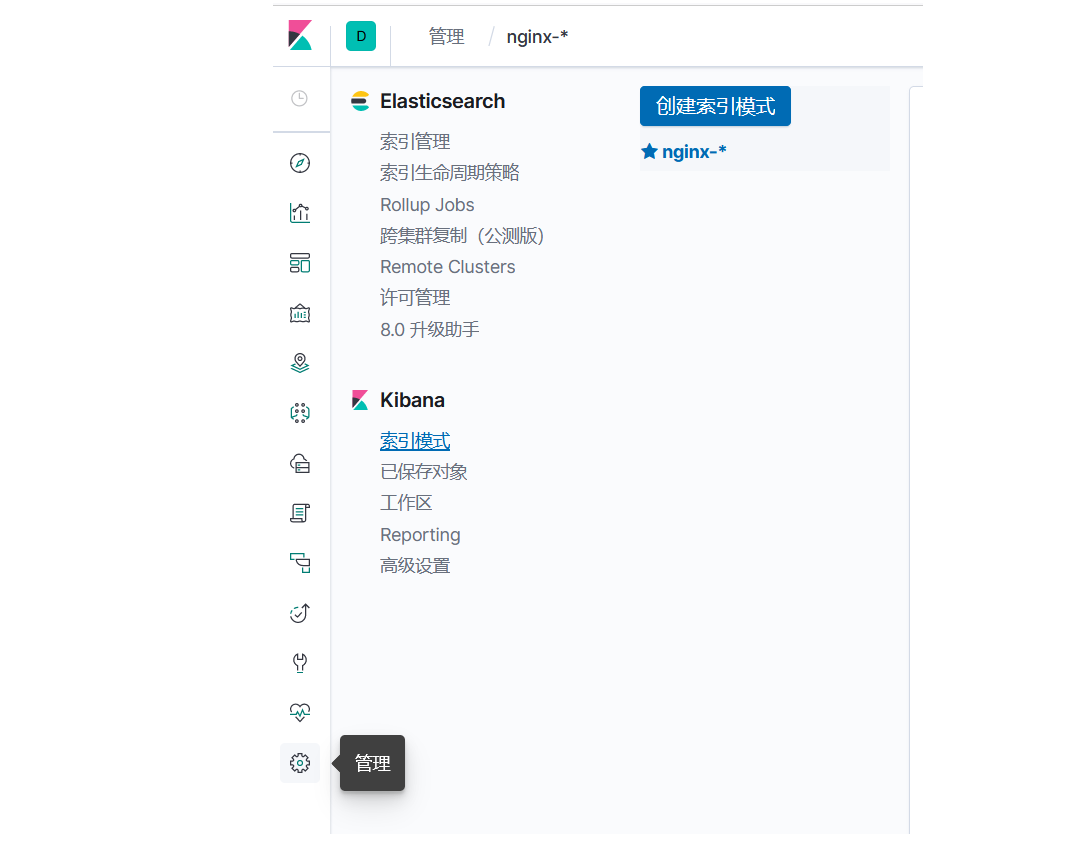 **创建筛选** 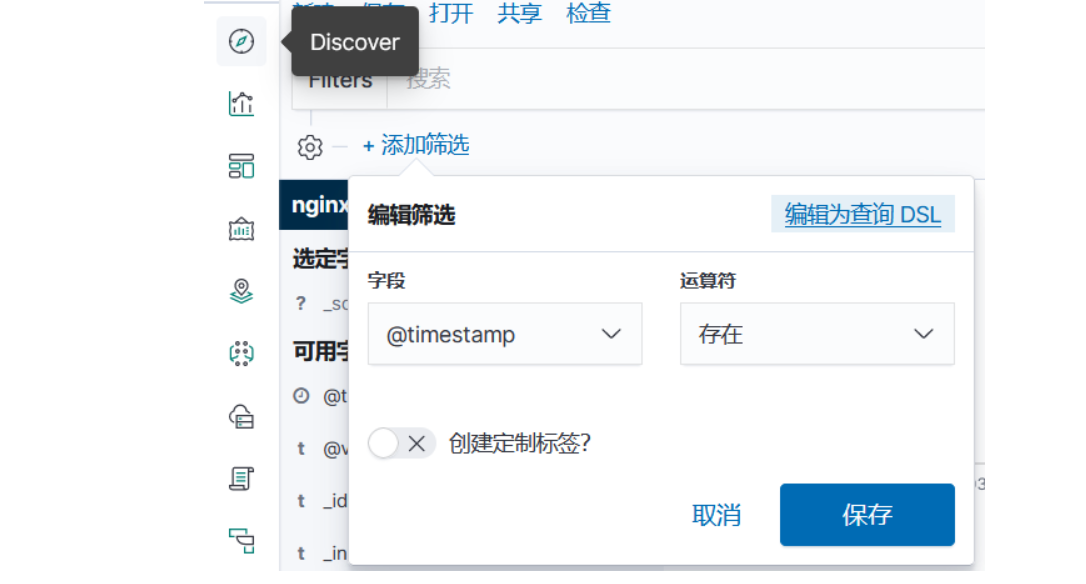 **添加仪表盘**